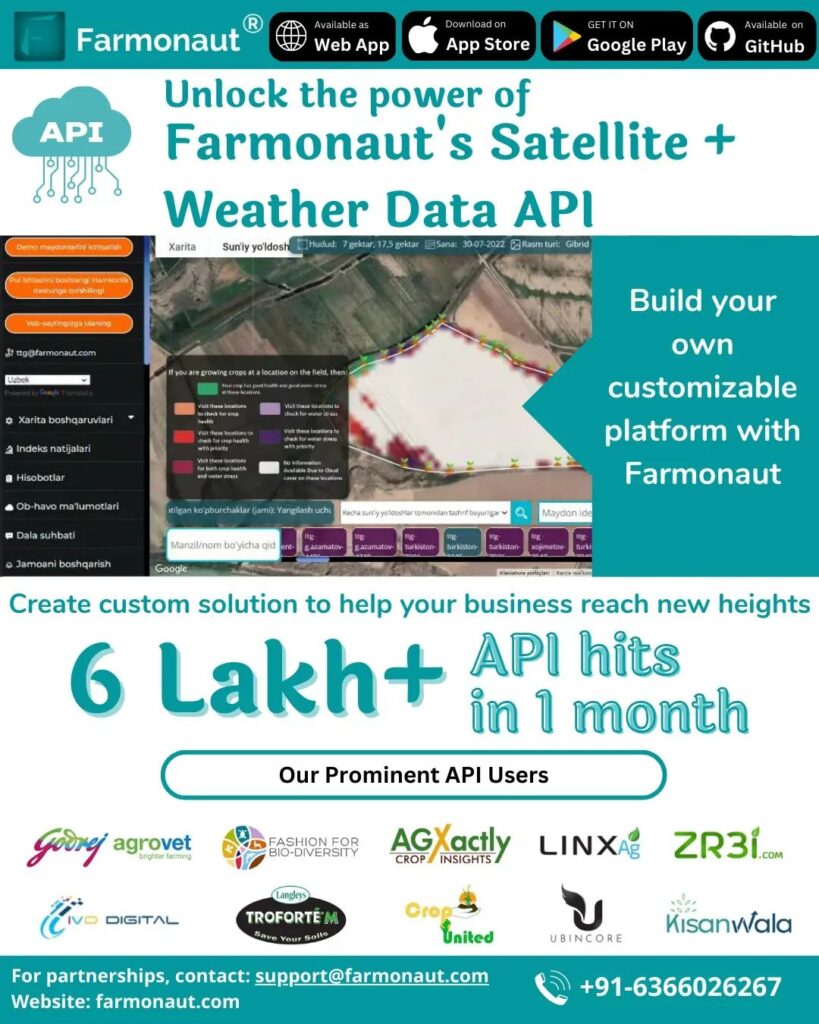
Revolutionizing Agriculture: How Historical Weather Data API Enhances Crop Yield Optimization
“Farmonaut’s API integrates over 10 weather parameters, including hourly temperature and atmospheric pressure, for precise agricultural planning.”
In the ever-evolving landscape of modern agriculture, we find ourselves at the forefront of a technological revolution that promises to transform the way we approach farming. At the heart of this revolution lies the power of data – specifically, historical weather data. As we delve into the world of precision agriculture, we’ll explore how Farmonaut’s innovative Historical Weather Data API is changing the game for farmers and agronomists alike, paving the way for unprecedented crop yield optimization.
The Power of Historical Weather Data in Agriculture
Historical weather data for agriculture has become an indispensable tool in the modern farmer’s arsenal. By harnessing the wealth of meteorological information accumulated over time, we can make more informed decisions about crop management, resource allocation, and long-term planning. Let’s break down the key components that make historical weather data so valuable:
- Temperature trends: Understanding past temperature patterns helps predict frost risks and optimal planting times.
- Rainfall patterns: Historical precipitation data aids in irrigation planning and drought preparedness.
- Atmospheric pressure: Long-term pressure data can indicate broader climate trends affecting crop growth.
- Wind speed and direction: This information is crucial for planning windbreaks and assessing pollination conditions.
By integrating these parameters into our agricultural decision-making process, we can significantly enhance crop yield optimization strategies. Farmonaut’s Historical Weather Data API brings all this information to your fingertips, allowing for seamless integration into existing farm management systems.
