Land Resource Management in India: 7 Sustainable Tips
Meta Description: Discover sustainable land resource management in India, integrated agriculture, forestry conservation, and digital innovations for productivity, biodiversity, and rural growth.
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Importance of Land Resource Management in India
- 7 Sustainable Tips for Land Resource Management in India
- 1. Promote Integrated Agroforestry Systems
- 2. Adopt Sustainable Agriculture Practices
- 3. Strengthen Forest Conservation and Reforestation
- 4. Foster Joint Forest Management with Local Communities
- 5. Expand Social Forestry Programs
- 6. Implement Digital Land Records India-wide
- 7. Prioritize Integrated Land Use Planning
- Comparative Table: 7 Sustainable Land Management Tips
- Harnessing Technology: How Farmonaut Supports Sustainable Land Management
- Challenges & Future Directions for Land Resource Management in India
- FAQs on Land Resource Management in India
- Conclusion: Towards a Sustainable, Productive & Equitable Future
Introduction: The Importance of Land Resource Management in India
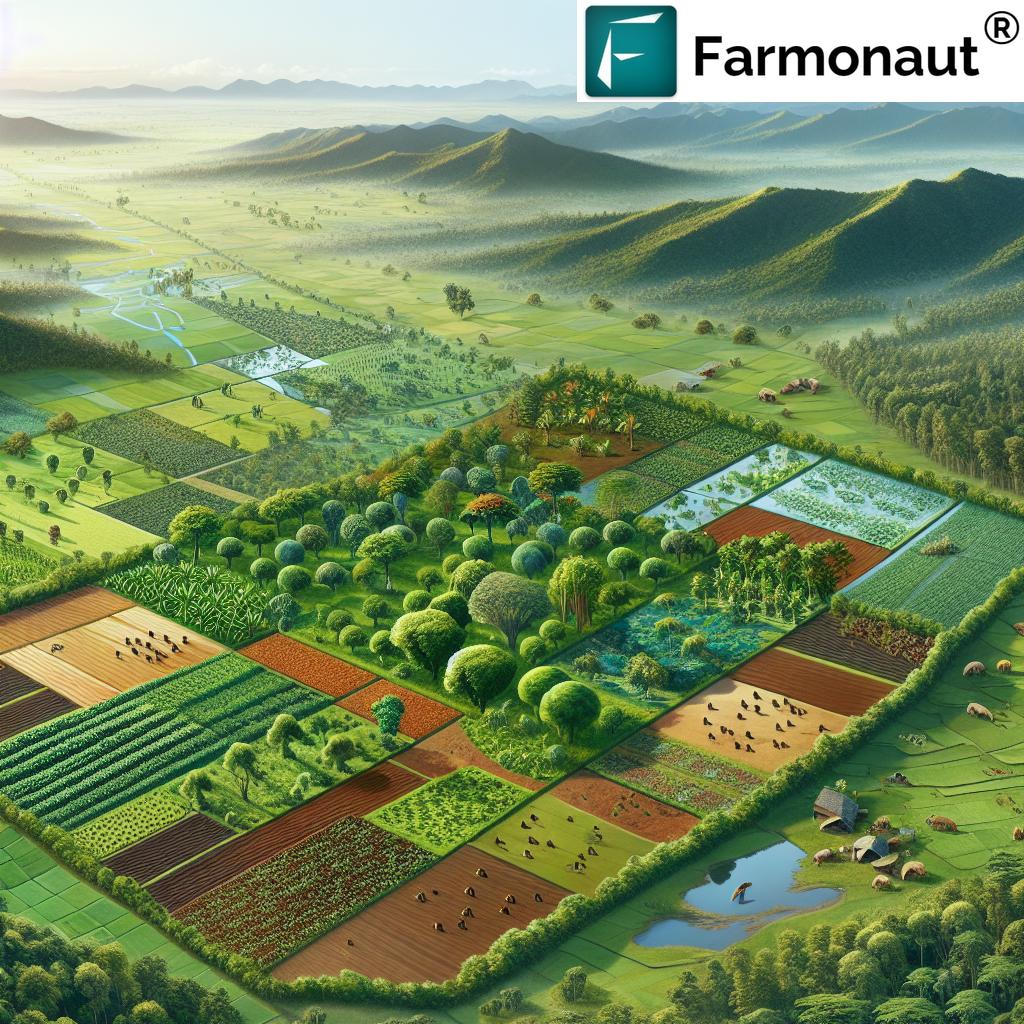
The vast and diverse landscape of India has always played a pivotal role in shaping our civilization, economy, and cultural vibrancy. As we support the needs of more than 17% of the world’s population with only 2.4% of its land resources, the effective management of these precious resources is not merely an environmental imperative but an existential one.
