- Introduction: Why Sustainable Irrigation Solutions Matter
- Understanding Sustainable Irrigation
- Traditional vs. Sustainable Irrigation Practices
- 7 Sustainable Irrigation Solutions to Double Your Yields
- Comparative Overview Table of Sustainable Irrigation Solutions
- Integrating Technology and Data – Farmonaut’s Role
- Practical Challenges & Implementation Considerations
- FAQ: Sustainable Irrigation Solutions & Efficient Water Management
- Conclusion: Shaping a Sustainable Agricultural Future
“Adopting sustainable irrigation can reduce water usage by up to 50% while potentially doubling crop yields in many regions.”
7 Sustainable Irrigation Solutions to Double Your Yields
Our world’s food security and environmental health are increasingly intertwined with how we manage agricultural water resources. As farmers, agribusinesses, and all stakeholders in agriculture and forestry, we face mounting challenges, including water scarcity, climate variability, soil degradation, and unpredictable yields.
Sustainable irrigation solutions are the cornerstone of modern food production. Efficient technologies—combined with eco-friendly water conservation practices, innovative irrigation systems, and informed management—empower us to double crop yields and sustain global food demand without exhausting our planet’s limited resources.
We invite you to explore these seven key sustainable irrigation solutions—from advanced sensors and AI to traditional rainwater harvesting—to boost your productivity, conserve resources, and minimize environmental impact.
Explore Farmonaut API Developer Docs
Understanding Sustainable Irrigation: Concepts, Scope & Importance
Sustainable irrigation is the practice of applying water to fields, crops, and forests—balancing immediate crop needs with long-term resource conservation and environmental protection. This approach transcends short-term yield maximization, integrating water management methods that safeguard our planet for future generations.
At its core, sustainable irrigation involves:
- Optimizing water usage by accurately selecting and managing systems
- Minimizing runoff, erosion, and nutrient leaching
- Enhancing soil health, fertility, and air balance
- Promoting ecological sustainability by preventing degradation of water and ecosystems
By pursuing efficient water management in agriculture, we create resilient, climate-smart, and productive landscapes.
Traditional vs. Sustainable Irrigation Practices: A Fundamental Shift
Conventional irrigation methods—notably flood and furrow irrigation—have underpinned farming and forestry for centuries. Yet, these approaches are often inefficient, driving:
- Major water losses through evaporation, deep percolation, and runoff
- Soil erosion, reducing nutrient retention and productivity
- Waterlogging and salinization that degrade soil quality
- High energy consumption due to excessive pumping
In contrast, sustainable irrigation practices aim to:
- Optimize efficiency by targeting water directly to the root zone
- Mitigate negative environmental impacts on soil, air, and surrounding ecosystems
- Leverage technology for precise distribution and smart management
Transitioning to sustainable approaches is critical for enduring food security and ecological balance.
“Efficient irrigation systems can increase water productivity by 70%, supporting both food security and environmental conservation.”
7 Sustainable Irrigation Solutions to Double Your Yields
Let us delve into the seven most impactful, sustainable irrigation solutions for modern agriculture, farming, and forestry. Each method combines science, innovation, and eco-friendly practice to propel crop productivity—all while conserving water and preserving our environment.
