“Over 80% of farmers using biological pest control report improved soil fertility within just two growing seasons.”
7 Shocking Sustainable Pest Management Hacks Revealed!
Modern agriculture stands at a pivotal crossroads: how do we manage pests sustainably, ensure bountiful harvests, and safeguard our planet’s delicate balance? Today, we tackle these questions head-on by delving into sustainable pest management, unveiling 7 field-tested hacks that leverage biological pest control, innovative technology, and natural pest control methods for farmers to transform the way we cultivate crops.
At Farmonaut, we believe in empowering farmers and agribusinesses with actionable insights driven by data and technology. As we explore these strategies, we will highlight the crucial role of integrated pest management (IPM), how environmentally friendly pest control contributes to ecological balance in agriculture, and why improving soil health in farming is foundational for both productivity and sustainability. These hacks not only reduce pesticide use in agriculture but also pave the way for resilient and profitable futures for all stakeholders in the agricultural ecosystem.
The 7 Shocking Sustainable Pest Management Hacks Every Farmer Should Know
These seven hacks integrate biological practices, cultural methods, cutting-edge technology, and community learning to create a sustainable, effective, and cost-efficient roadmap for pest control and enhancing farm productivity. Let’s break them down one by one.
1. Integrated Pest Management (IPM): The Sustainable Pest Management Foundation
At the very core of sustainable pest management stands Integrated Pest Management (IPM), a holistic, knowledge-driven strategy that combines cultural, biological, physical, mechanical, and—in the rare event necessary—chemical controls. By integrating these control methods, we can monitor pest levels, understand their biology, and target measures only when required. This approach minimizes interventions, reduces resistance in pest populations, and safeguards beneficial organisms, leading to a more robust ecosystem.
- Focus on Monitoring: Regularly inspect fields for signs of pest activity, thresholds, and the presence of natural enemies.
- Data-driven Decision Making: Employ advanced tools like Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop health monitoring and AI-driven advisory system to guide timely interventions.
- Mosaic of Methods: Combine multiple sustainable practices—instead of relying solely on chemical pesticides—to enhance ecological balance and soil integrity.
Embracing IPM enables us not only to control pests effectively, but also to protect environmental health, boost biodiversity, and maintain long-term crop productivity.
2. Cultural Pest Control Practices: Modify and Master the Ecosystem
Cultural controls are pivotal in sustainable pest management. By modifying how and what we plant, we can directly disrupt pest establishment, reproduction, and survival.
