Boosting Soil Health: The Essential Guide to Carbon Enrichment and Its Impact on Agriculture
In the ever-evolving world of agriculture, we at Farmonaut are committed to exploring innovative techniques that enhance soil health and promote sustainable farming practices. One of the most crucial aspects of soil management that has gained significant attention in recent years is the process of adding carbon to soil. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the importance of soil carbon, the carbon cycle in soil, and how farmers can effectively enrich their soil with carbon to boost crop productivity and contribute to environmental conservation.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Soil Carbon
- The Carbon Cycle in Soil
- Why is Soil Carbon Important?
- Methods for Adding Carbon to Soil
- Carbon Products for Soil
- Benefits of Carbon-Rich Soil
- Challenges in Soil Carbon Management
- Farmonaut’s Role in Soil Carbon Management
- Future Perspectives on Soil Carbon
- FAQs
1. Understanding Soil Carbon
Soil carbon refers to the carbon stored in soil organic matter. It’s a vital component of healthy soil and plays a crucial role in various soil functions. When we talk about adding carbon to soil, we’re essentially discussing ways to increase the organic matter content in the soil.
Soil organic matter consists of:
- Living organisms (bacteria, fungi, earthworms, etc.)
- Fresh organic residues
- Partially decomposed organic matter
- Humus (fully decomposed organic matter)
The amount of carbon in soil can vary greatly depending on factors such as climate, vegetation, soil type, and land management practices. In general, soils contain about 2-10% organic matter, which is approximately 58% carbon.
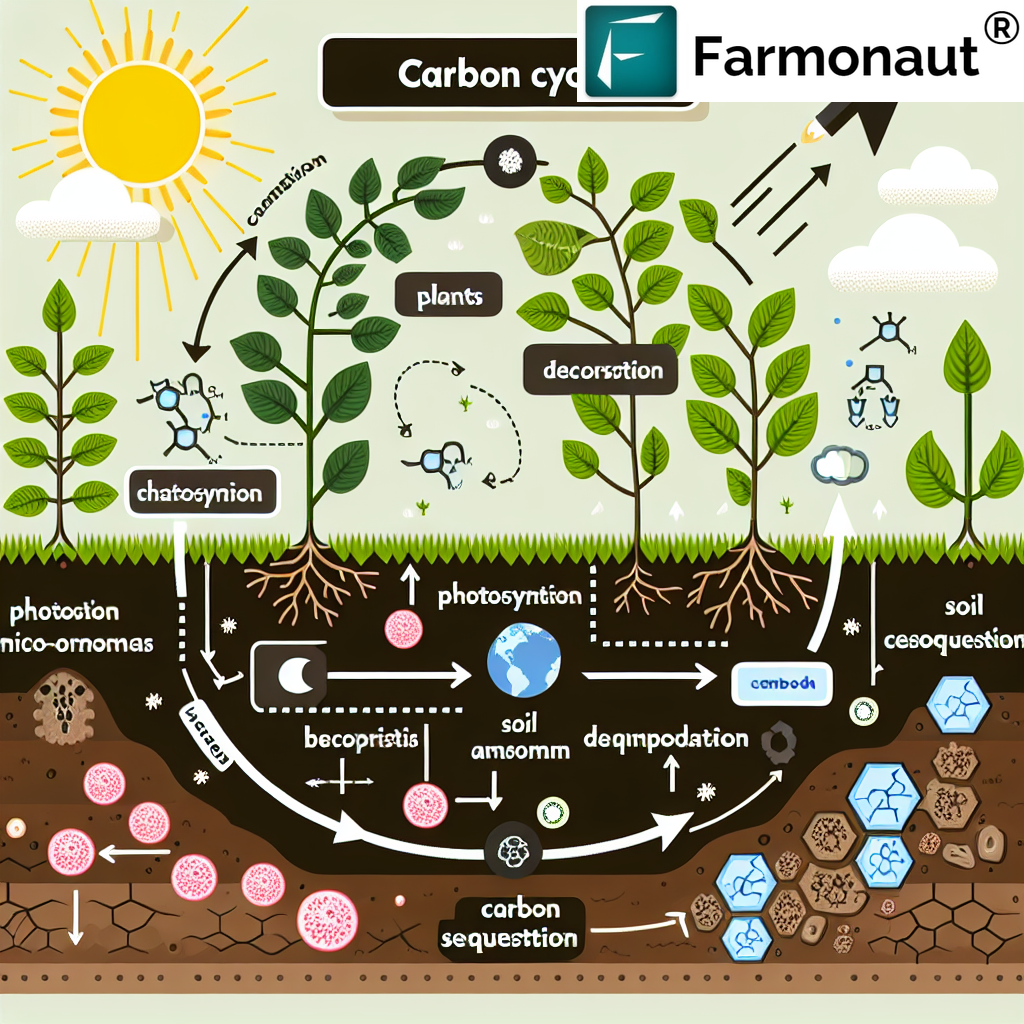
2. The Carbon Cycle in Soil
Understanding the carbon cycle in soil is crucial for effective soil management. This cycle involves the continuous exchange of carbon between the soil, plants, and the atmosphere.

