How to Grow a Lemon Tree Orchard: 7 Easy Steps
Meta Description: Establishing a lemon tree orchard is a rewarding endeavor, but it requires proper planning, soil preparation, and ongoing maintenance. Our lemon tree planting guide details seven easy steps for site selection, soil, irrigation, fertilization, pest management, and pruning to help your orchard thrive.
Table of Contents
- Lemon Tree Trivia
- Introduction
- Step 1: Site Selection and Soil Preparation
- Step 2: Planting Techniques
- Step 3: Lemon Tree Irrigation Techniques
- Step 4: Lemon Tree Fertilization Tips
- Step 5: Lemon Tree Pest and Disease Control
- Step 6: Maintaining Lemon Trees
- Step 7: When to Harvest Lemons
- Lemon Orchard Establishment and Care Timeline
- Advanced Orchard Management with Farmonaut
- FAQ: How to Grow Lemon Trees and Orchard Management
- Conclusion
“A single lemon tree can yield up to 600 pounds of fruit annually with proper care and fertilization.”
Introduction: Why Plant a Lemon Orchard?
There are few agricultural ventures as refreshing, aromatic, and profitable as establishing a thriving lemon tree orchard. Whether you are envisioning a commercial orchard or a sustainable family-run grove, following a comprehensive lemon tree planting guide sets the groundwork for healthy growth, productive trees, and a bounty of fruit for years to come.
This guide covers every essential step, including soil selection and preparation, precise planting techniques, irrigation strategies, targeted fertilization tips, robust pest and disease management, diligent maintenance, and the joy of harvesting lemons at their peak.
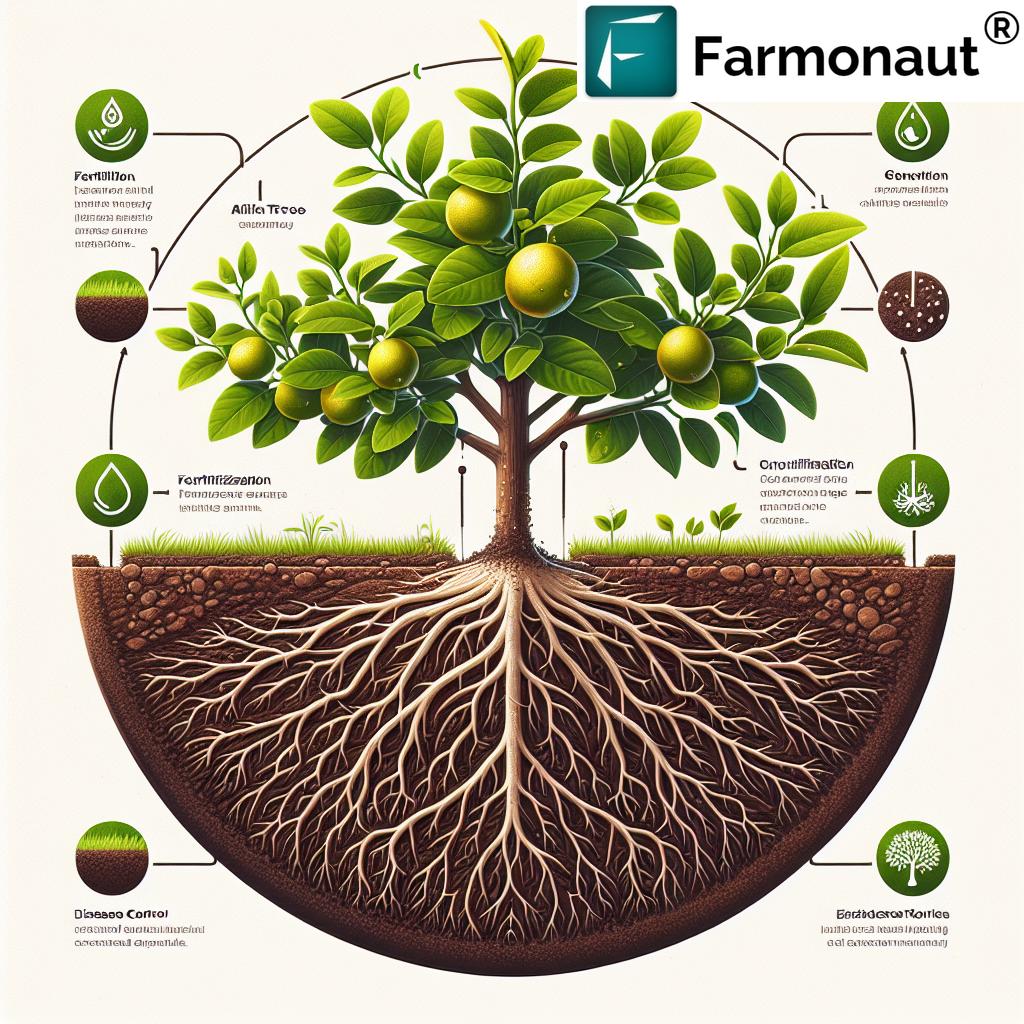
Lemons belong to the citrus family, thriving best in warm, sunny regions with well-drained soils. A successful orchard requires more than simply placing a few trees in the ground—careful planning and consistent care are needed to ensure healthy growth across every tree. Together, we will explore the science and art of cultivating a lemon orchard—the right way—and unlock practical techniques to help your orchard thrive, season after season.
