Table of Contents
- Summary: Aphid Control Methods in Agriculture, Farming, and Forestry
- Understanding Aphid Infestations
- Integrated Pest Management for Aphids
- Comparison Table: Aphid Control Methods
- Preventive Measures to Reduce Aphid Damage
- Technology in Aphid Management: Farmonaut’s Approach
- FAQ: Aphid Control Methods & Management
- Conclusion
Aphid Control Methods: 7 Powerful Ways for Healthy Plants
Summary: Aphid Control Methods in Agriculture, Farming, and Forestry
Aphids represent one of the most challenging pests in agriculture, farming, and forestry worldwide. As soft-bodied insects that rapidly reproduce and form large colonies, aphids feed on plant sap, cause deformation of plant structures, excrete honeydew that promotes sooty mold, and facilitate the transmission of viruses across crops and forests. Implementing effective aphid control methods and leveraging integrated pest management for aphids is crucial for healthy plants, robust yields, and sustainable food security.
This article outlines holistic approaches rooted in environmental responsibility, focusing on IPM strategies, natural ways to control aphids, and preventive solutions. We draw on expert insights to detail how to monitor, prevent, and reduce infestations in line with best practices for sustainability and optimal productivity in agriculture.
Understanding Aphid Infestations
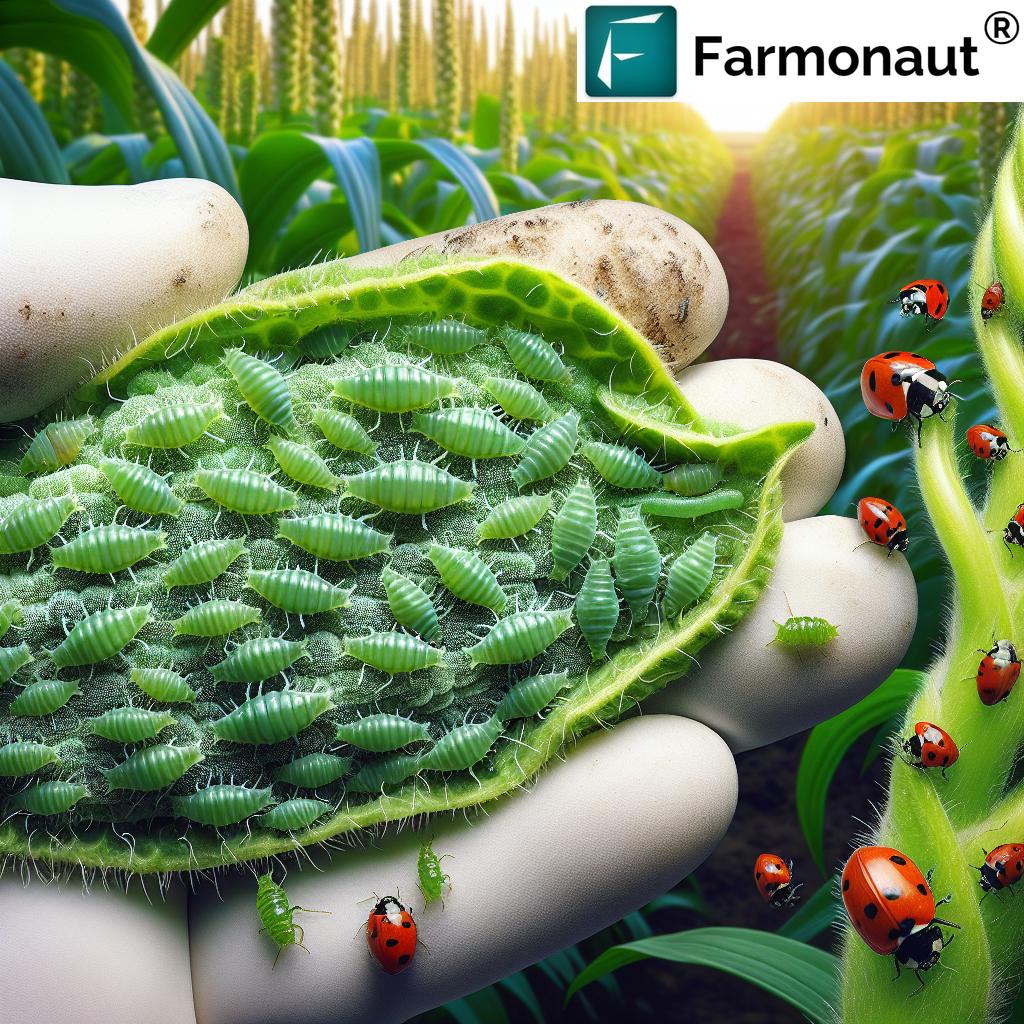
To manage aphids optimally, we must first understand their biology and impact on crops, forests, and ornamental plants. Aphids are small (1–10 mm), pear-shaped insects with soft bodies, forming dense colonies primarily on the undersides of tender leaves and shoots. Their rapid reproductive rate means that, left unchecked, populations can quickly reach damaging levels.