Land resource management in India encompasses the linked domains of agriculture, forestry, water conservation, and urban development, aiming to sustain up productivity, biodiversity, rural growth, and environmental balance.
Given mounting challenges like land degradation, unchecked urbanization, shifting climate patterns, and a burgeoning rural workforce, our approach demands innovation, integration, and sustainability. In this blog, we share seven actionable, sustainable tips—rooted in national policies and modern technology—for land resource management in India that foster productivity, conservation, and inclusive growth.
7 Sustainable Tips for Land Resource Management in India
Let’s explore seven integrated strategies that combine traditional Indian wisdom, policy innovations, and cutting-edge agri-tech—ensuring our farms, forests, and communities thrive for generations.
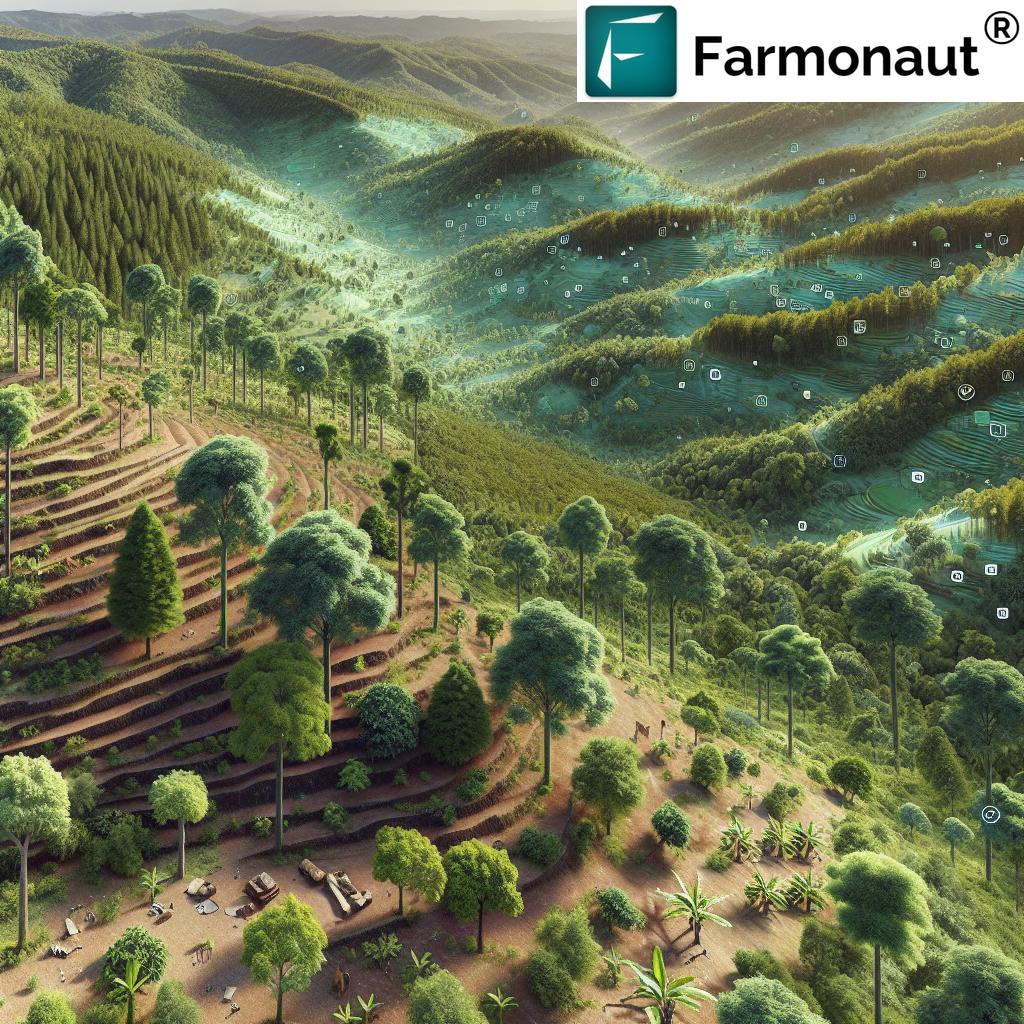
1. Promote Integrated Agroforestry Systems
Integrated agroforestry systems blend the cultivation of trees with crops and often livestock, maximizing the productivity and sustainability of our agricultural land. The National Agroforestry Policy (2014) promoted by India, is a landmark in the integration of agriculture and forestry, advocating for farm-woodlots and multi-layered cropping systems.
Benefits of Agroforestry:
- Improves soil health and productivity through nutrient cycling and organic matter addition.
- Enhances farm yield and income diversification by incorporating timber, fruit, fodder, and fuelwood.
- Contributes to biodiversity by creating varied habitats for flora and fauna.
- Regulates climate through carbon sequestration and mitigates erratic rainfall effects.
- Reduces risk of soil erosion and land degradation, especially in rainfed and hilly areas.
By promoting agroforestry systems, we create a resilient agricultural landscape, ensuring both ecological balance and rural prosperity.
Want to monitor the success of your agroforestry initiatives or crop plantations? Explore Farmonaut’s satellite and AI-based crop and plantation advisory tools.
2. Adopt Sustainable Agriculture Practices