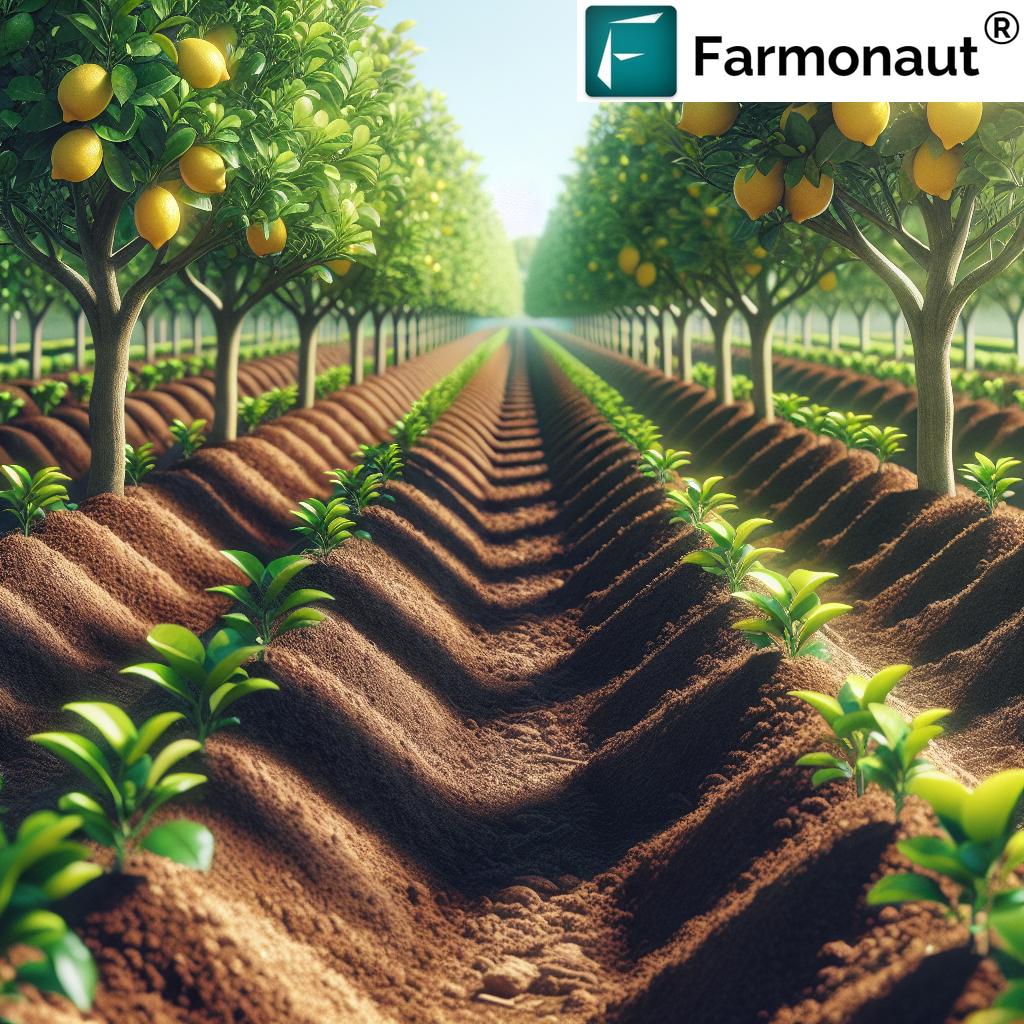
Step 1: Site Selection and Soil Preparation (Lemon Tree Planting Guide)
Choose the Right Location & Best Soil for Lemon Trees
The foundation of every thriving lemon orchard begins with site selection and precise soil preparation. Lemon trees flourish in regions characterized by warm, frost-free climates, abundant sunlight, and protection from harsh winds. Full sun exposure each day (at least 8-10 hours) ensures strong growth and optimal fruit development.
