Citrus and Black Aphid Life Cycles: Understanding and Managing These Common Orchard Pests
In the world of agriculture and horticulture, understanding pest life cycles is crucial for effective management and crop protection. At Farmonaut, we recognize the importance of this knowledge, especially when it comes to common orchard pests like citrus aphids and black aphids. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve deep into the citrus aphid life cycle and black aphid life cycle, providing valuable insights for farmers and gardeners alike.
Introduction to Aphids in Agriculture
Aphids are small, soft-bodied insects that can cause significant damage to crops worldwide. They are known for their rapid reproduction and ability to transmit plant viruses. Two particularly troublesome species in orchards are citrus aphids and black aphids. Understanding their life cycles is key to implementing effective control measures.
The Citrus Aphid Life Cycle
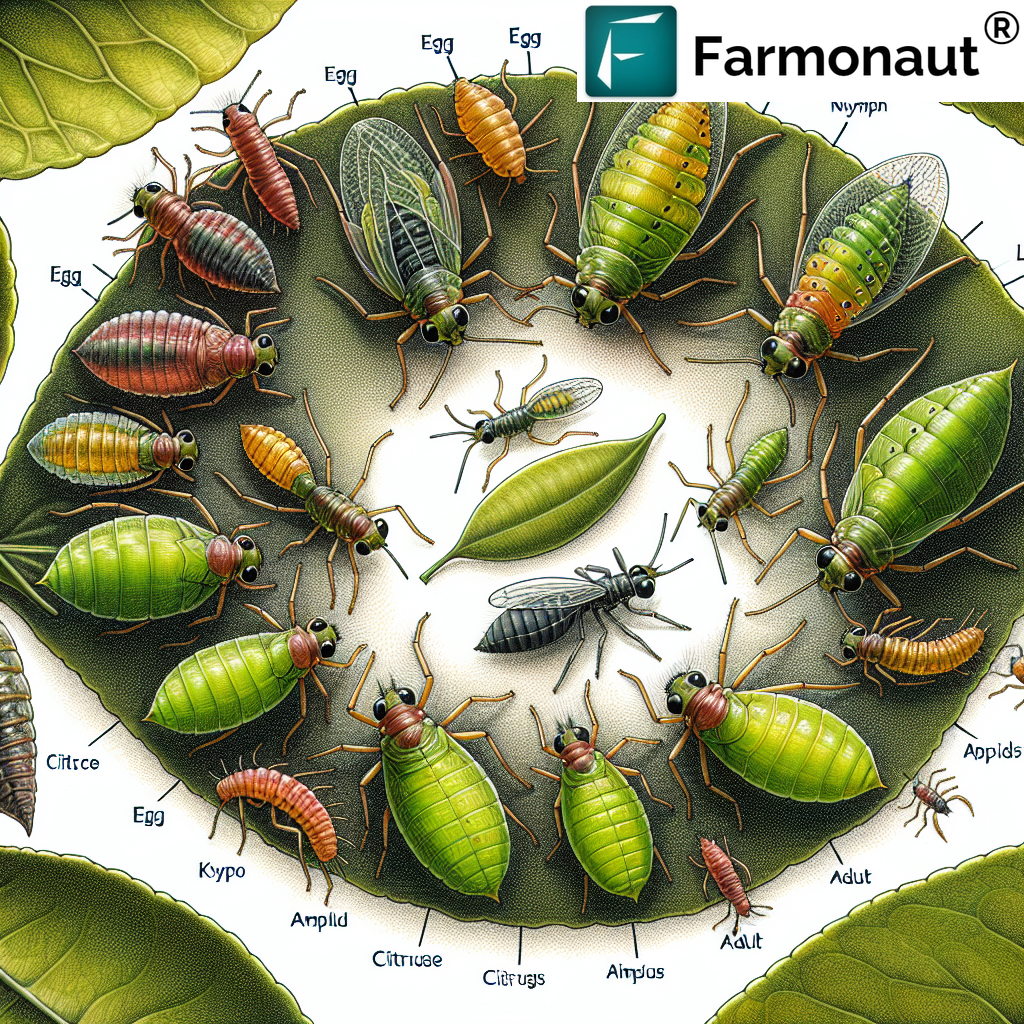
Citrus aphids, scientifically known as Toxoptera citricida, are a major pest in citrus orchards globally. Their life cycle is intricate and well-adapted to their host plants. Let’s break down the citrus aphid life cycle into its key stages:
- Egg Stage: Unlike some aphid species, citrus aphids rarely lay eggs in warm climates. Instead, they primarily reproduce through parthenogenesis (reproduction without fertilization).
