Crop Management Solutions: 7 Game-Changing Farm Tech
“Precision agriculture can increase crop yields by up to 20% using data-driven management techniques.”
Introduction: The Power of Effective Crop Management
In today’s rapidly evolving agricultural landscape, crop management solutions have never been more essential. As farmers, agribusinesses, and agricultural professionals, we are constantly adapting to new challenges—climate change, soil degradation, pest resistance, and market pressures. By leveraging advanced strategies and innovative agricultural technologies, we can optimize productivity, enhance soil health and fertility, and secure not only profitable harvests but also the ecological sustainability of our land.
This comprehensive guide explores 7 game-changing farm tech tools that are reshaping modern agriculture. We’ll delve into techniques such as precision agriculture, integrated pest management, conservation agriculture practices, and pioneering regenerative agriculture techniques. Our focus is to illuminate how these approaches combine to elevate sustainable farming strategies, boost yields, and reduce our environmental footprint, all while ensuring the long-term viability of our farms.
Why Crop Management Solutions Matter
- Achieving Optimal Productivity: Effective crop management ensures each plant receives the right nutrients, water, and protection—helping us maximize output without overtaxing natural resources.
- Enhancing Sustainability: By adopting advanced practices, we reduce waste, minimize chemical usage, and safeguard soil health for generations to come.
- Minimizing Risk & Loss: Integrated strategies reduce crop losses due to pests, diseases, and extreme weather, supporting the economic viability of our work.
- Promoting Responsible Resource Use: With technologies like precision agriculture and data-driven decision-making, we can optimize the application of water, fertilizers, and pesticides, reducing costs and environmental impact.
Let’s discover the 7 major crop management solutions and how each technology plays a critical role in modern agricultural productivity.
Feature Comparison: 7 Game-Changing Farm Tech Innovations
| Technology Name | Core Functionality | Estimated Yield Improvement (%) | Estimated Cost Savings ($/acre) | Impact on Soil Health (Score /10) | Sustainability Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Integrated Pest Management (IPM) | Combines biological, cultural, physical, and chemical tools to manage pest populations and minimize risks | 10–15% | 50–70 | 7 | Reduces pesticide use, supports beneficial species, minimizes environmental contamination |