Strong site selection also means considering air circulation. Avoid low-lying areas prone to cold air pooling or frost pockets – elevated ground encourages air flow and helps prevent disease build-up.
Assess and Prepare Your Soil for Lemon Trees
-
Soil Type:
The best soil for lemon trees is a well-draining, sandy loam enriched with organic matter. Sandy loam textures encourage robust root development and resist waterlogging, which can cause diseases such as root rot. -
Soil Drainage:
To test drainage, dig a hole about 30 cm (12 inches) deep, fill with water, and observe the drainage time. Water should soak away within 24 hours. Slow drainage signals clay-heavy soils or compaction—address this by incorporating sand, compost, or organic amendments.
-
Soil pH:
Ideal soil pH for lemon orchards ranges from 5.5 to 7.5, with 5.5–6.5 often cited as best for nutrient uptake and vigorous tree growth. -
Soil Testing and Correction:
Start by performing a laboratory soil analysis to identify current nutrient levels and the pH of your chosen site. For acidic soils (pH below 5.5), apply lime at rates recommended in your analysis to raise the pH. For alkaline conditions (pH above 7.5), apply sulfur to reduce pH. Re-test after 2-3 months for accuracy.
-
Incorporate Organic Matter:
Enrich the structure and fertility of your soil prior to planting by incorporating compost or well-rotted manure (2–4 kg/m2). This increases soil permeability, improves nutrient and water retention, and supports healthy root growth. -
Clear Competing Vegetation:
Remove all existing weeds, grasses, rocks, or debris. This minimizes competition for resources and creates a clean space for tree establishment.
Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop monitoring tools can assist in soil monitoring by providing real-time data on moisture levels, which is crucial for planning the ideal planting schedule and irrigation setup for your orchard. Learn more about large scale farm management with advanced digital mapping and satellite analytics.
Soil Preparation Checklist (Prior to Planting)
- Remove topsoil/vegetation (about 15-20 cm deep) to eliminate weed competition and pests.
- Plough and harrow the area for uniformity and aeration.
- Incorporate organic matter (e.g., compost) thoroughly for structure and fertility.
- Level the surface and mark the planting grid (see next section).
Step 2: Planting Techniques for Lemon Tree Orchards
Planting is more than just digging a hole. Proper planting techniques influence early root establishment, tree growth, and fruit yield in subsequent years. Here’s how to master this crucial step of your lemon tree planting guide:
Selecting Quality Lemon Tree Seedlings
- Buy only certified, disease-free seedlings from trusted nurseries. Inspect each tree for healthy leaves, firm roots, and absence of visible pests or diseases.
- Popular lemon varieties for robust commercial and home orchards include Eureka, Lisbon, and Primofiori – select varieties suitable for your region and climate.
When to Plant Lemon Trees
- Spring and early autumn are best for planting, when the weather is mild and moisture is adequate for strong root growth.
Spacing, Hole Preparation, and Planting Depth
- Space lemon trees 4.5–6 meters (15–20 feet) apart. This ensures ample sunlight penetration and air circulation, reducing disease risk.
- Dig holes twice the width and equal to the depth of the root ball (typically 60 cm wide x 60 cm deep).
