Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Rise of Environmental Monitoring in Agriculture & Forestry
- Understanding Environmental Monitoring
- Key Components of Environmental Monitoring
- 7 Tech Secrets Revolutionizing Environmental Monitoring
- Comparative Benefits Table of Environmental Monitoring Technologies
- Key Applications—Agriculture & Forestry
- Farmonaut’s Advanced Environmental Monitoring Solutions
- Challenges in Environmental Monitoring & Future Directions
- Conclusion: Empowering Sustainability and Productivity with Monitoring
- FAQ: Environmental Monitoring in Agriculture and Forestry
“Over 80% of global biodiversity hotspots are monitored using remote sensing technologies for conservation.”
Environmental Monitoring: 7 Tech Secrets You Must Know!
Meta Description: Discover 7 essential technology secrets driving environmental monitoring in agriculture and forestry. Learn how remote sensing, AI, and advanced data analysis optimize sustainability, boost productivity, and enable informed decision-making for a greener future.
As the global population continues to grow and climate change impacts intensify, sustainable agriculture and forestry become ever more critical. Environmental monitoring in agriculture, farming, and forestry stands at the forefront of this transformation, leveraging advanced technologies to observe, analyze, and manage ecosystems effectively. With the integration of remote sensing, AI, IoT sensors, and sophisticated data analysis techniques, we are now empowered to make informed decisions that balance ecological health with economic viability.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll uncover the 7 revolutionary technology secrets transforming environmental monitoring. Join us as we dive into the mechanisms, benefits, and practical applications that are shaping a more sustainable future for our land, water, forests, and biodiversity.
Understanding Environmental Monitoring
At its core, environmental monitoring is the systematic, periodic measurement and tracking of various environmental parameters. This can include monitoring soil quality, water resources, air conditions, biodiversity, and more. In the context of agriculture, forestry, and farming, such observations enable us to proactively address changes, detect anomalies, and implement strategies to mitigate potential environmental impacts.
- Purpose: To provide timely, accurate data for well-informed land management and resource allocation decisions.
- Outcome: Enhanced sustainability, optimized productivity, and proactive ecological management.
Let’s explore the critical components involved in effective environmental monitoring in agriculture and forestry.
Key Components of Environmental Monitoring
1. Soil Condition Monitoring
One of the most foundational elements of environmental monitoring is soil quality assessment. By systematically measuring parameters such as:
- Soil moisture content: Crucial for irrigation and drought planning.
- Nutrient levels (N, P, K, etc.): Drives fertilization schedules and crop selection.
- pH: Influences plant growth and nutrient uptake.
- Erosion rates: Guides soil conservation and land management practices.
We empower farmers and land managers to implement optimized fertilization, targeted irrigation, and effective erosion control practices.
Technologies such as remote sensing, in-situ IoT sensors, and satellite imagery enable real-time data acquisition. For instance, the European Space Agency’s WORLD SOILS project is pioneering a global Soil Monitoring System via Earth Observation data to estimate Soil Organic Carbon—a critical factor for agricultural productivity and sustainability.
2. Vegetation Monitoring
By observing plant health, biomass, and vegetation cover, we:
- Assess crop conditions and forecast yields.
- Detect pest and disease outbreaks before they spread.
- Support sustainable land management and forest degradation assessments.
Integration of Earth Observation multisensor data with field measurements delivers comprehensive reporting on forest health, carbon stocks, and biodiversity. Modern algorithms even identify subtle changes in vegetative indices, speeding up decision-making and allowing for targeted interventions.
3. Water Resource Management
No ecosystem thrives without water. Water resource monitoring involves tracking:
- pH and turbidity levels: Ensures water safety for crops, livestock, and wildlife.
- Contaminant presence: Prevents pollution, protects human and ecosystem health.
- Availability & consumption: Facilitates sustainable irrigation, drought planning, and resource allocation.
The use of sensors and advanced water monitoring technologies allows us to maximize water-use efficiency, protect freshwater ecosystems, and improve overall agricultural output.
4. Biodiversity Conservation
Biodiversity is the engine of ecosystem resilience. Our approach to biodiversity conservation strategies includes:
- Monitoring species diversity and abundance, informing wildlife habitat preservation and land-use planning.
- Designing wildlife corridors to facilitate animal movement and genetic exchange.