- Crop Rotation: Change crops in the same plot over consecutive seasons. This disrupts the life cycles of species thriving on particular crops and prevents them from consolidating in one area.
- Diversification and Intercropping: Plant a variety of crops or pest-repelling species such as Desmodium alongside main crops. Intercropping legumes, for instance, can enhance soil fertility and attract beneficial insects while deterring pests.
- Sanitation and Field Hygiene: Remove crop residues and weeds that could harbor pests or pathogens.
- Timely Planting: Adjust sowing dates to avoid peak pest populations.
These cultural pest control practices are cost-effective, easy to implement, and focus on improving soil health in farming while promoting sustainable pest management.
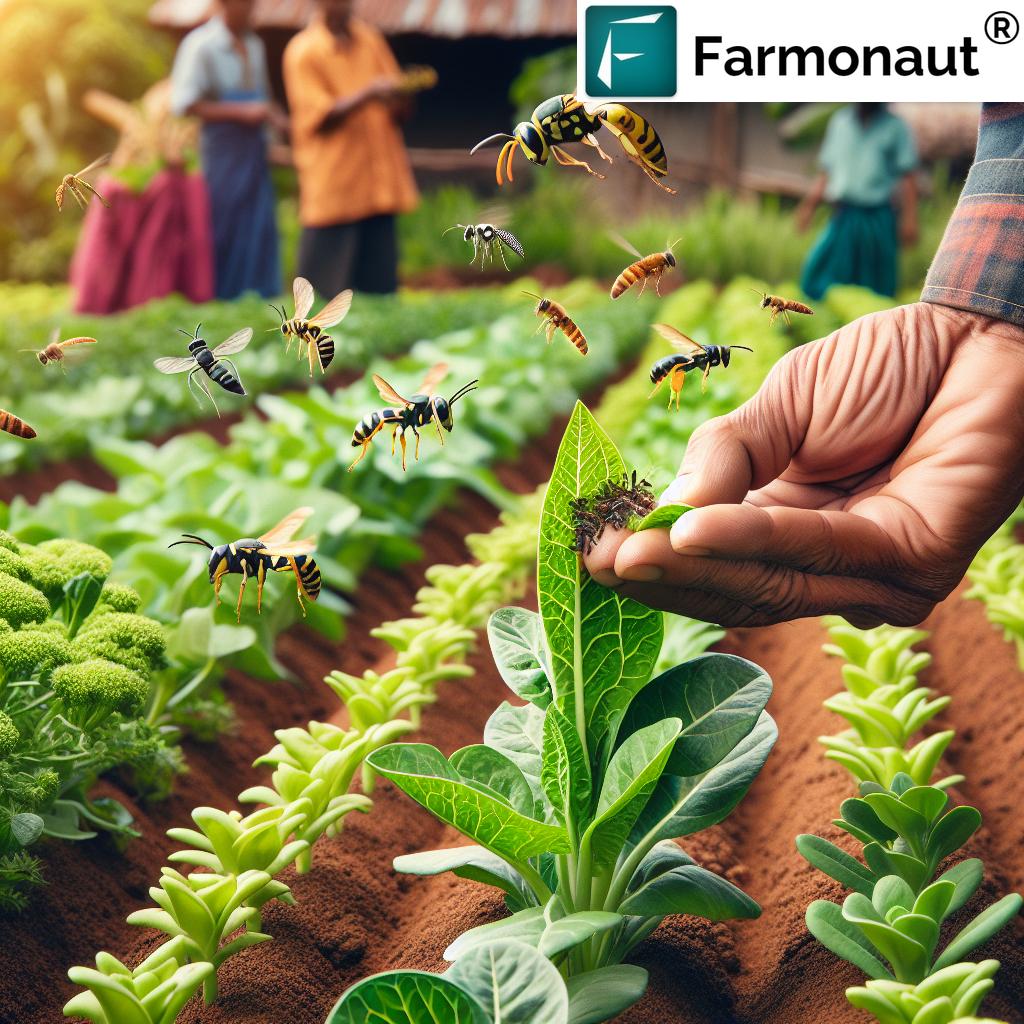
3. Biological Pest Control: Harnessing Nature’s Own Warriors
Biological pest control involves employing natural enemies—predators, parasites, and pathogens—to manage pest populations. This method is crucial for sustainable pest management and significantly reduces our reliance on chemical interventions.
- Conservation Biological Control: Enhancing habitats to support natural pest enemies. For example, planting nectar-rich flowers and creating beetle banks can help attract and sustain beneficial insects across the field.
- Augmentative Biological Control: Releasing additional natural enemies in infested areas. For greenhouse farming, releasing predatory mites to target spider mites—or Trichogramma wasps to parasitize caterpillar eggs—is highly effective.
- Classical Biological Control: Introducing pest enemies from the pest’s place of origin. This technique, when carefully researched, controls new invasive species without harming local ecological balance.
By integrating biological control into our routine, we not only prevent pest outbreaks but also maintain ecological balance in agriculture.
“Sustainable pest management can reduce chemical pesticide use by up to 70%, enhancing ecological balance on farms.”
4. Technological Innovations: Smart Systems for Sustainable Pest Management
Modern technology is reshaping sustainable pest management with smart, data-driven solutions:
- Aerial Biological Control: Using drones or UAVs to release beneficial insects or distribute bio-pesticides over crops. This method allows for targeted, large-scale interventions without extensive chemical use.
- AI and Machine Learning: Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI Advisory System analyzes satellite images, in-field data, and weather predictions to detect and predict pest outbreaks early. Real-time alerts enable timely, precise action, drastically reducing resource wastage and unnecessary pesticide application.
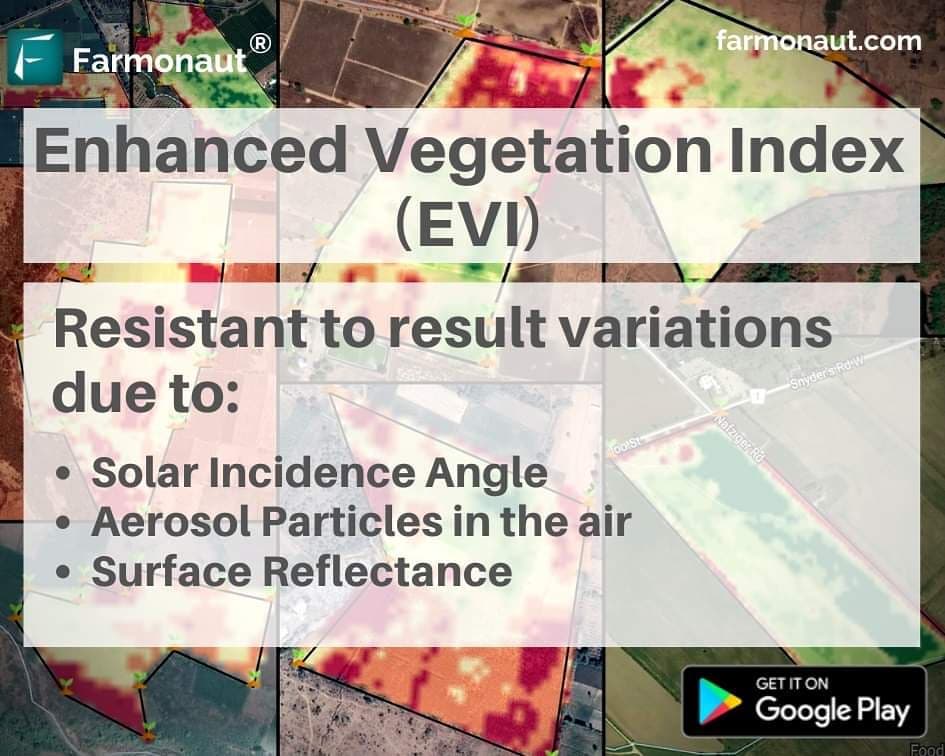
- GIS & Satellite Monitoring: Platforms like Farmonaut provide satellite-based crop health monitoring, heatmaps, and geotagging, enabling farmers to monitor pest levels across large areas, even in inaccessible fields.