The carbon cycle in soil involves several processes:
- Carbon Input: Plants absorb CO2 from the atmosphere through photosynthesis and convert it into organic compounds.
- Carbon Transfer: Some of this carbon is transferred to the soil through root exudates and when plant parts die and decompose.
- Decomposition: Soil microorganisms break down organic matter, releasing some carbon back into the atmosphere as CO2.
- Carbon Stabilization: Some carbon becomes stabilized in the soil, forming long-lasting organic compounds.
- Carbon Loss: Carbon can be lost from the soil through erosion, leaching, and human activities like tillage.
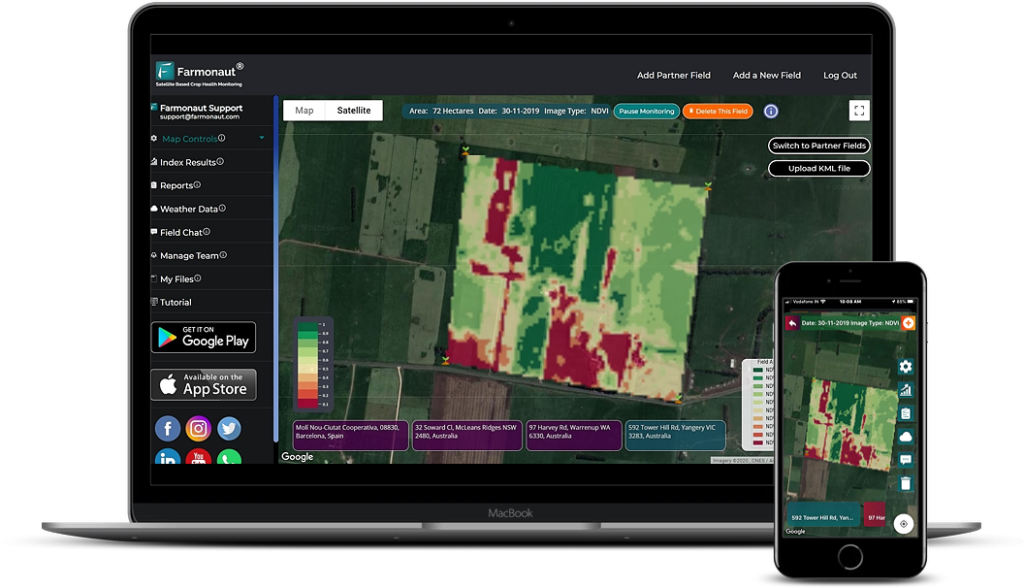
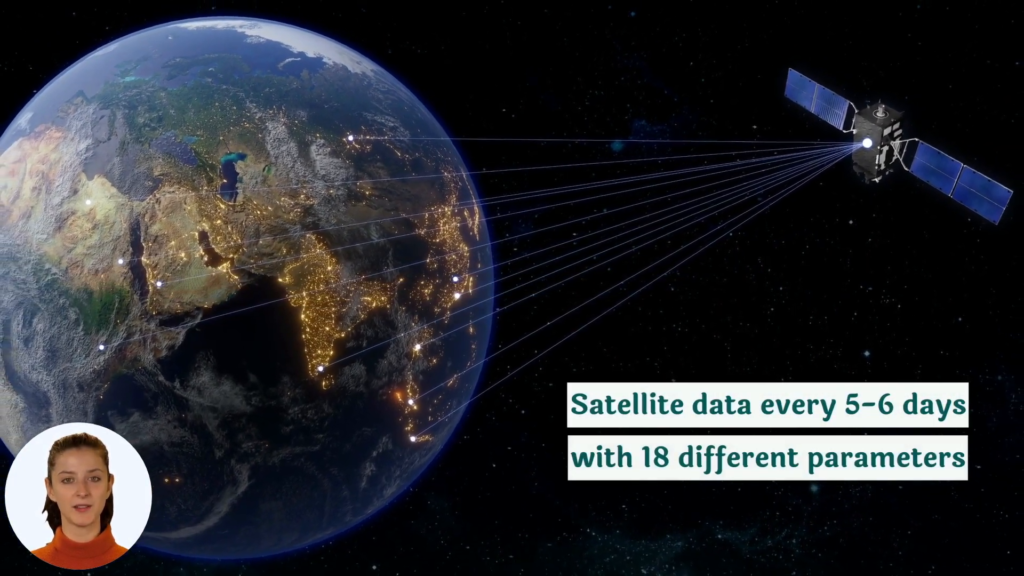
At Farmonaut, we recognize the importance of this cycle and provide farmers with tools to monitor and manage their soil health effectively. Our satellite-based crop monitoring system can help detect changes in vegetation health, which can be indicative of soil carbon levels. Learn more about our services here.