- Place seedlings gently, ensuring the root collar (where roots meet trunk) is flush with the soil’s surface.
Backfilling and Watering
- Refill the hole with a 1:1 mix of native soil and organic matter (e.g., compost or aged manure).
- Press soil around the roots firmly (but gently) to eliminate air pockets.
- Water deeply and thoroughly immediately after planting to help settle soil and support deep root anchorage.
Example Planting Layout for 1 Hectare Orchard
To maximize space and reduce pest transmission, plant 350–500 lemon trees per hectare, spaced in a grid. For smaller plots or home gardens, adjust to local dimensions and sunlight constraints.
“Optimal soil pH for lemon trees is 5.5–6.5, crucial for nutrient absorption and healthy orchard growth.”
Step 3: Lemon Tree Irrigation Techniques—Managing Moisture for Optimal Growth
Consistent moisture is the cornerstone for healthy growth and prolific fruit set. Lemon trees are especially sensitive during early years and major growth phases.
How Often Should You Water Lemon Trees?
-
Water deeply but not too frequently.
Frequent shallow watering promotes weak surface roots vulnerable to drought. - During spring and summer (growth period), maintain soil in a consistently moist but not waterlogged state. Allow surface to dry slightly between deep waterings.
- In hot or dry weather, trees may need irrigation every 5–7 days for mature trees, or every 2–3 days for young/newly planted seedlings.
- Adjust watering intervals based on rainfall, soil type, and drainage. Sandy soils need more frequent watering; loamy/lighter soils require less.
Best Lemon Tree Irrigation Techniques
- Drip irrigation systems deliver water slowly and directly to the root zone, minimizing waste, weed growth, and disease risk.
- Basin irrigation is suitable for small- to medium-scale orchards. Form a shallow basin around each tree (60–100 cm wide) to concentrate water near the roots.
- Avoid overhead sprinklers where possible: they increase leaf wetness, predisposing trees to fungal disease.
- Mulch (with straw, wood chips, or compost) around trunks to reduce evaporation and regulate soil temperature.
By using Farmonaut’s soil moisture monitoring features, orchardists can automate and optimize their irrigation regimes—responding directly to measured moisture levels and reducing water waste. Farmonaut also provides weather forecasts to further refine irrigation planning. Discover more about carbon footprinting and water resource management for sustainable citrus farming!
Step 4: Lemon Tree Fertilization Tips for Vigorous Orchards
Effective fertilization provides the nutrients lemon trees require for strong growth, abundant fruit set, and stress resistance. Balanced, timely inputs optimize tree health and prevent problems due to deficiencies or excesses.
Nutrient Requirements by Life Stage
-
Young Trees (0-2 years):
Limited fertilizer required—focus on small, frequent applications to support root establishment. -
Mature Trees (fruit bearing):
Require increased Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K) for shoot, flower, and fruit development.
How to Apply Fertilizer for Lemon Trees
- Apply granular NPK fertilizer around the root zone, not directly against the trunk, using doses recommended by soil analysis and tree age.
- Typical schedule: Early spring (just before bud break) and late spring/early summer. Split doses may be used for sandy soils.
- Avoid over-fertilization—excess Nitrogen produces excessive shoot growth at the expense of flowers and fruit formation.
- Micronutrient supplements: Apply zinc, iron, and magnesium chelates as needed (deficiencies often appear as yellowing leaves or stunted growth).
- Use organic matter (e.g., compost or vermicompost) annually to promote soil structure and microbial activity.
Looking for tips on efficiency and digital record keeping? Farmonaut’s digital farm management tools allow growers to track fertilizer use precisely via mobile or web, ensuring both cost-effectiveness and sustainability.
Step 5: Lemon Tree Pest and Disease Control—Management Strategies for Healthy Orchards
Pest and disease management is essential to protect your investment and maximize fruit output. Lemons are susceptible to several insects and pathogens, but integrated management strategies safeguard trees and encourage healthy growth.
Common Pests Affecting Lemon Orchards
- Scale Insects: Small, hard-shelled sap-suckers that weaken trees.
- Citrus Mealybugs: White, cotton-like pests damaging shoots and fruit.
- Aphids, Leaf Miners, and Mites: Cause distorted leaves, yellowing, and reduce photosynthetic efficiency.