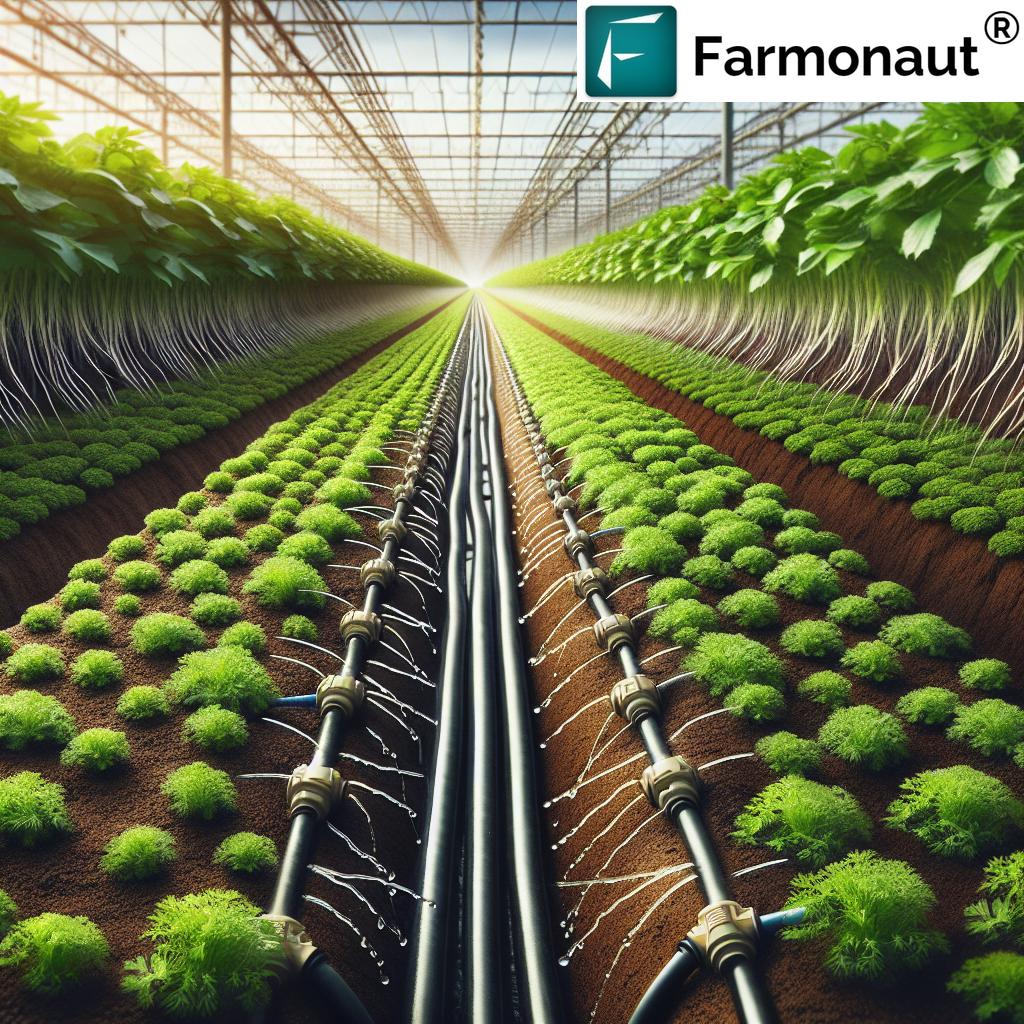
1. Micro-Irrigation Systems: Drip, Sprinkler, and Beyond
Micro-irrigation techniques—including drip, micro-sprinkler, and emitter-based setups—direct water through networks of slender tubes, pipes, and emitters right to the plant’s root zone. The result: minimal evaporation, virtually no runoff, and efficient use of every drop.
- Benefits: Drip systems can cut water usage by over 50% and plant-friendly uniformity assures healthier growth.
- Applications: Fruit orchards, vineyards, row crops (tomato, corn), greenhouse farming, and specialty horticulture.
- Features: Filters and pressure regulators maintain water quality; controllers enable precision scheduling for optimal distribution.
Learn more about Micro-Irrigation Systems.
Sustainable irrigation solutions begin here, combining classic efficiency with advanced control.
2. Subsurface Textile Irrigation (SSTI): Deep Efficiency Beneath the Surface
In subsurface textile irrigation (SSTI), a network of geotextile materials is installed beneath the soil, channeling water directly to the root zone. This approach delivers exceptional efficiency and all but eliminates water lost to evaporation and surface runoff.
- Water Savings: SSTI can reduce usage by up to 75% compared to traditional methods.
- Suitability: Urban landscaping, high-value horticulture, arid-zone agriculture, and sites with contaminated surface soil.
- Unique Advantage: SSTI supports the safe use of recycled or treated water—as all irrigation takes place below the surface, preventing aboveground contamination.
Explore Subsurface Textile Irrigation (SSTI).
3. Alternate Wetting and Drying Rice (AWD): Smarter Water Management in Paddy Fields
Alternate wetting and drying rice (AWD) is one of the most innovative irrigation systems for paddy fields. Instead of continued flooding, paddies are periodically drained, allowing the soil to dry for several days before being re-flooded.