| Precision Agriculture | Uses GPS, remote sensing, and analytics for resource optimization and site-specific management | 15–20% | 60–120 | 8 | Decreases chemical/fertilizer waste, lowers resource input, improves environmental outcomes |
| Conservation Agriculture | No-till farming, soil cover, and diverse cropping to conserve soil and boost fertility | 8–12% | 50–90 | 9 | Prevents erosion, builds organic matter, conserves water, encourages biodiversity |
| Cover Cropping | Non-cash crops grown for soil health, erosion control, and weed/pest suppression | 8–10% | 40–65 | 9 | Improves organic matter, boosts nutrient cycling, assists carbon sequestration |
| Push–Pull Pest Management | Intercropping repellents and trap plants for targeted, ecologically sound pest management | 7–10% | 30–60 | 8 | Lowers chemical pesticide reliance, supports pollinators and natural enemies |
| Soil Conservation Techniques | Contour plowing, terracing, agroforestry to control erosion and enhance soil retention | 4–8% | 25–45 | 10 | Protects against land degradation, builds resilience to climate change |
| Technological Innovations in Crop Management | AI, satellite monitoring, automation for real-time detection, advisory, and labor efficiency | 12–18% | 80–130 | 8 | Reduces labor, improves timing of interventions, lowers chemical inputs |
Watch: How Farmonaut Empowers Crop Management
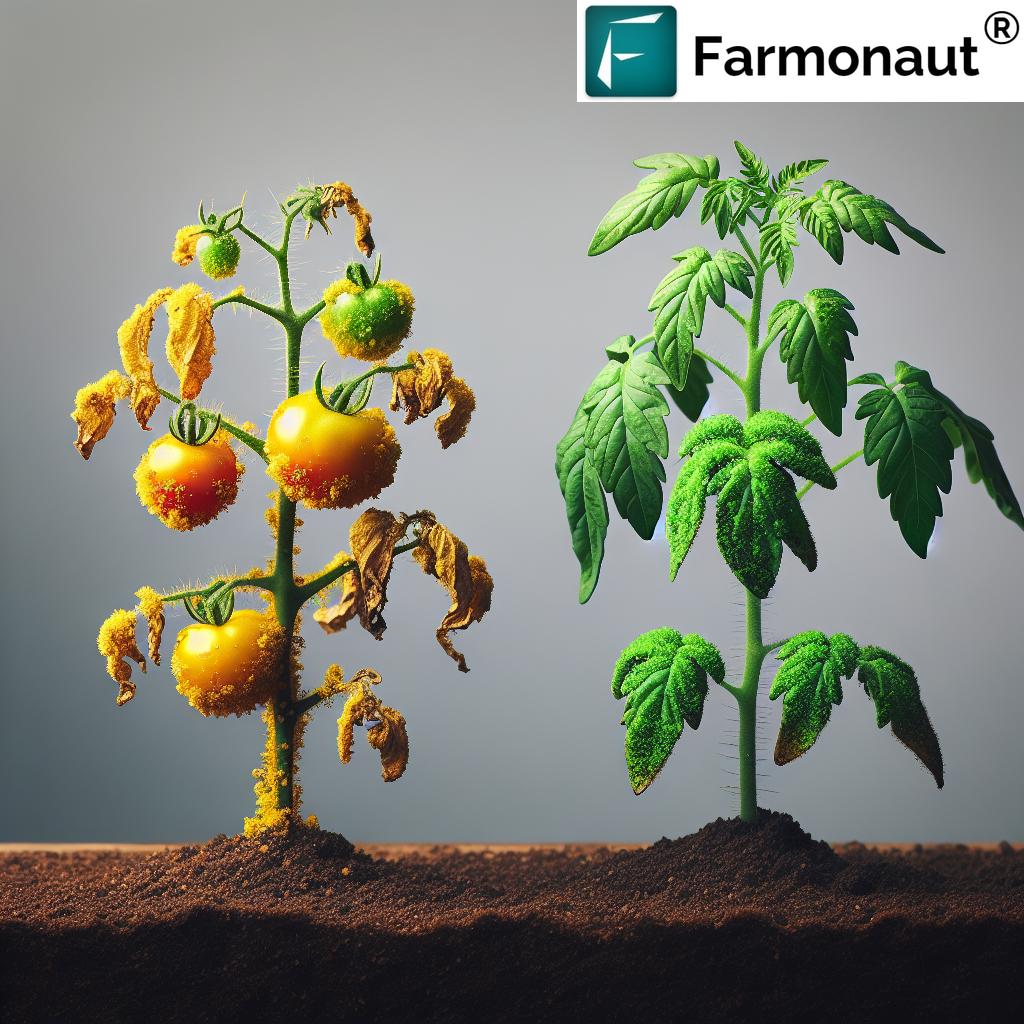
Integrated Pest Management (IPM): A Holistic Solution
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is an economically and ecologically sound strategy, combining multiple approaches to manage pest populations in crops while minimizing risks to human health, soil health, and the environment.
What Does IPM Involve?
- Biological Controls: Utilizing natural predators and parasitoids to suppress pest populations.
- Cultural Practices: Crop rotation, proper spacing, and planting schedules to disrupt pest lifecycles.
- Physical Methods: Barriers, traps, and mechanical removal to keep pests below economic thresholds.
- Chemical Control: Judicious, targeted use of pesticides only when thresholds are exceeded, reducing reliance and mitigating resistance.
This holistic approach not only keeps damage-causing pests in check but also minimizes pesticide residues, encourages beneficial species, and improves the overall resilience of our fields. By regularly monitoring pest levels and setting action thresholds, IPM ensures measures are applied only when necessary, reducing environmental contamination and economic harm.
- Proven to cut chemical inputs by 30–40% in many agricultural systems.
- Supports sustainable farming by slowing the rise of pesticide-resistant pest populations.
