Crop Conditions: 7 Shocking Tech Hacks for Yields!
“Precision agriculture can boost crop yields by up to 20% through real-time monitoring and data-driven decisions.”
Table of Contents
- Summary: Understanding Crop Conditions in Agriculture, Farming, and Forestry
- Environmental Factors Influencing Crop Conditions
- Biological Factors Affecting Crop Conditions
- Management Practices to Optimize Crop Conditions
- Impact of Climate Change on Crop Conditions
- Crop Conditions: 7 Shocking Tech Hacks for Yields
- Comparative Benefits Table: Tech Hacks & Their Yield Impact
- Farmonaut’s Role in Transforming Crop Conditions & Yields
- Recent Developments in Crop Conditions and Agricultural Practices
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Farmonaut Subscription Plans
Summary: Understanding Crop Conditions in Agriculture, Farming, and Forestry
Crop conditions are a critical determinant of both agricultural productivity and food security. By influencing the quantity and quality of yields, crop conditions form a bridge between environmental factors, biological processes, and on-ground management practices. Plant development, soil health, pest and disease pressures, and climate dynamics are all interconnected components requiring comprehensive understanding for optimal agricultural performance.
As we navigate the future of farming and forestry, technological advancements in crop monitoring, precision agriculture tools, and data-driven insights have become essential. In this guide, we’ll dive into how modern innovations—like satellite crop monitoring, AI advisory systems, and blockchain traceability—are transforming our approach to farming and enabling greater, more sustainable yields.
Environmental Factors Influencing Crop Conditions
To achieve high-quality yields, we must holistically assess the environmental factors influencing crop conditions. Let’s explore the crucial variables affecting every stage of crop development:
1. Climate and Weather Patterns
- Temperature: Each crop species has an optimal temperature range for growth. Deviations—like excessive heat or unexpected cold spells—can stress plants, stunt growth, or even result in crop failure. Heat stress leads to wilting, flower or fruit drop, and reduced yields. Temperature anomalies, as observed in recent years, emphasize the vital need for adaptive practices.
- Precipitation: Adequate rainfall is as important as sunlight. Prolonged droughts or excessive rainfall can delay planting, reduce usable field days, and lead to poor crop establishment. Farmers in parts of the U.S. have observed delayed planting schedules due to high rainfall, showing the impact of weather on crop productivity (AP News).
- Sunlight: The intensity and duration of sunlight directly affect plant photosynthesis and growth rates. Persistent cloud cover or climatic changes that reduce sunlight can greatly reduce yields, particularly in sensitive species.
Other Atmospheric Elements:
- Wind: Strong winds may cause physical damage, increase water loss (transpiration), and spread pests and diseases.
- Humidity: High humidity can promote fungal growth and exacerbate certain diseases, while low humidity may lead to water stress and leaf desiccation.
2. Soil Quality and Crop Growth
- Soil Fertility: High levels of essential nutrients in the soil, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, are fundamental for robust plant growth.
- pH Levels: The acidity or alkalinity of the soil affects nutrient availability. For instance, certain crops thrive in slightly acidic soils while others require alkaline conditions.
- Soil Texture and Water Retention: Clay, silt, and sand proportions influence water retention and aeration—both vital for root development and plant health.
- Regular Soil Testing: Proactive, data-driven soil testing helps identify deficiencies and enables farmers to apply precise amendments, optimizing crop performance.
For seamless soil quality and crop growth monitoring, platforms like Farmonaut bring science-driven insights to every field, ensuring timely action and sustainable management. Discover how carbon footprint tracking supports sustainable agriculture by measuring soil and emission health.