- Preventing habitat fragmentation and enabling targeted restoration efforts.
Modern remote sensing and AI-based techniques revolutionize large-scale biodiversity tracking by analyzing spatial changes and identifying critical conservation zones.
“AI-driven environmental monitoring can analyze up to 1 million satellite images daily to track forest health.”

7 Tech Secrets Revolutionizing Environmental Monitoring
Let’s unlock the seven key environmental monitoring technologies reshaping how we observe, analyze, and manage our ecosystems for better soil, crop, forest, and biodiversity health. Each solution harnesses modern science, data, and digital tools to strengthen our role as environmental stewards.
1. Remote Sensing for Environmental Management
– What is it?
Remote sensing harnesses satellite imagery, aerial photography, and drone-based data collection to monitor large tracts of land, forest, and agricultural areas without physical presence.
- Primary Use: Large-scale observation of land use, vegetation health, water bodies, and wildlife habitats.
- Benefits: Delivers near real-time, high-resolution data for forest monitoring technologies and satellite imagery for agriculture—essential for detecting trends, risks, and opportunities at scale.
- Impact: Enables informed decision-making and rapid response to deforestation, crop stress, or resource depletion.
2. IoT Sensors: Precision Data for Soil, Water, and Crop Health
– What is it?
The Internet of Things (IoT) sensors network together to measure soil moisture, pH, nutrient levels, microclimates, and more—often in real time and at high spatial detail.
- Primary Use: Supporting precision farming solutions, enabling efficient irrigation, fertilization, and crop care.
- Benefits: Drives resource optimization and cost savings by reducing input waste and maximizing outputs.
- Impact: Empowers farmers to act on exact field-level data, adapting quickly to changes and mitigating environmental impacts.
3. AI in Environmental Monitoring: From Big Data to Actionable Insights
– What is it?
By tapping into machine learning algorithms and AI models, we rapidly parse massive environmental datasets (up to a million satellite images daily!), detecting subtle patterns and predicting environmental threats.
- Primary Use: Guides pest and disease prediction, carbon stock assessment in forestry, and species distribution modeling.
- Benefits: Reduces the human effort in data analysis and enhances accuracy in forecasting risks and opportunities.
- Impact: Translates big data into prioritized actions for sustainable resource management and conservation strategies.
- Example: Using AI to forecast pest outbreaks enables timely, eco-friendly interventions, reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
4. Satellite Imagery for Agriculture and Forestry
– What is it?
High-resolution satellite imagery reveals real-time data on crop health, biomass production, forest degradation, and land use.
- Primary Use: Monitoring crop growth, tracking deforestation, and assessing forest health on local to global scales.
- Benefits: Allows farmers and forest managers to identify risks early and optimize resource allocations.
- Impact: Increases efficiency in land management while supporting food security and carbon sequestration efforts.
5. Blockchain for Environmental Data Traceability
– What is it?
Blockchain secures, chronologically tracks, and authenticates data about crop journeys, farm produce, and resource use, ensuring transparency across the supply chain.
- Primary Use: Delivers product traceability for agriculture and forestry, from field to consumer.
- Benefits: Builds consumer trust, reduces fraud, and supports sustainability certifications.
- Impact: Makes data tamper-proof, supporting supply chain integrity in both local and global markets.
Explore how Farmonaut’s blockchain tools enhance supply chain transparency—discover our traceability suite.
6. Carbon Footprinting and Emission Tracking
– What is it?
By continuously monitoring emissions from agriculture, farming, and forestry, businesses can implement targeted strategies to track, report, and reduce their environmental impact.
- Primary Use: Carbon stock assessment in forestry and emission reduction verification for agriculture.
- Benefits: Promotes sustainable practices, supports regulatory compliance, and helps businesses achieve sustainability certification.
- Impact: Drives climate-positive actions and enhances reputation in green markets.
Empower your farm or agri-business with Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting platform for real-time, science-backed, emission control.
7. Integrated Platform and API Connectivity
– What is it?
Combining various environmental monitoring technologies into unified, API-driven platforms enables seamless access to global satellite, sensor, and AI data.
- Primary Use: APIs for developers and businesses to integrate environmental insights directly into their applications or platforms.