- Nymph Stage: Nymphs are born live and go through four instars (molting stages) before reaching adulthood. This stage typically lasts 6-8 days, depending on environmental conditions.
- Adult Stage: Adult citrus aphids can be winged or wingless. Winged forms typically appear when populations are high or food sources are scarce, allowing for dispersal to new host plants.
- Reproduction: Adult females can produce up to 100 offspring in their lifetime, which typically spans about 20-30 days.
The entire citrus aphid life cycle can be completed in as little as 7-10 days under optimal conditions, leading to rapid population growth and potential crop damage.
The Black Aphid Life Cycle
Black aphids, or Aphis fabae, are another common pest in various crops, including fruit trees and vegetables. The black aphid life cycle shares similarities with citrus aphids but has some unique characteristics:
- Egg Stage: Unlike citrus aphids, black aphids typically overwinter as eggs on primary host plants like euonymus or viburnum.
- Nymph Stage: Nymphs hatch in spring and go through four instars, similar to citrus aphids. This stage lasts about 7-10 days.
- Adult Stage: Adults can be winged or wingless. Winged forms are more common in black aphids and play a crucial role in colonizing new host plants.
- Reproduction: Adult females can produce 20-40 offspring over their lifetime, which is typically 20-30 days.
The black aphid life cycle is slightly longer than that of citrus aphids, typically taking 10-14 days to complete under favorable conditions.
Comparing Citrus and Black Aphid Life Cycles
While both citrus and black aphids can cause significant damage to crops, there are notable differences in their life cycles:
- Overwintering: Citrus aphids rarely produce eggs and can reproduce year-round in warm climates, while black aphids typically overwinter as eggs.
- Host Range: Citrus aphids are more specialized, primarily affecting citrus trees, while black aphids have a broader host range.
- Reproduction Rate: Citrus aphids generally have a higher reproductive rate, potentially producing more offspring per female.
- Dispersal: Black aphids tend to produce more winged forms for dispersal compared to citrus aphids.
Impact on Agriculture and Horticulture
Both citrus and black aphids can have severe impacts on crop health and yield:
- Direct Damage: Aphids feed on plant sap, causing leaf curling, stunted growth, and reduced fruit quality.
- Honeydew Production: Aphids excrete honeydew, which can lead to sooty mold growth on leaves and fruits.
- Virus Transmission: Both species can transmit plant viruses, potentially causing widespread crop losses.
- Economic Losses: Infestations can result in significant economic losses for farmers and orchardists.