Major Lemon Tree Diseases
- Root Rot (Phytophthora): Waterlogged soil and poor drainage increase incidence. Prevent with good site preparation and irrigation practices.
- Greasy Spot and Citrus Canker: Fungal/bacterial infections; remove and destroy infected material promptly.
- Fungal Leaf Spots and Sooty Mold: Linked to pest honeydew; manage pests to control secondary diseases.
Integrated Lemon Orchard Management Practices
- Monitor regularly: Inspect for pests/diseases every 1–2 weeks during growth and fruit development.
- Promote orchard hygiene: Remove fallen leaves and fruit, prune diseased branches, and destroy infested debris.
- Encourage beneficial insects: Ladybugs, lacewings, and spiders feed on pests and assist in natural management.
- Sensible pesticide use: If organic and biological controls are insufficient, spot-spray approved insecticides or fungicides, following label directions and safety measures.
Thinking about traceability in your commercial orchard? Farmonaut’s blockchain-based traceability technology (learn more here) enables secure and transparent product tracking from farm to market—giving your customers trust in the authenticity and health of your harvest, and supporting pest and disease management documentation!
Step 6: Maintaining Lemon Trees—Ongoing Maintenance Routines
Routine maintenance is central to a healthy, productive orchard: it minimizes diseases, boosts growth, and ensures trees produce fruit for years to come.
Annual Lemon Tree Pruning Practices
- Prune annually in early spring before new shoot growth begins.
- Remove dead, diseased, or crossing branches to improve air circulation and sunlight penetration in canopies.
- Thin dense areas to shape the tree for stability against wind or fruit load.
- Weak, spindly growth should be cut back to stimulate robust branching.
- Disinfect pruning tools between trees to prevent disease spread.
Ongoing Orchard Maintenance Checklist
- Monitor soil moisture: Use digital sensors or field checks to adjust irrigation and maintain ideal conditions.
- Mulch: Apply mulch (5–10 cm deep) at the base but keep 15 cm clear of the trunk.
- Clean heavily: Remove all fallen leaves and fruit regularly to minimize disease and pest reservoirs.
- Scout for nutrient deficiencies and apply necessary amendments promptly.
Our team at Farmonaut offers real-time, satellite-based health monitoring for lemon orchards, enabling growers to catch nutrient deficits, disease outbreaks, or irrigation stress early. Access precision orchard advisory solutions via Farmonaut’s web and mobile apps or through our robust API for tech-savvy managers. Integration with fleet & resource management further boosts productivity for large orchards.
Step 7: When to Harvest Lemons—Achieving the Perfect Crop
After several years of hard work and consistent care, your orchard will begin to produce a bountiful lemon harvest. But when to harvest lemons is as important as the growing methods themselves.
Identifying Mature, Ready-to-Pick Lemons
- Lemons are harvest-ready when they are fully yellow (or pale green-yellow, depending on variety), have a glossy surface, and yield slightly but firmly to gentle pressure.
- Fruit will usually mature 90–120 days after flowering, depending on weather and variety.
- Avoid leaving mature lemons too long on the tree; they may become pithy or susceptible to rot.
Harvesting Techniques
- Use sharp pruning shears or fruit clippers; snip lemons with a small portion of the stem attached to protect the fruit.
- Avoid pulling or twisting, which can damage both fruit and branches.
- Multiple harvests may be needed throughout the season—a healthy orchard may yield several flushes of fruit!
Harvesting regularly encourages further growth and maintains tree health for subsequent seasons.