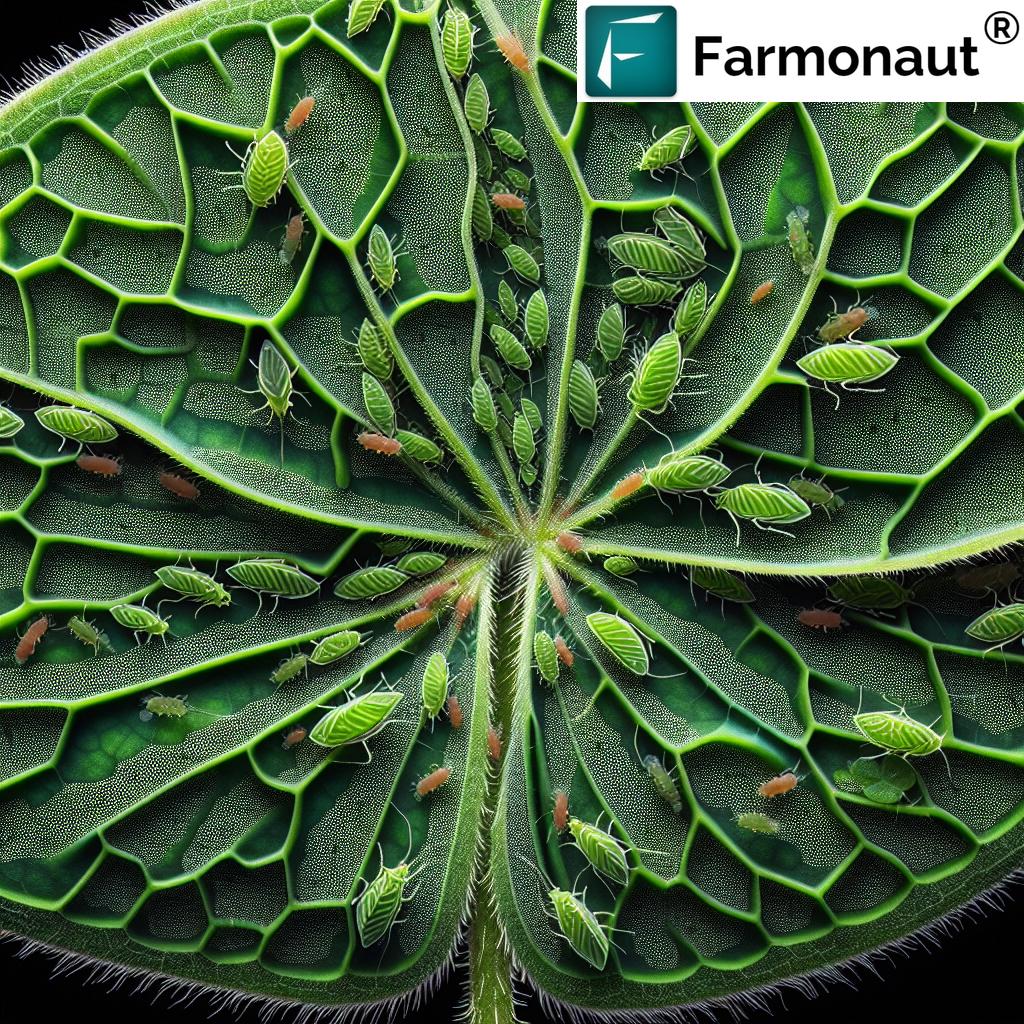
3. Biotic Stressors: Pests and Diseases
- Pests: Insects, nematodes, and other biotic stressors can cause severe damage to crops if not detected early. Their populations and activity are closely linked to temperature, humidity, and crop selection.
- Diseases: Fungi, bacteria, and viruses—often linked to shifting climate patterns—can spread quickly, especially when optimal environmental conditions are met.
- Disease Management in Farming: Technologies enabling integrated pest management (IPM) and disease surveillance drastically reduce the need for chemical intervention, supporting both yield and environmental health.
Climate change has led to the expanded range of certain pests and diseases, highlighting the critical need for predictive analytics and monitoring via platforms like Farmonaut.
Biological Factors Affecting Crop Conditions
While environmental influences set the framework for crop conditions, internal, biological factors dictate how each plant responds. This intricate dance of genetics and growth processes must not be overlooked.