- Promotes a stable, diverse agricultural environment, facilitating improving yields and effective pest control in crops.
Integrated Pest Management is a foundational element of crop management strategies—enabling us to protect yield and quality in the most sustainable and economically viable manner.
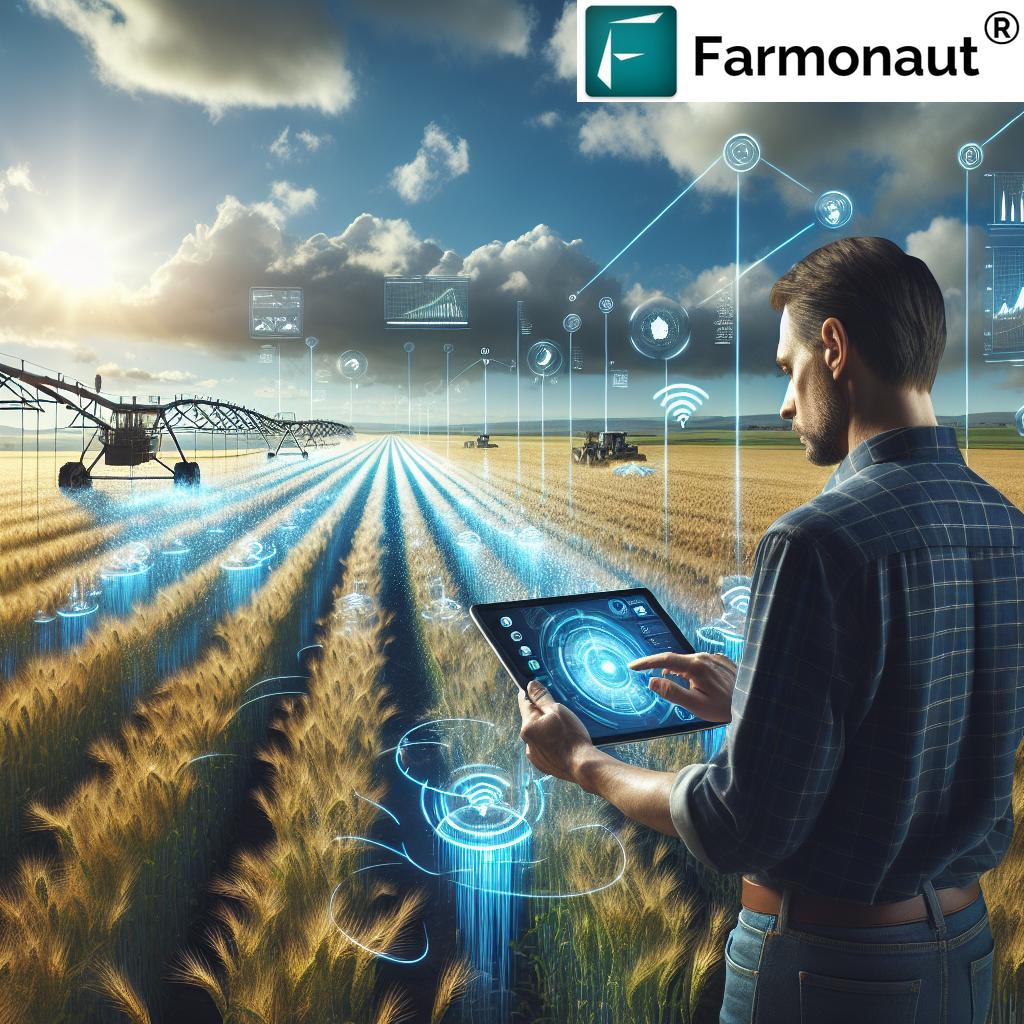
Precision Agriculture: Transforming Crops with Data
Precision agriculture represents a technological revolution in the way we manage our fields. By leveraging GPS, satellite imagery, remote sensing, and advanced data analytics, precision agriculture allows us to monitor field variability and optimize the application of every input across our farm.