The Threat Aphids Pose
- Stunted Growth & Deformed Structures: Aphid feeding causes yellowed, curled or distorted leaves and impairs normal plant development.
- Honeydew Production: Aphids excrete sugary honeydew, which attracts other pests and promotes the development of sooty mold, further hampering photosynthesis.
- Virus Transmission: Aphids are important vectors of plant viruses, facilitating transmission and spread across large agricultural areas.
Signs of aphid infestation include:
- Curling, cupping, or discoloration of leaves
- Sticky residue (honeydew) on plant surfaces
- Presence of sooty mold
- Visible colonies or clusters on leaf undersides and shoots
- Stunted or distorted plant growth
Given these challenges, our emphasis must be on early detection and rapidly implementing the right aphid control methods to protect our crops and forests.
Integrated Pest Management for Aphids: Sustainable Approaches
Integrated pest management (IPM) for aphids represents the gold standard in sustainable agriculture, combining multiple methods for long-term, environmentally responsible management. Our IPM toolkit utilizes monitoring, cultural, biological, mechanical, chemical, and natural strategies—minimizing environmental impact and maximizing crop health.
1. Monitoring and Early Detection of Aphid Populations
Monitoring for aphid populations is essential. By regularly inspecting plants, we enable early detection of infestations—critical for effective intervention and minimizing aphid damage to plants:
- Visual Inspection: Examine the undersides of leaves and new shoots for the presence of aphid colonies, especially during early growth stages.
- Sticky Traps: Place yellow sticky traps in fields—these traps attract and monitor winged aphids, offering valuable insights into migration and population spikes.
- Noting Signs of Infestation: Detect curled, stunted leaves, honeydew accumulation, and sooty mold to act before populations become unmanageable.
Routine checks—weekly in high-risk seasons—are a cornerstone for preventing aphids in crops. For digital and remote sensing solutions, Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop health monitoring empowers farmers to monitor large areas, identify early stress symptoms, and act decisively.
Pro Tip: Implement a logbook or use digital tools to track aphid presence over time. This informs our management strategies, allowing us to understand outbreak patterns and anticipate seasonal threats.
2. Cultural Control Methods for Aphids
Cultural control methods—strategies built on smart agronomic practices—are among the most effective, low-cost ways to reduce aphid populations without harming the environment. Here’s how we can physically deter and hinder aphids:
- Choose Aphid-Resistant Varieties: Select plant species or cultivars less attractive or tolerant to aphid feeding.
- Proper Plant Spacing: Ensure adequate spacing between plants to reduce humidity and discourage colony establishment, especially in greenhouses or intensive cropping systems.
- Reflective Silver Mulches: Use reflective mulches beneath crops to repel aphids and prevent them from settling on tender shoots (source).
- Remove Plant Debris: Clean up crop residues and weeds that can harbor overwintering aphids or host alternate pest species.
- Timely Planting: Adjust planting dates to avoid periods of high aphid migration.
These approaches are highly compatible with all scales of agriculture, farming, and forestry.
3. Biological Control of Aphids
Biological control of aphids leverages nature’s own pest management solutions by encouraging or introducing predators and parasites. This approach offers a cornerstone in any integrated pest management plan:
- Lady Beetles (Ladybugs): Both larvae and adults feed voraciously on aphids, capable of clearing large populations rapidly.
- Lacewing Larvae & Hoverflies: These beneficial insects are renowned aphid predators. Introducing or conserving them helps keep aphid numbers under control.