- Benefits: Streamlines large-scale farm management, enhances cross-platform visibility, and supports policy or financial assessments.
- Impact: Democratizes access to advanced monitoring tools for organizations of all sizes and geographical locations.
Access detailed developer documentation for Farmonaut’s Satellite & Weather Data API and power up your custom analytics.
Comparative Benefits Table of Environmental Monitoring Technologies
| Technology Name | Primary Use Case | Estimated Reduction in Environmental Impact (%) | Key Benefit | Notable Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Remote Sensing | Large-scale ecosystem observation, crop monitoring, forest health | 25–45% | Enables rapid detection of changes and anomalies at landscape level | European agriculture, Brazilian rainforests |
| IoT Sensors | Field-level soil, water, and crop health data | 15–30% | Supports precision inputs and real-time interventions | Smart farms in India, Netherlands |
| AI & ML Analysis | Predictive modelling for pests, diseases, yield, and carbon | 25–40% | Accelerates big data analysis and improves forecast precision | US corn belt pest prediction |
| Satellite Imagery | Remote crop and forest monitoring, land use assessment | 30–50% | Grants timely, scalable, and unbiased ecosystem insights | Farmonaut global platform |
| Blockchain Traceability | Supply chain authentication, resource transparency | 10–20% | Secures data and builds stakeholder & consumer trust | Textile production in Europe |
| Carbon Footprinting | Emission tracking, sustainability reporting | 20–35% | Empowers climate-positive decisions and compliance | Agtech in Southeast Asia |
| Integrated Platforms/API | Centralized data access, multi-source analysis | 15–25% | Unifies technologies for scalable, actionable oversight | Farmonaut API/Web app |
Key Applications—Agriculture & Forestry
Applications of Environmental Monitoring in Agriculture
- Precision Farming Solutions:
- By analyzing spatial and temporal field data, farmers can apply water, nutrients, and pesticides with high efficiency, reducing waste and minimizing environmental impact.
- Soil quality assessment drives variable-rate irrigation, targeted fertilization, and crop disease intervention.
- Satellite monitoring platforms like Farmonaut deliver actionable insights for real-time irrigation and resource allocation.
- Climate Adaptation:
- Ongoing tracking of weather, soil moisture, and temperature variability enables selection of climate-resilient crop varieties and adaptive management strategies.
- Farmers use these insights to avoid climate-related losses, boost yields, and ensure food security.
- Pest and Disease Management:
- Constant monitoring of environmental parameters and presence of pests enables early warning and the use of ecological Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategies.
- Reduces reliance on chemical pesticides, aligning with sustainability and biodiversity goals.
- Water Resource Use Optimization:
- Data-driven irrigation management and automated decision tools enhance water-use efficiency, particularly important in regions facing water scarcity or drought.
Ready to manage large plantations with integrated satellite-based crop, field, and forest advisory? Try Farmonaut’s Agro Admin App for Large-Scale Farm Management.
Applications of Environmental Monitoring in Forestry
- Forest Monitoring Technologies:
- Multi-temporal satellite imagery and AI support the mapping of deforestation, biodiversity loss, and forest degradation over time.
- IoT sensors in forests track changes in microclimate, soil, and species presence, critical for ecosystem health assessments.
- Carbon Stock Assessment in Forestry:
- Precise data empowers forest managers to model carbon sequestration, develop climate mitigation strategies, and report on sustainability initiatives.
- Farmonaut’s carbon tracking suite is ideal for organizations seeking real-time, accurate verification of their climate-positive conservation and planting efforts.
- Wildlife Habitat and Biodiversity Conservation Strategies:
- Continuous data collection on species and canopy structure guides targeted conservation, restoration, and reforestation efforts.
- Algorithms help identify key biodiversity corridors and regeneration zones for optimal resource allocation.
- Traceability, Resource, and Fleet Management:
- From plantation logistics to monitoring resource use, integrated platforms—like Farmonaut’s Fleet Management tools—reduce operational costs and mitigate environmental impacts.
Explore carbon footprinting tools to invigorate your forest, crop, or agroforestry sustainability strategy.
Farmonaut’s Advanced Environmental Monitoring Solutions
At Farmonaut, we are passionate about making precision agriculture accessible for farmers and agribusinesses of all sizes.