How Precision Agriculture Works
- Satellite and Drone Imagery: Identify zones with water stress, pest outbreaks, or nutrient deficiencies for timely interventions.
- Variable Rate Application: Adjust seeding, fertilizing, and irrigation rates according to real-time soil and crop data, reducing resource use.
- Sensors: Soil moisture probes, weather stations, and plant health detectors provide continuous monitoring for smarter decisions.
- Data-Driven Decisions: By collecting and analyzing detailed field data, we make informed management choices, optimizing yields and efficiency.
The outcome? Increased precision, higher productivity, and far less resource waste. According to leading studies, these technologies can result in:
- 15–20% yield improvement by placing nutrients and water only where needed.
- Up to 120 $/acre in cost savings due to better targeting of agricultural inputs.
- Drastic reduction in runoff, chemical residues, and greenhouse gas emissions.
With platforms such as Farmonaut, precision agriculture is now accessible and affordable—even for smallholder farms. Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop monitoring empowers us to manage crop health, soil moisture, and resource allocation instantly via Android, iOS, and web apps. Discover how large-scale farm management benefits from Farmonaut’s data-driven approach.
Conservation Agriculture Practices: Protecting Soil Health and Fertility
Conservation agriculture focuses on enhancing soil health and fertility by reducing soil disturbance, maintaining continuous soil cover, and diversifying plant species. These practices provide long-term resilience and sustainability for our farms.
Key Conservation Agriculture Strategies
- No-till and Minimum-till Farming: Prevents soil structure disturbance, increasing organic matter and reducing erosion risks.
- Permanent Soil Cover: Use of cover crops and crop residues to protect soil, retain moisture, and suppress weeds.
- Crop Diversification: Rotating species to break pest cycles and stimulate soil biology, enhancing biodiversity.
- Water Retention Enhancement: Better soil structure promotes infiltration, retaining water during dry periods.
The shift to conservation agriculture practices results in:
- Major reductions in topsoil loss.
- Restored fertility and higher water-holding capacity.
- Increased presence of beneficial microbes, worms, and insects—key drivers of organic matter decomposition and nutrient cycling.
By adopting these sustainable farming strategies, we not only improve soil fertility year after year, but also reduce our farms’ carbon footprint. Explore Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting technology for sustainable agriculture—track emissions and implement practices that support a climate-friendly farm system.
“Regenerative farming methods can improve soil organic matter by 15% within five years, boosting sustainability.”
Cover Cropping Benefits: Nurturing Healthy Soil
Cover crops are grown primarily to improve and protect the soil between main crop cycles. This approach is one of the simplest yet most effective ways to promote soil health and boost field productivity with minimal environmental impact.
How Cover Cropping Improves Farms
- Prevents Soil Erosion: The living roots of cover crops secure soil particles, minimizing wind and water erosion.
- Enhances Soil Organic Matter: As these plants decompose, they increase the organic content, which is vital for soil fertility and water retention.
- Suppresses Weeds & Pests: Dense canopy cover shades out weeds, disrupts pest life cycles, and supports beneficial insects.
- Nitrogen Fixation: Leguminous cover crops draw atmospheric nitrogen into the soil, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers.
- Boosts Carbon Sequestration: Assists in climate mitigation by storing atmospheric carbon.
Examples of common cover crops: clover, vetch, rye, radish, and buckwheat. By integrating these species into crop rotations, we can safeguard our most precious agricultural asset—healthy, living soil.
Push–Pull Pest Control in Crops: Innovative Strategies
The push–pull pest management strategy leverages plant biodiversity for pest suppression in our fields. This innovative agricultural technology involves “pushing” pests away from the main crop using repellent plants and “pulling” them to trap crops, reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
How Push–Pull Works
- Push: Intercrop repellent plants (e.g., Desmodium) within cash crop rows to fend off target pests.
- Pull: Plant attractive trap species (e.g., Napier grass) along field borders to lure pests away from the main crop.
- Reduces chemical pesticide use by up to 50% in some systems.
- Promotes pollinators and beneficial predator insects, enhancing biodiversity.