- Parasitic Wasps (*Aphidius* species): Females lay their eggs inside aphids, which then become “mummies”—organisms that die and cease feeding, breaking the cycle. (source)
- Protecting Natural Enemies: Avoid broad-spectrum pesticides to prevent unintentional harm to these beneficial species.
One of the natural ways to control aphids is to plant nectar- and pollen-rich flowers near at-risk crops. These attract natural predators and keep populations in check. For IPM management across wide areas, using platforms that provide real-time insights on crop health—like Farmonaut’s advisory tools—help us target interventions and reduce unnecessary chemical applications.
4. Mechanical Control Methods for Aphids
For smaller plots and gardens, or during the early stages of infestation, mechanical controls are direct, immediate solutions to aphid outbreaks:
- Direct Water Sprays: Use a strong jet of water to dislodge aphids from leaves and stems. This reduces their numbers significantly, particularly when populations are low (source).
- Hand Removal: On small plants, crush or brush off aphid clusters, including removing infested plant parts.
- Pruning: Cut away heavily infested shoots or leaves and dispose of them away from crops to prevent the spread of aphids and secondary viruses.
These methods help prevent aphid populations from becoming established, especially in early detection and preventive frameworks.
Looking for large-scale management for commercial farms, forests, or plantations? Discover Farmonaut’s large-scale management solution for satellite-driven farm advisory, resource tracking, and data-based intervention planning.
5. Chemical Control of Aphids: Use Responsibly
We recommend chemical control of aphids only if other methods have not achieved sufficient results or populations threaten significant yield losses. Always choose targeted, eco-friendly options first:
- Insecticidal Soaps: Effective against aphids but safer for beneficial insects. Spray thoroughly, focusing on the undersides of leaves where colonies hide. (source)
- Neem Oil: A plant-based oil derived from the neem tree that disrupts aphid feeding, reproduction, and population growth. This is an organic, less toxic solution especially suitable for IPM systems. (Farmonaut neem oil usage details here)
Take care to:
- Always follow product label instructions and safety guidelines
- Minimize exposure to beneficial organisms
- Apply in the evening or early morning to avoid beneficial insect activity
For updates on safe pesticide use, integrated pest management trends, and customized remote advisory, don’t miss our developer API documentation for integration with your agri-applications and monitoring solutions.
6. Botanical and Natural Ways to Control Aphids
We recognize a growing demand for natural, chemical-free solutions that control aphids while protecting pollinators and biodiversity. Leading botanical pesticides and organic extracts include:
- Papaya Leaf Extracts: Research confirms papaya leaf extracts significantly reduce aphid populations on vegetable crops like okra, with minimal risk to beneficial insects. (source)
- Mint & Catnip Extracts: Mint and catnip essential oils act as natural repellents, driving aphids away from sensitive crops. (source)
- Garlic Spray: Homemade garlic-extract sprays deter aphids and other soft-bodied pests.
When trialing any botanical or natural product, always test first on a small area to ensure plant safety and avoid phytotoxicity.
7. Intercropping and Companion Planting
Finally, use intercropping and companion planting strategies which rely on plant diversity and ecosystem balance to disrupt aphid colonization:
- Intercropping: Combine different plant species in a single plot—this reduces monoculture susceptibility and provides habitat for aphid predators.
- Companion Planting: Grow onion family plants (garlic, chives), nasturtiums, or marigolds adjacent to main crops. These can repel aphids or act as “trap crops.” (source)
- Benefits: Enhanced habitat for natural enemies, improved soil health, and lower aphid pressure.
Such preventive methods help safeguard sensitive crops—including vegetables, fruit trees, cotton, and agroforestry plantations.