Sustainable agriculture practices form the backbone of responsible land management in India. Techniques such as crop rotation, cover cropping, organic amendments, and reduced tillage preserve soil health, improve water retention, and increase resilience to climate change.
Key components of modern sustainable farming in India include:
- Crop Rotation: Alternating crop types across seasons breaks pest cycles and replenishes soil nutrients, enhancing yield and soil health and productivity.
- Organic Farming: Reduces reliance on synthetic inputs, enhances soil biodiversity, and lowers input costs.
- Precision Agriculture: Utilizing technological tools—like Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting, real-time crop health monitoring, and AI advice—enables efficient fertilizer and water use, reducing waste.
- Conservation Tillage: Minimal soil disturbance preserves biological activity and reduces erosion.
These sustainable agriculture practices not only help in maximizing crop productivity but also conserve land resources and promote long-term sustainability in our rural economy.
Looking for advanced crop management insights? Farmonaut’s large-scale farm management solutions empower agribusinesses and government organizations across India.
3. Strengthen Forest Conservation and Reforestation
Forest conservation in India is crucial for preserving biodiversity, combating climate change, and protecting our soil and water resources. Our forests are home to invaluable ecosystems—including tropical wet evergreen, tropical dry deciduous, and subtropical pine types—each supporting unique flora and fauna.
India’s National Forest Policy (1988) commits to increasing forest cover to 33% of our country’s land area, underlining the importance of reforestation (afforestation and reforestation) and sustainable forest utilization.
Quick facts:
- Tropical wet evergreen forests exist along Western Ghats and North-East India, rich in biodiversity and rainfall regulation.
- Tropical dry deciduous forests dominate central India—crucial for groundwater recharge and fuelwood production.
- Subtropical pine forests of the Himalayas help prevent soil erosion and landslides.