- Water Conservation: AWD can save up to 30% water over continual flooding.
- Productivity: Enhanced root growth, improved grain filling, and reduced methane emissions align with both yield and ecological goals.
- Suitability: Rice-growing regions such as South and Southeast Asia; particularly impactful where irrigation water is limited.
Learn about AWD for rice cultivation.
4. Deficit Irrigation Strategies: Balancing Economical Use and High Yields
Deficit irrigation strategies involve providing less than the full water requirements of crops during select growth phases—especially when they are less sensitive to water stress. The key: precise timing, careful management, and in-depth crop understanding.
- Benefits: Significant water savings without substantial yield losses for many drought-tolerant crops.
- Risks: Requires close monitoring (soil moisture, meteorology) and technical know-how.
- Applications: Cereals, grapes, olives, and some fruit crops; especially in regions experiencing water scarcity.
Follow deficit irrigation best practices.
Farmonaut’s real-time satellite-based crop monitoring (learn more about large-scale farm management) empowers agribusinesses to implement precision deficit irrigation, maximizing water productivity and maintaining optimal crop health.
5. Solar-Powered Irrigation Systems: Clean Energy for Farming
Harnessing solar power for irrigation not only cuts operational costs but also advances climate goals by reducing fossil fuel reliance.
- How it Works: Solar-powered pumps tap into groundwater or move surface water through fields and distribution systems.
- Advantages: Ideal in sun-rich areas; lowers CO2 emissions; can operate off-grid for remote operations; reduces long-term expenditure on energy.
- Additional sustainability: Integrating solar power with micro-irrigation techniques further boosts water and energy efficiency.
Boost your sustainability metrics by tracking environmental impacts with Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting tools, ensuring measurable improvements while deploying innovative irrigation systems.
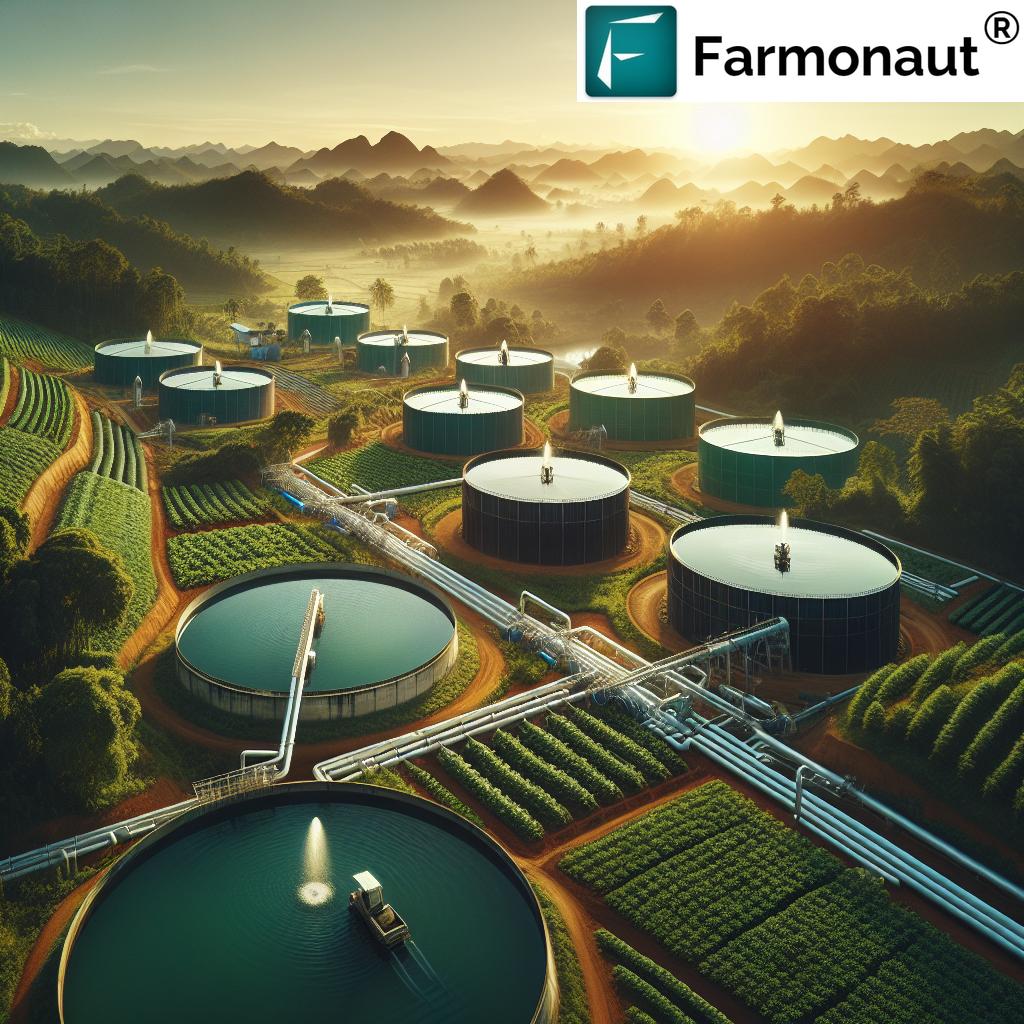
