“Canada produces over 32% of the world’s potash, leading global innovation in fertilizer technology.”
Table of Contents
- Potash Fertilizer Production: An Overview
- Global Potash Reserves & Market Dynamics
- Canada’s Potash Extraction Methods
- Canada’s 7 Game-Changers in Potash Fertilizer Production
- Sustainable Potash Mining & Environmental Practices
- Potash Application in Agriculture
- Technological Advancements Revolutionizing Potash
- Farmonaut & Precision Agriculture Fertilizer Applications
- Alternative Potash Fertilizer Products & Market Trends
- Potash Market Dynamics & Future Outlook
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion: Farmonaut Empowering Agriculture
Potash Fertilizer Production: Canada’s 7 Game-Changers!
In today’s rapidly evolving world of agriculture, potash fertilizer production stands as a vital engine driving global food security, crop yields, and sustainable farming. As we collectively strive to feed a growing population while conserving our planet’s resources, understanding potash—particularly Canada’s role as a leading producer and innovator—is more crucial than ever.
Potash fertilizers, primarily composed of potassium chloride (KCl), play a central role in plant nutrition, ensuring nutrient uptake, facilitating photosynthesis, and ultimately improving crop quality and yields. With roughly 90–95% of global potash production utilized in agriculture, the significance of these fertilizers cannot be overstated.
Global Potash Reserves & Market Dynamics
The global potash market centers around a few dominant regions and producers, with Canada at the forefront. Let’s explore the comprehensive backdrop of production, reserves, and market dynamics.
- Largest reserves: Saskatchewan, Canada accounts for over 30% of the world’s potash reserves, making it the most significant producer globally. Together with Russia and Belarus, these countries dominate production and export.
- Other notable producers: China, Germany, Israel, Jordan, the United States also contribute substantially to global potash output.
- 2020 Production figures: Worldwide potash production reached ~45 million metric tons, with Canada contributing about 13.9 million metric tons (~32% global share).
- Industrial vs. agricultural use: While most potash is used in agriculture, about 5–10% goes to industrial purposes (like glass manufacturing and pharmaceuticals).
The market dynamics for potash are closely tied to global geopolitical factors, supply-demand ratios, production costs, and international trade policies.
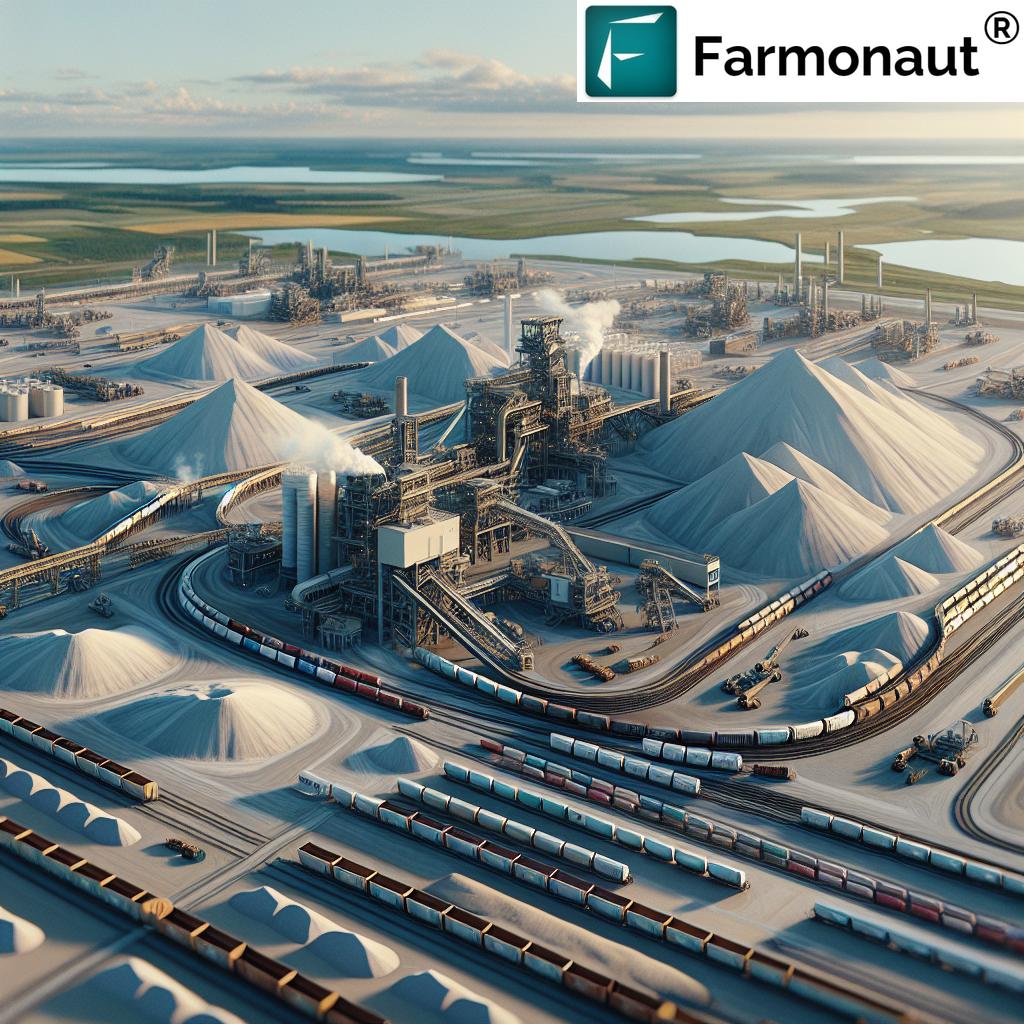
Canada’s Potash Extraction Methods: From Conventional Mining to Sustainable Innovation
Potash extraction methods determine not only production capacity but also environmental impact and long-term viability. In Canada, two main techniques dominate:
- Conventional Underground Mining: Canadian miners extract ore from deep underground deposits (over 1,000 meters deep in many Saskatchewan mines). The ore is processed to separate potassium chloride (KCl)—our primary potash fertilizer ingredient—from other minerals. These operations are highly mechanized, leveraging automation and data tracking for efficiency.