- Traceability and Transparency: Farmonaut’s blockchain-based product traceability enhances supply chain transparency, ensuring safe, sustainably-managed crops reach consumers.
Integrating technological innovations in pest management not only improves productivity and cost-efficiency, but also supports more sustainable farming practices.
Farmonaut’s API & API Developer Docs allow developers and agribusinesses to integrate powerful remote sensing and weather data for sustainable farm management!
5. Physical and Mechanical Controls: Tactile and Direct Approaches
Sometimes the simplest pest management methods are the most effective. Physical and mechanical controls employ barriers, traps, and environmental modifications to keep pest populations in check without chemical residues.
- Soil Solarization: Covering soil with clear plastic sheeting to increase temperature and eradicate soil-borne pests, weeds, and pathogens. For even more impact, biosolarization involves adding organic amendments, which trap additional heat and release beneficial byproducts as they decompose.
- Pheromone Disruption: Pheromone-based traps confuse pest mating patterns, preventing reproduction and limiting population booms without harming non-target species.
- Traps and Barriers: Sticky traps, fine mesh netting, row covers, or trap cropping block or capture pests before they attack crops.
Deploying these techniques ensures targeted, minimal-impact pest management and fosters a safe, healthy farm ecosystem.
6. Educational and Community-Based Approaches: The Power of Shared Wisdom
Effective, lasting change happens when farmers are united, educated, and empowered. Sustainable pest management thrives on knowledge exchange, collective action, and persistent learning:
- Farmer Field Schools (FFS): Community-based programs where farmers learn IPM techniques, explore natural pest control methods, and experiment with new sustainable practices in a real-field setting.
- Group Buying and Resource Sharing: Enable access to biological controls, specialized traps, or monitoring kits by pooling resources or negotiating better prices collectively.
- Advisory Platforms: Leverage remote learning, online forums, and tailored advisories (like Farmonaut’s digital platform) to learn from experts and peers.
Educational approaches equip farmers to make evidence-based decisions, supporting ecosystem health and food security for communities.
Explore Farmonaut Carbon Footprinting for tools that track and reduce your farm’s environmental impact—crucial for sustainable farming and a greener planet.
7. Holistic Monitoring and Advisory Systems: Precision-Based, Scalable Solutions
Finally, precision agriculture tools bring holistic, scalable, and tailored pest management strategies into every farmer’s hands. The future is data-driven:
- Satellite-Based Surveillance: Monitor multiple fields over large areas, assess vegetation indices, soil moisture, and locate pest hotspots rapidly.
- Automated Alerts and Forecasts: Real-time notifications of emerging threats help farmers take timely action—saving labor, reducing costs, and minimizing pesticide use.
- Data Centralization: Integrating weather data, field history, and pest trends offers unparalleled insight, supporting strategic decision-making at every level.
- Access and Affordability: Farmonaut’s large-scale farm management platform empowers not just individual farmers but cooperatives and government agencies to manage, monitor, and support vast landscapes efficiently.
These holistic systems support every hack we’ve covered and accelerate the adoption of sustainable pest management strategies globally.