6. Rainwater Harvesting for Farming: Making Every Drop Count
Rainwater harvesting for farming is both an age-old practice and a 21st-century imperative. By collecting, storing, and reusing rainwater from rooftops, roads, or fields, producers lessen reliance on traditional water sources and safeguard groundwater reserves.
- Benefits: Enhances water availability during dry spells; improves resilience to climate variability; recharges aquifers and sustains local ecology.
- Systems: Gutters, tanks, farm ponds, check-dams—each tailored to the farm’s size and rainfall patterns.
- Integration: Rainwater, when combined with modern irrigation methods, can buffer seasonal or annual rainfall uncertainty.
For ongoing advisory about integrating harvested water with precision irrigation, Farmonaut’s crop, plantation, and forest advisory tools offer science-based, data-driven recommendations across all climate regions.
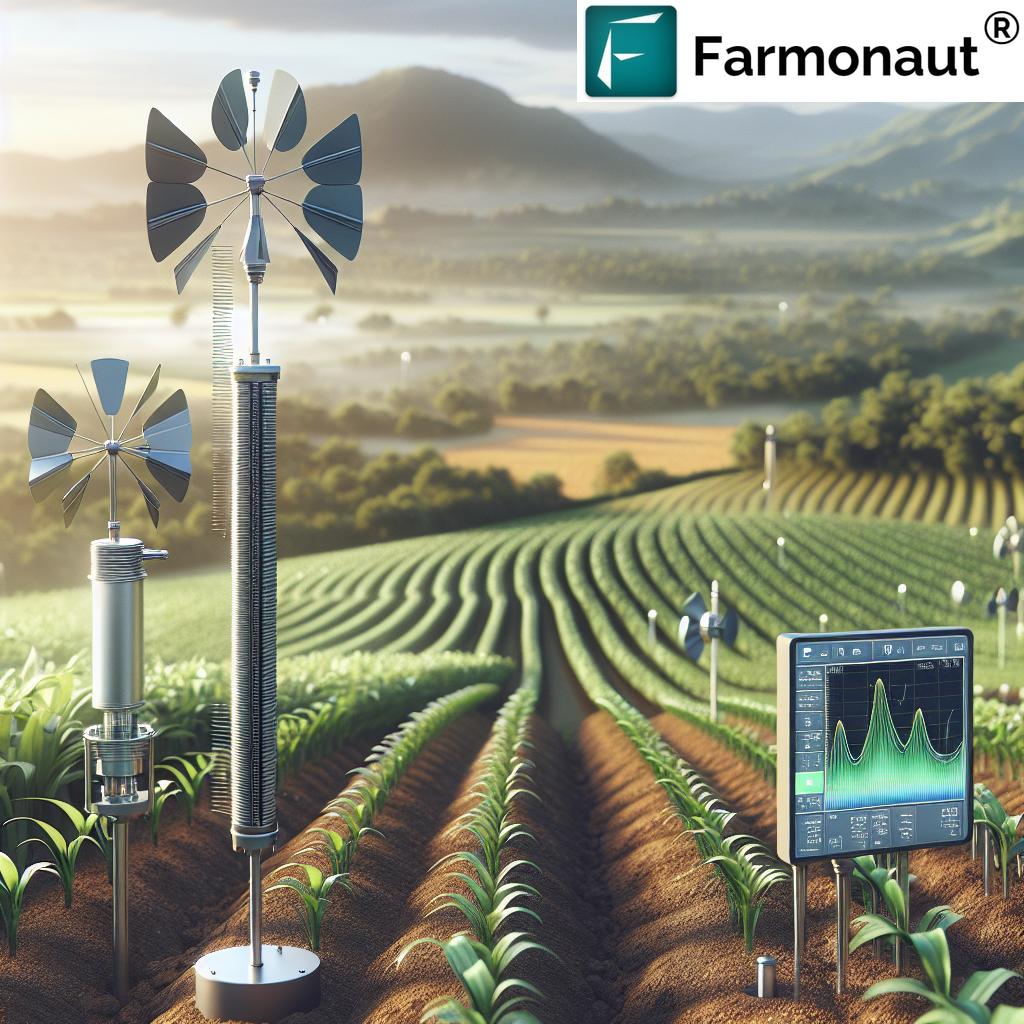
7. Smart & Automated Irrigation Technologies: Data-Driven Precision for Sustainable Yields
Modern irrigation management harnesses automation, sensors, remote monitoring, and AI-driven controls for real-time, site-specific water delivery.
- Key Components: Soil moisture sensors, weather stations, app-based scheduling, AI-powered advisory, automated zone valves, and satellite field monitoring.
- Benefits: Ensures optimal water conditions, reduces waste, lowers costs, and improves crop health. Real-time precision allows us to adapt to dynamic weather, growth, and soil quality metrics.
Leverage innovation instantly: Farmonaut’s fleet and resource management systems coordinate on-field irrigation tasks, save operational time, and reduce input wastage, especially across large plantations and contract farming ventures.
Comparative Overview Table of Sustainable Irrigation Solutions
| Irrigation Solution | Estimated Water Savings (%) | Potential Yield Increase (%) | Initial Investment (Estimated) | Environmental Impact | Suitability (Crop/Region) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Micro-Irrigation Systems | 40–60 | 20–40 | Medium–High | Reduces runoff, erosion, and improves soil health | Row crops, orchards, vineyards, greenhouses (global) |