- Improves resilience against pest outbreaks.
This approach exemplifies how sustainable farming strategies and innovative agricultural technologies can be adapted for effective pest control in crops while minimizing adverse impacts on the environment.
Interested in satellite-based pest monitoring and advisory?
Try Farmonaut’s AI-driven crop advisory and real-time pest alerts, available on Android, iOS, and web.
Soil Conservation Techniques: Reducing Erosion, Retaining Fertility
Soil conservation is vital to long-term agricultural productivity and sustainability. When soil erodes, we lose nutrients, water-holding capacity, and ultimately, the capacity to grow healthy crops.
Top Soil Conservation Techniques
- Contour Plowing: Plowing along the natural contours of the land reduces runoff and prevents soil erosion.
- Terracing: On slopes, terraces act as barriers to slow water, capture sediments, and maintain fertility.
- Agroforestry: Integrating trees with crops supports water retention, improves biodiversity, and adds organic matter to the soil.
- Grass Buffer Strips: Planted on field edges, they filter runoff and trap sediments—I.E., a sustainable farming solution for riverine zones.
Adopting soil conservation methods ensures our lands remain productive and resilient, even in the face of climate change and extreme weather events. By managing our farm’s physical structure and water flows, we help avoid the devastating loss of irreplaceable topsoil.
Innovative Agricultural Technologies: AI, Satellites & Automation
Advancements in digital technologies have introduced radical changes in crop management. Artificial Intelligence (AI), satellite monitoring, automation, and blockchain tools have not only made farming more efficient but also more sustainable and climate-resilient.
How Technology is Redefining Crop Management
- AI-Powered Analytics & Monitoring: Identifies stress symptoms in crops using satellite imagery and remote sensors—enabling early, precise intervention before losses occur.
- Smart Automation: Autonomous irrigation systems, planting robots, and drone-based mapping reduce labor costs and deliver greater precision in resource application.
- Data-Driven Decision Support Systems: Delivers insights into crop rotations, fertilization schedules, and risk forecasts for optimal outcomes.
- Blockchain Traceability: Records every step from planting through to shipment—ensuring food chain transparency and promoting sustainable, traceable production.
Test the benefits: Product traceability for your supply chain.
Farmonaut is at the forefront of technological innovation in agriculture. Our Jeevn AI Advisory System delivers personalized, real-time crop management guidance by analyzing satellite data and weather information, supporting smarter farming decisions globally.
Farmonaut’s platform also offers API access for agricultural data solutions and detailed developer documentation—making it easier to integrate these powerful tools into your daily farm management.
Regenerative Agriculture Techniques: Restoring Farms Sustainably
Regenerative agriculture is more than just a buzzword; it’s a commitment to restoring, preserving, and actively improving the health and fertility of our agricultural ecosystems. This comprehensive approach focuses on building rich, living soils, promoting biodiversity, and establishing resilient landscapes that can weather the shocks of climate change.
Core Regenerative Practices
- No-till or Minimum-Till Farming: Reduces soil disturbance, increases soil organic matter, and preserves the microbial ecology.
- Permanent Ground Cover: Ensures living plants protect the soil year-round—either as main crops or cover crops.
- Diverse Rotations: Rotates crops and integrates livestock for maximum ecological benefit.
- Compost & Organic Inputs: Replaces synthetic chemicals with nutrient-rich, biologically active alternatives.
- Restorative Grazing: Livestock practices that help rebuild organic matter and increase carbon sequestration.
Evidence shows that regenerative agriculture techniques can increase soil carbon by 15% over five years, double worm counts, and drastically improve water infiltration. The result: improved yields, reduced climate impact, and vibrant, self-sustaining farm ecosystems.
Dive deeper with Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting solution—track your soil carbon, emissions, and optimize for a truly regenerative system.
Regenerative practices are no longer “alternative”—they’re essential for future-ready, resilient farming.