- Solution Mining: This innovative method involves injecting water into potash-bearing formations. The water dissolves potash, creating a KCl-rich brine that’s pumped to the surface and processed to extract pure potash. For Saskatchewan’s deep or low-quality ores, this approach is considered more environmentally friendly—it reduces surface disturbance and energy consumption compared to traditional mining.
Both methods have become technological testbeds for sustainability, automation, and reduced environmental impact—qualities driving sustainable potash mining and propelling Canada’s leadership position.
“Seven Canadian advancements in potash extraction have boosted crop yields by up to 60% worldwide.”
Canada’s 7 Game-Changers in Potash Fertilizer Production
Canada’s remarkable influence in the global potash market can be traced to its leading mines and technological innovators. Let’s review these seven powerhouses and the game-changing advancements they have introduced to potash fertilizer production.
Sustainable Potash Mining & Environmental Practices
As a scientific and technological community, we recognize that the legacy of mining comes with environmental responsibility. Thus, sustainable potash mining is at the center of industry progress:
- Lower surface disturbance: Solution mining dramatically reduces land use and minimizes water table disturbance compared to conventional underground mining.
- Energy efficiency: New processing facilities invest in renewable energy (solar, wind, hydroelectric). Many Canadian sites integrate power from regional grids or invest in on-site renewables to reduce emissions.
- Water recycling: Leading producers have initiated closed-loop water systems, recapturing and reusing water from potash processing to decrease environmental impact.
- Carbon footprint tracking: Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting service provides essential real-time data for agribusinesses aiming to monitor and reduce their emissions. This solution helps farms and fertilizer producers align with the latest sustainability frameworks.
- Habitat conservation: Mines implement reclamation and habitat offset programs post-extraction, ensuring agricultural and forestry land returns to productive or ecological use.
Our focus on sustainable practices not only reduces environmental impact but also aligns with consumer and regulatory pressures for eco-conscious agriculture and food systems.
Potash Application in Agriculture: Methods & Impact
When it comes to potash application in agriculture, the efficiency of delivery methods makes a tangible difference in nutrient utilization and crop yields.
Key Application Methods:
- Broadcasting: Fertilizer is spread across the soil’s surface, often pre-planting, ensuring even distribution. This is suitable for crops with uniform nutrient requirements.