Lemon Orchard Establishment and Care Timeline
| Step | Action/Task | Estimated Timeframe | Purpose | Key Quantitative Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Site Selection & Soil Preparation | 3-4 weeks before planting | Ensure ideal site, drainage, and pH | Soil pH: 5.5-7.5 Drainage: <24 hr/30cm |
| 2 | Planting Lemon Trees | Early spring/autumn | Establish healthy, well-spaced trees | Spacing: 4.5–6m Hole: 60x60cm |
| 3 | Irrigation Setup | Immediately post-planting, ongoing | Support deep root growth & prevent stress | Water: 20–40L/tree/week Mulch: 5–10cm |
| 4 | Fertilization | Twice per year (spring, early summer) | Promote growth, flowering, fruit set | NPK: 250–500g/tree Micros: As per deficiency |
| 5 | Pest & Disease Management | Monthly, year-round | Reduce crop loss, ensure healthy trees | Manual checks: every 1–2 weeks |
| 6 | Pruning & General Maintenance | Annual (early spring), ongoing | Shape canopy, improve air and sunlight flow | Prune: Remove 10–20% of canopy as needed |
| 7 | Harvesting | 3–5 years after planting, then ongoing | Gather mature, high-quality fruit | Yield: Up to 600 lbs/tree annually |
Advanced Lemon Orchard Management with Farmonaut
Modern orchardists can achieve superior outcomes by integrating digital management systems, automation, and satellite-derived insights. At Farmonaut, our precision agriculture platform helps lemon growers improve soil and moisture awareness, schedule timely interventions, and enhance fruit quality, all from a simple dashboard.
- Satellite-Based Monitoring: View NDVI, soil moisture, and pest risk maps for advance warning and targeted action.
- Fleet & Resource Management: Optimize machinery use, fuel costs, and logistics for large lemon orchards with our fleet management solutions.
- Crop Health Notifications: Get AI-powered alerts and recommendations for disease and deficiency detection via our app—and take immediate, informed action!
- Traceability: Assure buyers and regulators about your fruit’s origin with blockchain traceability.
- API & Developer Integrations: For advanced users, our API and developer documentation enable seamless integration into custom apps or reporting systems.
- Subscription Flexibility: Whether you manage a family grove or commercial acreage, access custom service levels (see below).
FAQs: How to Grow Lemon Trees and Orchard Management
What is the best soil for lemon trees?
Well-draining, sandy loam soils with a pH between 5.5 and 6.5 provide the best conditions for lemon tree growth, root health, and nutrient availability.
What are the optimal planting distances for lemon orchards?
Plant lemon trees 4.5–6 meters (15–20 feet) apart. This spacing maximizes sunlight penetration and air circulation, reducing pest and disease risk.
How and when should I fertilize lemon trees?
Apply a balanced NPK fertilizer twice yearly (early spring and early summer). Adjust rates according to tree age and soil nutrient analysis recommendations.
How do I manage common lemon tree pests organically?
Regular inspection, maintaining orchard hygiene, introducing beneficial insects (like ladybugs), and using approved organic pesticides help control scale, aphids, and mealybugs.
How long does it take for a lemon tree to bear fruit?
Lemon trees usually begin bearing fruit 3 to 5 years after planting, depending on variety and management practices.
Why is pruning important for lemon trees?
Annual pruning removes diseased or dead branches, enhances air flow, and shapes the canopy, improving both health and fruit yield.
How can Farmonaut help with precision orchard management?
Farmonaut delivers satellite-based crop and soil moisture monitoring, AI advisory for timely interventions, traceability for supply chains, and robust resource management tools to make orchard management more efficient, data-driven, and sustainable.
Conclusion: Bringing It All Together for Orchard Success
Establishing a lemon tree orchard is a rewarding journey filled with scientific planning and nurturing care. By mastering these seven steps—site selection, soil preparation, planting, irrigation, fertilization, pest and disease management, pruning, and harvesting—you ensure that your lemon grove will thrive and yield high-quality fruit for countless years.
Remember that healthy soil, good drainage, targeted irrigation, balanced nutrition, and keen observation are keys to orchard longevity. Regular maintenance—as detailed in this lemon tree planting guide—keeps your trees productive and your harvests bountiful.
For growers eager to take their orchard management to the next level, Farmonaut delivers affordable, accessible, and advanced tech tools across web, Android, iOS, and via API. Whether for a family grove or a commercial operation, leverage data-driven solutions for soil health, irrigation efficiency, activity mapping, and supply chain traceability—ensuring your farming enterprise is scalable, profitable, and sustainable.
Ready to transform your orcharding with intelligence, precision, and innovation? Download the Farmonaut app today and elevate your lemon orchard to new heights!
Happy lemon growing — may your orchard flourish for generations to come!