Carbon Farming Australia: 7 Shocking Soil Hacks Revealed
“Australian carbon farming can boost soil organic carbon by up to 30% in just five years.”
Carbon Farming in Australia: A Comprehensive Overview
As Australians, we’re uniquely positioned at the forefront of climate change mitigation and sustainable land management. Carbon farming, the process of capturing and storing atmospheric CO₂ in soils and vegetation through agricultural and forestry practices, has emerged as one of Australia’s most effective strategies to reduce emissions, enhance soil health, and provide new economic opportunities for our landholders. From farm paddocks in New South Wales to savannas in Northern Territory, this powerful approach is reshaping the future of farming, restoration, and environmental management across the country.
In this in-depth guide, we’ll reveal 7 shocking soil hacks from carbon farming Australia that are driving transformation in both environmental and agricultural sectors. Join us as we unpack advanced soil management techniques, government incentives, AI technologies in carbon monitoring, and more—putting actionable solutions at the hands of every Australian farmer, landholder, and eco-focused stakeholder.
Understanding Carbon Farming Australia
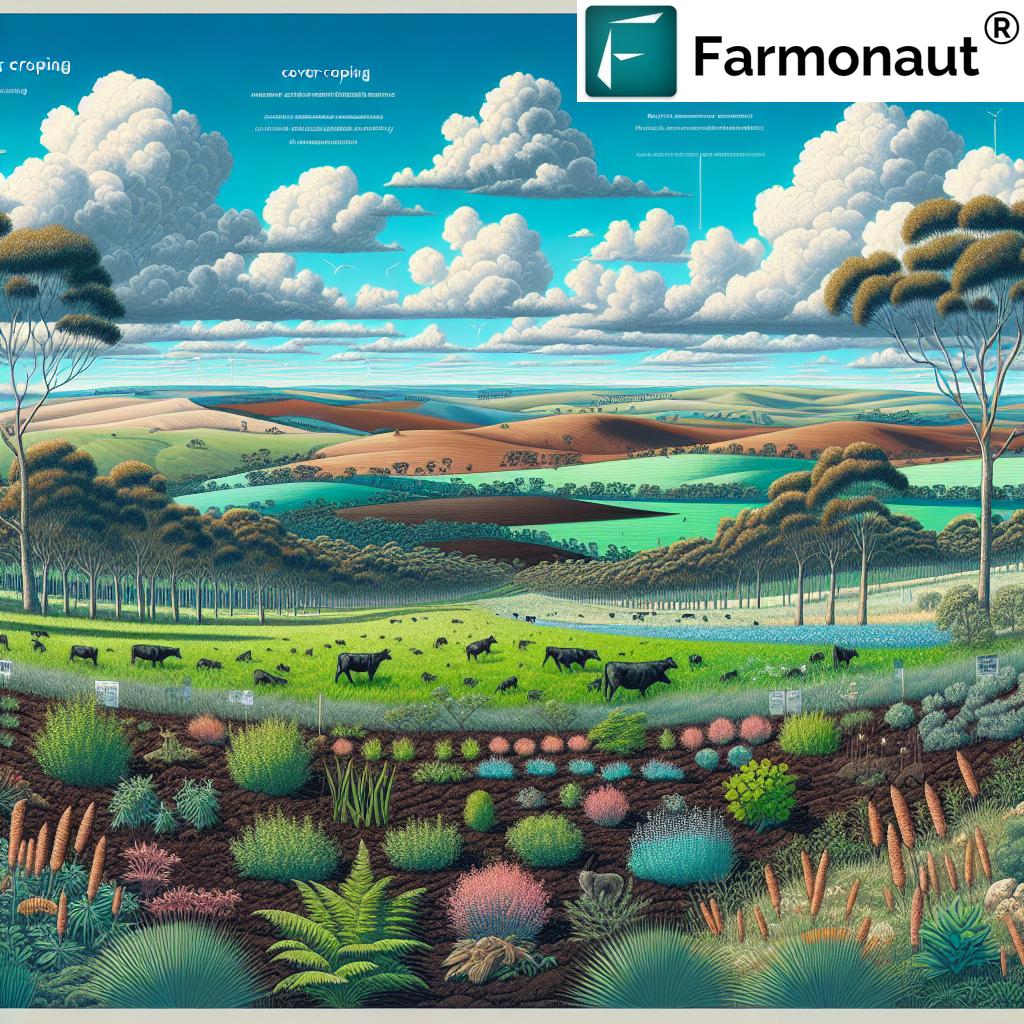
Carbon farming Australia refers to a suite of farming, land management, and forestry activities that capture, store, and maintain carbon in our soils and vegetation. The goal is twofold: enhance the health and resilience of Australia’s unique soils and mitigate the country’s greenhouse gas emissions—delivering critical environmental and economic outcomes for current and future generations.