- Banding: Potash is placed in concentrated “bands” near the root zone—either below or beside the seed. This method reduces nutrient loss and optimizes uptake by providing targeted delivery.
- Foliar sprays: A solution containing KCl is sprayed directly on plant leaves. This technique allows for rapid nutrient absorption and prompt correction of potassium deficiencies, especially during growth spurts or environmental stress.
The choice of application method depends on soil conditions, crop type, equipment availability, and desired outcomes (quality, yields, resilience).
Factors Enabling Potash for Crop Yields:
- Photosynthesis and water uptake: Potash regulates water flow and enhances photosynthesis, ensuring robust plant growth.
- Improving crop quality: By supporting nutrient balance, potash boosts taste, color, and storage life of crops.
- Stress control: Adequate KCl fertilization enhances crops’ ability to withstand drought and disease.
- Farmonaut’s NDVI-driven technology (Large-scale farm monitoring) supports growers in tracking potash impacts on plant health, enabling real-time adjustment to fertilization strategies.
Technological Advancements Revolutionizing Potash Fertilizer Production
The last decade has seen extraordinary technological advancements in potash extraction, processing, and application—cementing Canada as an innovation powerhouse. Let’s explore how technology continues to disrupt and redefine this sector.
- Mining automation & robotics: Autonomous drilling, digital mapping, and remote-controlled vehicles vastly increase mining safety and productivity while minimizing human risk.
- Sensors & monitoring: Integrating IoT sensors throughout potash mines and mills tracks air quality, machine health, temperature, and safety—minimizing downtime while optimizing energy use.
- AI-driven analysis: AI analyzes massive datasets from operations and satellites, improving exploration, yield forecasting, and preventative maintenance. AI-powered platforms, like Farmonaut’s Jeevn Advisory, guide farmers and enterprises with personalized, data-driven crop and soil recommendations—ensuring optimal fertilizer and resource input.
- Resource optimization: Advanced fleet management tools (Fleet & resource optimization) allow producers and suppliers to reduce emissions, cut costs, and improve safety across large facilities.
- Blockchain traceability: Farmonaut’s traceability system assures every batch of food or fertilizer is tracked from mine to market, enhancing consumer trust and regulatory compliance.
- API-driven integration: Developers and partners can use the Farmonaut API and developer docs to build scalable data solutions for the entire agricultural value chain.
Farmonaut & Precision Agriculture Fertilizer Applications
Precision agriculture is the future of sustainable farming and efficient fertilizer usage. Using satellite imagery, AI, and field data, Farmonaut empowers growers, agribusinesses, governments, and institutions to maximize yields while minimizing waste and environmental impact.
- Real-time crop health monitoring: Farmonaut’s platform delivers up-to-date NDVI images, soil moisture analytics, and vegetation health summaries, helping farmers and agribusinesses identify areas needing intervention.
- AI-based advisory: The Jeevn advisory tool provides actionable guidance on fertilizer timing, type, and dose, aligning with field conditions and weather patterns.
- Resource and fleet management: Tools to track heavy equipment and vehicles optimize application schedules, fuel use, and emissions.
- Supply chain transparency: Blockchain ensures everyone along the chain—from producer to consumer—can verify the source, quality, and sustainability of fertilizer and produce.
This data-driven approach embodies the essence of precision agriculture fertilizers, supporting the global transition to sustainable, high-yield food production.
- Crop Plantation & Forest Advisory: Get AI-powered expert support for plantation planning, soil management, and fertilizer decisions.
- Crop Loan & Insurance: Use satellite-based verification to streamline crop credit and insurance processes, facilitating faster approvals while safeguarding against fraud.
Alternative Potash Fertilizer Products & Market Trends
Alongside traditional potassium chloride (KCl) fertilizers, the sector sees rapid growth in alternative potash fertilizer products—enabling tailored nutrient management and environmental stewardship.
- Slow-release potash: These innovative products release nutrients over weeks or months, reducing leaching, improving root uptake, and boosting consistency across variable soils.
- Multi-nutrient blends: Potash is mixed with other macros (N, P, S, Mg) and vital micros, providing balanced solutions for high-value crops.