- Satellite-Based Crop and Forest Health Monitoring:
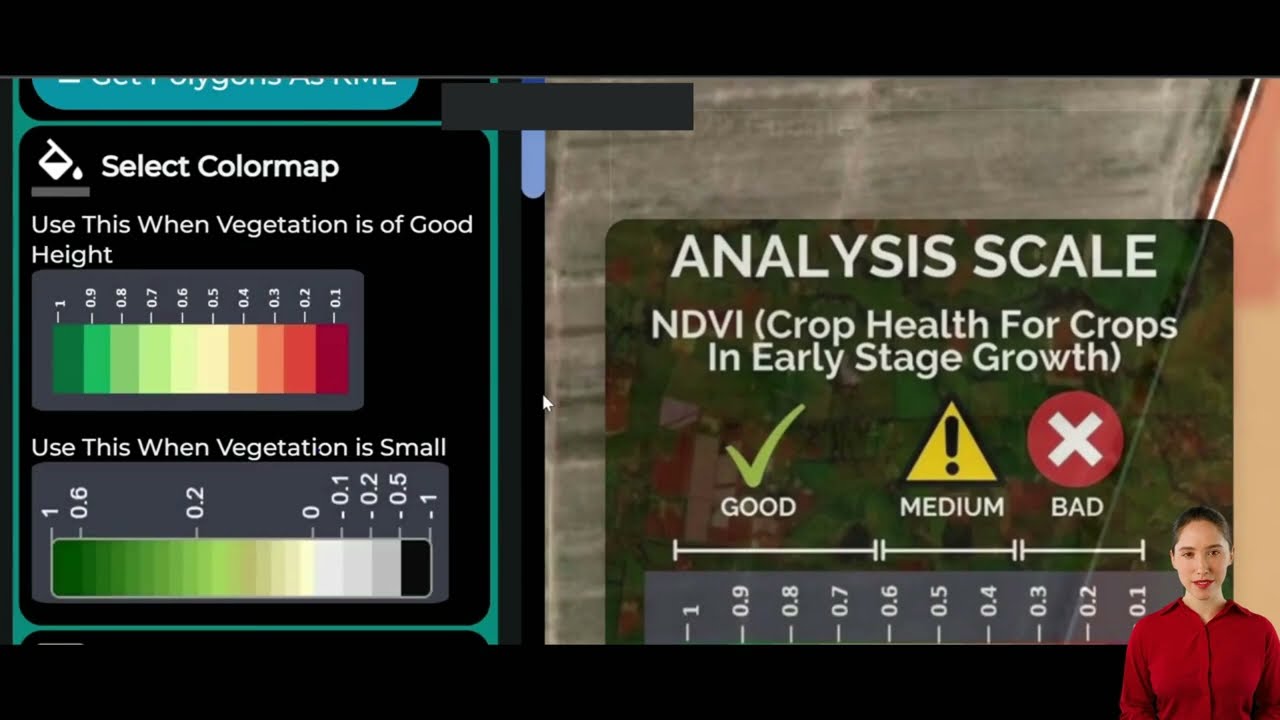
- Our technology leverages multispectral satellite imagery to provide real-time crop monitoring and predictive analysis on soil moisture, vegetation indices (NDVI), pest and disease outbreaks, and more—to optimize yield and sustainability.
- Jeevn AI Advisory System:
- This AI-based farm advisory tool delivers personalized insights, actionable recommendations, and local weather forecasts—helping you make informed management decisions.
- Blockchain-Based Traceability and Data Integrity:
- Provides robust supply chain authentication, transparency, and quality assurance—track your crop journey and protect your brand and customers.
- Fleet, Resource, and Loan Management Tools:
- Our platform extends to fleet management, plantation logistics, and crop loan/insurance validation to multi-field, cooperative, and government users—reducing costs and ensuring financial resilience. For details see our Crop Loan and Insurance page.
- Carbon Footprinting Platform:
- Track your real-time environmental footprint, comply with regulations, and unlock new green finance opportunities.
Our API-first approach opens up advanced satellite and weather data, empowering agri-developers and organizations to integrate monitoring technology at scale.
Challenges in Environmental Monitoring & Future Directions
Despite astonishing advances, several persistent challenges face the widespread adoption and optimization of environmental monitoring in agriculture and forestry:
- Data Integration:
- Combining satellite, sensor, and field data requires advanced data management platforms and skilled data analysis capabilities.
