Idaho’s Battle Against Invasive Quagga Mussels: Protecting Waterways and Agriculture
“Idaho allocated $6.6 million for fiscal year 2025 to combat invasive species, including quagga mussels in the Snake River.”
In the heart of the American West, Idaho faces a formidable challenge that threatens its pristine waterways and thriving agricultural sector. The battle against invasive quagga mussels has intensified, prompting a critical conversation about the future of the state’s natural resources and the measures needed to protect them. As we delve into this pressing issue, we’ll explore the multifaceted approach Idaho is taking to safeguard its waters and the implications for the broader Columbia River Basin.
Understanding the Quagga Mussel Threat
Quagga mussels, originally from the waters of Eastern Europe, have become a significant environmental concern across North America. These small but prolific invaders have the potential to wreak havoc on ecosystems, water infrastructure, and local economies. In Idaho, the discovery of quagga mussels in the Snake River in 2023 set off alarm bells, mobilizing state agencies and conservationists alike.
- Origin: Native to the Dnieper River drainage of Ukraine
- Size: Typically no larger than 20mm
- Reproduction: A single female can produce up to 1 million eggs per year
- Spread: Primarily through ballast water and attached to boats
The rapid spread of quagga mussels across the United States, from the Great Lakes to Western states like Arizona and Colorado, serves as a stark warning of their adaptive capabilities and the challenges of containment.
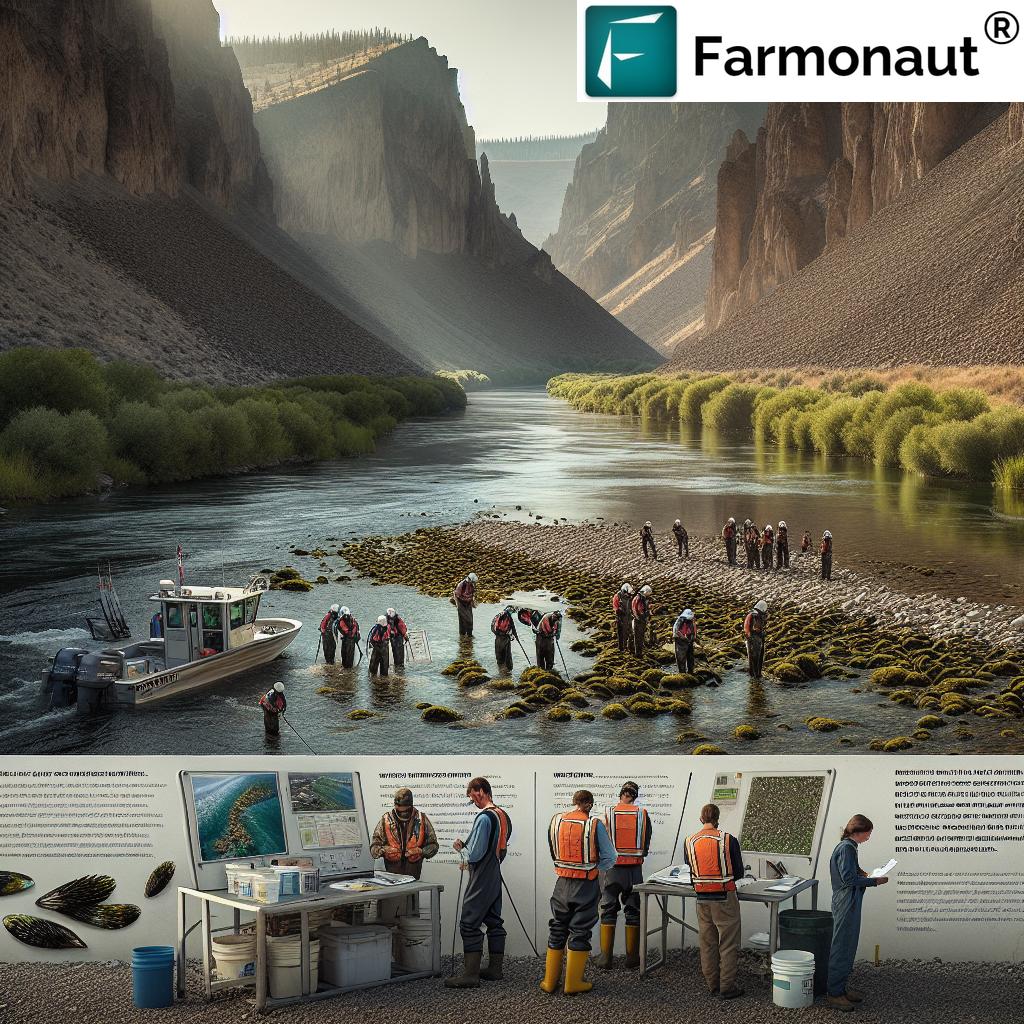

The Idaho State Department of Agriculture’s Response
At the forefront of Idaho’s defense against quagga mussels is the Idaho State Department of Agriculture (ISDA). Under the leadership of Director Chanel Tewalt, the department has spearheaded aggressive control measures to combat the invasion. The ISDA’s approach encompasses several key strategies:
- Watercraft Inspection: Rigorous checks on boats entering Idaho, especially from out-of-state
- Public Education: Informing residents and visitors about the risks and prevention methods
- Chemical Treatment: Utilization of EPA-approved pesticides in affected areas
- Monitoring and Research: Ongoing surveillance of waterways and study of mussel behavior
The department’s efforts are underpinned by the Idaho Invasive Species Act of 2008, which provides the legal framework for these initiatives. This proactive stance reflects Idaho’s commitment to preserving its natural heritage and agricultural productivity.
