Oregon City Council Tackles Biosolids Disposal: Balancing Agriculture and Environmental Safety
“Oregon City Council’s biosolids plan shifts from 100% landfill disposal to agricultural use as fertilizer on local farms.”
In the picturesque city of Enterprise, Oregon, a significant shift in waste management practices has sparked a heated debate among local officials, farmers, and residents. The Enterprise City Council’s recent decision to transition from landfill disposal to agricultural use of biosolids has brought to light the complex interplay between environmental stewardship, public safety, and sustainable farming practices. As we delve into this multifaceted issue, we’ll explore the challenges faced by the city council, the concerns of local residents, and the potential benefits and risks associated with biosolids disposal methods.
Understanding Biosolids: From Waste to Resource
Before we dive into the specifics of Enterprise’s situation, it’s crucial to understand what biosolids are and why they’ve become a topic of such importance in waste management circles.
Biosolids are nutrient-rich organic materials resulting from the treatment of domestic sewage in a wastewater treatment facility. Essentially, they are the solid byproducts of the municipal wastewater treatment process. While the term might sound clinical, biosolids are, in essence, a resource that can be recycled and applied as fertilizer to improve and maintain productive soils and stimulate plant growth.

The use of biosolids in agriculture is not a new concept. For decades, farmers around the world have recognized the value of these materials in enhancing soil fertility and crop yields. However, the practice is not without controversy, as concerns about potential contaminants and long-term environmental impacts persist.
Enterprise’s Biosolids Dilemma: A Case Study in Municipal Waste Management
The city of Enterprise, like many municipalities across the United States, has been grappling with the challenge of biosolids disposal. For years, the city had been drying biosolids from its sewage treatment plant and transporting them to the county’s Ant Flat Landfill. However, this practice was no longer sustainable as the landfill informed the city that it was running out of space.
Faced with this predicament, the Enterprise City Council had to explore alternative disposal methods. After careful consideration, they proposed a solution that would transform waste into a valuable agricultural resource: applying biosolids to local farmland as fertilizer.
The Cornerstone Farms Agreement
In late 2024, the city reached an agreement with Cornerstone Farms Joint Venture, one of the largest agricultural operations in Wallowa County. Under this arrangement, the city would pay Cornerstone $2,250 to accept biosolids for the first half of 2025, with the cost increasing to $4,500 per fiscal year thereafter.
This agreement marked a significant shift in the city’s waste management strategy. Dave Wilkie, the wastewater plant operator, noted that while this expense was new to the city, it represented a more sustainable long-term solution compared to landfill disposal.
Public Concerns and Environmental Safety
The council’s decision, however, was met with apprehension from some local residents. At a recent city council meeting, members of the Hanna family voiced their concerns about potential groundwater contamination. Their property, located downhill from Cornerstone Farms on Highway 82 between Enterprise and Joseph, could potentially be affected by runoff from fields treated with biosolids.
Kathleen Hanna and her daughter Jeanette expressed worries about monitoring contaminants and the potential impact on their property. These concerns highlight the critical need for robust environmental safeguards and transparent communication between local authorities and residents.
Regulatory Framework: The Role of the Oregon Department of Environmental Quality (DEQ)
Central to the discussion of biosolids management is the regulatory framework that governs their use. In Oregon, the Department of Environmental Quality (DEQ) plays a crucial role in overseeing the application of biosolids to agricultural land.
“DEQ regulations require extensive soil testing, with over 20 parameters monitored for biosolids application safety.”
The DEQ’s involvement ensures that strict guidelines are followed to protect public health and the environment. Some key aspects of their regulatory oversight include:
- Soil Testing Requirements: The DEQ mandates comprehensive soil testing to monitor various parameters that could affect environmental and human health.
- Public Notification: There are specific requirements for informing the public about biosolids application plans, allowing for community feedback and concerns to be addressed.
- Permit Process: Municipalities and farms must obtain proper permits before implementing biosolids application programs.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Regular testing and reporting are required to ensure continued compliance with environmental standards.
Lucas Stangel, representing Anderson Perry Engineers, the city’s engineering firm, emphasized the importance of these DEQ requirements during the council meeting. He explained the necessity of soil testing and public notification procedures, underlining the city’s commitment to regulatory compliance.
