Table of Contents
- Introduction: Meeting the Need for Higher Greenhouse Crop Yields
- 1. Environmental Control in Greenhouses
- 2. Leveraging Advanced Greenhouse Technologies
- 3. Efficient Resource Management in Greenhouse Operations
- 4. Sustainable Greenhouse Practices for Lasting Success
- 5. Data-Driven Agriculture Strategies in Greenhouses
- 6. The Power of Staff Training & Continuous Education
- Comparative Summary Table: 7 Ways to Improve Greenhouse Crop Yields
- Farmonaut: Accelerating Precision Greenhouse Management
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion: Maximizing Sustainability & Yields Together
7 Shocking Ways to Improve Crop Yields in Greenhouse Systems
As the global demand for food continues to soar, enhancing greenhouse crop yields is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity. Greenhouses are at the forefront of modern agriculture, enabling us to provide a controlled environment where plants thrive regardless of unpredictable weather patterns. But, to truly optimize greenhouse crop yields, we must leverage advanced technologies, adopt sustainable greenhouse practices, and actively engage in efficient management strategies.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the seven most impactful, sometimes surprising, methods to maximize yields in greenhouse systems. Each strategy is grounded in science, evidence, and the latest in agriculture technology—including data-driven tools like those from Farmonaut, which empower growers with real-time insights and actionable analytics.
From environmental control in greenhouses to the integration of automated greenhouse systems and the implementation of integrated pest management in greenhouses, let’s delve into how we can not only increase yield and improve plant health but also do so in a way that’s responsible for our environment and future generations.
1. Environmental Control in Greenhouses: The Foundation of Crop Yields
Maintaining optimal greenhouse conditions is fundamental for elevating both the productivity and quality of vegetables, fruits, and other high-value crops. The primary environmental factors—temperature control, humidity regulation, and light management—govern nearly every aspect of plant growth and yield formation.
-
Temperature Management: Most greenhouse crops thrive between 21℃ and 29℃ (70°F to 85°F) during the day, with slightly cooler nights supporting optimal metabolic activities.
- Installing thermostats and automated climate systems helps us precisely regulate temperatures and reduce the risks of heat stress or cold damage.
- Sudden temperature swings can hinder fruit set and lead to lower yields—continuous monitoring and automated adjustments help us stay ahead.
-
Humidity Control: High humidity can boost fungal diseases while low humidity may cause water stress and slow plant growth.
- Utilizing hygrometers and ventilation systems allows us to maintain balanced and healthy humidity levels for each crop stage.
- Automated systems for fogging, misting, or dehumidifying can be programmed for precise control and minimal waste.
-
Light Management: Sufficient and consistent light intensity is non-negotiable for photosynthesis and robust plant metabolism.
- In regions or seasons with limited sunlight, we can install supplemental lighting—LEDs or high-pressure sodium lamps—and use shading systems to manage excess light and regulate plant growth cycles.
- Ventilation and Air Flow: Ensuring proper air movement prevents heat build-up, distributes CO₂ evenly, and aids in disease management.
Modern climate control technologies have made it possible to automatically monitor and adjust each parameter based on crop type and growth stage. This is the cornerstone for optimal greenhouse conditions and the launchpad for implementing other advanced greenhouse technologies.
2. Leveraging Advanced Greenhouse Technologies for Unmatched Productivity
The exponential rise of advanced greenhouse technologies has allowed us to shift from manual guesswork to data-driven, automated greenhouse systems. These technologies continuously monitor, predict, and self-adjust crucial growing parameters, unlocking substantial improvements in both yield and resource efficiency.
-
Automated Control Systems:
- We can now automate nearly every aspect of environmental control in greenhouses using real-time sensors and actuators.
- Examples: Automated irrigation (like drip fertigation), ventilation, lighting, and shading—all operate on triggers based on actual crop and environmental data.
-
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration:
- IoT devices in our greenhouses collect continuous data about temperature, soil moisture, humidity, CO₂, and even plant health status using spectral sensors.
- This information is analyzed (often using machine learning algorithms) to predict optimal timing for irrigation, fertilization, pest intervention, and yield forecasting.
-
Smart Agriculture Platforms:
- Solutions like iGrow use a Markov decision process to dynamically optimize all greenhouse operations, resulting in significant yield and profit increases.
- Farmonaut, for example, delivers real-time satellite-based crop health monitoring, NDVI analysis, AI advisory, and blockchain traceability—empowering us to make better, more sustainable decisions.
-
AI-Powered Advisory:
- Artificial intelligence can predict diseases, recommend the exact amount of fertilizer or water needed, and even advise on crop rotation cycles for maximizing profit and sustainability.
