Maximizing Plant Health: Essential Soil, Water, and Pest Management Practices for Organic Garden Yield

In the world of gardening and agriculture, achieving optimal plant health and maximizing crop yield is a constant challenge. As we delve into the intricacies of organic gardening practices, we’ll explore the essential components that contribute to thriving plants and bountiful harvests. From soil management to water conservation, pest control to nutrient optimization, we’ll cover a comprehensive range of topics that will help you cultivate a flourishing garden while maintaining environmental sustainability.
Understanding the Importance of Soil Health
The foundation of any successful garden lies in the quality of its soil. Healthy soil is teeming with life, rich in nutrients, and provides the perfect environment for plants to grow and thrive. Let’s explore the key aspects of soil health and how we can improve it for optimal plant growth.
Soil Composition and Structure
Soil is composed of mineral particles, organic matter, water, and air. The ideal soil structure allows for proper drainage, aeration, and root penetration. To achieve this, we need to focus on:
- Balancing soil texture (sand, silt, and clay)
- Improving soil aggregation
- Increasing organic matter content
By incorporating organic matter such as compost, we can significantly enhance soil structure and create a favorable environment for beneficial microorganisms.
The Role of Soil pH
Soil pH plays a crucial role in nutrient availability and plant health. Most plants prefer a slightly acidic to neutral pH range (6.0-7.0). However, some plants thrive in more acidic or alkaline conditions. To manage soil pH effectively:
- Regularly test your soil pH
- Use organic amendments to adjust pH levels
- Choose plants that are well-suited to your soil’s natural pH
For acidic soils, adding lime can help raise the pH, while elemental sulfur can lower pH in alkaline soils.
Nutrient Management in Organic Gardening
Proper nutrient management is essential for healthy plant growth and optimal yield. In organic gardening, we focus on natural sources of nutrients and sustainable practices to maintain soil fertility. Key aspects of nutrient management include:
- Understanding macronutrients (N-P-K) and micronutrients
- Implementing crop rotation to prevent nutrient depletion
- Using organic fertilizers and amendments
- Practicing composting to recycle nutrients
By adopting these practices, we can ensure that our plants receive the essential nutrients they need for robust growth and abundant harvests.
Water Management: The Lifeblood of Your Garden
Water is a precious resource, and efficient water management is crucial for both plant health and environmental sustainability. Let’s explore strategies to optimize water usage in your garden.
Understanding Plant Water Requirements
Different plants have varying water needs depending on factors such as:
- Species and growth stage
- Climate and season
- Soil type and drainage
By understanding these requirements, we can tailor our irrigation practices to provide just the right amount of water for optimal growth.
Efficient Irrigation Techniques
Implementing efficient irrigation techniques can significantly reduce water waste and improve plant health. Some effective methods include:
- Drip irrigation systems
- Soaker hoses
- Mulching to retain soil moisture
- Rainwater harvesting
These techniques help deliver water directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff.