The Science Behind Biosolids: Benefits and Potential Risks
To fully understand the implications of using biosolids as agricultural fertilizer, it’s essential to examine both the potential benefits and risks associated with this practice.
Benefits of Biosolids Application
- Nutrient-Rich Fertilizer: Biosolids contain essential plant nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus, which can enhance soil fertility and crop yields.
- Organic Matter Addition: They improve soil structure, water retention, and overall soil health by adding organic matter.
- Reduced Synthetic Fertilizer Use: By utilizing biosolids, farmers can decrease their reliance on synthetic fertilizers, potentially reducing costs and environmental impacts.
- Waste Reduction: Applying biosolids to farmland diverts waste from landfills, extending their lifespan and reducing methane emissions.
Potential Risks and Concerns
- Contaminants: Biosolids may contain trace amounts of heavy metals, pharmaceuticals, and other chemicals that could accumulate in soil over time.
- Pathogen Exposure: If not properly treated, biosolids could potentially harbor harmful pathogens.
- Groundwater Contamination: There are concerns about the potential for contaminants to leach into groundwater, especially in areas with high water tables or porous soils.
- Odor Issues: Application of biosolids can sometimes lead to unpleasant odors, which may affect nearby residents.
It’s important to note that many of these risks are mitigated through proper treatment, testing, and application procedures as mandated by regulatory bodies like the DEQ.

Biosolids Management: A Comparative Analysis
To provide a clearer picture of the options available for biosolids management, let’s examine a comparative analysis of different disposal methods:
| Disposal Method | Environmental Impact | Cost Efficiency | Regulatory Compliance | Public Perception | Soil Nutrient Benefits | Groundwater Contamination Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landfill Disposal | High | Low | Easy | Neutral | None | Medium |
| Agricultural Use as Fertilizer | Medium | High | Moderate | Mixed | High | Low-Medium |
| Incineration | High | Low | Difficult | Negative | None | Low |
| Composting | Low | Medium | Moderate | Positive | High | Low |
This comparison illustrates why many municipalities, including Enterprise, are moving towards agricultural use of biosolids. While it presents some challenges, particularly in terms of public perception and regulatory compliance, it offers significant benefits in terms of cost efficiency and soil nutrient enrichment.
The Role of Technology in Modern Agriculture and Environmental Monitoring
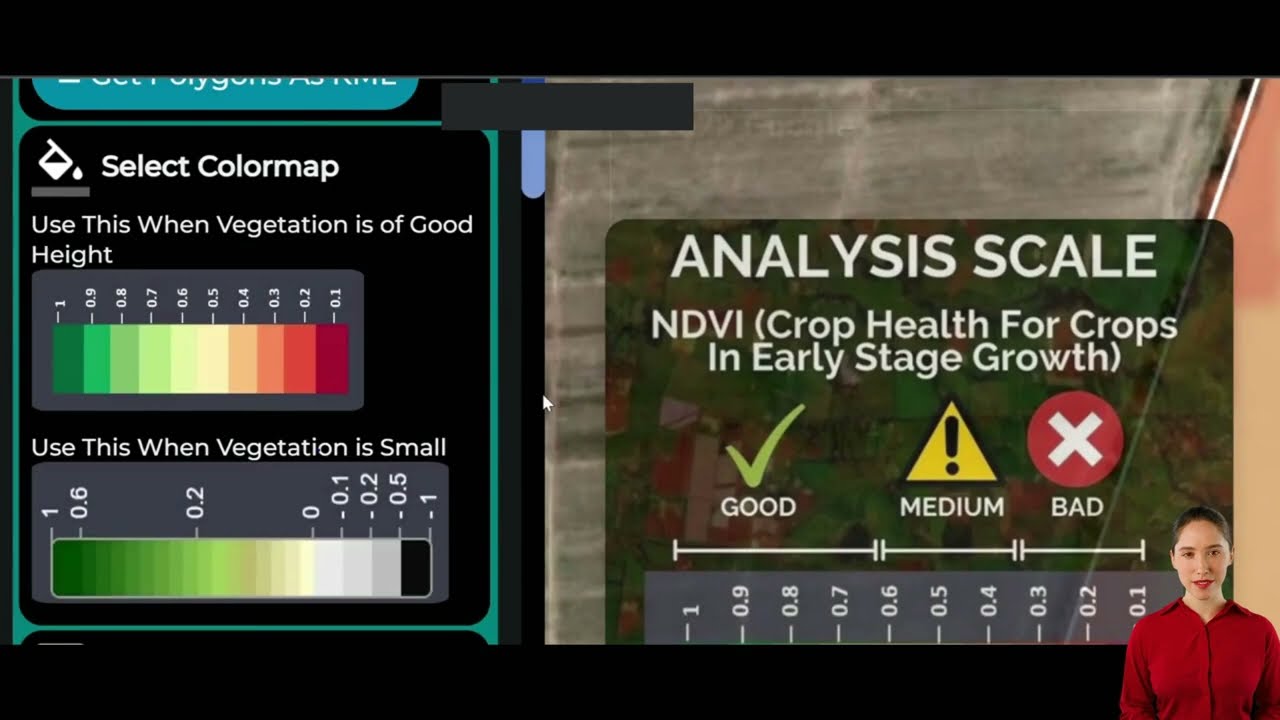
As we navigate the complexities of biosolids management and sustainable agriculture, it’s important to recognize the role that advanced technologies play in monitoring and optimizing these practices. One such technology that has gained prominence in recent years is satellite-based farm management and monitoring systems.