3. Why is Soil Carbon Important?
The question “why is soil carbon important?” is fundamental to understanding modern agricultural practices. Soil carbon plays a crucial role in various aspects of soil health and overall ecosystem functioning:
- Soil Structure: Carbon helps bind soil particles together, improving soil structure and reducing erosion.
- Water Retention: Carbon-rich soils can hold more water, reducing the need for irrigation and improving drought resistance.
- Nutrient Retention: Organic matter increases the soil’s cation exchange capacity, enhancing nutrient retention and availability.
- Microbial Activity: Soil carbon supports a diverse and active microbial community, which is essential for nutrient cycling and plant health.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Soil can act as a significant carbon sink, helping to mitigate climate change by sequestering atmospheric CO2.
- Crop Productivity: Soils with higher carbon content generally have higher fertility and can support better crop yields.
Given these benefits, adding carbon to soil has become a key focus in sustainable agriculture practices. At Farmonaut, we provide farmers with the tools to monitor their soil health and make informed decisions about carbon management. Our Satellite API can be integrated into farm management systems to track vegetation health, which is often indicative of soil carbon levels.
4. Methods for Adding Carbon to Soil
There are several effective methods for adding carbon to soil. These practices not only increase soil carbon but also improve overall soil health and productivity:
- Cover Cropping: Planting cover crops during fallow periods adds organic matter to the soil and prevents erosion.
- No-Till or Reduced Tillage: Minimizing soil disturbance helps preserve existing soil carbon and promotes carbon accumulation.
- Crop Rotation: Diversifying crops can increase the variety of organic matter inputs and improve soil health.
- Compost Application: Adding compost to soil directly increases organic matter content.
- Biochar Application: Biochar is a stable form of carbon that can persist in soil for long periods.
- Agroforestry: Integrating trees into agricultural landscapes can significantly increase soil carbon over time.
- Managed Grazing: Proper grazing management can stimulate plant growth and increase carbon inputs to soil.
- Residue Retention: Leaving crop residues on the field after harvest adds carbon to the soil as they decompose.
At Farmonaut, we help farmers monitor the effectiveness of these practices through our advanced satellite monitoring system. Our technology can track changes in vegetation health and soil moisture, providing insights into the impact of carbon management strategies. Download our app for Android or iOS to start monitoring your fields today.
5. Carbon Products for Soil
In addition to natural methods, there are several carbon products for soil that can be used to enhance soil carbon content:
- Biochar: A carbon-rich material produced by burning organic matter in a low-oxygen environment. It can persist in soil for hundreds to thousands of years.
- Compost: Decomposed organic matter that provides a rich source of carbon and other nutrients.
- Humic Substances: These are complex organic compounds that are the end products of microbial decomposition and chemical alteration of plant and animal matter.
- Carbon-based Fertilizers: Some fertilizers are formulated with organic carbon to improve soil health alongside nutrient provision.
- Microbial Inoculants: These products contain beneficial microorganisms that can enhance organic matter decomposition and carbon cycling in soil.