The Columbia River Basin: A Ecosystem at Stake
The Snake River, where quagga mussels were first detected in Idaho, is a critical component of the larger Columbia River Basin. This vast watershed spans seven U.S. states and parts of British Columbia, Canada, making it a region of immense ecological and economic importance.
- Area: Approximately 258,000 square miles
- Major Rivers: Columbia, Snake, Willamette
- Economic Value: Billions in annual revenue from agriculture, hydropower, and tourism
The potential spread of quagga mussels throughout this system could have devastating consequences, affecting not only Idaho but the entire Pacific Northwest. It’s a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of our waterways and the need for coordinated conservation efforts.
Impact on Agriculture and Water Resources
Idaho’s agricultural sector, a cornerstone of the state’s economy, stands to lose significantly if quagga mussels gain a foothold. These invasive species can clog irrigation systems, affect water quality, and disrupt the delicate balance of aquatic ecosystems that support farming communities.
- Irrigation Systems: Mussels can block pipes and reduce water flow
- Water Quality: Increased algae blooms due to mussel filtering
- Crop Yields: Potential reductions due to compromised water delivery
Moreover, the impact extends beyond agriculture. Hydroelectric facilities, crucial for Idaho’s power generation, face the risk of reduced efficiency and increased maintenance costs if infested by quagga mussels.
The Zero-Tolerance Policy and Its Challenges
Idaho’s approach to quagga mussel management is characterized by a zero-tolerance policy. This stringent stance acknowledges the severe threat posed by even a small number of mussels, given their rapid reproduction rates. However, implementing this policy comes with its own set of challenges:
- Resource Intensity: Constant vigilance requires significant manpower and funding
- Public Cooperation: Success depends on widespread compliance with inspection protocols
- Ecological Balance: Aggressive treatments can have unintended consequences on native species
The use of copper-based pesticides like Natrix in 2023, while effective against mussels, resulted in unfortunate fish mortality, including some prized white sturgeon. This incident underscores the delicate balance between eradication efforts and ecosystem preservation.