Comparison Table: Aphid Control Methods at a Glance
| Control Method | How It Works | Effectiveness (Est. % Aphid Reduction) | Eco-Friendliness (1-5) | Application Frequency (per season) | Best For (Crop Types) | Drawbacks/Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biological Control (Ladybugs, Lacewings, Parasites) | Release/encourage predators and parasites, which feed on or parasitize aphids | Up to 80% | 5 | 1–2 (boost with habitat plants) | Vegetables, fruit, field crops, forestry | Slow initial effect; impacted by pesticide use |
| Neem Oil Spray | Natural extract inhibits feeding and reproduction, deters colonies | 65–75% | 4 | 2–3 (as needed) | Vegetables, fruits, ornamentals | May harm bees if applied during bloom |
| Insecticidal Soap | Damages aphid membranes, causing rapid mortality | 70–85% | 3 | 3+ | Most crops, small/large scale | Non-target impacts if misapplied; repeat applications needed |
| Cultural Practices (Spacing, Resistant Varieties, Mulches) | Modify environment to make it less hospitable for aphids | 30–50% | 5 | 1 (design-stage) | All crops, forestry | Less effective alone during severe infestations |
| Water Sprays/Pruning | Physically removes aphids from plant surfaces | 40–60% | 4 | As needed | Gardens, greenhouses, orchards | Impractical for large fields; temporary effect |
| Botanical Extracts (Papaya, Mint, Catnip) | Plant-derived sprays deter or disable aphids | 50–70% | 5 | 2+ | Vegetables, okra, soft fruit | Phytotoxicity risk; variable effect |
| Intercropping & Companion Planting | Mix “repellent” or “trap” crops to disrupt aphid colonization and support natural enemies | 35–60% | 5 | 1 (planting-time) | Row crops, orchards, vegetable beds | Complex planning; inconsistent results if not combined with other methods |
Farmonaut Subscription Plans: Affordable Access to Precision Data for Crop Health, Pest and Aphid Management
Harness real-time satellite data for monitoring crop health, predicting pest risks, and optimizing IPM strategies. Suitable for farmers, cooperatives, agribusinesses, and governments.
Preventive Measures to Reduce Aphid Damage
An essential part of aphid control is building a preventive framework to reduce outbreaks before they start. We can minimize aphid risk—and thus viral transmission and yield loss—by taking these practical steps:
- Consistent Monitoring: Track signs of aphid infestation at least weekly. Speed is vital to preventing major damage.
- Healthy Plant Growth: Maintain balanced nutrition and regular irrigation. Robust plants resist aphid feeding and recover from minor attacks more quickly.
- Encourage Biodiversity: Foster a mix of plant species and beneficial insects to naturally suppress aphids (predator and prey balance).
- Sanitation: Remove plant debris and weeds asap after harvest to deny overwintering habitats.
Incorporate biodiversity-friendly tools like Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting tool to measure sustainability impacts and promote regenerative farming.
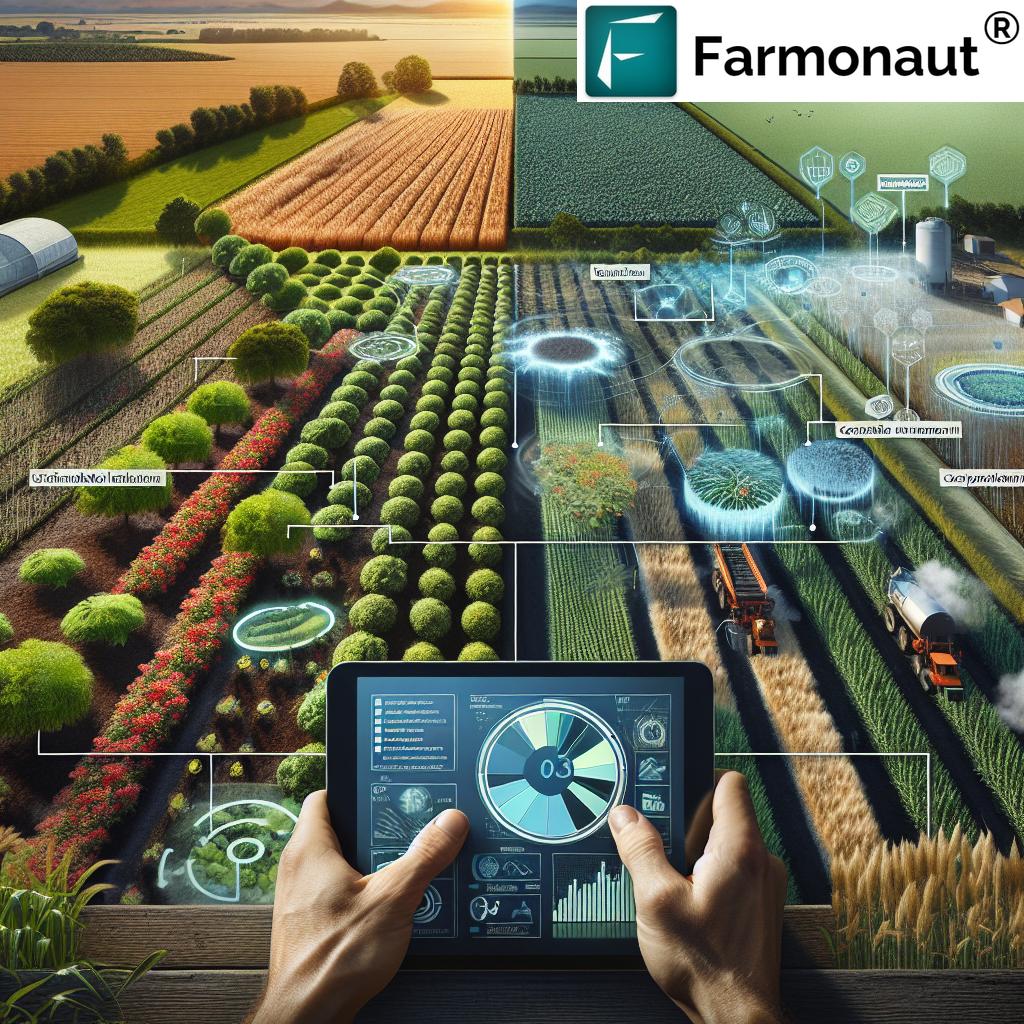
Technology in Aphid Management: Farmonaut’s Approach
Precision agriculture technologies are revolutionizing how we detect, monitor, and manage aphids and other pests. Farmonaut leads the field by providing accessible, satellite-powered tools and AI advisory for:
- Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring: Identify early plant stress, irregularities in canopy growth, or water anomalies—potential flags for aphid infestation—across large and small fields in real time (NDVI, Soil Moisture Maps).
- AI-Driven Pest Advisory: Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI delivers targeted advice based on satellite and weather data, improving decision-making for aphid control and resource optimization.
- Blockchain Traceability: Use product traceability solutions to guarantee sustainability in pest management and ensure all interventions are transparent from farm to consumer.
- Subscription-based Access: Options for individuals, co-ops, and large agribusinesses; API access for seamless integration into your existing ecosystem (learn more).
- Finance and Insurance: Accurate, satellite-based verification services empower banks to offer crop loans/insurance while reducing fraud risks and providing coverage for pest-related crop loss.
Ready to modernize your aphid and pest management? Experience comprehensive data-driven crop protection via Farmonaut’s multi-platform app.
FAQ: Aphid Control Methods & Management
1. What are the most effective natural ways to control aphids in crops?
Biological control (introduction and conservation of lady beetles, lacewings, and parasitoids) and the use of plant-based extracts (neem oil, papaya, mint) are highly effective and eco-friendly.
2. How can we detect aphid infestations early?
Regular monitoring—including visual inspections of leaves, yellow sticky traps, and satellite crop health scanning—enables early identification of signs of aphid infestation (deformed or curled leaves, honeydew, visible colonies).
3. When is it acceptable to use chemical control of aphids?
Apply insecticidal soaps or neem oil only when populations are high, early interventions have failed, and non-target impacts are minimized. Always prioritize IPM methods first.
4. How does integrated pest management (IPM) reduce reliance on chemical pesticides?
IPM strategies combine cultural, mechanical, biological, and targeted chemical controls—minimizing environmental and health hazards while achieving effective aphid population suppression.
5. Can technology help with large-scale aphid monitoring?
Yes! Farmonaut’s platform delivers satellite-driven insights and AI advisories for early stress detection, resource management, and timely intervention on even the largest plantations or forestry projects.
Conclusion: Building Sustainable Aphid Control Systems for Healthy Plants
Effective aphid control methods require a combination of science, experience, and commitment to sustainability. By focusing on integrated pest management for aphids—spanning early monitoring, cultural and botanical approaches, natural predators, and advanced technologies—we can reduce aphid populations, safeguard yields, and ensure healthy, resilient crops for the future.
Farmonaut empowers every stakeholder in agriculture, farming, and forestry with data-driven solutions that make professional-grade, environmentally responsible aphid management accessible, affordable, and scalable worldwide. Join us in building a more sustainable food system—where every plant can thrive and every farmer has the tools to succeed.
Ready to explore the future of pest management? Download the Farmonaut App, or explore our web, mobile, and API platforms for comprehensive, actionable crop insights today.