Farmonaut: Empowering Efficient, Sustainable Farming Globally
At Farmonaut, our mission is to make precision agriculture tools accessible and affordable for farmers everywhere. We recognize that every farm is unique—and so are its challenges. That’s why we’ve built a platform that combines the power of satellite technology, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and blockchain to deliver actionable insights, better resource management, and environmental sustainability.
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Farmonaut continuously analyzes multispectral imagery to detect crop health issues, soil moisture levels, and vegetation stress, enabling timely interventions for optimal productivity.
- AI-Driven Advisory: With Jeevn AI, farmers get real-time, personalized recommendations—whether it’s irrigation, fertilization, or pest management.
- Blockchain Traceability: Supply chain verification with immutable records, building trust and transparency from farm to fork. Explore product traceability for agri-food supply chains.
- Resource & Fleet Management: Optimize the scheduling, routing, and utilization of agricultural machinery with Fleet Management.
- Carbon Footprint Tracking: Monitor emissions, set sustainability goals, and align with global standards using Farmonaut’s environmental modules.
Our platform spans a broad audience—from individual smallholder farmers to large agribusinesses, research bodies, NGOs, and government organizations. With flexible subscription plans and easy-to-use mobile/web apps, Farmonaut puts innovation in every farmer’s pocket—enabling better yields, cost savings, and a greener planet.
Farmonaut Subscription Plans
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ): Crop Management Solutions
What is crop management, and why is it essential?
Crop management refers to the set of practices and strategies aimed at optimizing the growth, yields, and health of crops while ensuring sustainability of the farm’s resources, particularly soil, water, and biodiversity. It is essential for achieving high productivity, reducing losses, managing resources responsibly, and maintaining economic, environmental, and societal viability in agriculture.
How does precision agriculture improve farm outcomes?
Precision agriculture uses cutting-edge technologies like GPS, remote sensing, satellite imagery, and analytics to monitor field variability and optimize input usage at a micro level. This leads to higher yields, reduced input costs, improved soil health, and minimized environmental harm.
What are the main benefits of conservation and regenerative agriculture techniques?
Both approaches focus on minimizing soil disturbance, maximizing biodiversity, and enhancing organic matter content. Benefits include improved soil fertility, greater resilience to climate shocks, lower erosion rates, and increased carbon sequestration—leading to healthier, more sustainable farms.
Can I access Farmonaut’s crop management services on my smartphone?
Yes. Farmonaut offers powerful satellite-based crop monitoring and advisory services via Android and iOS apps, as well as a web platform, making high-tech farm management accessible anywhere, anytime.
How do satellite and AI innovations help with pest management?
Satellite imagery and AI-powered analytics continuously scout large fields, detecting early stages of pest infestations and crop stress. This ensures that interventions are timely, targeted, and environmentally friendly—reducing chemical use and maximizing efficacy.
What is the value of product traceability in agriculture?
Blockchain-based traceability solutions record every stage of the agricultural supply chain, from planting to delivery. This increases food safety, prevents fraud, and adds value for brands and consumers who prioritize sustainability and origin authenticity.
Who should consider adopting these crop management innovations?
Individual farmers, cooperatives, agribusinesses, government bodies, research organizations, and corporate supply chains all stand to benefit from adopting these technologies and practices. Farmonaut’s modular, scalable solutions fit every size and need.
Conclusion: The Future of Sustainable, Effective Crop Management
In summary, crop management solutions are crucial to the future of agriculture. By uniting best-in-class methods—like integrated pest management, precision agriculture, conservation agriculture practices, cover cropping benefits, push–pull pest strategies, soil conservation techniques, and innovative agricultural technologies—we empower ourselves to grow more with less, restore the land, and future-proof our livelihoods.
As we look ahead, integrating data-driven solutions, embracing sustainability, and prioritizing soil health must be at the core of our agricultural strategies. Companies like Farmonaut make it possible for every farmer and agribusiness to access and leverage these breakthrough technologies—at an affordable cost, through intuitive mobile and web platforms, and with global reach.
The era of reactive, unsustainable agriculture is over. The future is holistic, informed, and innovative—focused on achieving optimal productivity, economic viability, and environmental stewardship. Let’s cultivate that future, together.