Regional Partnerships and Collaborative Efforts
Recognizing that invasive species don’t respect state boundaries, Idaho has forged strong partnerships with neighboring states and various stakeholders. These collaborations are crucial for developing comprehensive strategies to protect the Columbia River Basin.
- Interstate Agreements: Coordinated inspection protocols with Washington, Oregon, and Montana
- Federal Cooperation: Working with agencies like the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
- Research Initiatives: Partnerships with universities and scientific institutions
By pooling resources and sharing information, these partnerships enhance the effectiveness of invasive species management across the region.
“The discovery of quagga mussels in Idaho’s waterways in 2023 prompted aggressive control measures using EPA-approved pesticides.”
Technological Innovations in Invasive Species Management
As we face the challenge of quagga mussel invasion, technological advancements play a crucial role in enhancing our detection and management capabilities. At Farmonaut, we recognize the importance of leveraging cutting-edge technology in environmental monitoring and agricultural management.
While our primary focus is on crop health and agricultural productivity, the principles of satellite-based monitoring and data analysis that we employ can be adapted to support invasive species management efforts. Here’s how technology is revolutionizing the fight against quagga mussels:
- Satellite Imagery: High-resolution images can help detect changes in water bodies that might indicate mussel infestation
- AI and Machine Learning: Advanced algorithms can process vast amounts of data to identify potential hotspots
- Remote Sensing: Drones and other remote sensing tools can access hard-to-reach areas for inspection
- Mobile Apps: Citizen science initiatives allow the public to report sightings and contribute to monitoring efforts
While Farmonaut’s technology is specifically designed for agricultural applications, the principles of remote sensing and data analysis that we use could potentially be adapted to support environmental monitoring efforts in the future.
Economic Implications of Invasive Species Control
The battle against quagga mussels comes with a significant price tag. Idaho’s allocation of $6.6 million for invasive species management in fiscal year 2025 underscores the economic commitment required to protect the state’s waterways. However, this investment must be weighed against the potential costs of inaction:
- Infrastructure Damage: Repairs and maintenance of water systems
- Agricultural Losses: Reduced crop yields and increased irrigation costs
- Tourism Impact: Potential decline in water-based recreational activities
- Energy Production: Decreased efficiency of hydroelectric facilities
By investing in prevention and control measures now, Idaho aims to avoid the much higher long-term costs associated with widespread mussel infestation.
Public Awareness and Education Initiatives
A critical component of Idaho’s strategy against quagga mussels is public education. The ISDA has launched comprehensive awareness campaigns to inform residents and visitors about the threats posed by invasive species and the role everyone can play in prevention.
- Signage: Informative displays at boat launches and water access points
- Educational Programs: School outreach and community workshops
- Media Campaigns: TV, radio, and social media outreach
- Volunteer Programs: Engaging citizens in monitoring and reporting efforts
These initiatives aim to create a culture of vigilance and responsibility among all who enjoy Idaho’s waterways.
Legislative Support and Policy Development
The Idaho State Legislature has played a crucial role in supporting invasive species management efforts. The Idaho Invasive Species Act of 2008 laid the groundwork for current initiatives, and ongoing legislative support ensures that these programs receive necessary funding and legal backing.
- Annual Budget Allocations: Consistent funding for prevention and control programs
- Policy Reviews: Regular assessments of existing laws and regulations
- Interstate Cooperation: Legislation supporting regional partnerships
- Research Funding: Allocations for scientific studies on invasive species
This legislative commitment reflects the state’s recognition of invasive species management as a long-term priority.