By integrating automated greenhouse systems and IoT for continuous monitoring, we can substantially improve plant growth in greenhouses while conserving resources and minimizing costs.
3. Efficient Resource Management in Greenhouse Operations
Effective resource management is the backbone of efficient greenhouse management—helping us reach economic and environmental sustainability. Key strategies include:
-
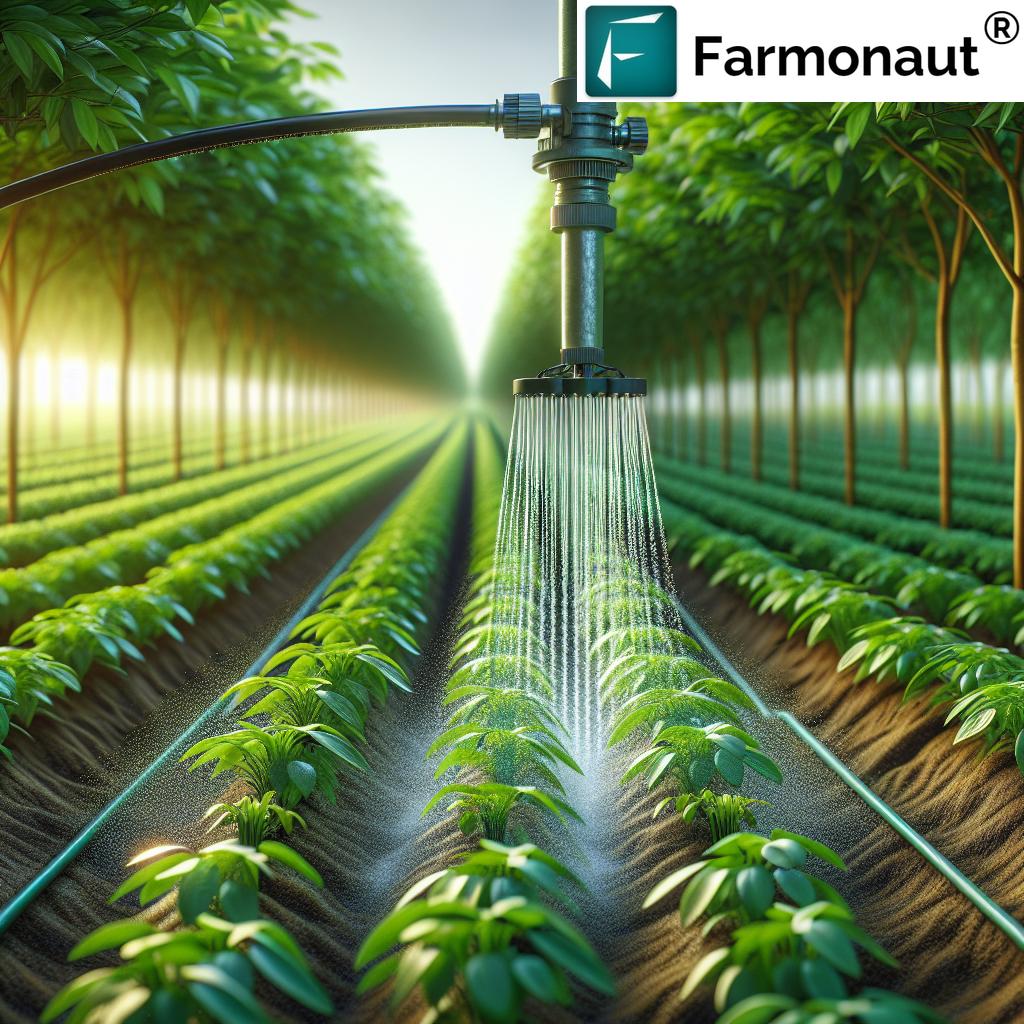
Precision Irrigation & Fertigation:
- Drip irrigation targets water supply directly to the root zone, hugely reducing evaporation and runoff. This ensures plants receive consistent moisture without waste.
- Fertigation introduces nutrients directly through irrigation systems, ensuring precise and timely nutrient delivery tailored to crop development stages.
- Automated irrigation systems can be programmed using weather data, soil moisture sensors, and crop water use models to optimize timing and amount of each watering event.
-
Integrated Nutrient Management (INM):
- INM fosters the judicious use of both organic and chemical fertilizers to preserve soil health and maximize crop potential, while minimizing nutrient leaching and emission.
- Organic matter, compost, and microbial inoculants boost soil biodiversity, structure, and yield.