- Soil Carbon Sequestration: Increasing organic matter and carbon stored in soils by using methods such as reduced tillage, cover cropping, and rotational grazing.
- Reforestation Initiatives Australia: Planting and restoring native tree species, afforestation, and establishing carbon sink forests to absorb atmospheric CO₂.
- Savanna Fire Management: Controlled burns and savanna fire management in Northern Australia, reducing wildfire frequency and intensity while maintaining healthy ecosystems.
- Cultural Burning: Indigenous traditional burning practices to promote healthy land, biodiversity, and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Why Soil Carbon Sequestration Matters
Our Australian soils are the largest terrestrial carbon store we have. The better we manage them, the more carbon we can sequester, not just fighting climate change but enhancing agricultural productivity and land health for our communities. It’s an approach that delivers robust co-benefits: increased water retention, improved nutrient cycling, greater drought resilience, and boosted biodiversity.
7 Shocking Soil Hacks: Carbon Farming Australia’s Game-Changers
Let’s break down the top techniques revolutionizing carbon farming in Australia. These innovative methods go beyond basic soil conservation—each is a powerful tool to capture and store atmospheric carbon dioxide, improve soil health, and support Australia’s sustainable land management.
-
Reduced Tillage
By minimizing or eliminating traditional ploughing, we reduce soil disturbance, preserve organic carbon in soils, and prevent it from oxidizing and escaping as CO₂. Reduced tillage also minimizes erosion, improves water infiltration, and supports soil ecosystem health.
-
Cover Cropping
Growing cover crops (like clover, vetch, or rye) in fallow periods increases organic matter, locks in soil nutrients, and prevents erosion. These fast-growing crops capture carbon, enhance soil structure, and provide habitat for beneficial soil microbes—a win-win for soil carbon sequestration and agricultural productivity.
-
Rotational Grazing
Rotating livestock across different paddocks gives the land time to recover and regrow, helping to enhance root biomass, organic matter, and carbon storage. One of the best carbon farming hacks for Australia’s vast pastoral landscapes.
-
Reforestation & Afforestation
Planting native trees and creating new forest zones greatly increases long-term carbon storage while offering additional restoration benefits—soil stabilization, improved rainfall infiltration, and habitat for endangered species. This is the backbone of many carbon credit programs Australia supports.
-
Savanna Fire Management
By implementing controlled, low-intensity burns early in the dry season (especially across northern Australia), we reduce the severity of wildfires, promote new growth, and significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions. This is central to Australia’s savanna regions and embedded in both Indigenous and modern approaches.
-
Organic & Compost Amendments
Adding compost, biochar, or organic waste to soils increases stable carbon levels, feeds beneficial microbial communities, and improves overall fertility. This boosts soil’s capacity to store both water and carbon, providing resilience against drought and degraded land.
-
Microbial Inoculation
Cutting-edge companies—and keen Australian farmers—are harnessing specialized microbes and fungi that accelerate the conversion and stabilization of atmospheric carbon into organic soil matter. These solutions represent the frontier of climate change mitigation strategies.
“Over 19 million hectares in Australia are managed under carbon farming for sustainable land use.”
Comparison Table: Soil Hacks & Environmental Benefits
How do these soil hacks stack up? Here’s a comparison of each method’s impact on carbon sequestration, other soil health benefits, and estimated costs for Australian landholders and agribusinesses.
| Soil Hack | Main Action | Estimated Carbon Sequestration Benefit (tonnes CO₂e/ha/year) |
Other Soil Health Benefits | Estimated Cost Range (AUD/ha) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reduced Tillage | Minimise or eliminate ploughing | +0.2 to +0.4 | Improved structure, reduced erosion | $10 – $30 |
| Cover Cropping | Plant cover crops during fallow | +0.3 to +0.7 | Organic matter, weed suppression | $15 – $60 |
| Rotational Grazing | Move livestock, rest paddocks | +0.15 to +0.3 | Enhanced root growth, fertility | $8 – $25 |
| Reforestation & Afforestation | Plant native trees/establish forests | +2.0 to +9.0 | Habitat, rainfall infiltration | $500 – $2000* |
| Savanna Fire Management | Controlled/early burns | +0.1 to +0.5 | Reduce wildfires, increase biodiversity | $5 – $20 |
| Organic & Compost Amendments | Add compost/biochar | +0.1 to +0.4 | Increased microbial health, moisture retention | $20 – $150 |
| Microbial Inoculation | Apply beneficial microbes/fungi | +0.1 to +0.9 | Nutrient cycling, rapid carbon lock-in | $25 – $110 |
*Higher cost reflects establishment of trees; financial incentives & government programs can offset substantial portions.