Management Strategies for Aphid Control
At Farmonaut, we advocate for integrated pest management (IPM) strategies to control aphid populations effectively. Here are some key approaches:
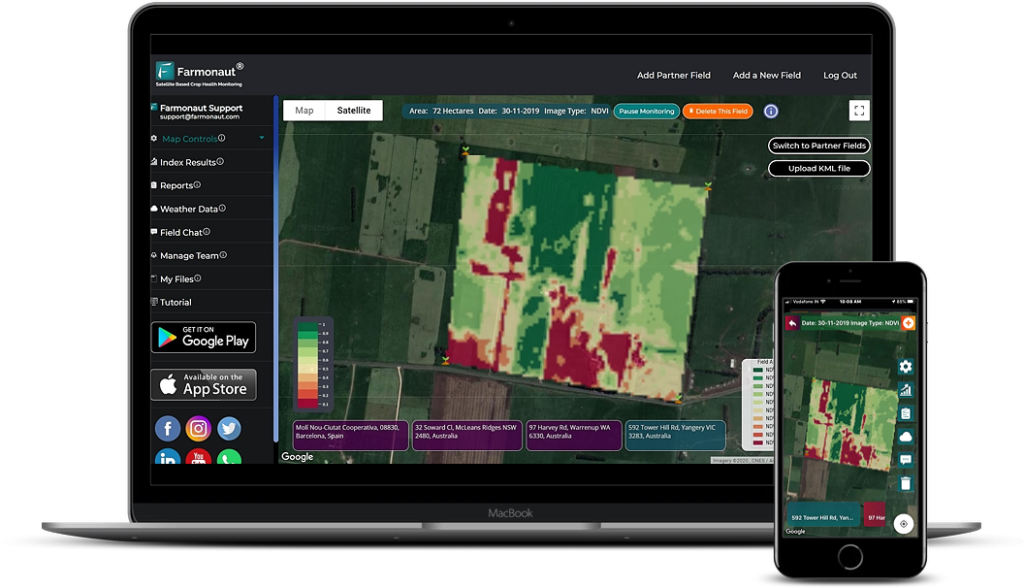
- Monitoring: Regular scouting and early detection are crucial. Our satellite-based crop health monitoring system can help detect stress signs in orchards, potentially indicating aphid infestations. Learn more about our monitoring tools here.
- Biological Control: Encourage natural predators like ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitic wasps. These beneficial insects can help keep aphid populations in check.
- Cultural Practices: Proper pruning, adequate spacing, and balanced fertilization can reduce plant stress and make them less susceptible to aphid infestations.
- Chemical Control: When necessary, targeted insecticide applications can be effective. However, it’s crucial to use them judiciously to prevent resistance and protect beneficial insects.
- Resistant Varieties: Planting aphid-resistant crop varieties can be an effective long-term strategy, especially in areas prone to heavy infestations.
Farmonaut’s Role in Aphid Management
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to helping farmers and orchardists manage pests like aphids more effectively through our advanced agricultural technologies:
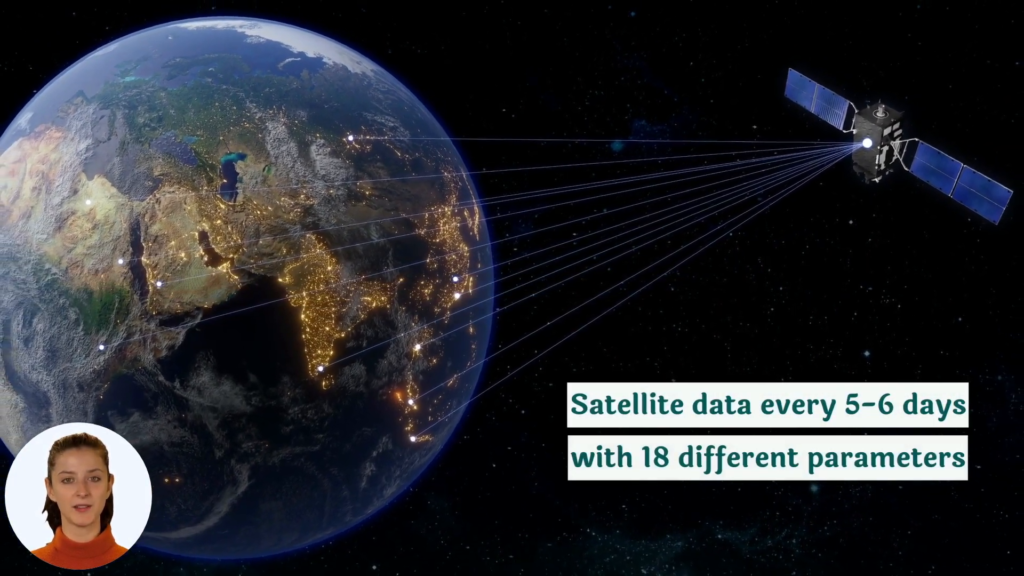
- Satellite-Based Monitoring: Our satellite imagery can detect early signs of crop stress, potentially indicating aphid infestations before they become severe.
