Innovative Pest Control: 7 Powerful New Methods Revolutionizing Sustainable Agriculture
Meta Description: Innovative pest control methods are revolutionizing agriculture by providing sustainable, efficient, and eco-friendly alternatives to traditional chemical pesticides, ensuring crop protection and enhanced biodiversity.
“Over 60% of new pest control patents in 2023 involved AI or biological agents for sustainable agriculture.”
Introduction: Rethinking Pest Control for the Future
Innovative pest control methods are rapidly revolutionizing agriculture, farming, and forestry. As the world faces increased risks of pest infestations due to changing climates, global trade, and resistance to older pesticides, there is a clear need for eco friendly pesticide alternatives that deliver both efficiency and sustainability. Modern agriculture is moving beyond traditional chemical pesticides, embracing a wider variety of technologies and biological solutions that target pests while preserving beneficial organisms, soil health, and ecosystem balance.
This evolution in sustainable agriculture pest management is not just about protecting our crops and forests—it’s about promoting biodiversity, ensuring food security, and reducing environmental harm. In this blog, we examine 7 powerful, innovative methods that are setting new standards for pest control, including integrated pest management, biological agents, push–pull strategies, biosolarization, biofumigation, AI-powered technologies, drone surveillance, and genetic approaches.
Scroll on to discover detailed explanations, comparative data, and real-world applications of these groundbreaking techniques, as well as how Farmonaut is driving innovation through satellite and AI-powered agricultural intelligence.
Comparative Features and Impact Table
| Method | How It Works | Est. Adoption Rate (%) | Est. Effectiveness (% crop damage reduction) | Environmental Impact | Est. Annual Cost per Hectare (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Integrated Pest Management (IPM) | Combines biological, cultural, mechanical, and targeted chemical controls for holistic pest management. | 60 | 55 | Low | 30-90 |
| Biological Control Agents | Deploys natural predators, parasites, or pathogens to manage pest populations without synthetic pesticides. | 35 | 45 | Low | 35-120 |
| Push–Pull Pest Management | Uses repellant plants to push pests away and trap crops to pull them in, reducing infestations naturally. | 18 | 40 | Low | 40-80 |
| Biosolarization | Combines soil solarization with biological amendments to suppress soil-borne pests and diseases. | 11 | 40 | Low | 35-110 |
| Biofumigation | Incorporates Brassica plant residues that release pest-toxic compounds (isothiocyanates) when decomposed in soil. | 8 | 37 | Low | 50-100 |
| AI & Drones | AI-driven sensors and drone surveillance enable targeted intervention and real-time pest detection. | 21 | 48 | Low-Medium | 65-150 |
| Genetic Control (Including SIT) | Applies genetic engineering, gene drives, or sterile insect release to suppress or eradicate key pest species. | 7 | 55 | Low | 80-160 |
*Adoption rates, effectiveness, and costs are broad estimates and can vary by region, infrastructure, and target crop.
*Environmental impact considers overall chemical usage, biodiversity effects, and persistence.
“Biological pest control methods have reduced chemical pesticide use by up to 40% in pilot agricultural projects worldwide.”
1. Integrated Pest Management (IPM): The Cornerstone of Innovative Pest Control Methods
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) stands at the forefront of innovative pest control methods in agriculture. By harmoniously combining biological, cultural, physical, and chemical tools, IPM minimizes the need for chemicals while maximizing effectiveness. The holistic approach analyzes the life cycle of pests, environmental factors, and the health of crops and soil to create a custom management plan.
A great example from apple orchards perfectly illustrates IPM’s strength: farmers often introduce predatory mites to control spider mites (a biological agent approach), regularly monitor pest populations, employ pheromone traps as mechanical management, and only utilize targeted pesticide sprays if truly necessary. This strategy reduces pesticide usage while protecting beneficial organisms and minimizing environmental impact.
- Key mechanisms: Integrated combinations of scouting, monitoring, traps, resistant plant varieties, biological pest control agents, habitat modification, and minimal chemical inputs.
- Benefits: Cuts chemical use, strengthens ecosystem health, delays resistance in pest populations, and raises biodiversity on farms.
- Popular in: Fruit and vegetable farms, horticulture, orchards, and large-scale agricultural operations.
See also:
- Farmonaut Large-Scale Farm Management – Maximize IPM benefits with satellite-driven crop and pest monitoring; optimize interventions and reduce chemical usage with precise data.
2. Biological Control Agents: Harnessing Nature’s Own Solutions
Biological pest control agents are transforming the way we manage agricultural pests. This method utilizes natural predators, parasites, or pathogens—such as insects, fungi, and bacteria—to suppress pest populations, offering a safe, sustainable alternative to synthetic pesticides.