Government Initiatives & Financial Incentives
Australia’s government is a global leader in supporting carbon farming projects and soil carbon sequestration. Here’s how we’re helping landholders and industries transition to sustainable management:
- Emissions Reduction Fund (ERF): This federally-backed program provides financial incentives for farmers, companies, and communities who integrate carbon sequestration into their land management. Projects earn Australian Carbon Credit Units (ACCUs)—tradable assets in carbon credit programs Australia relies on for compliance and voluntary offset markets.
- National Soil Carbon Innovation Challenge: With $50 million committed to reduce the cost and increase the reliability of soil carbon measurement, this initiative makes it easier for everyone to participate—whether they’re overseeing 10 or 10,000 hectares.
- State-Based Programs:
- Queensland’s Land Restoration Fund—$500 million financing diverse land restoration/cropping practices.
- Western Australia’s Carbon Farming & Land Restoration Program—up to $15 million for carbon farming projects, with a particular focus on soil carbon sequestration and plantation forestry.
To streamline participation in these programs, digital platforms like Farmonaut—which provides AI-powered monitoring and government-compatible carbon footprinting tools—are making processes easier, more reliable, and accessible for all stakeholders.
View Farmonaut API Developer Docs—integrate advanced satellite and climate data
Economic & Environmental Benefits of Carbon Farming Projects
Why is carbon farming Australia so persuasive for farmers, companies, and government alike? Here’s what we all stand to gain:
- Diversified Revenue & Income Security: Landholders can sell carbon credits via official programs or to voluntary offset buyers. This adds a valuable and often reliable revenue stream on top of traditional agricultural earnings.
- Enhanced Soil Health & Productivity: Reduced tillage, cover cropping, and amendments improve organic matter, increase resilience to drought and extreme weather, and result in more stable yields.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Planting native trees and restoring degraded land boosts wildlife corridors, restores habitats, and maintains strong ecosystems for future agricultural success.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Every tonne of carbon sequestered reduces greenhouse emissions, helping Australia reach its Paris Agreement targets and boosting our global climate reputation.
- Community Engagement: Carbon farming projects provide employment, skills training, and cultural benefits for local and especially Indigenous communities.
Platforms such as Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting tool enable both individual farmers and large agribusinesses to track and verify real-time reductions, ensuring credible claims to credits and financial incentives.
Challenges & Considerations for Australian Carbon Farming
Like all sustainability journeys, carbon farming Australia faces its share of obstacles:
- Measurement & Verification: Precisely quantifying how much carbon is actually sequestered, and then reliably reporting it, can be technically challenging. That’s why innovations in AI-based carbon monitoring and remote sensing are becoming increasingly critical.
- Volatility in Carbon Credit Markets: The value of carbon credits can fluctuate, meaning farmers’ income from these sources can be uncertain and requires risk management.
- Changing Government Policies: Regulatory shifts can affect funding and the attractiveness of long-term carbon farming projects, requiring ongoing engagement with government and industry bodies.
Academic, government, and private sector stakeholders are all working to address these hurdles and optimize carbon farming for national climate change mitigation strategies.
Innovation & AI in Carbon Monitoring
Next-generation technologies are unlocking unprecedented potential for soil carbon sequestration and emissions tracking—making carbon farming projects more efficient, scalable, and financially rewarding.
- Remote Sensing & AI-driven Soil Monitoring: Farmonaut and other leading companies now use high-frequency satellite imagery and AI analysis (e.g., Jeevn AI advisory) to assess soil health, organic carbon levels, and even predict pest threats for smarter management and higher carbon storage.
- Automated Verification & MRV (Monitoring, Reporting, Verification): Digital tools streamline the often complex process of recording and reporting carbon gains, helping both landholders and regulators trust the outcomes—and getting you to payment faster.
- Microbial & Biotechnological Innovations: Pioneering companies are breeding specialized microbial products that can dramatically increase carbon locked in soils, accelerate organic matter decomposition, and restore land faster.
If you’re an agritech developer or digital service provider, access Farmonaut’s powerful carbon and weather API to build or integrate robust carbon monitoring tools into your platform.
Indigenous Land Management Australia: Custodians of Sustainable Change
No overview of carbon farming Australia is complete without recognizing the central role of Indigenous land management Australia, particularly in our savannas, semi-arid, and remote areas.
- Cultural Burning: Traditional owners—whose practices pre-date modern science by tens of thousands of years—apply early, strategic fire to maintain country, restore native grasses, limit invasive weeds, support biodiversity, and reduce carbon emissions.