| Subsurface Textile Irrigation (SSTI) | 60–75 | 25–50 | High | Minimizes evaporation, enables recycled water use, protects water quality | High-value horticulture, urban landscapes, dry/arid zones |
| Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD) | 20–35 | 10–25 | Low–Medium | Reduces methane emissions, slows surface water loss | Rice paddy fields, SE Asia, S Asia, water-limited regions |
| Deficit Irrigation | 25–45 | 5–20 | Low | Conserves water, limits overuse of resources | Cereals, grapes, olives; semi-arid & arid lands |
| Solar-Powered Irrigation | 10–35* | 10–15 | Medium | Reduces emissions, renewable energy source | Farms in sun-rich regions, off-grid rural areas |
| Rainwater Harvesting | 10–35 | 10–20 | Low–Medium | Improves water table, prevents runoff and erosion | Regions with seasonal rainfall, rainfed crops |
| Smart/Automated Irrigation | 30–55 | 20–35 | Medium–High | Prevents overwatering, data-driven conservation | All crop types, scalable, tech-enabled farmers |
Integrating Technology and Data: Farmonaut’s Role in Sustainable Irrigation Management
Implementing sustainable irrigation solutions is increasingly data-driven and tech-enabled. Farmonaut empowers farmers, agribusinesses, and governments with affordable, scalable, and actionable farm management technology.
Key services influencing irrigation and resource management include:
- Satellite-based crop health monitoring: Real-time, field-wide tracking of NDVI (vegetation health), soil moisture, and risk alerts for disease, drought, and nutrient deficiencies. This enables us to optimize irrigation scheduling and intervene exactly where (and when) water is needed.
- AI-powered advisory (“Jeevn”): The Jeevn system leverages weather forecasts, crop-specific models, and satellite data to deliver farm-level suggestions for irrigation timings and volumes—saving us time, effort, and resources.
- Blockchain-based traceability: For corporates and supply chains, transparency in resource use and irrigation methods not only builds trust but also supports eco-labeling and regulatory compliance. Learn about Farmonaut Product Traceability.