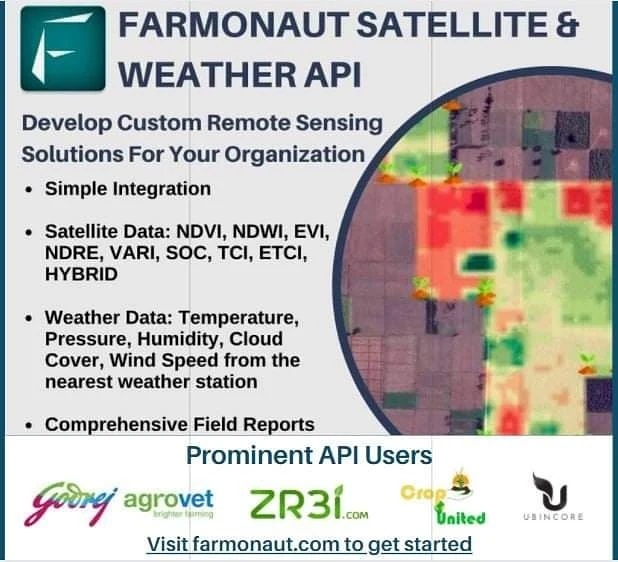
Integrating Historical Weather Data into Modern Farming Practices
The integration of historical weather data into modern farming practices marks a significant leap forward in agricultural technology. By leveraging this data, we can:
- Optimize planting schedules: Analyze past weather patterns to determine the best planting times for different crops.
- Improve irrigation efficiency: Use rainfall history to create more effective watering schedules, conserving water and reducing costs.
- Enhance pest management: Predict pest outbreaks based on historical weather conditions that favor their proliferation.
- Fine-tune fertilizer application: Adjust fertilizer use based on past weather impacts on soil nutrient levels.
Farmonaut’s API makes it easy to access and utilize this wealth of information, providing a robust foundation for data-driven farming decisions.
The Role of Satellite Imagery in Precision Agriculture
Satellite imagery in agriculture has revolutionized the way we monitor and manage crops. When combined with historical weather data, it provides an unparalleled view of farm performance over time. Here’s how satellite imagery enhances our agricultural practices:
- NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index): This indicator of plant health can be tracked over seasons, correlating with weather patterns to predict crop performance.
- Soil moisture monitoring: Satellite data can reveal soil moisture levels, which, when analyzed alongside historical rainfall data, inform irrigation strategies.
- Crop stress detection: Early identification of crop stress through satellite imagery, combined with weather history, allows for timely interventions.
Farmonaut’s platform integrates satellite imagery with historical weather data, offering a comprehensive tool for precision agriculture technology implementation.
Explore Farmonaut’s API for advanced agricultural insights
Leveraging Weather Forecasting for Crop Planning
While historical data provides a solid foundation, integrating current and forecasted weather information is crucial for proactive farm management. Farmonaut’s API offers robust weather forecasting capabilities that, when combined with historical trends, enable farmers to:
- Anticipate extreme weather events and take preventive measures
- Adjust planting and harvesting schedules based on short-term weather predictions
- Optimize resource allocation in response to forecasted conditions
By leveraging both historical and forecasted weather data, farmers can make more informed decisions, reducing risks and maximizing crop yields.

“Historical weather data analysis combined with NDVI satellite imagery can increase crop yield predictions by up to 30% in some regions.”
The Power of NDVI Data in Field Monitoring
NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) data is a powerful tool in modern agriculture. When combined with historical weather data, it provides invaluable insights into crop health and productivity. Here’s how we can leverage NDVI data for enhanced field monitoring:
- Crop health assessment: NDVI values indicate plant vigor, allowing for early detection of stress or disease.
- Yield prediction: By correlating NDVI data with historical weather patterns, we can make more accurate yield forecasts.
- Resource allocation: Identifying areas of low NDVI can help target resources more effectively, improving overall field productivity.
- Long-term trend analysis: Tracking NDVI over multiple seasons alongside weather data reveals patterns in crop performance.
Farmonaut’s API integrates NDVI data seamlessly with historical weather information, providing a comprehensive view of field conditions over time.
Customizable Parameters for Tailored Agricultural Insights
One of the key strengths of Farmonaut’s Historical Weather Data API is its flexibility. Users can customize parameters to suit their specific needs, including:
- Time period selection: Choose specific date ranges for analysis
- Geographic precision: Define exact coordinates or polygons for targeted data retrieval
- Parameter selection: Focus on specific weather variables relevant to your crops
- Data format options: Receive data in formats that integrate seamlessly with your existing systems
This level of customization ensures that farmers and agronomists can access precisely the data they need for their unique situations.
Check out our comprehensive API Developer Docs
Enhancing Decision Support Systems in Agriculture
Agricultural decision support systems are becoming increasingly sophisticated, and historical weather data plays a crucial role in their effectiveness. By incorporating Farmonaut’s API into these systems, we can:
- Improve risk assessment models by factoring in long-term weather trends
- Enhance crop simulation models with accurate historical meteorological data
- Develop more precise recommendations for crop management practices
- Create alerts and notifications based on historical weather thresholds
These enhancements lead to more robust and reliable decision support tools for farmers and agricultural professionals.
The Impact of Historical Weather Data on Sustainable Farming Practices
As we strive for more sustainable agricultural practices, historical weather data becomes an invaluable asset. Here’s how it contributes to sustainability:
- Water conservation: By understanding past rainfall patterns, we can implement more efficient irrigation strategies.
- Reduced chemical use: Accurate weather history helps optimize the timing and amount of pesticide and fertilizer applications.
- Energy efficiency: Historical data informs better planning for energy-intensive farm operations.
- Soil health preservation: Long-term weather trends guide soil management practices to prevent erosion and maintain fertility.