-
Crop Rotation & Cover Cropping:
- Rotating crops prevents soil depletion and disrupts pest and disease cycles.
- Planting cover crops (like clover or vetch) between main cropping cycles enriches soil nitrogen and organic matter, boosting subsequent yields and supporting sustainable soil management.
By implementing precision resource management, we not only minimize water and nutrient losses but also improve greenhouse crop yield and optimize inputs for sustainability.
4. Sustainable Greenhouse Practices for Lasting Success
Adopting sustainable greenhouse practices is essential for the future of global food supply and the environment. By integrating environmentally friendly methods, we protect natural resources, promote biodiversity, and ensure food security for generations to come.
-
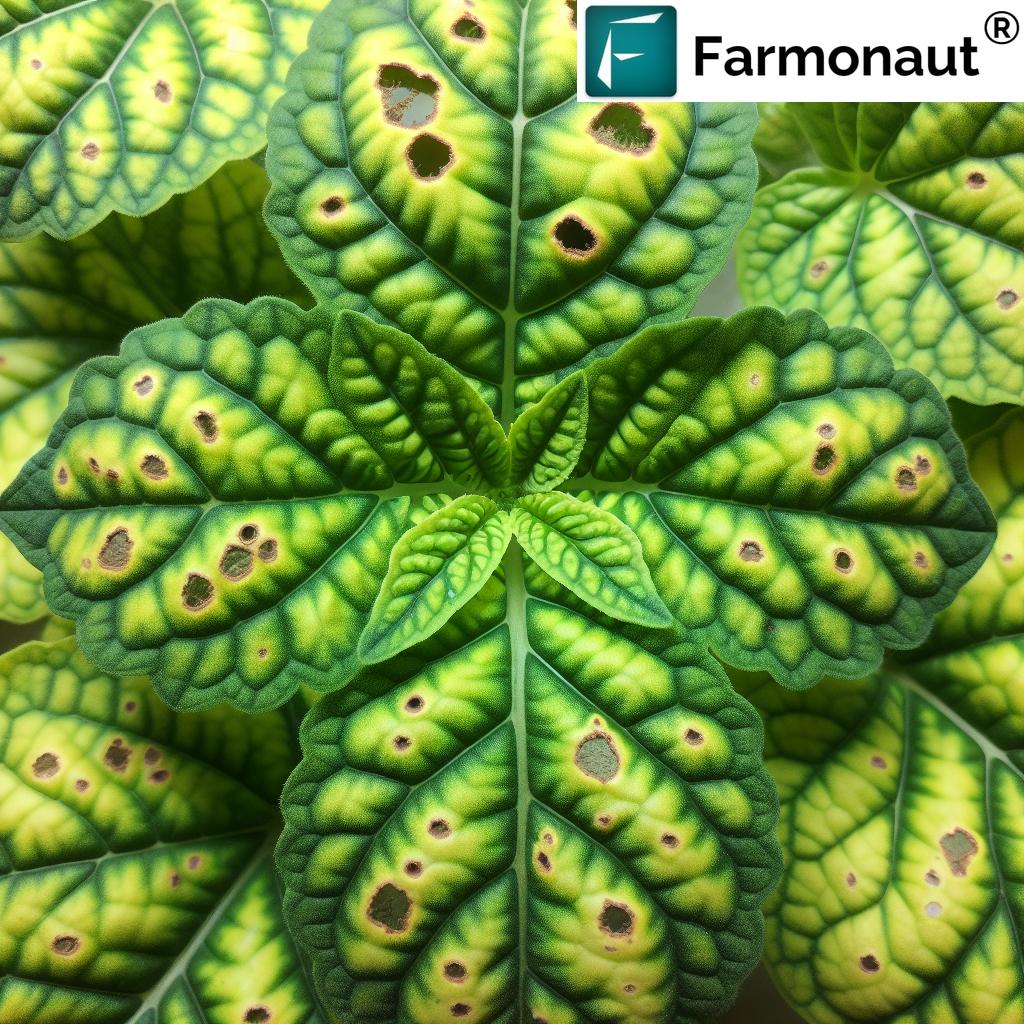
Integrated Pest Management (IPM):
- IPM in greenhouses combines biological controls (beneficial insects), mechanical methods (traps, screening), and targeted chemical interventions only when absolutely necessary.
- Regular monitoring and thresholds for action keep crop health strong and chemical input minimal.
-
Pruning and Plant Training:
- Techniques like trellising, staking, and selective pruning improve light penetration, air flow, and ultimately maximized yield per square meter.