1. Genetic Factors
- Cultivar Choice: The selection of crop species and specific cultivars determines their baseline resistance to drought, disease, pests, and temperature extremes.
- Plant Breeding: Advances in breeding—including the use of data-powered insight—allow the creation of plant varieties better suited for fluctuating climates and evolving environmental challenges.
The Farmonaut crop, plantation & forest advisory apps provide actionable intelligence to choose the right varieties for each unique microclimate and landscape.
2. Planting and Harvesting Practices
- Optimal Timing: The timing of planting and harvesting affects success. Early or late operations may expose crops to abnormal weather, pests, or suboptimal sunlight.
- Population Density: Proper seeding rate and spatial arrangement maximize exposure to light, air movement, and reduce pest incidence.
- Synchronized Management: Digital farm management tools help us synchronize these operations with real-time climate data, increasing the likelihood of success.
Effective biological processes management begins with deep understanding—something only possible with reliable, continuous data.
Management Practices to Optimize Crop Conditions
Optimizing field conditions, minimizing failure, and sustaining long-term agricultural productivity depend on smart, evolving management approaches. Technology is our strongest ally.
1. Precision Agriculture Technologies
-
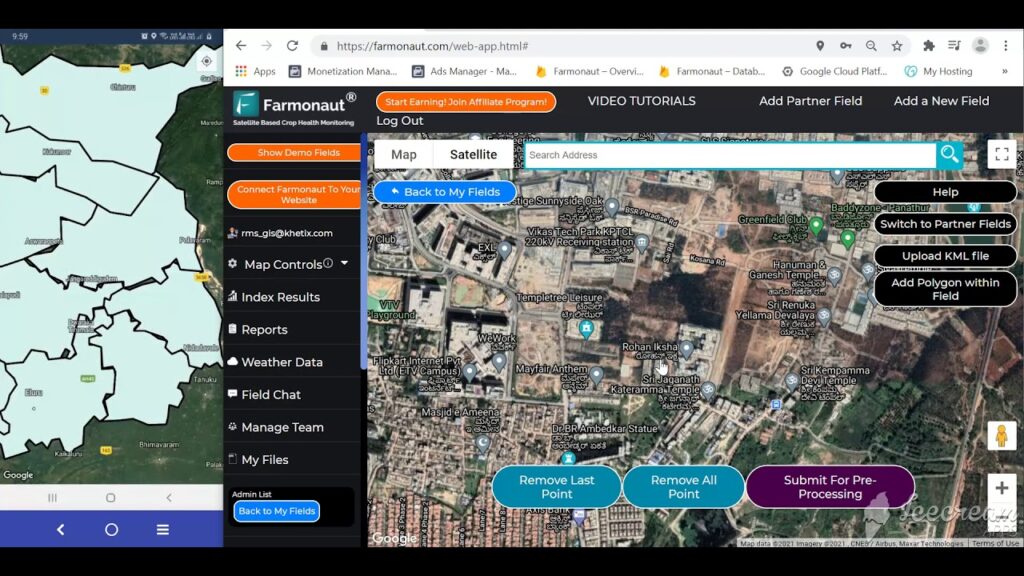
Precision agriculture technologies involve using satellite data, GPS, remote sensing, and field sensors to monitor variability and inform decision-making. Farmonaut’s real-time satellite crop monitoring tools make high-tech solutions truly accessible.
Learn more about large-scale farm management with Farmonaut. - These technologies help tailor irrigation, fertilization, and pest control precisely to crop needs, reducing input waste and environmental harm while boosting yields.
2. Crop Rotation and Diversification
- Crop Rotation: Regularly changing the type of crops planted in a field disrupts the lifecycle of pests and diseases, improves soil health, and reduces the risk of nutrient depletion.
- Diversification: Transitioning from mono-cropping to diversified systems helps buffer against market disruptions, pest outbreaks, and climate uncertainties.
3. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
- Integrated pest management (IPM): Blending biological, cultural, mechanical, and chemical control options minimizes reliance on pesticides.