- Bio-based & organic potash: Leveraging fermentation and natural sources, these fertilizers support regenerative agriculture and address the rising demand for organic food.
By integrating these alternative fertilizers with precision agriculture (like Farmonaut’s real-time recommendations), farmers optimize both economic returns and environmental health.
Potash Market Dynamics & Future Outlook
Potash prices (2024) reflect complex global geopolitics, supply chain disruptions, and region-specific demand surges. For example, recent trade tensions between major producers have spiked fertilizer costs; however, increased shipments from Russia and Belarus to Asia and South America have brought prices closer to pre-war levels. Leading producers now adjust output to avoid oversupply, stabilizing markets and supporting long-term investment.
- In South America: Nations like Brazil invest in local production (e.g., the Autazes Potash Project) to reduce reliance on imports—a signal of rising regional demand.
- In Asia: Food giants like China and India count on stable potash imports for food security, pressuring global supply and prices.
The future of potash will be shaped by sustainability regulations, new mining technologies, alternative fertilizer blends, and digital transformation of agriculture.
- Emerging trends: Widespread adoption of precision agriculture, data analytics, and real-time resource monitoring platforms—led by companies such as Farmonaut—will define the next decade.
By utilizing AI, satellite monitoring, and blockchain, the industry is uniquely positioned to balance rising food demand, resource limitations, and ecological stewardship.
Frequently Asked Questions: Potash Fertilizer Production
What is potash, and why is it essential in agriculture?
Potash refers generally to potassium-bearing minerals, primarily potassium chloride (KCl), used as fertilizers. Its essential nutrient—potassium—is vital to plant growth, supporting key processes such as photosynthesis, water/nutrient uptake, protein synthesis, and disease resistance. Over 90% of potash produced annually is utilized in modern agriculture.
How is potash extracted in Canada?
Canada uses two main potash extraction methods: (1) Conventional underground mining removes ore from deep beneath the surface, which is then processed to obtain potassium chloride. (2) Solution mining injects water into underground formations to dissolve potash, pumps the brine to the surface, and processes it to separate pure potash. Solution mining is more environmentally sustainable for difficult-to-mine deposits.
What is the role of technology in potash fertilizer production?
Technology improves every step of potash production—automation and digital monitoring increase mining efficiency and safety, AI provides data-driven insight for crop management, and blockchain ensures traceability in supply chains. Innovations like Farmonaut’s platform deliver precision agriculture tools, enabling optimized fertilizer application and resource conservation.
Are there sustainable potash mining practices?
Yes. Leading companies deploy closed-loop water recycling, renewable energy sources, land reclamation, and carbon emission monitoring. Solution mining greatly reduces surface disturbance. Adoption of sustainability tracking, such as carbon footprinting, is on the rise.
How are potash fertilizer prices set, and what about Potash Prices 2024?
Potash prices fluctuate, influenced by global supply-demand, geopolitical factors, export policies, input costs, and international agreements. In 2024, increased global shipments following earlier trade disruptions helped stabilize potash prices, with producers managing output to prevent oversupply.
What are alternative potash fertilizer products?
These include slow-release potash for reduced leaching, blends combining potash with other nutrients, and organic/bio-based options created from natural sources. Such innovations address environmental and crop-specific demands.
How does Farmonaut enhance potash and fertilizer application?
Farmonaut delivers satellite-driven crop health data, AI-based recommendations, and resource management tools to optimize fertilizer input—yielding better crops, higher efficiency, and sustainable practices.
Conclusion: Farmonaut Empowering Agriculture’s Future with Potash Innovation
As we look ahead to a world where every input must count, potash fertilizer production will remain a linchpin in our quest for sustainable, high-yield agriculture. Canada’s 7 game-changing approaches—from advanced mining and environmental innovation to real-time precision agriculture—are shaping the global market and enabling us to meet tomorrow’s food security challenges with confidence.
Farmonaut stands at the intersection of technology and sustainable farming, offering affordable tools for plant monitoring, resource management, and traceability—directly supporting the judicious, data-driven application of fertilizers like potash. By leveraging real-time data, AI, and blockchain, we bring actionable insights within reach for every farmer, agribusiness, and institution—empowering global agriculture to thrive.
Join us, as together, we cultivate a smarter, greener, and more resilient food future!