When considering the use of these products, it’s important to assess their suitability for your specific soil conditions and crop needs. Our Farmonaut system can help you monitor the impact of these products on your soil and crop health over time.
6. Benefits of Carbon-Rich Soil
The question “is carbon good for soil?” can be answered with a resounding yes. Carbon-rich soils offer numerous benefits:
- Improved Soil Structure: Carbon helps bind soil particles, creating a crumbly structure that’s ideal for root growth and water infiltration.
- Enhanced Water Holding Capacity: Organic matter can hold up to 20 times its weight in water, improving drought resistance.
- Increased Nutrient Availability: Carbon-rich soils have a higher cation exchange capacity, retaining and releasing nutrients more effectively.
- Better Soil Biology: Higher carbon levels support a more diverse and active soil microbial community.
- Reduced Erosion: Improved soil structure and vegetation cover in carbon-rich soils reduce the risk of erosion.
- Higher Crop Yields: All these factors contribute to potentially higher and more stable crop yields.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Increasing soil carbon helps sequester atmospheric CO2, contributing to climate change mitigation.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to helping farmers achieve these benefits through our advanced monitoring and advisory services. Our AI-powered system, Jeevn AI, provides personalized recommendations to optimize soil health and crop productivity.
7. Challenges in Soil Carbon Management
While the benefits of adding carbon to soil are clear, there are several challenges that farmers may face:
- Time: Building soil carbon is a slow process that can take years or even decades to show significant results.
- Cost: Some carbon-building practices may require initial investments in new equipment or inputs.
- Knowledge Gap: Effective carbon management requires understanding complex soil processes and adapting practices to local conditions.
- Measurement Difficulties: Accurately measuring changes in soil carbon can be challenging and expensive.
- Climate Variability: Changing weather patterns can affect the rate of carbon accumulation and loss in soil.
- Competing Priorities: Farmers often need to balance carbon management with other agricultural priorities.
Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring system helps address some of these challenges by providing real-time data on crop and soil health. Our technology allows farmers to track the impact of their carbon management practices over time without the need for expensive on-ground measurements.
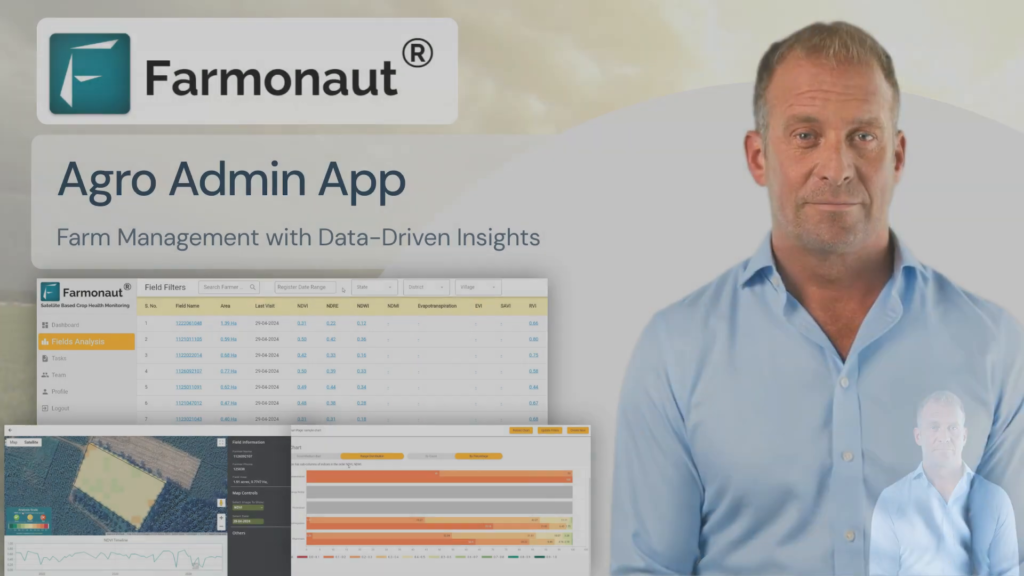
8. Farmonaut’s Role in Soil Carbon Management
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to supporting farmers in their soil carbon management efforts. Our advanced technologies offer several key advantages:
- Satellite Monitoring: Our satellite-based system provides regular updates on vegetation health, which can be indicative of soil carbon levels.
- AI-Powered Insights: Our Jeevn AI system analyzes data to provide personalized recommendations for soil health improvement.