- This approach reduces input costs, minimizes resistance development, and is aligned with sustainable agricultural practices.
- Farmonaut’s AI-based advisories empower timely, targeted interventions reducing chemical use while sustaining productivity.
“Climate variability affects over 30% of global crop production, making tech-driven condition analysis crucial for food security.”
Impact of Climate Change on Crop Conditions
The climate impact on agriculture can no longer be ignored. Extreme weather patterns, rising temperatures, unpredictable rainfall, and new disease pressures pose complex challenges to agricultural and forestry sectors worldwide.
- Increased Droughts & Floods: More frequent droughts and floods reduce field access, delay planting/harvesting, and can destroy standing crops. This increases risk of total crop loss and subsequently affects global food security.
- Shifts in Pest & Disease Patterns: Warmer, wetter environments facilitate the spread of unfamiliar pests and diseases—often into new regions.
- Shortened or Altered Growing Seasons: Changes in temperature and rainfall can force earlier or staggered planting, potentially leading to mismatched crop cycles and lower yields.
Making sense of the complex climate-crop relationship is where AI advisory systems, like Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI, and remote sensing technologies really shine. By analyzing historical patterns and real-time data, these solutions allow us to adapt rapidly to changing conditions, minimize losses, and ensure sustainability.
For data-hungry developers and businesses, Farmonaut’s Satellite & Weather API for crop monitoring provides reliable, programmatic access to the latest field and climate data.
Key Factors Affecting Crop Yields:
- Temperature deviations and heat stress
- Excessive or insufficient rainfall