Farmonaut’s commitment to sustainability is reflected in the comprehensive data provided through our API, enabling farmers to make environmentally conscious decisions.
Integrating Historical Weather Data with Soil Analysis
The combination of historical weather data and soil analysis provides a powerful tool for optimizing crop production. Here’s how we can leverage this integration:
- Nutrient management: Correlate past weather patterns with soil nutrient levels to refine fertilization strategies.
- Soil moisture optimization: Use historical rainfall data to improve soil moisture management techniques.
- Erosion prevention: Identify periods of high erosion risk based on past weather events and soil types.
- Crop rotation planning: Determine optimal crop rotations based on historical weather impacts on soil health.
By combining these data sources, farmers can make more informed decisions about soil management and crop selection, leading to improved yields and soil health.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning in Weather Data Analysis
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are revolutionizing the way we analyze and utilize historical weather data in agriculture. Here’s how these technologies enhance our capabilities:
- Pattern recognition: AI algorithms can identify subtle weather patterns that might be missed by human analysis.
- Predictive modeling: ML models can forecast crop yields based on historical weather data and current conditions.
- Anomaly detection: AI can quickly identify unusual weather patterns that may impact crop health.
- Automated decision-making: ML algorithms can provide real-time recommendations based on historical and current weather data.
Farmonaut’s API is designed to integrate seamlessly with AI and ML systems, allowing for advanced analysis and insights.
Comparative Analysis: Historical Weather Data and Crop Yields
To illustrate the impact of historical weather data on crop yields, let’s examine a comparative analysis:
| Time Period | Average Temperature (°C) | Rainfall (mm) | Atmospheric Pressure (hPa) | Crop Yield (tons/hectare) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 Spring | 18.5 | 250 | 1013 | 5.2 |
| 2019 Spring | 19.2 | 220 | 1012 | 5.0 |
| 2020 Spring | 17.8 | 280 | 1014 | 5.5 |
| 2021 Spring | 18.9 | 260 | 1013 | 5.3 |
| 2022 Spring | 19.5 | 200 | 1011 | 4.8 |
This table demonstrates the correlation between historical weather patterns and crop yields. We can observe that years with moderate temperatures and adequate rainfall tend to produce higher yields, while extreme conditions can negatively impact productivity.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementing Historical Weather Data API
While the benefits of using historical weather data in agriculture are clear, there are challenges to implementation. Here are some common issues and how Farmonaut’s API addresses them:
- Data accuracy: Farmonaut ensures data quality through rigorous validation processes and multiple data sources.
- Integration complexity: Our API is designed for easy integration with existing farm management systems.
- Data volume management: We offer scalable solutions to handle large volumes of historical data efficiently.
- Interpretation of data: Farmonaut provides comprehensive documentation and support to help users interpret and apply the data effectively.
By addressing these challenges, we make it easier for farmers and agronomists to leverage the power of historical weather data in their operations.
Future Trends in Agricultural Weather Data Analysis
As we look to the future of agricultural weather data analysis, several exciting trends are emerging:
- IoT integration: Combining historical weather data with real-time sensor data from the field.
- Blockchain for data integrity: Ensuring the authenticity and traceability of historical weather records.
- Edge computing: Processing weather data closer to the source for faster, more localized insights.
- Advanced visualization tools: Developing more intuitive ways to present complex weather data to farmers.
Farmonaut is committed to staying at the forefront of these trends, continually enhancing our API to meet the evolving needs of the agricultural sector.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Data-Driven Agriculture
As we’ve explored throughout this blog post, historical weather data API integration is revolutionizing agriculture, offering unprecedented opportunities for crop yield optimization. By leveraging Farmonaut’s comprehensive agtech solutions, farmers and agronomists can make more informed decisions, implement precision agriculture techniques, and adapt to changing climate conditions.
The power of combining historical weather data with satellite imagery, soil analysis, and advanced AI algorithms opens up new horizons for sustainable and productive farming practices. As we move forward, the role of data in agriculture will only grow, and those who embrace these technologies will be best positioned to thrive in an increasingly complex and challenging agricultural landscape.
We invite you to explore Farmonaut’s Historical Weather Data API and discover how it can transform your approach to modern farming. Together, we can build a more resilient, efficient, and sustainable agricultural future.
FAQs
- Q: How far back does Farmonaut’s historical weather data go?
A: Our historical weather data typically extends back several decades, providing a comprehensive long-term view for agricultural analysis. - Q: Can the API be integrated with existing farm management software?
A: Yes, Farmonaut’s API is designed for easy integration with a wide range of farm management systems and software. - Q: How often is the historical weather data updated?
A: Our historical data is regularly updated to include the most recent weather information, ensuring you always have access to the latest data. - Q: Is the data available for all geographic locations?
A: Farmonaut offers extensive global coverage, but the availability and detail of data may vary by region. Contact us for specific location inquiries. - Q: What support is available for users of the Historical Weather Data API?
A: We offer comprehensive documentation, tutorial videos, and dedicated customer support to help you make the most of our API.