- Examples:
- Beauveria bassiana fungus, used widely as a biological insecticide, targets pests like termites or whiteflies without harming crops or beneficial organisms. The spores are sprayed onto crops—once contact is made, pests are infected in a natural and efficient way.
- Release of ladybugs to prey on aphids in greenhouse vegetable farms.
- Key advantages:
- Reduces reliance on chemical pesticides, lowers residue risk in food, and protects soil and water health.
- Preserves biodiversity and beneficial insect populations, essential for healthy ecosystems.
While adoption rates are rising, using biological agents does require careful monitoring—timing and environmental factors matter. Nonetheless, these agents are crucial in sustainable agriculture pest management.
Quick Link:
- Crop Loan & Insurance Verification: Biological pest control improves sustainability scores, which platforms like Farmonaut’s can verify and report for better loan eligibility and lower insurance risk.
3. Push–Pull Pest Management: Smart Farming Strategies
The push–pull pest management method is an ingenious example of eco friendly pest control. This intercropping strategy utilizes spatial arrangements and planting of specific “push” (repellent) plants within fields to drive pests away from crops and “pull” (attractant) plants surrounding fields to lure and trap pests.
- In maize fields in Africa: Desmodium is intercropped between rows, “pushing” stem borer moths from the maize, while Napier grass is planted as a border, “pulling” and trapping the pests.
- Benefits:
- Reduces need for chemical pesticides while enhancing soil health (as “push” plants like desmodium are nitrogen fixers).
- Boosts biodiversity, promotes sustainable agriculture pest management, and often results in higher yields.
- Flexible Adaptations: The basic concept works with many crops by selecting appropriate push/pull plant combinations for the pest lifecycle involved.
Tech + Nature:
Modern platforms, such as Farmonaut, can monitor the impact of push–pull methods over large-scale fields using satellite data. We help farmers assess effectiveness, identify pest hotspots, and support precision interventions that save both resources and protect crop health.
4. Biosolarization for Soil Health: Eco-Friendly Pesticide Alternatives
Biosolarization is a cutting-edge method that unites solar energy and organic soil enrichment, representing an eco friendly pesticide alternative ideal for intensive farming systems and greenhouses.
Biosolarization for soil health involves incorporating organic matter, like compost or plant residues, into the soil, then covering the area with transparent plastic. Solar radiation heats the soil, while microbial activity under the film accelerates the release of pest-toxic compounds and increases lethal temperatures, killing nematodes, weed seeds, and soil-borne pathogens.
- Benefits:
- Reduces or eliminates the need for toxic chemical fumigants.
- Improves soil structure, boosts microbial diversity, and supports long-term productivity.
- Ideal where regulations limit pesticide usage near urban or protected areas.
- Limitations: Requires adequate sunlight, plastic removal, and specific timing for maximum effectiveness.
This method is especially useful in horticulture and for high-value crops grown in “protected” agriculture settings.
It stands as a prominent example of innovative pest control methods with broad implications for sustainable agriculture pest management.
Access real-time carbon footprint tracking for your biosolarization project with Farmonaut’s app, enabling farmers and organizations to track reductions in greenhouse gas emissions and enhance their environmentally friendly operations.
5. Biofumigation: Using Plants to Combat Pests
Biofumigation is an innovative method in which certain plants (mainly Brassicaceae, like mustard, broccoli, and cauliflower) are incorporated into soil to release natural chemicals that are toxic to nematodes, fungi, and harmful soil pests. As the chopped plant material decomposes, it releases isothiocyanates—potent natural fumigants.
- Procedure:
- Mow and chop up the biofumigant crop at the right growth stage (when chemical content is highest).
- Incorporate the green biomass into the soil using a rotavator.
- Cover the area with an impermeable plastic film for up to 4 weeks to trap gases and maximize pest-suppressing effects.
- After removal, the soil is ready for planting, often with drastically reduced pest loads.
- Advantages:
- Reduces need for synthetic pesticides, supporting organic crop certification.
- Improves overall soil health and encourages beneficial soil microbe populations.
- Best for: Market gardeners, high-value horticulture, and restricting persistent soil-borne pests without risk to humans, pollinators, or the broader environment.
Biofumigation is increasingly adopted in places like California, India, and the Mediterranean as regulations against chemical soil sterilants become stricter. It is another star example of sustainable agriculture pest management.
6. AI Powered Pest Detection & Drones for Crop Monitoring
A. AI and IoT: Revolutionizing Detection and Targeted Interventions
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) are revolutionizing pest control in agriculture. With ai powered pest detection and IoT-enabled sensors, farmers today can remotely monitor environmental conditions (e.g., temperature, humidity, soil moisture) and detect pests or disease outbreaks at their earliest onset. Here’s how:
- IoT sensors continuously relay real-time crop data, monitoring microclimates and the presence of pests such as mites or insect larvae.