Monitoring Soil Moisture
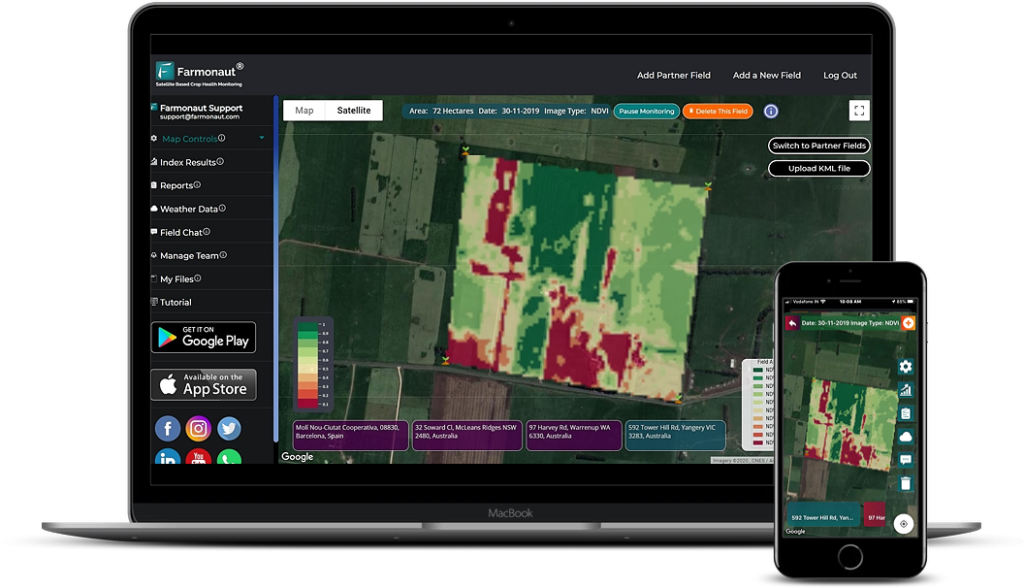
Accurate soil moisture monitoring is essential for effective water management. Traditional methods like the finger test can be supplemented with modern technology for more precise measurements. At Farmonaut, we offer satellite-based soil moisture monitoring that provides real-time data on your garden’s water needs. This technology allows for precise irrigation scheduling, ensuring that your plants receive the right amount of water at the right time.
Pest Management in Organic Gardening
Dealing with pests is one of the biggest challenges in organic gardening. However, with the right approach, we can manage pest populations effectively while maintaining ecological balance.
Identifying Common Garden Pests
The first step in pest management is proper identification. Some common garden pests include:
- Aphids
- Caterpillars
- Slugs and snails
- Spider mites
- Whiteflies
By accurately identifying pests, we can implement targeted control measures.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Integrated Pest Management is a holistic approach that combines various strategies to control pests while minimizing environmental impact. Key components of IPM include:
- Cultural controls (crop rotation, companion planting)
- Physical controls (handpicking, traps)
- Biological controls (beneficial insects, natural predators)
- Chemical controls (as a last resort, using organic pesticides)
By implementing IPM, we can maintain a healthy balance in our garden ecosystem.
Encouraging Beneficial Insects
Beneficial insects play a crucial role in controlling pest populations naturally. To attract and support these helpful creatures:
- Plant diverse flowering species to provide nectar and pollen
- Create insect habitats (e.g., bug hotels)
- Avoid broad-spectrum pesticides that harm beneficial insects
By fostering a diverse ecosystem, we can harness nature’s own pest control mechanisms.
Organic Disease Management
Plant diseases can devastate crops and reduce yields significantly. In organic gardening, we focus on prevention and natural remedies to manage diseases effectively.
Common Plant Diseases
Understanding common plant diseases is crucial for early detection and management. Some widespread diseases include:
- Powdery mildew
- Blight (early and late)
- Fusarium wilt
- Root rot
- Viral diseases
Early identification of these diseases can help prevent their spread and minimize crop losses.
Disease Prevention Strategies
Preventing diseases is often easier and more effective than treating them. Key prevention strategies include:
- Crop rotation to break disease cycles
- Proper plant spacing for good air circulation
- Using disease-resistant varieties
- Maintaining proper soil health and nutrition
- Implementing good sanitation practices
By focusing on prevention, we can significantly reduce the incidence of plant diseases in our gardens.
Natural Disease Control Methods
When diseases do occur, organic gardeners have several natural control options:
- Neem oil for fungal diseases
- Copper-based fungicides for bacterial infections
- Baking soda solutions for powdery mildew
- Pruning and removing infected plant parts
- Compost tea to boost plant immunity
These natural remedies can help manage diseases while minimizing environmental impact.
Maximizing Crop Yield in Organic Gardens
The ultimate goal of gardening is to produce a bountiful harvest. Let’s explore strategies to maximize crop yield while maintaining organic principles.