-
Energy Efficiency:
- Switching to energy-efficient lighting, optimizing thermal screens, and considering renewable energy (e.g., solar panels) all lower our environmental footprint without sacrificing crop productivity.
Embracing sustainable greenhouse practices isn’t just responsible—it’s often a gateway to unlocking premium markets, subsidy programs, and long-term profitability.
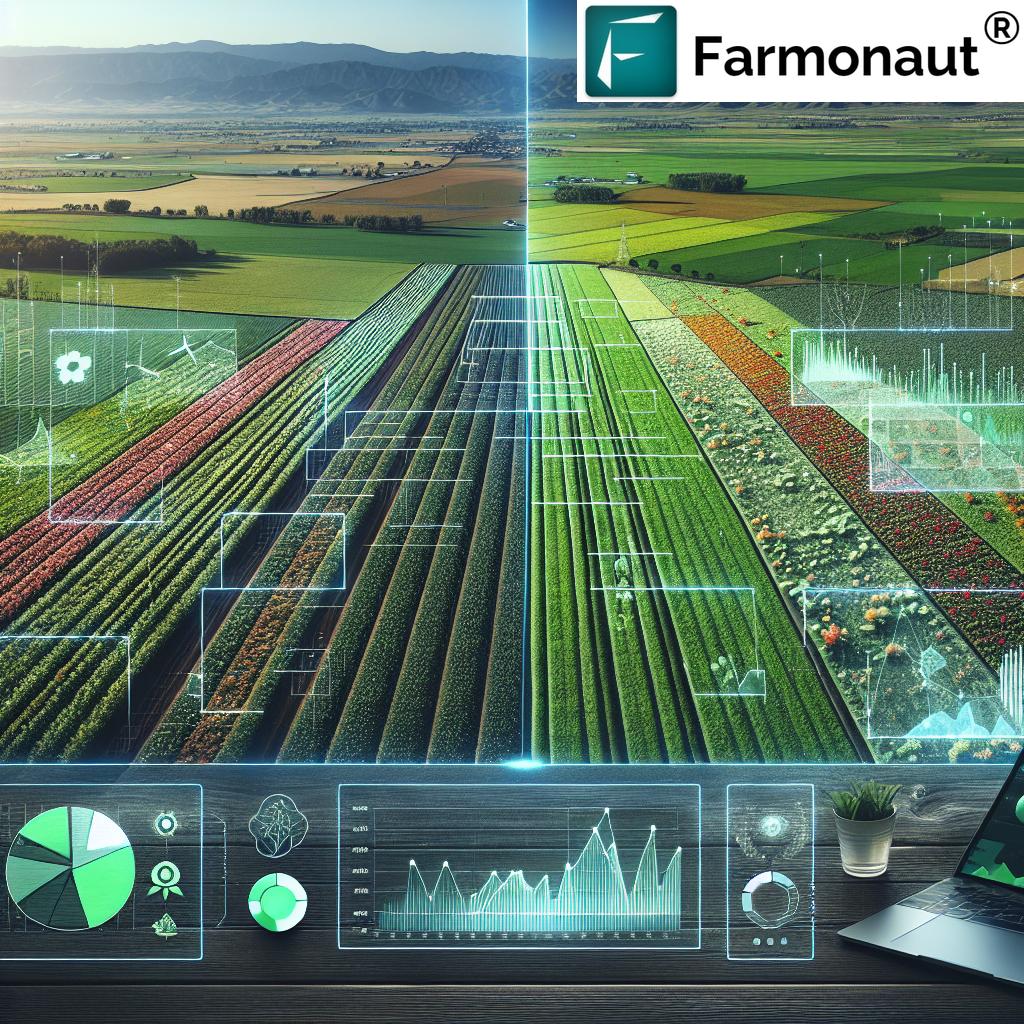
5. Data-Driven Agriculture Strategies in Greenhouses
Data-driven agriculture strategies have revolutionized how we monitor, analyze, and optimize greenhouse systems. By converting raw sensor data and satellite imagery into actionable intelligence, we move beyond reactive management into proactive interventions that boost yield and sustainability.
-
Real-Time Monitoring:
- Continuous, sensor-based monitoring of environmental parameters (temperature, humidity, light, CO₂, moisture, and plant health) enables instant detection of abnormalities.
- Satellite-based NDVI and thermal imaging (offered by Farmonaut) provide bird’s-eye views of crop vigor, stress, and irrigation needs at any time, from anywhere.
-
Predictive Analytics & AI:
- Machine learning models predict disease risk, irrigation requirements, and nutrient needs—allowing us to optimize actions well before visible issues arise.