Community-driven reforestation and vigilant forest protection efforts are key to restoring degraded areas and regulating India’s climate.
Map your reforestation project and monitor forest health with Farmonaut’s forest and tree monitoring capabilities.
4. Foster Joint Forest Management with Local Communities
The Joint Forest Management (JFM) movement recognizes the power of community action for forest conservation. Under JFM, state forest departments collaborate with local villages to protect and regenerate degraded forests. Learn more about JFM.
Key Elements:
- Communities help fight fire, prevent illegal harvesting, and watch over timber and forest products.
- In sharing arrangements, villages get rights to non-timber forest products (NTFPs) and sometimes a share of revenue from timber.
- JFM is instrumental in restoring degraded forest areas and improving rural livelihoods.
Empowering communities for joint management steers forest governance towards sustainability while ensuring social and economic inclusivity.
Digitally track and monitor community-managed forest zones using precision tools like Farmonaut’s advisory modules.
5. Expand Social Forestry Programs
Social forestry programs promote planting trees on common lands, margins of roads, water bodies, and in and around villages. Initially launched in the 1970s to meet the fuelwood, fodder, and small timber needs of rural families, these programs are pivotal for climate adaptability and rural development.
Key advantages:
- Enhance tree cover in barren and deforested areas through afforestation.
- Support environmental conservation and offer economic returns to local communities by supplying forest products.
- Improve biodiversity and soil health.
Expanding social forestry builds climate resilience, preserves our ecosystems, and strengthens local economies across India.
Monitor social forestry outcomes with satellite-enabled solutions like Farmonaut’s real-time monitoring modules.
6. Implement Digital Land Records India-wide
In pursuit of transparency and empowerment, the Digital India Land Record Modernization Programme (DILRMP) and modern tools like Farmonaut’s digital resource tracking are revolutionizing land management.
Advantages of digital land records in India:
- Reduce land disputes via clear, updated, and accessible digital ownership records.
- Empower rural communities and farmers with formal documentation, increasing access to crop loans and insurance (see Farmonaut’s crop loan & insurance solutions).
- Facilitate effective land resource management, urban/rural planning, and resource sharing.
Want to integrate digital verifications into your agri-business or research? Use the Farmonaut Satellite Resource Management API and access full documentation in the Developer Docs.
7. Prioritize Integrated Land Use Planning
The bedrock of sustainable land resource management in India is the cross-sectoral coordination of land, water, and vegetation resources—achieved through integrated land use planning. This approach balances environmental, economic, and social demands across the landscape.
Key Components:
- Mapping and zoning for sustainable agriculture, forestry, industry, and settlement, prioritizing ecological balance.
- Applying geospatial and satellite data (as offered by Farmonaut) to optimize land utilization and monitor environmental impacts.
- Involving communities in decision-making—for equitable and context-specific solutions.
Integrated planning ensures that our land resources are used efficiently, with minimal damage to our environment, and maximum benefit to our rural and urban populations.
Comparative Practices Table: 7 Sustainable Tips for Land Resource Management in India
| Practice Name | Estimated Impact on Productivity (% Increase) | Biodiversity Enhancement | Estimated Cost Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Integrated Agroforestry Systems | 10-30% | High | Medium |
| Sustainable Agriculture Practices | 20-30% | Medium-High | Low-Medium |
| Forest Conservation and Reforestation | 5-15% | Very High | Medium-High |
| Joint Forest Management | 5-10% | High | Low |
| Social Forestry Programs | 5-10% | Medium | Low-Medium |
| Digital Land Records India | Indirect – improves access & utilization | Low | Medium |
| Integrated Land Use Planning | 15-25% | High | High |
Harnessing Technology: How Farmonaut Supports Sustainable Land Management
The journey to effective land resource management in India is now empowered by technology. At the forefront, Farmonaut delivers precision, transparency, and scalability—all tailored to Indian needs.