- Farmonaut’s integrated data approach addresses this, simplifying insights delivery for all stakeholders.
- Cost and Accessibility:
- Access to high-resolution satellite imagery and IoT sensors is sometimes cost-prohibitive for small and marginal farmers.
- Farmonaut breaks this barrier by offering affordable, modular subscription models and global accessibility via web/mobile/API platforms.
- Data Interpretation & Skill Gaps:
- Making sense of complex multi-modal environmental data requires upskilling farmers, managers, and decision-makers.
- Our AI-driven advisories automate key analyses and present information in user-friendly, actionable formats.
- Infrastructure & Internet Penetration:
- Some rural areas still lack robust connectivity and digital infrastructure, hampering technology uptake.
Future-Proofing Environmental Monitoring
As we look ahead, the field of environmental monitoring in agriculture and forestry is set to benefit from:
- Affordable Sensors & Platforms: The cost of IoT and remote sensors is dropping, fostering wider adoption.
- Stronger AI Integration: Advanced AI models will automate more of the analysis and deliver simpler, faster insights for actionable resource management.
- Local Community Empowerment: Involving regional communities in monitoring strengthens data quality and ecological stewardship, especially in biodiversity-rich areas.
- Blockchain Verification: Expansion of blockchain-based traceability ensures trust across agricultural supply chains on a global scale.
Conclusion: Empowering Sustainability and Productivity with Monitoring
Environmental monitoring stands as the cornerstone of sustainable agriculture, farming, and forestry. Coupling cutting-edge technology with real-world applications, we empower all stakeholders—from smallholder farmers to multi-national agri-enterprises—to proactively address ecological challenges, optimize productivity, and chart a path toward a more resilient and sustainable future.
With the rise of satellite imagery, AI analysis, IoT sensors, and integrated platforms, tools such as those offered by Farmonaut amplify our ability to track, analyze, and act on complex environmental changes. This fosters not only better yields and operational efficiency, but also protects forests, conserves biodiversity, and supports climate goals.
Now is the time for all stakeholders—farmers, agribusinesses, corporates, and governments—to leverage these technological advancements for sustainable resource management and a thriving ecological future.
Ready to make your land, water, and environment monitoring smarter and more sustainable? Start your journey with Farmonaut today!
FAQ: Environmental Monitoring in Agriculture and Forestry
What is environmental monitoring in agriculture?
It is the continuous or periodic measurement and tracking of environmental parameters—such as soil quality, water resources, vegetation, and biodiversity—to support sustainable and productive farming practices. It relies on modern technologies like satellite imagery, IoT sensors, and AI analytics.
How does remote sensing benefit environmental management?
Remote sensing enables large-scale, real-time environmental monitoring using satellite imagery and aerial photography, offering comprehensive insights into land use changes, crop health, forest degradation, and water resources without on-ground intervention.
Why is AI important for environmental monitoring?
AI and machine learning can analyze massive datasets from satellites and sensors rapidly, identifying patterns, predicting risks (such as pest outbreaks or carbon stock fluctuations), and enabling proactive management strategies for ecosystem health.
How do IoT sensors improve farming outcomes?
IoT sensors provide real-time, on-site data about soil condition, water levels, microclimate, and crop health—enabling precision agriculture, optimized resource use, and early identification of stressors to maximize yield and sustainability.
Can environmental monitoring help in climate adaptation?
Yes! With continuous tracking of climate patterns, soil moisture, and temperature, farmers and land managers can make data-driven decisions to adapt to changing climates, reducing losses and strengthening long-term agricultural viability.
What makes Farmonaut unique in this space?
Farmonaut leverages satellite imagery, AI-driven advisory, blockchain-based traceability, and cloud-based APIs to make advanced environmental monitoring accessible and affordable for farmers, agribusinesses, and governments globally—without requiring expensive hardware investments.
Where can I access more information or subscribe to Farmonaut’s solutions?
Visit our web/mobile applications or explore API integration via our API page and developer documentation.
Environmental monitoring is not just a tool—it’s the backbone of a more sustainable, productive, and resilient future for our agriculture, farming, and forestry sectors. Together, let’s champion these advances for a greener planet.