- Increasing biotic stressors (insects, fungi, bacteria)
- Changing duration and intensity of sunlight/cloud cover
- Soil nutrient deficits due to erosion or leaching
Crop Conditions: 7 Shocking Tech Hacks for Yields!
Modern-day agriculture is undergoing a revolution. Let’s uncover the seven most impactful, technology-powered hacks for optimizing crop conditions, combatting climate variability, and securing abundant, sustainable yields.
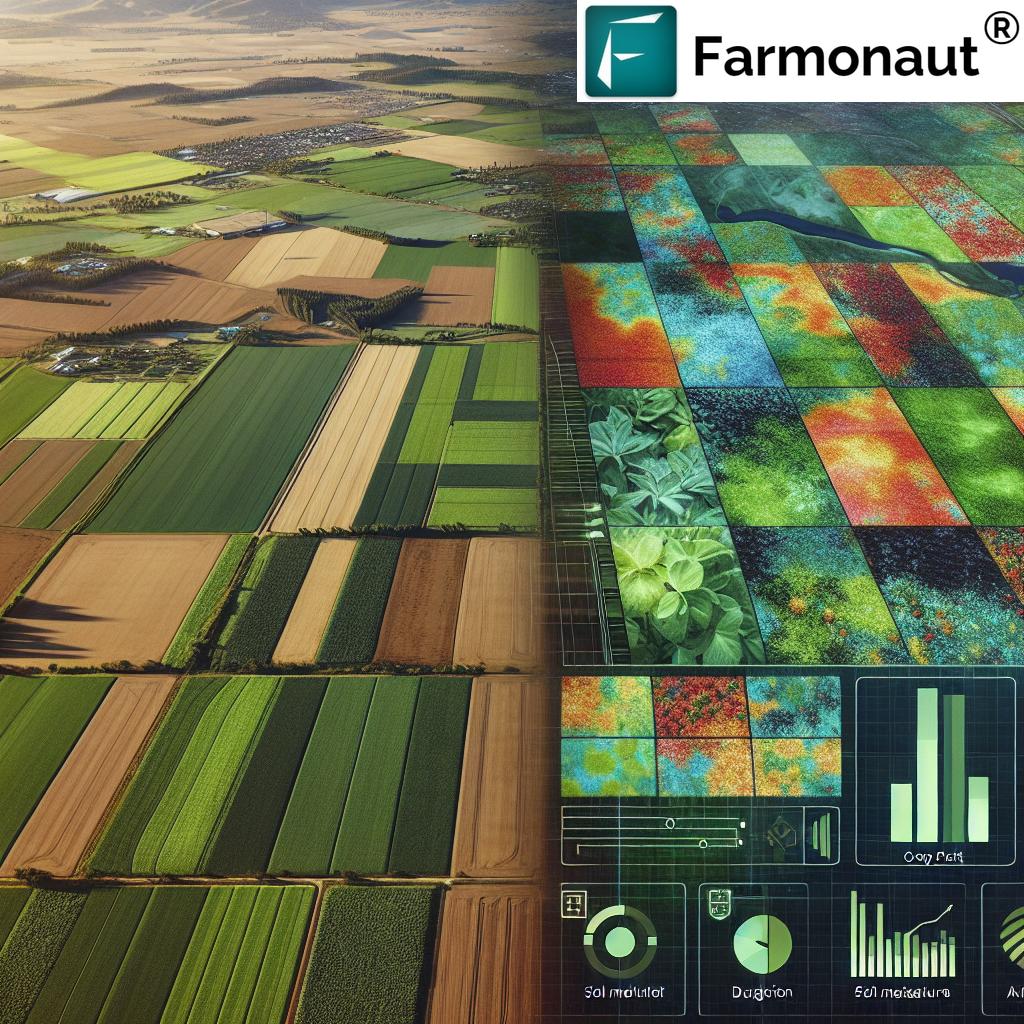
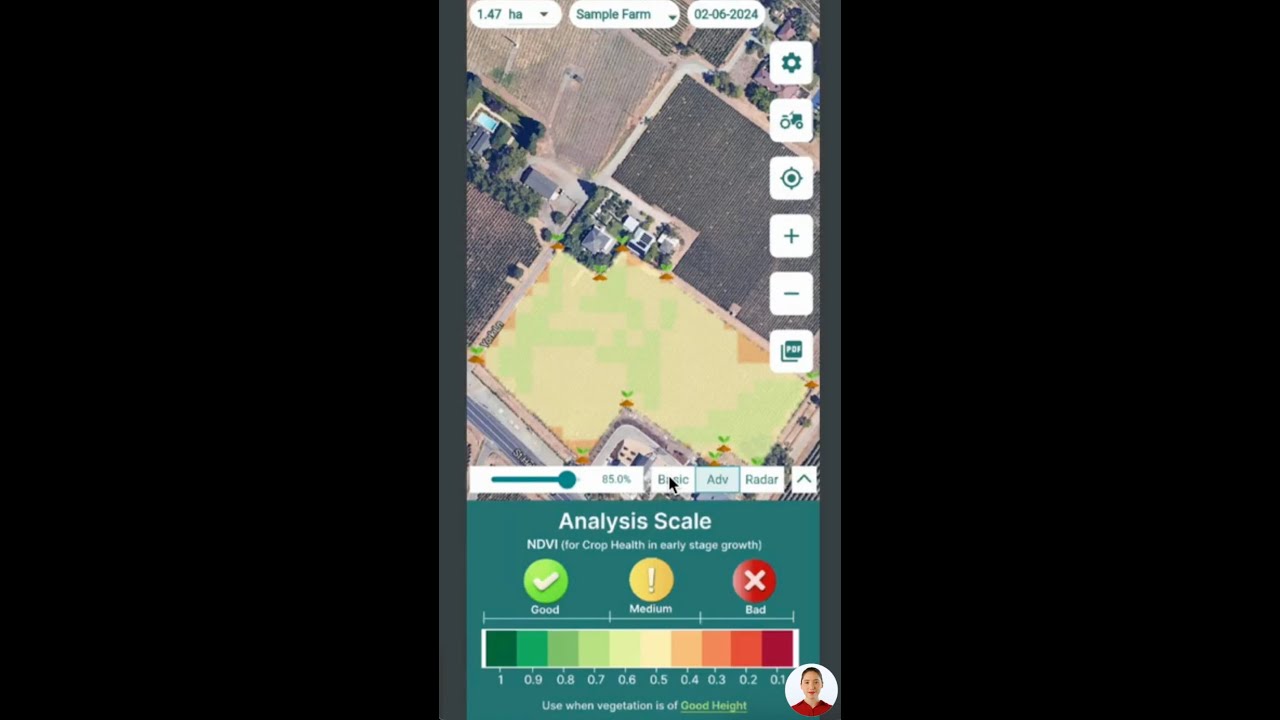
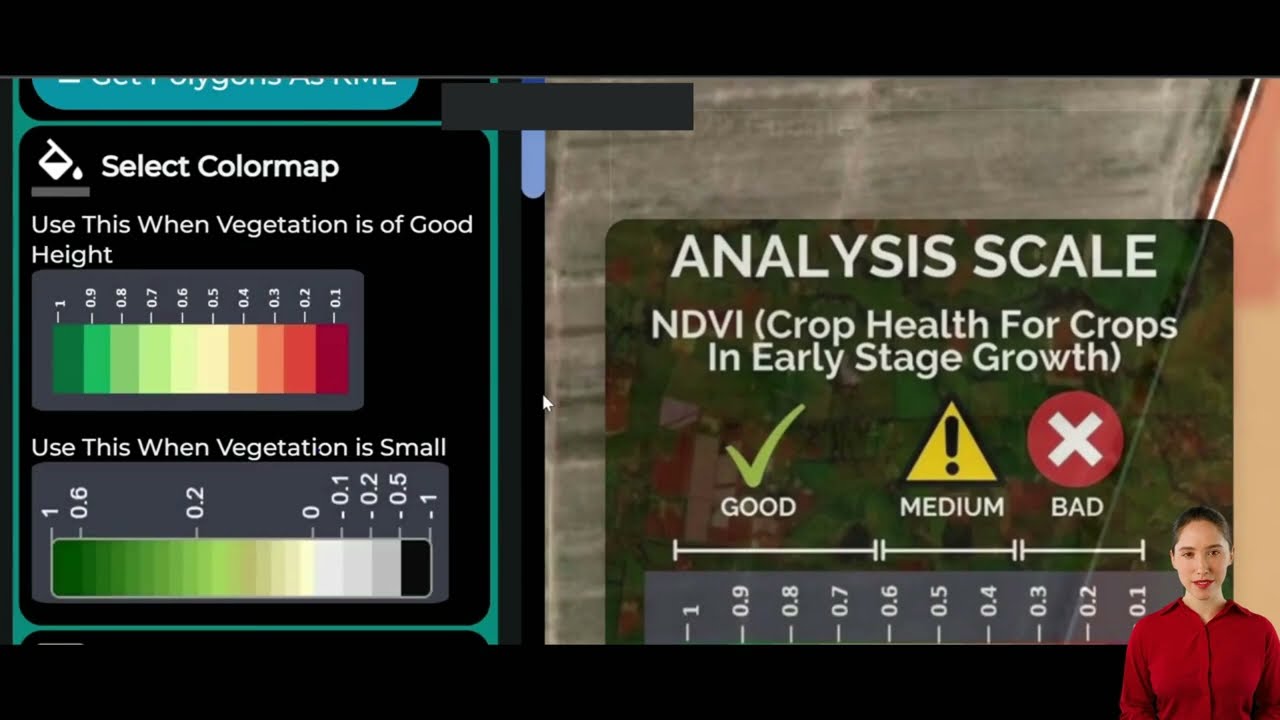
1. Satellite Crop Monitoring
- What It Is: Real-time, multispectral imagery of fields enables remote assessment of crop health, soil moisture, canopy growth, and possibly even early signs of stress.
- Impact: Satellite crop monitoring provides actionable data on a continental, national, or even per-field scale. This boosts yield by enabling fast, localized interventions.