Optimal Plant Spacing and Companion Planting
Proper plant spacing ensures that each plant has adequate access to sunlight, nutrients, and water. Companion planting can further enhance growth and yield by:
- Improving nutrient uptake
- Deterring pests
- Attracting beneficial insects
- Maximizing space utilization
By carefully planning your garden layout, you can create a thriving ecosystem that supports optimal plant growth.
Pruning and Training for Increased Productivity
Proper pruning and training techniques can significantly boost crop yield by:
- Improving air circulation
- Directing plant energy towards fruit production
- Facilitating easier harvesting
- Controlling plant size and shape
Different plants require specific pruning methods, so it’s essential to research the best techniques for each crop in your garden.
Harvesting Techniques for Maximum Yield
Proper harvesting techniques can extend the productive period of your plants and increase overall yield. Consider the following tips:
- Harvest regularly to encourage continued production
- Pick fruits and vegetables at their peak ripeness
- Use clean, sharp tools to minimize plant damage
- Practice succession planting for continuous harvests
By implementing these harvesting strategies, you can maximize the productivity of your organic garden.
Leveraging Technology for Precision Agriculture
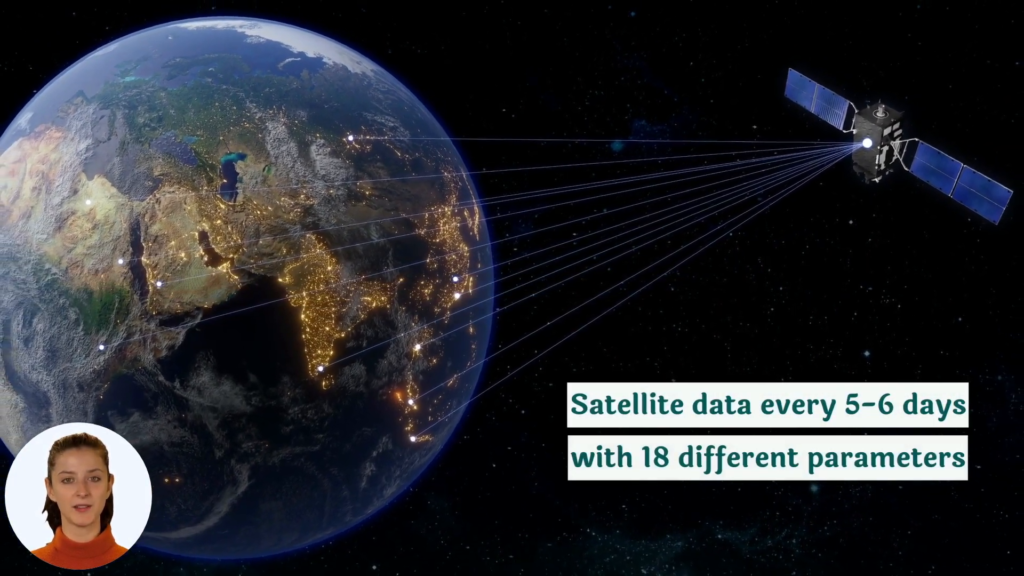
While traditional organic gardening practices form the foundation of sustainable agriculture, modern technology can significantly enhance our ability to manage gardens efficiently and maximize yields. At Farmonaut, we’re at the forefront of integrating satellite technology and artificial intelligence into agricultural practices.
Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring
Our satellite-based crop monitoring system provides real-time data on various aspects of plant health and soil conditions. This technology offers several benefits:
- Early detection of crop stress
- Precise mapping of field variability
- Accurate estimation of crop yields
- Optimization of resource allocation
By leveraging this technology, gardeners and farmers can make data-driven decisions to improve crop management and increase productivity.