Key Features That Empower Indian Farmers, Communities, and Agencies:
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Farmonaut uses multispectral data for real-time insights on crop health, soil moisture, and vegetation. This facilitates targeted irrigation, fertilizer usage, and pest management—significantly reducing resource wastage and enhancing productivity.
-
AI and Blockchain Technology: Personalized AI advisory tools (like Jeevn AI) provide real-time support to farmers. Blockchain-based product traceability ensures transparency from farm to consumer.
Strengthen your supply chain with Farmonaut’s blockchain Traceability solution. -
Resource & Fleet Management: Farmonaut optimizes logistics and operational management for large-scale agribusinesses.
Explore fleet management advantages for efficient agricultural operations. - Carbon Footprinting: Track and reduce your emission profile using Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting modules—meeting global sustainability standards.
-
Credible Financing: Farmonaut helps financial institutions via satellite-based verification, reducing fraud and boosting access to credit and insurance for Indian farmers.
Learn how you can tap into satellite-based loan and insurance solutions for agriculture. - API & Developer Integrations: Agritech developers and research institutions can access advanced weather, satellite, and soil data directly via the Farmonaut API with comprehensive documentation at the API Docs.
These digital tools, accessible via App or Web, are affordable and scalable—bridging urban and rural divides, and making integrated land resource management in India a cooperative reality.
Challenges & Future Directions for Land Resource Management in India
Despite significant national efforts, we continue facing critical challenges in land resource management in India:
- Deforestation in tropical and dry deciduous zones—increased pressure on forests for land and fuelwood.
- Land degradation due to overuse, poor irrigation practices, urban expansion, and unsustainable farming.
- Pressures from urbanization, industrialization, and infrastructure development on agricultural land and ecological balance.
- Insufficient adoption of digital and precision agriculture tools in rural areas.
- Fragmented land records and limited community participation in planning and conservation.
Future Directions:
- Wider adoption of integrated land use planning supported by satellite technology and geospatial intelligence.
- Stricter enforcement of environmental regulations at state and local levels.
- Enhancing community involvement in resource management, especially through JFM and social forestry programs.
- Expanding digital resource management systems and affordable advisory platforms across rural India.
- Promoting sustainable agricultural practices and reforestation initiatives to restore degraded areas.
With holistic policy, grassroots action, and technology, we can usher in a sustainable, productive, and inclusive land management system.
FAQs on Land Resource Management in India
What is land resource management in India?
Land resource management in India involves the strategic planning, use, protection, and restoration of land, integrating agricultural, forestry, and technological practices to enhance productivity, conserve biodiversity, and promote rural development.
How do sustainable agriculture practices improve productivity?
Sustainable agriculture practices, such as crop rotation, organic farming, and precision inputs, improve soil health and water use, resulting in higher yields, reduced input costs, and better resilience to climate risks.
What is the role of digital land records in India?
Digital land records in India improve transparency, reduce disputes, and empower rural communities by making land ownership clear and facilitating better access to credit, insurance, and government schemes.
How does Farmonaut help in land management?
Farmonaut offers satellite-based crop and forest monitoring, AI-based advisories, blockchain-powered traceability, and API-based integration—helping farmers and agribusinesses optimize resources, increase productivity, and achieve sustainability.
Why is forest conservation in India critical?
Forest conservation in India preserves biodiversity, maintains ecological balance, controls climate, prevents soil erosion, and contributes to river and groundwater recharge—safeguarding both the environment and livelihoods.
Conclusion: Towards a Sustainable, Productive & Equitable Future
At the crossroads of a growing population, climate uncertainties, and economic transformation, land resource management in India is our linchpin for resilient national development. Implementing integrated sustainable agriculture practices, robust forest conservation in India, community-centric models like joint forest management, and embracing digital land records India-wide should be our collective commitment.
Let us tap the power of innovation—tools like Farmonaut’s satellite-enabled monitoring, AI-driven workflow, and blockchain-secured resources—to ensure our lands remain productive, livelihoods secure, and our nation’s natural legacy preserved for generations.