- When AI models identify a sudden uptick in pest signatures, farmers are notified instantly and can apply targeted interventions—from the release of beneficial insects to limited, precision pesticide application.
- Benefits:
- Reduces unnecessary spraying by up to 25%.
- Increases crop yields by more than 10% on average—data from recent studies support this claim.
- Log data can be used to demonstrate sustainable practices, supporting compliance and market access.
B. Drones for Crop Monitoring and Aerial Application
Drones for crop monitoring and aerial surveillance are transforming the fight against pests across large fields or in inaccessible areas.
- High-resolution images and sensors on drones detect crop stress, pest hotspots, and disease spread at an early stage.
- In countries like India, drones spray neem-based biopesticides directly onto affected patches, minimizing both chemical use and human exposure.
- Precise application: Drones quickly apply biological agents or biopesticides only where needed, reducing input waste and environmental impact.
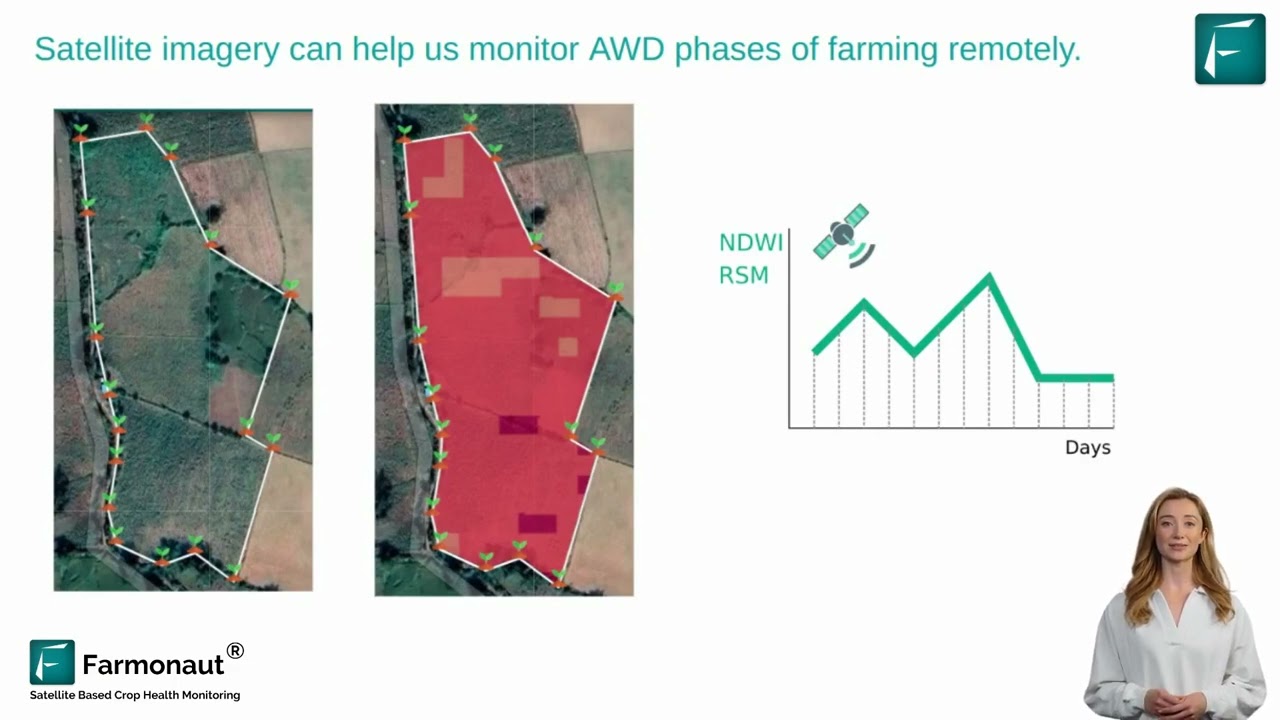
Modern platforms like Farmonaut empower this revolution with satellite-based crop health monitoring and AI-based advisory. Our solution leverages drone and satellite data to track vegetation health, pest outbreaks, and even predict infestation risk before visible symptoms emerge. The outcome? Better decisions, less waste, improved crop health, and a major step forward in sustainable agriculture pest management.
Don’t forget to explore the Farmonaut API and see our developer documentation to integrate advanced crop, weather, and pest data with your agri-tech solution or agribusiness.
7. Genetic Pest Control Technology & the Sterile Insect Technique (SIT)
Genetic pest control technology is at the cutting edge of 21st-century pest management. It employs modern genetic engineering techniques to alter or suppress pest populations with incredible precision.