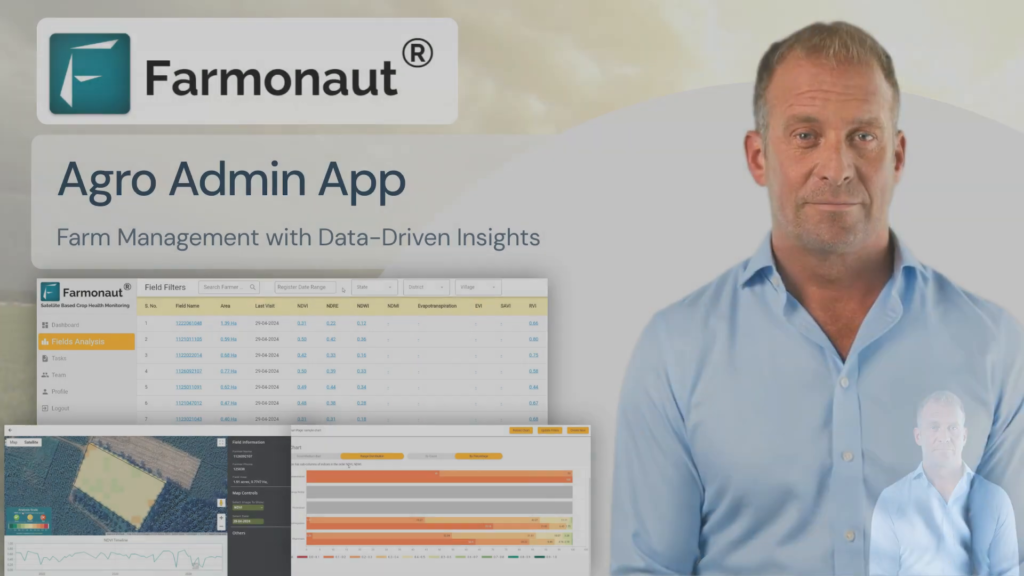
AI-Powered Advisory Systems
Our Jeevn AI advisory system combines satellite data with machine learning algorithms to provide personalized recommendations for crop management. This system offers:
- Customized irrigation schedules
- Targeted fertilizer recommendations
- Early pest and disease warnings
- Optimal planting and harvesting dates
These AI-driven insights help gardeners implement precision agriculture techniques, even on a small scale.
Integrating Technology with Organic Practices
While embracing technology, it’s crucial to maintain the core principles of organic gardening. Here’s how we can integrate modern tools with traditional organic practices:
- Use satellite data to inform compost and organic fertilizer application
- Implement precision irrigation based on real-time soil moisture data
- Utilize early warning systems for pest and disease management, focusing on organic control methods
- Optimize crop rotations and companion planting based on field performance data
By combining the best of both worlds, we can create highly efficient and sustainable organic gardens.
Comparing Traditional Methods with Farmonaut’s Satellite System
| Gardening Aspect | Traditional Method | Farmonaut Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Soil Health Monitoring | Manual soil testing, visual inspection | Real-time satellite-based soil health indices, AI-driven analysis |
| Water Management | Manual irrigation, based on visual cues or schedules | Precision irrigation recommendations based on satellite-derived soil moisture data |
| Pest Detection | Regular visual inspections, manual scouting | Early pest detection through spectral analysis, AI-powered pest risk alerts |
| Crop Yield Estimation | Manual counting, historical data | Accurate yield estimation using satellite imagery and machine learning models |
| Disease Identification | Visual symptoms, lab testing | Early disease detection through spectral anomalies, AI-assisted diagnosis |
This table highlights how Farmonaut’s precision agriculture capabilities can significantly enhance traditional garden management practices, leading to improved efficiency and productivity.
Sustainable Practices for Long-Term Garden Health
Creating a thriving organic garden is not just about short-term gains; it’s about establishing sustainable practices that ensure long-term soil health and ecosystem balance. Let’s explore some key strategies for maintaining a sustainable garden.