-
KPIs & Continuous Improvement:
- Establishing performance metrics (KPIs) for every process—yield per square meter, water use efficiency, labor hours—lets us continually refine our strategies.
- Regular reviews ensure that all improvements are data-backed, scalable, and cost-effective.
For greenhouse managers keen on maximizing yield and minimizing input waste, data-driven agriculture is the gold standard—paving the way for rapid, sustainable growth and informed decision-making.
6. The Power of Staff Training & Continuous Education
Continuous learning and hands-on staff training are often underestimated drivers of efficient greenhouse management. With the rapid evolution of advanced greenhouse technologies, our workforce needs to remain technically skilled, highly adaptive, and sustainability-focused.
- Technical Training: Ongoing education on sensor installation, automated equipment troubleshooting, and interpreting data dashboards ensures top system performance.
- Sustainable Practices: Staff must be versed in best sustainable agriculture practices, enabling them to minimize environmental impact, cut resource costs, and meet certification requirements.
- Continuous Learning Culture: Promoting knowledge sharing, workshops, and digital upskilling prepares our team to adapt quickly to new challenges, technologies, and regulatory changes.
When we invest in staff training and education, we empower our teams to make informed, data-driven decisions, improve plant health, and unlock the full potential of our greenhouse investments.
Comparative Summary Table: 7 Ways to Improve Greenhouse Crop Yields
Tip: Stack these methods together—synergistic gains in yield, resource efficiency, and sustainability await!
Farmonaut Subscriptions: Precision Management for Every Scale
Farmonaut: Accelerating Precision Greenhouse Management
Farmonaut stands at the cutting edge of agricultural technology, delivering real-time, data-centric solutions for greenhouse crop yields and sustainability:
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Make informed decisions with NDVI, soil moisture, and vegetation health maps—vital for optimizing irrigation, pest control, and fertilizer use.
- AI-Powered Farm Advisory: Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI delivers personalized, real-time insights and recommendations for greenhouse management—boosting efficiency and yield.
- Resource & Fleet Management: Enhance on-site logistics for larger horticultural facilities with real-time tracking, route optimization, and cost reduction.
- Blockchain Product Traceability: Meet modern demands for supply chain transparency. Farmonaut’s traceability solutions verify product origin, reduce fraud, and increase trust for greenhouse produce.
- Carbon & Sustainability Analytics: Quantify and systematically reduce your greenhouse operation’s carbon impact using dedicated carbon footprinting analysis.
- Accessible Software on All Devices: Use Farmonaut via sleek Android, iOS, or web apps, or integrate its robust data into your enterprise platform through flexible APIs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Maximizing Greenhouse Crop Yields
- Q: What is the single most important factor for maximizing greenhouse crop yield?
A: Optimal environmental control (temperature, humidity, light) ensures the best growth and health for the crop. Integrating automated control systems and continuous monitoring amplifies the effect.
- Q: How can I monitor crop health and irrigation needs in real time?
A: Use digital tools like Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring and in-house IoT sensors for instant updates on plant stress, soil moisture, and environmental parameters for precise, timely interventions.
- Q: Which resource conservation methods are most effective in greenhouses?
A: Drip irrigation and fertigation are highly efficient, followed by integrated nutrient management and crop rotation/cover cropping for year-round soil and water savings.
- Q: Is integrated pest management (IPM) really necessary if I use modern pesticides?
A: Absolutely. Integrated pest management in greenhouses mitigates pest risk while minimizing chemical exposure, safeguarding crop quality, food safety, and environmental health.
- Q: How do smart agriculture platforms like Farmonaut help with greenhouse systems?
A: They provide AI-powered advisories, API-integrated weather and satellite data, and analytics dashboards—offering data-driven agriculture strategies for informed, efficient decisions and sustained yield increases.
- Q: How can I access Farmonaut solutions?
A: Sign up on the Farmonaut platform, download the iOS or Android app, or use the web dashboard for instant access. For API and developer resources, see API page and API documentation.
Conclusion: Maximizing Sustainability & Yields Together
Maximizing crop yields in greenhouse systems is not only about pushing productivity—it’s about building a more sustainable, profitable future for all. Each of the seven methods discussed—environmental control, advanced greenhouse technologies, efficient resource management, sustainable practices, data-driven decision-making, continuous staff education, and technology integration—unlocks new levels of efficiency, quality, and stewardship.
Embrace data-driven agriculture strategies, invest in state-of-the-art greenhouse tools like Farmonaut, and foster a culture of sustainable innovation. When we combine science, technology, and smart management, we can meet the world’s growing demand for food—while preserving our planet’s precious resources for generations to come.