- AI-Powered Advisories: Our Jeevn AI system provides personalized recommendations for pest management based on real-time data and local conditions.
- Weather Forecasting: Accurate weather predictions help farmers time their pest control measures for maximum effectiveness.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: By integrating various data sources, we help farmers make informed decisions about when and how to intervene in aphid infestations.
To learn more about how Farmonaut can help you manage aphids and other pests, visit our app page or explore our API documentation.
The Future of Aphid Management
As we look to the future, innovative technologies will play an increasingly important role in managing aphids and other agricultural pests:
- Precision Agriculture: Advanced sensors and drones may provide even more detailed pest monitoring capabilities.
- Genetic Engineering: Development of more resistant crop varieties through genetic modification or gene editing techniques.
- Pheromone-Based Controls: Advanced pheromone traps and disruptors could offer more targeted and environmentally friendly pest control options.
- AI and Machine Learning: Improved predictive models for pest outbreaks and more precise treatment recommendations.
At Farmonaut, we’re constantly innovating to stay at the forefront of these technological advancements, ensuring that our farmers have access to the best tools for pest management.
Why Choose Farmonaut for Pest Management?
Farmonaut’s satellite-based system offers several advantages over traditional drone and IoT-based farm monitoring:
| Feature | Farmonaut Satellite System | Drone-based Monitoring | IoT-based Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage Area | Large scale (hundreds to thousands of hectares) | Limited by flight time and regulations | Limited by sensor placement |
| Frequency of Data Collection | Regular updates (every 3-5 days) | Dependent on manual flights | Continuous but localized |
| Initial Setup Cost | Low | High (equipment purchase) | Moderate to High (sensor network) |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Regular (battery, repairs) | Regular (battery, sensor calibration) |
| Data Processing | Automated with AI | Often requires manual processing | Automated but limited to sensor data |
| Weather Independence | High (can penetrate clouds) | Low (affected by wind, rain) | Moderate (some weather impact) |
Conclusion
Understanding the citrus aphid life cycle and black aphid life cycle is crucial for effective pest management in orchards and other agricultural settings. By combining this knowledge with advanced technologies like those offered by Farmonaut, farmers and orchardists can significantly improve their pest control strategies, leading to healthier crops and better yields.
We invite you to explore how Farmonaut can revolutionize your approach to pest management and overall farm productivity. Download our app for Android or iOS, or check out our API documentation for custom integrations.
FAQ Section
- Q: How long does the citrus aphid life cycle typically last?
A: The citrus aphid life cycle can be completed in as little as 7-10 days under optimal conditions. - Q: Do black aphids lay eggs?
A: Yes, black aphids typically overwinter as eggs on primary host plants, unlike citrus aphids which rarely produce eggs in warm climates. - Q: How can Farmonaut help in managing aphid infestations?
A: Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring system can detect early signs of crop stress, potentially indicating aphid infestations. Our AI-powered advisories also provide personalized pest management recommendations. - Q: Are there any natural predators of aphids?
A: Yes, ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitic wasps are natural predators of aphids and can be effective in biological control strategies. - Q: How often should I monitor my orchard for aphids?
A: Regular monitoring is crucial. With Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring, you can get updates every 3-5 days, allowing for early detection of potential infestations.
Ready to take your pest management to the next level? Subscribe to Farmonaut today!