Cover Cropping and Green Manures
Cover crops and green manures are essential tools for maintaining soil health and fertility. These practices offer numerous benefits:
- Preventing soil erosion
- Suppressing weeds
- Fixing nitrogen in the soil
- Improving soil structure
- Increasing organic matter content
By incorporating cover crops into your rotation, you can significantly enhance the long-term productivity of your garden.
Composting and Organic Matter Management
Composting is a cornerstone of organic gardening, providing a sustainable source of nutrients and organic matter. To maximize the benefits of composting:
- Create a balanced mix of green and brown materials
- Maintain proper moisture and aeration
- Monitor temperature for optimal decomposition
- Use finished compost as a soil amendment and mulch
Regular addition of compost to your garden beds will improve soil structure, water retention, and nutrient availability over time.
Biodiversity and Habitat Creation
Promoting biodiversity in your garden is crucial for long-term ecosystem health. Consider the following practices:
- Plant a diverse range of native species
- Create wildlife habitats (e.g., bird baths, insect hotels)
- Establish pollinator-friendly areas
- Maintain some “wild” areas in your garden
A diverse garden ecosystem is more resilient to pests and diseases, and provides numerous ecological benefits.
Adapting to Climate Change in Organic Gardening
As climate patterns continue to shift, adapting our gardening practices becomes increasingly important. Here are some strategies to make your organic garden more resilient to climate change:
Drought-Resistant Gardening Techniques
To prepare for potential water scarcity, consider implementing these drought-resistant techniques:
- Choose drought-tolerant plant varieties
- Implement water-efficient irrigation systems
- Use mulch to retain soil moisture
- Create swales and berms for water harvesting
- Practice deep watering to encourage deep root growth
These practices will help your garden thrive even in water-limited conditions.
Adapting Planting Schedules
Changing climate patterns may require adjustments to traditional planting schedules. Consider the following strategies:
- Monitor local climate trends and adjust planting dates accordingly
- Extend the growing season with season extenders (e.g., row covers, hoop houses)
- Experiment with new crop varieties suited to changing conditions
- Implement succession planting to spread out harvests and reduce risk
Flexibility in planting schedules can help mitigate the impacts of unpredictable weather patterns.
Building Resilient Soil Systems
Healthy, resilient soil is key to adapting to climate change. Focus on these soil-building practices:
- Increase organic matter content to improve water retention
- Encourage deep root systems through proper soil management
- Implement no-till or minimal tillage practices
- Use cover crops to protect and improve soil during off-seasons
These practices will help your soil better withstand extreme weather events and changing climate conditions.
The Role of Technology in Sustainable Gardening
While organic gardening emphasizes natural processes, technology can play a crucial role in enhancing sustainability and efficiency. At Farmonaut, we’re committed to bridging the gap between traditional organic practices and cutting-edge technology.
Precision Agriculture for Small-Scale Gardens
Our satellite-based monitoring system brings precision agriculture techniques to gardeners of all scales. Benefits include:
- Optimized resource use (water, nutrients, labor)
- Early detection of plant stress and disease
- Improved decision-making based on real-time data
- Reduced environmental impact through targeted interventions
By leveraging these technologies, even small-scale gardeners can achieve professional-level crop management.
Weather Forecasting and Climate Adaptation
Accurate weather forecasting is crucial for effective garden management. Our system provides:
- Hyperlocal weather predictions
- Frost and extreme weather warnings
- Long-term climate trend analysis
- Customized planting and harvesting date recommendations
These tools help gardeners adapt to changing climate patterns and optimize their growing practices.
Data-Driven Crop Selection and Rotation
Our AI-powered advisory system can help optimize crop selection and rotation by:
- Analyzing soil health and nutrient levels
- Recommending suitable crop varieties based on local conditions
- Suggesting optimal crop rotations for soil health and pest management
- Providing yield estimates for different crop combinations
This data-driven approach helps gardeners make informed decisions that maximize productivity while maintaining soil health.