- Farmonaut Solution: Farmonaut’s satellite platform delivers NDVI and other indices to track plant health and optimize input allocation without the need for expensive on-ground sensors,
Try satellite crop monitoring FREE with Farmonaut’s Apps.
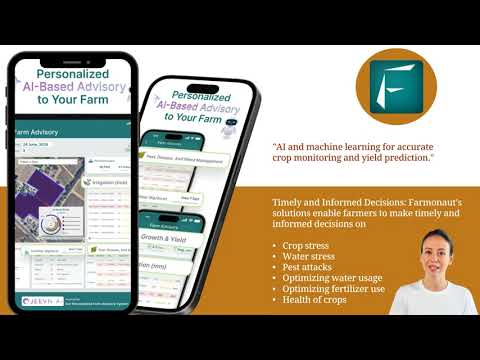
2. AI-Based Farm Advisory Systems (Jeevn AI)
- What It Is: Artificial intelligence analyzes historic field data, real-time satellite images, and weather conditions to provide actionable, tailored recommendations—right to your device.
- Impact: Reduces guesswork, improves timing, lowers losses from mismanagement, and enhances resource optimization.
- Farmonaut Solution: Jeevn AI delivers customized expert insights for each farm, factoring in all of the unique local variables and environmental risks.
3. Blockchain-Based Product Traceability
- What It Is: Blockchain securely records the journey of agricultural products from field to store. Full traceability means you know each crop’s health, origin, and handling history.
- Impact: Prevents fraud, bolsters food safety, and appeals to increasingly conscious consumers.
Explore Farmonaut’s blockchain-based traceability system.
4. Fleet and Resource Management
- What It Is: Monitor and optimize usage of tractors, harvesters, irrigation equipment and more—remotely.
- Impact: Reduces downtime, fuel waste, unauthorized use, and machinery wear and tear.
- Farmonaut Solution: Take farm management digital—see how Farmonaut simplifies fleet tracking & resource allocation.
5. Drones and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)
- What It Is: UAVs equipped with multispectral sensors offer high-resolution field-level condition analysis.
- Impact: Pinpoint pest or nutrient issues, map variability, and deploy treatments with surgical precision—saving inputs and boosting yields.
- Integration: UAV-captured data complements remote satellite monitoring for the most granular field intelligence.
6. Carbon Footprinting and Sustainability Tools
- What It Is: Measure and manage your field’s greenhouse gas emissions, soil carbon content, and overall environmental impact.
- Impact: Positions farming operations for compliance, market access, and carbon credit opportunities in an increasingly eco-conscious global economy.
Discover how Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting system is shaping sustainable agriculture.
7. Crop Loan and Insurance Verification via Satellite
- What It Is: Lenders and insurers leverage satellite-generated, verified data on crop development, acreage, and risk.
- Impact: Reduces premium costs, minimizes fraud, and offers fairer loan access for farmers.
Read how Farmonaut supports secure crop loans and insurance.
Comparative Benefits Table: Tech Hacks & Their Yield Impact
Each technology-driven solution directly boosts resilience, precision, and sustainability in modern farming, addressing factors affecting crop yields and helping farmers thrive amidst climate and market uncertainties.
Farmonaut’s Role in Transforming Crop Conditions & Yields
Farmonaut is at the frontier of affordable and accessible precision agriculture technologies. Our mission is to put data and high-tech intelligence in the hands of every farmer, regardless of field size or geography.
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: View your farm’s NDVI, soil moisture, and nutrient status via clear maps and reports. No special sensors or drones are required—just log in and get insights anytime, anywhere.
- AI-Based Jeevn Advisory: Personalized, actionable suggestions for each field help optimize planting, irrigation, fertilizer usage, and pest control.
- Blockchain Traceability: Supply chain traceability builds trust and enables compliance.
- Fleet & Resource Management: Streamline all your on-farm machinery and logistics through our unified dashboard.
- Carbon Footprinting: Accurately track and manage your agricultural emissions, making true sustainability and carbon trading possible.
- API Access: Developers and agribusinesses can integrate Farmonaut’s API directly into existing platforms for seamless data automation.