-
Sterile Insect Technique (SIT):
- A proven method where sterilized male insects (e.g., through radiation or genetic alteration) are released into wild populations.
- When females mate with sterile males, no offspring result, leading to a gradual population decline.
- Used successfully to eradicate the screwworm pest in many regions; the USDA’s sterile fly facility in Texas is a leading example for controlling screwworm in North America.
-
Gene Drives and Genetic Suppression:
- Advanced methods (under research and regulatory oversight) engineer insects so targeted genes spread rapidly through populations, either sterilizing pests or making pests more susceptible to natural pathogens.
- Benefits: These methods offer targeted control with minimal non-target impact, long-term effectiveness, and reduced chemical pesticide use.
- Considerations: Addressing ecological and ethical concerns is critical; rigorous monitoring is essential to prevent unintended consequences.
Emerging Pest Management Technologies
In addition to the main seven methods, several innovations are redefining how we detect and manage pests in modern farming and forestry:
- Electronic Noses (E-noses): Devices that instantly “smell” volatile compounds released by infestations in stored grains or harvested crops.
- Thermal and Infrared Imaging: Pinpoint hidden pests in walls, under floors, or in dense crop canopies—facilitating early detection and reducing unnecessary pesticide application.
- Farmonaut’s Blockchain-Based Traceability: Our traceability solution allows sustainable pest control practices to be traced through the entire agri supply chain, adding value and trust for conscious consumers and global buyers.
Farmonaut’s Innovations and Value For Modern Agriculture
At Farmonaut, we help drive the future of innovative pest control methods by empowering farmers, agribusinesses, and governments with actionable, real-time data and AI-powered insights. Here’s how our platform enhances sustainable agriculture pest management:
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Track crop stress, disease onset, and pest outbreaks—from large-scale forests to smallholder fields, with detailed vegetation indices and soil moisture analytics.
- Jeevn AI Advisory: Receive personalized, AI-based pest and crop management advice, integrating weather forecasts and real-time field data for smarter interventions.
- Blockchain Traceability: (See above) Certifies sustainable pest management practices from field to shelf, opening up eco-conscious markets.
- Fleet and Resource Management: (Link: Fleet Management) Deploy vehicles, implements, and drones precisely to optimize the application of biological agents or beneficial insects—reducing costs and environmental impact.
- Carbon Footprinting: (Discussed above) Keep track of emissions linked to chemical usage and document improvements achieved through sustainable approaches.
Our subscription-based model enables everyone from individual farmers to large agribusinesses and government bodies to access the advantages of affordable, automated precision agriculture. Scalability and mobile access ensure these innovations reach everyone who needs them—no matter the field size, region, or infrastructure.
If you’re committed to modern, efficient, and environmentally friendly pest control, join us in adopting these transformative solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ): Innovative Pest Control Methods
-
What is the difference between integrated pest management (IPM) and traditional pest control?
IPM blends biological, cultural, mechanical, and chemical approaches, focusing on long-term prevention and minimum pesticide use. Traditional pest control often applies chemicals reactively, sometimes harming beneficial species and leading to resistance. -
Are biological pest control agents safe for the environment and consumers?
Yes, when properly managed, they selectively target pests and preserve beneficial insects, people, and ecosystem health. -
Can Farmonaut’s satellite and AI solutions reduce my need for chemical pesticides?
Absolutely. By detecting early signs of pest stress and guiding targeted intervention, our platform helps reduce unnecessary chemical applications and optimize beneficial biological solutions. -
How does biosolarization differ from biofumigation?
Biosolarization uses heat from trapped solar energy and organics to kill pests, while biofumigation leverages natural chemicals from specific plants to suppress soil-borne pests. -
What crops are suitable for push–pull pest management?
Maize, sorghum, and other cereals benefit greatly, but push–pull is adaptable to various crops when the appropriate repellent and trap plants are chosen. -
Is AI-powered pest detection cost-effective for smallholders?
With platforms like Farmonaut offering flexible subscriptions and mobile access, even small farms can now leverage satellite, AI, and IoT-driven advisories for pest and resource management. -
Where can I see pricing or subscribe?
Check our Stripe pricing table above or download our app to get started!
Conclusion: A Sustainable Path Forward
Innovative pest control methods are transforming the landscape of agriculture, farming, and forestry. By integrating biological, technological, and ecological solutions, we can manage pests with minimal chemical input, protect our crops and forests, and promote biodiversity and ecosystem health.
The future lies in sustainable agriculture pest management—one that’s efficient, environmentally friendly, and adaptable to changing threats and climates.
Ready to make your farming or agribusiness more resilient, productive, and climate-smart?
Join Farmonaut for the journey to the next generation of precision pest management.
Explore more with Farmonaut—where innovative, data-driven agriculture meets sustainability and productivity.