Farmonaut, a pioneering agricultural technology company, offers advanced satellite-based farm management solutions that could be particularly relevant in situations like Enterprise’s biosolids management plan. While not directly involved in the city’s decision-making process, technologies like those offered by Farmonaut demonstrate the potential for data-driven approaches in modern agriculture and environmental monitoring.
Through satellite imagery and AI-driven analytics, farmers and environmental agencies can monitor crop health, soil moisture levels, and other critical metrics. This type of technology could potentially be adapted to track the effects of biosolids application on soil and crop health over time, providing valuable data for both farmers and regulatory bodies.
Potential Applications in Biosolids Management
- Crop Health Monitoring: Satellite imagery could be used to track the impact of biosolids on crop growth and health.
- Soil Moisture Analysis: Advanced sensors and satellite data could help monitor soil moisture levels, ensuring optimal application of biosolids and minimizing runoff risks.
- Environmental Impact Assessment: By analyzing vegetation patterns and soil characteristics over time, technology could help assess the long-term environmental impacts of biosolids application.
While these technologies are not currently part of Enterprise’s biosolids management plan, they represent the kind of innovative approaches that could shape the future of sustainable agriculture and waste management.
Community Engagement and Public Safety
The Enterprise City Council’s approach to biosolids management underscores the importance of community engagement in local government decision-making. The council’s willingness to hear and address public concerns demonstrates a commitment to transparency and collaborative problem-solving.
Addressing Public Concerns
In response to the concerns raised by the Hanna family and other residents, the city has taken several steps to ensure public safety and address community apprehensions:
- Public Comment Period: The DEQ has opened a public comment period until March 13, allowing residents to voice their concerns and provide input on the biosolids management plan.
- Access to Information: City Administrator Lacey McQuead urged residents to review the city’s Biosolids Management Plan, which is available through the DEQ website, promoting transparency and informed discussion.
- Ongoing Dialogue: Council President Jeffery Yanke recommended direct communication between concerned residents and Cornerstone Farms, fostering open dialogue between all stakeholders.
Broader Community Issues
The city council meeting also touched on other important community issues, highlighting the multifaceted nature of local governance:
- Dog Control: Leita Barlow presented a petition signed by 138 residents concerned about aggressive dogs, urging the council to consider implementing a public safety officer for dog control.
- Downtown Improvement Grants: The council approved up to $10,000 in Downtown Improvement Grants to help beautify the city’s downtown area, demonstrating a commitment to urban development and community aesthetics.
These discussions underscore the diverse range of issues that local governments must navigate, balancing environmental responsibilities with public safety and urban development concerns.