- Community Carbon Projects: Indigenous rangers and organizations are increasingly winning contracts for carbon farming projects, supporting local economies through jobs, training, and ongoing knowledge transfer.
These approaches not only reduce emissions but deeply enhance the health of our ecosystems—showing the power of blending ancient wisdom and new technology for Australia’s sustainable land management future.
What is the Future of Carbon Farming Australia?
Looking ahead, the sector’s growth is almost guaranteed:
- Expanding Industry & Markets: The Australian Carbon Farming Industry Roadmap predicts a major boost in industry scale, market value, and employment by 2030, with increasing participation from both private landholders and government.
- More Policy Support: Ongoing government initiatives, funding programs, and regulatory clarity are making it easier and more appealing to adopt sustainable land management practices nationwide.
- Scalable, Digital Technologies: Platforms like Farmonaut continue to lower the cost and complexity of carbon monitoring, reporting, and management for everyone—from individual graziers to large agribusinesses and even state governments.
- Direct Integration into Australian Supply Chains: Blockchain-based product traceability solutions now allow food, textile, and timber sectors to track and prove climate-friendly supply chains—giving consumers more confidence and rewarding regenerative land stewards.
Emerging tools like large-scale farm management apps and fleet management services position Australia for continued growth in carbon farming projects and emissions reduction at every scale.
How Farmonaut Supports Precision Carbon Farming Australia
Farmonaut stands at the intersection of agricultural tradition, digital innovation, and environmental responsibility. Here’s how our platform supports sustainable land management Australia and the carbon farming movement:
- Real-time Crop & Soil Health Monitoring: Our satellite-based tools provide instant insights into vegetation health (NDVI), soil moisture, and soil carbon status—empowering landholders to optimize inputs and maximize organic carbon sequestration.
- AI-based Advisory: Using our Jeevn AI system, landholders receive customized recommendations for crop management, carbon enhancement, pest prevention, and adaptive rotation schedules.
- Blockchain-backed Traceability: For those needing to certify carbon-neutral produce or climate-positive supply chains, our secure traceability solutions build customer trust and ensure compliance with global standards.
- Accessible, Affordable Tools: With subscription options for forest plantation and advisory, fleet resource management, and satellite-backed crop loan/insurance verification, Farmonaut enables forward-looking agribusinesses and landholders to maximize both profit and sustainability, no matter their size.
Our web, Android, and iOS apps put these world-class tools at your fingertips—whether you’re an individual grower, an agribusiness manager, or a government decision-maker. And with APIs ready for integration, technical users can build custom carbon farming solutions for every need.
FAQ: Carbon Farming Australia
-
What is soil carbon sequestration and why is it important for Australia?
Soil carbon sequestration is the process of capturing and storing atmospheric CO₂ in soil, primarily through organic matter. In Australia, it enhances drought resilience, improves agricultural productivity, and helps us meet international emissions reduction targets. -
What are the best carbon farming practices for Australian graziers and landholders?
The most effective practices include reduced tillage, cover cropping, adaptive rotational grazing, reforestation, early controlled burning, organic amendments, and new microbial inoculation methods. -
How do government incentives and the Emissions Reduction Fund work?
By joining the Emissions Reduction Fund or a state program, landholders who implement eligible carbon farming techniques can generate Australian Carbon Credit Units (ACCUs), which can be sold for income or used to offset their emissions. -
How does AI in carbon monitoring benefit my farm?
AI-enabled tools like Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI system analyze satellite and environmental data to provide accurate, real-time advisory—helping you plan, track, and optimize carbon farming for both productivity and compliance. -
Can carbon farming support Indigenous communities?
Yes! Indigenous landholders play a vital role in carbon farming projects through cultural burning, restoration, and community carbon management initiatives. These not only offer economic benefits but also support cultural knowledge and environmental stewardship. -
Where can I get started with digital carbon farming management tools?
Sign up for a subscription or explore Farmonaut’s mobile/web apps and API services—designed to help you unlock the full value of carbon farming Australia, no matter your scale or location.
Conclusion: Soil, Carbon, & Australia’s Green Destiny
The future of carbon farming Australia is bright. As we face climate change head-on, adopting evidence-based, innovative soil hacks not only reduces emissions and strengthens our agricultural sector—it protects Australia’s precious environments and delivers real economic rewards for landholders, Indigenous communities, and every stakeholder in our land restoration journey.
Are you ready to harness the power of soil for climate change mitigation, land restoration, and economic resilience?
Get started today with Farmonaut’s comprehensive suite of digital carbon management tools—and join the movement towards a cleaner, greener, and more productive Australia.
Supercharge your platforms with carbon, weather, and vegetation analytics via the Farmonaut API — review detailed docs here.