Community Engagement and Knowledge Sharing
Sustainable gardening is not just an individual effort; it thrives on community engagement and knowledge sharing. Here’s how we can foster a community of organic gardeners:
Local Gardening Networks
Engaging with local gardening communities offers numerous benefits:
- Sharing of local knowledge and best practices
- Exchange of seeds and plant varieties
- Collaborative pest management strategies
- Community composting initiatives
These networks can significantly enhance the collective knowledge and resources available to organic gardeners.
Online Resources and Forums
The digital age has made it easier than ever to access gardening information and connect with experts. Consider utilizing:
- Online gardening forums and discussion boards
- Social media groups dedicated to organic gardening
- Webinars and online workshops
- Digital libraries of gardening resources
These online platforms provide a wealth of information and allow gardeners to share experiences across geographical boundaries.
Citizen Science Projects
Participating in citizen science projects can contribute to broader agricultural research while enhancing your own gardening knowledge. Consider getting involved in:
- Pollinator monitoring programs
- Soil health assessment projects
- Climate change impact studies
- Biodiversity mapping initiatives
These projects not only provide valuable data for researchers but also deepen your understanding of your local ecosystem.
Conclusion: Embracing a Holistic Approach to Organic Gardening
As we’ve explored throughout this comprehensive guide, successful organic gardening requires a holistic approach that integrates various aspects of plant and soil health, water management, pest control, and environmental stewardship. By combining traditional organic practices with modern technology and community engagement, we can create thriving, sustainable gardens that produce abundant yields while nurturing the earth.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to supporting gardeners and farmers in their journey towards sustainable agriculture. Our satellite-based monitoring system and AI-powered advisory tools are designed to complement and enhance organic gardening practices, providing the data-driven insights needed to make informed decisions and optimize resource use.
Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting your organic journey, remember that every small step towards sustainability makes a difference. By nurturing the soil, conserving water, promoting biodiversity, and embracing innovation, we can cultivate not just healthy plants, but a healthier planet for generations to come.
FAQs
1. What is the most important factor in organic gardening?
Soil health is arguably the most crucial factor in organic gardening. Healthy soil supports plant growth, retains water, and hosts beneficial microorganisms.
2. How can I improve soil fertility without synthetic fertilizers?
Use compost, cover crops, and organic amendments like bone meal or seaweed extract. Crop rotation also helps maintain soil fertility.
3. What are some natural ways to control garden pests?
Companion planting, encouraging beneficial insects, using physical barriers, and applying organic pest control solutions like neem oil are effective natural pest control methods.
4. How often should I water my organic garden?
Watering frequency depends on factors like soil type, climate, and plant species. Generally, deep, infrequent watering is better than frequent shallow watering.
5. Can technology really improve organic gardening practices?
Yes, technologies like Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring system can provide valuable insights into soil health, water needs, and plant stress, helping gardeners make more informed decisions.
6. What are the benefits of crop rotation in organic gardening?
Crop rotation helps prevent soil depletion, reduces pest and disease pressure, and can improve overall soil health and structure.
7. How can I start composting at home?
Begin with a mix of green (nitrogen-rich) and brown (carbon-rich) materials, keep the pile moist but not wet, and turn it regularly to aerate. There are various composting methods suitable for different spaces and needs.
8. What’s the best way to manage weeds in an organic garden?
Mulching, hand-pulling, using cover crops, and implementing proper crop spacing are effective organic weed management strategies.
9. How can I adapt my garden to climate change?
Choose drought-resistant plants, implement water-saving techniques, use season extenders, and stay informed about changing local climate patterns to adapt your gardening practices.
10. Is organic gardening more expensive than conventional methods?
While initial costs may be higher, organic gardening can be more cost-effective in the long run due to improved soil health, reduced input costs, and potentially higher yields.
For more information on how Farmonaut can help you optimize your organic gardening practices, visit our app page or explore our API documentation. Download our mobile app for on-the-go garden monitoring:
For developers interested in integrating our satellite and weather data into their own applications, check out our developer documentation.