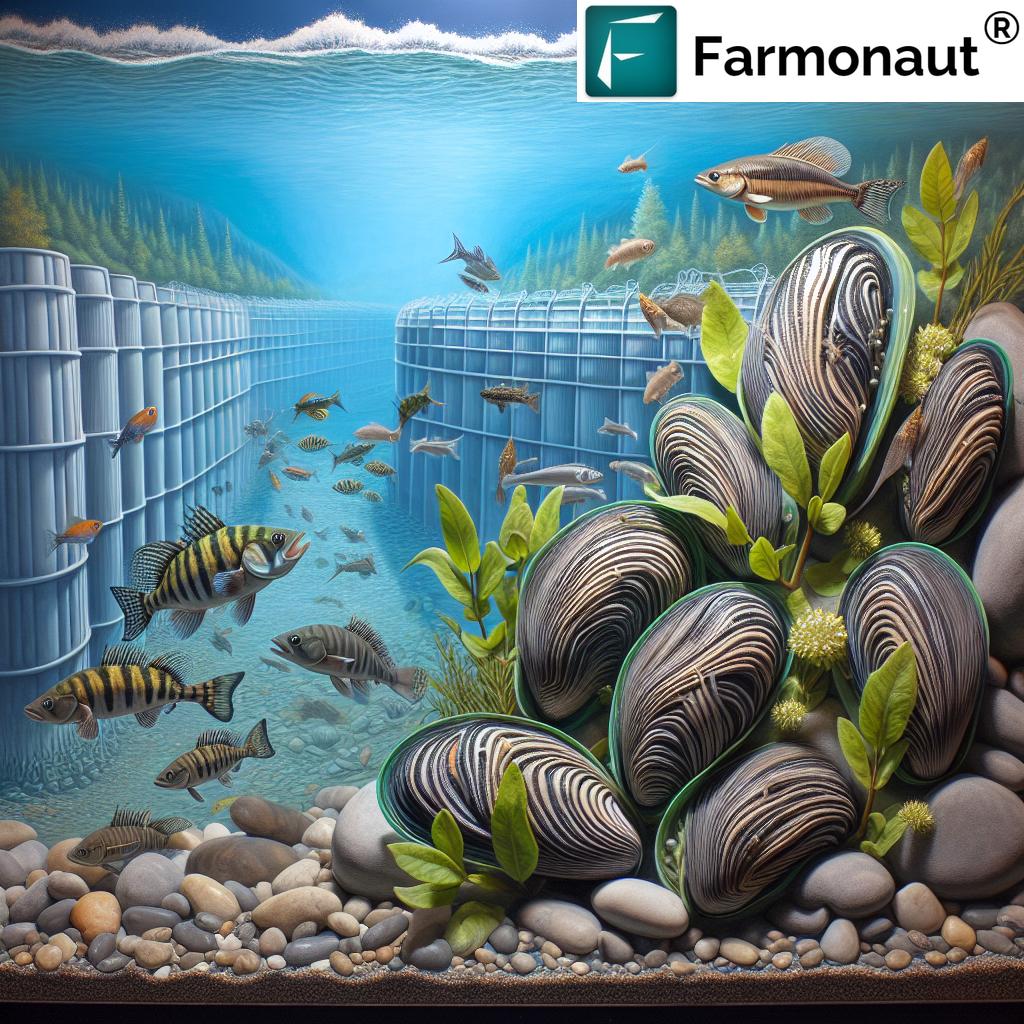

The Role of Technology in Environmental Monitoring
At Farmonaut, we understand the importance of leveraging technology for environmental monitoring and resource management. While our focus is on agricultural applications, the principles of satellite-based monitoring and data analysis that we employ can provide valuable insights for various environmental challenges, including invasive species management.
Our satellite-based crop health monitoring system demonstrates how remote sensing technology can be used to track changes in vegetation and land use over time. Similar approaches could potentially be adapted to monitor water bodies for signs of mussel infestation or changes in aquatic vegetation patterns that might indicate their presence.
Explore Farmonaut’s API for satellite data integration
Furthermore, our AI-driven advisory systems show how machine learning can process complex environmental data to provide actionable insights. While our Jeevn AI focuses on crop management, similar AI applications could be developed to analyze water quality data, predict potential infestation hotspots, or optimize treatment strategies for invasive species control.