Comparison Table: Sustainable Pest Management Hacks—Benefits & Practical Insights
| Hack Name | Description | Estimated Pest Reduction (%) | Impact on Soil Fertility | Environmental Impact | Cost Savings (Est. %) | Implementation Difficulty |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Integrated Pest Management (IPM) | Holistic management integrating all sustainable methods | 60–85% | High | Positive | 30–50% | Moderate |
| Cultural Controls (Rotation, Intercropping) | Modifying farming/cropping techniques to disrupt pest cycles | 40–65% | High | Positive | 20–40% | Easy |
| Biological Control | Promoting natural pest enemies (predators, parasitoids, pathogens) | 55–80% | Medium–High | Positive | 30–60% | Moderate |
| Technological Innovations (AI, Satellite, Drones) | AI-based analysis, remote sensing, targeted drone release | 60–90% | High | Positive | 40–70% | Hard |
| Physical & Mechanical Controls | Barriers, solarization, pheromone traps, mechanical removal | 35–75% | Medium | Positive | 25–55% | Easy–Moderate |
| Educational & Community Approaches | Knowledge sharing, Farmer Field Schools, collective actions | 20–60% | High | Positive | 10–35% | Easy |
| Holistic Monitoring & Advisory Systems | Precision-based, real-time crop monitoring and AI-enabled decisions | 70–95% | High | Positive | 50–80% | Moderate |
Benefits of Sustainable Pest Management
- Economic Benefits: Sustainable methods often generate cost savings by reducing chemical inputs, increasing yields through pollination and natural pest control, and improving market acceptance for sustainable produce.
- Environmental Benefits: Minimize pollution, conserve water, protect non-target species, and enhance soil fertility—all while continually improving ecosystem health.
- Social Benefits: Educated, empowered farmers make better decisions that positively impact community health, food security, and resilience against climate shocks.
- Increased Sustainability: Promote ecological balance in agriculture, helping secure long-term productivity and profitability.
To further integrate economic and environmental benefits on your farm, explore Farmonaut’s fleet management tools—optimized for reducing travel, labor, and input costs across farming operations.
If you’re interested in forestry, multi-crop, or plantation agriculture, Farmonaut’s Crop, Plantation & Forest Advisory delivers targeted, science-backed field guidance.
Additionally, get peace of mind with Farmonaut’s crop loan and insurance verifications, using real-time satellite imagery to reduce risk and support financial decisions in agriculture.
Challenges and Considerations for Sustainable Pest Management
- Knowledge Gaps: Many farmers need increased access to up-to-date resources, training on sustainable practices, and ongoing advisory support.
- Economic Constraints: Initial investments in new systems or transitioning away from chemical pesticides may require planning and financing, though long-term savings are significant.
- Policy and Support: Robust government policies, incentives, and research support accelerate adoption and ensure future food security.
- Monitoring and Results: Measuring outcomes and fine-tuning strategies are essential. Tools such as the Farmonaut platform provide invaluable data-driven insights for continuous improvement.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is sustainable pest management?
Sustainable pest management is an approach in agriculture that controls harmful pest populations while preserving soil health, biodiversity, and environmental integrity. It integrates cultural, biological, mechanical, and technological strategies to reduce dependence on chemical pesticides, supporting long-term farm productivity and ecological balance.
How can biological pest control benefit my farm?
Biological pest control employs natural enemies—such as predators, parasitoids, and pathogens—to manage pest populations. This method can significantly improve soil fertility and crop health, while lowering input costs and reducing chemical residues in the environment.
What are cultural pest control practices?
These are farming techniques like crop rotation, diversification, intercropping, and sanitation that disrupt pest life cycles and reduce pest establishment, reproduction, and survival, often while simultaneously enhancing soil fertility and crop resilience.
How does technology support sustainable pest management?
Technologies such as satellite-based crop health monitoring, AI-driven advisories, and blockchain-enabled traceability enable precision interventions, early pest detection, and transparent, traceable farming. This not only reduces pesticide use but also optimizes resources and supports ecological sustainability.
Is sustainable pest management scalable to large farms?
Yes. With platforms like Farmonaut, large-scale and even multi-regional farms can use satellite monitoring, AI advisories, and data integration to manage thousands of hectares efficiently.
How does reducing pesticide use relate to food security?
Reducing pesticide use improves health and environmental safety, preserves beneficial organisms (like pollinators), and builds long-term soil fertility, all of which are essential for securing consistent, quality food production into the future.
Where can I get training or support in adopting these methods?
Many agricultural extensions, advisory services, and digital platforms—including Farmonaut—offer specialized resources, learning modules, and real-time support for farmers worldwide.
Conclusion: Farming Greener, Smarter, and Stronger for the Future
Sustainable pest management is more than a set of techniques—it’s an ethos, a commitment to balancing effective pest control with ecological stewardship and long-term prosperity for all. By integrating IPM, biological and cultural controls, innovative technology, and continuous learning, we can enhance crop health, safeguard the environment, and future-proof our farms for generations to come.
Solutions like Farmonaut’s satellite, AI, and blockchain-powered apps remove barriers and democratize access, making sustainable agriculture smarter and more accessible for every farmer, anywhere.
Ready to transform your farm’s productivity and environmental impact? Join Farmonaut’s platform today—experience advanced sustainable farming solutions and unlock a greener, more profitable path forward!
Farmonaut Subscription Plans
For more information, visit the official Farmonaut website or download our mobile & web apps.