The Future of Biosolids Management in Enterprise
As Enterprise moves forward with its biosolids management plan, several key factors will shape the success and sustainability of this initiative:
- Ongoing Monitoring: Regular testing and reporting will be crucial to ensure compliance with DEQ regulations and to address any emerging environmental concerns.
- Public Education: Continued efforts to educate the public about the benefits and safeguards associated with biosolids use will be essential in building community trust and support.
- Adaptive Management: The city should remain open to adjusting its approach based on new scientific findings, technological advancements, and community feedback.
- Collaboration: Partnerships between the city, local farmers, environmental agencies, and technology providers could lead to more innovative and effective biosolids management strategies.
The transition from landfill disposal to agricultural use of biosolids represents a significant shift in waste management practices for Enterprise. While challenges remain, this approach has the potential to turn a waste product into a valuable resource, supporting local agriculture while addressing pressing waste management needs.
Conclusion: Balancing Progress and Precaution
The Enterprise City Council’s decision to implement a new biosolids management plan highlights the complex challenges faced by local governments in balancing environmental stewardship, economic considerations, and public safety. As municipalities across Oregon and the United States grapple with similar waste management issues, the Enterprise case study offers valuable insights into the importance of community engagement, regulatory compliance, and adaptive management strategies.
By embracing innovative solutions while remaining responsive to public concerns, Enterprise is charting a course towards more sustainable waste management practices. The ongoing dialogue between city officials, residents, farmers, and regulatory bodies will be crucial in refining and improving these practices over time.
As we look to the future, it’s clear that the intersection of waste management, agriculture, and environmental protection will continue to be a critical area of focus for communities large and small. By leveraging scientific research, advanced technologies, and collaborative approaches, we can work towards solutions that benefit both our communities and our environment.
FAQ: Biosolids Management in Enterprise, Oregon
Q: What are biosolids?
A: Biosolids are nutrient-rich organic materials resulting from the treatment of domestic sewage in a wastewater treatment facility. They can be recycled and applied as fertilizer to improve and maintain productive soils and stimulate plant growth.
Q: Why is Enterprise changing its biosolids disposal method?
A: The county’s Ant Flat Landfill informed the city that it was running out of space, necessitating an alternative disposal method for biosolids from the sewage treatment plant.
Q: How will biosolids be used in agriculture?
A: Biosolids will be applied to farmland as fertilizer, providing essential nutrients to crops and improving soil health.
Q: What safeguards are in place to protect the environment?
A: The Oregon Department of Environmental Quality (DEQ) oversees the application of biosolids, requiring extensive soil testing, public notification, and ongoing monitoring to ensure environmental safety.
Q: How can residents voice their concerns about the biosolids management plan?
A: Residents can submit comments to the DEQ through their online comment portal until March 13. They can also review the city’s Biosolids Management Plan on the DEQ website and attend city council meetings to express their concerns.
Q: What are the potential benefits of using biosolids in agriculture?
A: Benefits include nutrient-rich fertilization for crops, improved soil structure, reduced reliance on synthetic fertilizers, and diversion of waste from landfills.
Q: Are there any risks associated with biosolids application?
A: Potential risks include the presence of contaminants, pathogen exposure, and groundwater contamination. However, these risks are mitigated through proper treatment, testing, and application procedures as mandated by regulatory bodies.
Q: How will the city monitor the impact of biosolids application?
A: The city will follow DEQ regulations, which include regular soil testing and monitoring of various environmental parameters to ensure safety and compliance.
Earn With Farmonaut: Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!
Learn More About Farmonaut’s Affiliate Program
As we conclude our exploration of Enterprise’s biosolids management journey, it’s clear that the path forward requires a delicate balance of scientific understanding, community engagement, and adaptive management. By embracing innovative solutions and remaining responsive to public concerns, communities like Enterprise can lead the way in sustainable waste management practices, turning challenges into opportunities for environmental stewardship and agricultural advancement.
For those interested in learning more about advanced agricultural monitoring technologies, visit Farmonaut’s API or check out their API Developer Docs. While not directly related to Enterprise’s biosolids management, these resources showcase the cutting-edge tools available for modern agricultural practices and environmental monitoring.