Who Benefits?
- Individual Farmers: Boost productivity, reduce risk, and maximize profits by making smarter decisions.
- Agribusinesses: Manage thousands of hectares efficiently with a single dashboard.
- Governments & NGOs: Implement monitoring programs, support subsidy allocation, and encourage long-term food security.
- Financial Institutions: Reduce fraud risks, automate field verification, and expand crop lending.
- Corporate Clients: Guarantee traceability, authenticity, and sustainability of raw materials in the supply chain.
Experience the Farmonaut advantage on our web platform, Android, or iOS apps.
Key Value Propositions:
- Accessible, cost-effective, subscription-based precision agriculture.
- Modular tools; scalable for small farms, plantations, entire regions.
- Real-time, actionable insights—no hardware required.
- Focused on sustainable agricultural practices and food security.
Tip: For tailored forest plantation guidance, visit Farmonaut’s Crop Plantation & Forest Advisory.
Learn with Farmonaut: Video Tutorials & Demos
- Interpret satellite crop health data effectively.
- Use apps for yield prediction and management.
- Access the full guide for satellite-based monitoring on the web.
Scroll up to view embedded tutorial videos or browse more on Farmonaut Official YouTube.
Recent Developments in Crop Conditions and Agricultural Practices
-
World food prices dip in May as cereal, sugar and vegoils drop
– Signals market adjustments impact on farm planning and yields. -
Crop Watch: Corn improves but soy health is lacking
– Crop health monitoring helps spot issues early before yield impact is irreversible. -
Climate change adds anxiety to spring planting rituals
– Climate anomalies disrupt seasonality, prompting farmers to watch crop conditions closely and integrate tech solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most important crop conditions to monitor for optimal yields?
The most critical crop conditions include soil moisture and fertility, temperature, precipitation patterns, pest and disease presence, and overall plant health status. Monitoring these through satellite data and AI-driven advisories ensures proactive, precise management.
How does climate change impact crop conditions and food security?
Climate change causes more unpredictable weather, temperature extremes, altered growing seasons, and greater pest/disease pressures, all of which threaten crop yields and long-term food security. Adaptive, technology-enabled practices are essential for resilience.
Can smallholder farmers access advanced monitoring tools?
Yes! Farmonaut is dedicated to affordability and accessibility, offering subscription-based, hardware-free platforms where even small farms can benefit from precision agriculture technologies, real-time crop health monitoring, and climate adaptation advisories.
What role does satellite crop monitoring play in sustainable agriculture?
Satellite crop monitoring enables timely detection of water deficits, pest outbreaks, and nutrient stress, which reduces chemical/fertilizer use and prevents waste. It ensures sustainability by supporting data-driven management and environmental stewardship.
How can I access Farmonaut’s tools and services?
Farmonaut’s solutions are available via web, Android, and iOS apps. Developers and enterprises can integrate Farmonaut’s APIs into their own systems. Visit the app section above for direct links to each version!
What is Integrated Pest Management (IPM)?
IPM is a holistic approach integrating biological, cultural, mechanical, and chemical measures to manage pests sustainably, reduce dependency on chemicals, and minimize environmental impact in agriculture.
Farmonaut Subscription Plans
Our tiered pricing supports everyone—from independent farmers to large estates and agribusinesses. No hardware or technical expertise needed; just accurate, actionable insights at your fingertips!
Conclusion: Data, Tech & Adaptation—The New Foundation of Yields
Understanding and optimizing crop conditions is now inseparable from embracing technological innovation. By leveraging satellite crop monitoring, AI-powered advisories, blockchain traceability, and sustainable resource management, we can minimize environmental uncertainties, enhance crop health, and secure food production for the future.
As climate patterns shift and challenges mount, data-driven, sustainable agricultural practices will continue to shape resilient, productive fields worldwide. Let’s employ every tool at our disposal to support optimal growth, deliver top yields, and keep agriculture thriving—securely, efficiently, and sustainably.