- Historical Data Analysis: We help farmers track changes in their soil health over time, allowing them to assess the impact of their carbon management practices.
- Integration with Farm Management: Our API allows for seamless integration with existing farm management systems.
- Accessibility: Our services are available through web and mobile platforms, making it easy for farmers to access insights anytime, anywhere.
| Feature | Farmonaut Satellite System | Drone-based Monitoring | IoT-based Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage Area | Large scale (Global) | Limited (Local) | Very Limited (Point-based) |
| Frequency of Data | Daily to Weekly | On-demand (Labor intensive) | Continuous (Limited points) |
| Cost-effectiveness | High | Medium | Low |
| Ease of Use | High (No on-ground equipment) | Medium (Requires piloting skills) | Low (Requires installation and maintenance) |
| Data Analysis | Advanced AI-powered analysis | Requires separate analysis tools | Limited to sensor capabilities |
By leveraging our technology, farmers can make more informed decisions about their soil carbon management strategies, ultimately leading to healthier soils and more productive farms.
9. Future Perspectives on Soil Carbon
As we look to the future, the importance of soil carbon in agriculture and environmental management is only set to increase:
- Carbon Markets: There’s growing interest in developing carbon markets that would allow farmers to earn credits for sequestering carbon in their soils.
- Precision Carbon Management: Advances in technology, like those offered by Farmonaut, will enable more precise and efficient carbon management practices.
- Policy Developments: We expect to see more policies and incentives aimed at promoting soil carbon sequestration as a climate change mitigation strategy.
- Research and Innovation: Ongoing research is likely to uncover new methods and technologies for enhancing soil carbon levels.
- Consumer Awareness: As consumers become more environmentally conscious, there may be increased demand for products from farms practicing good carbon management.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to staying at the forefront of these developments, continually improving our services to help farmers adapt to and benefit from these changes.
10. FAQs
Q: How long does it take to increase soil carbon levels?
A: Increasing soil carbon levels is a gradual process that can take years to decades, depending on the practices used and local conditions. Some changes may be noticeable within 3-5 years, but significant increases often take longer.
Q: Can adding carbon to soil improve crop yields?
A: Yes, increasing soil carbon content can lead to improved crop yields. Carbon-rich soils generally have better structure, water-holding capacity, and nutrient availability, all of which contribute to healthier plants and potentially higher yields.
Q: What’s the best way to add carbon to soil?
A: There’s no one-size-fits-all approach. The best method depends on your specific soil conditions, climate, and farming system. Common effective practices include cover cropping, reduced tillage, adding compost or biochar, and implementing crop rotations.
Q: How can I measure the carbon in my soil?
A: While laboratory tests provide the most accurate measurements, they can be expensive and time-consuming. At Farmonaut, we offer satellite-based monitoring that can provide insights into soil health and vegetation vigor, which are often indicative of soil carbon levels.
Q: Is adding carbon to soil expensive?
A: The cost can vary depending on the methods used. Some practices, like reduced tillage, can actually save money in the long run. Others, like applying biochar, may have upfront costs. However, the long-term benefits to soil health and productivity often outweigh the initial investments.
Q: Can soil carbon help combat climate change?
A: Yes, increasing soil carbon can help mitigate climate change. Soils can act as a significant carbon sink, removing CO2 from the atmosphere and storing it in a stable form. This is why soil carbon management is increasingly recognized as an important climate change mitigation strategy.
Conclusion
The importance of soil carbon in agriculture cannot be overstated. From improving soil health and crop productivity to mitigating climate change, the benefits of adding carbon to soil are far-reaching. While there are challenges in managing soil carbon, the long-term benefits make it a worthwhile endeavor for farmers worldwide.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to supporting farmers in their soil health management efforts. Our advanced satellite monitoring and AI-powered advisory systems provide valuable insights that can help farmers make informed decisions about their carbon management strategies.
As we move towards a more sustainable future in agriculture, practices that enhance soil carbon will undoubtedly play a crucial role. By embracing these practices and leveraging technologies like those offered by Farmonaut, farmers can not only improve their productivity but also contribute to global efforts in environmental conservation.
Ready to start your journey towards better soil health management? Subscribe to Farmonaut today:
Together, we can work towards healthier soils, more productive farms, and a more sustainable future for agriculture.