- Fleet, machinery & resource management: For contract farming, plantation owners, and large agribusinesses, Farmonaut’s platform supports optimal deployment of assets for sustainable irrigation, fertilizer planning, and harvest scheduling. Explore Fleet and Resource Management
- Real-time carbon footprinting: Use carbon tracking tools to measure progress and document your farm’s environmental impact of irrigation, fertilizer, and machinery use.
From large-scale agro management to smallholder farm tech, Farmonaut makes precision agriculture available to everyone via apps, web dashboard, and developer API.
Practical Challenges and Considerations for Implementing Sustainable Irrigation Solutions
While the environmental and yield benefits of sustainable irrigation solutions are well established, success relies on recognizing (and planning for) practical hurdles:
- Upfront investment: Technologies like micro-irrigation, SSTI, and automation systems may involve considerable initial costs—making access to financial support crucial. Farmonaut’s crop loan and insurance verification helps streamline and secure funding for such upgrades.
- Technical expertise: Many advanced methods demand skill in installation, maintenance, and ongoing management. Extension services and digital advisory platforms bridge this knowledge gap.
- Water quality: Preventing soil and crop contamination from poor-quality irrigation water underscores the value of both pre-treatment and below-ground (e.g., SSTI) delivery.
- Climatic variability: Changing rainfall patterns, droughts, or flooding can challenge even the most advanced irrigation systems. Real-time monitoring and flexible scheduling, supported by digital platforms, build resilience into our water management strategies.
Tip: Reliable, affordable digital decision-support (like Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI) empowers stakeholders to select and manage irrigation methods best-suited to their unique field, climate, and resource conditions.
Connecting traceability & sustainability: Learn about product traceability for eco-friendly agricultural products on Farmonaut.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) – Sustainable Irrigation Solutions & Efficient Water Management
What is sustainable irrigation?
Sustainable irrigation involves delivering water to crops and forests efficiently, conserving resources, and protecting the environment. This includes methods like micro-irrigation, SSTI, and advanced scheduling, all aimed at optimizing use by matching water delivery to plant needs and minimizing environmental impacts.
Which irrigation system is most water-efficient?
SSTI (Subsurface Textile Irrigation) and drip (micro-irrigation) systems are recognized as the most water-efficient choices, providing targeted water to the root zone, minimizing evaporation and runoff, and supporting high-value or drought-prone crops.
How can small farmers adopt sustainable solutions affordably?
Options include phased upgrades (starting with micro-irrigation in key fields), rainwater harvesting for supplemental supply, and leveraging digital satellite monitoring (Farmonaut Web/App) to optimize irrigation without costly input waste.
Are there digital tools for efficient irrigation management?
Yes, platforms like Farmonaut offer accessible, AI-powered satellite monitoring and advisory tools for all farm sizes—supporting crop health, soil moisture, water stress alerts, and site-specific irrigation scheduling.
How to ensure sustainable practices in rice paddies?
Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD) is the recommended solution—supported by weather tracking and remote monitoring to ensure neither over-irrigation nor drought conditions prevail.
What’s the role of traceability in irrigation management?
Blockchain-based systems, like those from Farmonaut, document sustainable resource use—enabling branding, certification, and consumer trust.
How to measure the environmental impact of irrigation?
Quantify emissions, water use, and savings with Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting solutions.
Conclusion: Shaping a Sustainable Agricultural Future
Sustainable irrigation solutions are not only vital for maximizing yields—they are the bridge to an ecologically balanced, resilient, and prosperous future for all stakeholders in agriculture, farming, and forestry. By implementing innovative and resource-efficient irrigation systems, we:
- Conserve water and ensure its availability for the next generation
- Safeguard soils from degradation, erosion, and nutrient leaching
- Enhance both plant health and productivity, building global food security
- Reduce costs, boost profitability, and ensure compliance with modern sustainability standards
Utilizing accessible digital platforms (like Farmonaut) for monitoring, AI scheduling, and resource management takes the guesswork out of sustainable practices and accelerates positive environmental impact.
Join us in transforming agriculture with sustainable irrigation—where technology, tradition, and stewardship converge for a thriving planet and prosperous future.