Learn more about our API Developer Docs
Balancing Conservation and Economic Interests
Idaho’s approach to quagga mussel management exemplifies the delicate balance between environmental conservation and economic interests. The state must weigh the costs of aggressive control measures against the potential long-term economic and ecological impacts of mussel infestation.
- Short-term Costs: Inspection programs, treatment efforts, and public education
- Long-term Benefits: Preserved ecosystems, protected infrastructure, and sustained agricultural productivity
- Economic Considerations: Balancing tourism, agriculture, and conservation needs
- Ecological Priorities: Preserving native species and habitats while combating invasives
This holistic approach ensures that Idaho’s natural resources are protected for future generations while supporting current economic activities.
Future Challenges and Opportunities
As Idaho continues its battle against quagga mussels, several challenges and opportunities lie ahead:
- Climate Change: Shifting water temperatures may affect mussel distribution
- Technological Advancements: Emerging tools for detection and treatment
- Public Engagement: Increasing citizen participation in conservation efforts
- Regional Cooperation: Strengthening partnerships across the Columbia River Basin
By staying adaptable and leveraging new technologies and strategies, Idaho can enhance its resilience against invasive species threats.
Conclusion: A United Front Against Invasive Species
Idaho’s battle against quagga mussels is more than just a localized environmental issue; it’s a testament to the state’s commitment to preserving its natural heritage and agricultural prosperity. Through a combination of stringent policies, public education, technological innovation, and regional cooperation, Idaho is setting a standard for invasive species management that resonates far beyond its borders.
As we at Farmonaut continue to innovate in the field of agricultural technology, we recognize the interconnectedness of environmental challenges. While our focus remains on empowering farmers with satellite-based insights, we applaud and support efforts to protect vital ecosystems like the Columbia River Basin.
The ongoing vigilance against quagga mussels serves as a reminder of the delicate balance between human activity and natural systems. It underscores the importance of proactive measures, sustained investment, and collaborative efforts in safeguarding our environment for future generations.
Quagga Mussel Impact and Control Measures in Idaho
| Aspect | Pre-Invasion | Post-Invasion | Control Measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ecosystem Health | Balanced aquatic ecosystem | Disrupted food chains, altered water clarity | Chemical treatments, habitat restoration |
| Agricultural Impact | Unimpeded irrigation systems | Clogged pipes, increased maintenance costs | Regular cleaning, filtration systems |
| Water Infrastructure | Normal operational costs | Increased maintenance, reduced efficiency | Anti-fouling coatings, frequent inspections |
| Economic Cost | Minimal invasive species management costs | Millions in control and damage mitigation | $6.6 million budget allocation, prevention programs |
FAQ Section
Q: What are quagga mussels and why are they a problem in Idaho?
A: Quagga mussels are invasive freshwater mollusks native to Eastern Europe. They’re problematic in Idaho because they can rapidly reproduce, clog water infrastructure, disrupt ecosystems, and harm native species.
Q: How did quagga mussels enter Idaho’s waterways?
A: Quagga mussels likely entered Idaho’s waterways through contaminated boats or equipment from infested areas. They can attach to surfaces and survive out of water for extended periods.
Q: What measures is Idaho taking to control quagga mussels?
A: Idaho is implementing strict watercraft inspections, using EPA-approved pesticides in affected areas, conducting ongoing monitoring, and running public education campaigns to prevent further spread.
Q: How can the public help prevent the spread of quagga mussels?
A: The public can help by cleaning, draining, and drying all watercraft and equipment after use, reporting suspected mussel sightings, and complying with inspection stations when entering Idaho.
Q: What is the economic impact of quagga mussels in Idaho?
A: The economic impact includes costs for control measures, potential damage to water infrastructure, and effects on agriculture and tourism. Idaho has allocated $6.6 million for fiscal year 2025 to combat invasive species.
Earn With Farmonaut
Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!
Learn More About Our Affiliate Program
Farmonaut Subscriptions