Best Alternaria Leaf Spot Treatment & Fungicide 2025: Effective Strategies for Sustainable Crop Protection
“Over 30% of global tomato yield losses are linked to Alternaria leaf spot without effective, sustainable fungicide strategies.”
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Call for Sustainable Alternaria Leaf Spot Treatment in 2025
- Understanding Alternaria Leaf Spot and Its Impact on Crop Production
- Recognizing Alternaria Leaf Spot: Key Symptoms Across Crops
- Best Treatment for Alternaria Leaf Spot: Integrated and Sustainable Approaches
- Best Alternaria Treatment Fungicide Guide for 2025
- Comparative Sustainability & Efficacy Table: Leading Treatments & Fungicides 2025
- Emerging Technologies: Precision Agriculture, Monitoring, and AI Solutions
- Future Perspectives: Innovations & Advances in Alternaria Leaf Spot Management
- Farmonaut’s Role in Sustainable Crop Protection
- FAQ: Alternaria Leaf Spot Treatment & Fungicide 2025
- Conclusion: Strategies for Effective Alternaria Control & Sustainable Agriculture
Introduction: The Call for Sustainable Alternaria Leaf Spot Treatment in 2025
Alternaria leaf spot continues to challenge farmers and agricultural professionals across the globe in 2025, impacting a wide range of crops including vegetables, cereals, and fruits. Caused by several species of the genus Alternaria—notably Alternaria solani and Alternaria alternata—this fungal disease leads to characteristic necrotic lesions on leaves. These spots reduce photosynthetic capacity and can ultimately diminish yield quality and quantity.
As stakeholders in modern agriculture, the pressure has never been higher to adopt sustainable practices for alternaria leaf spot treatment. Our mandate is clear: Protect crop yield and quality effectively, while minimizing environmental impact, reducing chemical overuse, and supporting long-term resilience.
This comprehensive guide brings together proven management strategies and advanced fungicides, offers a comparative sustainability table, and highlights technological and scientific advances for 2025. Whether you grow tomatoes, potatoes, cereals, or high-value fruits and vegetables, this is your roadmap to effective, sustainable alternaria species treatment and alternaria treatment fungicide decisions in the year ahead.
Understanding Alternaria Leaf Spot and Its Impact on Crop Production
Alternaria leaf spot is one of the most prevalent fungal diseases affecting agriculture today. The primary pathogens—Alternaria solani and Alternaria alternata—target plants under warm, humid conditions, making regions with such climates particularly vulnerable. Let’s break down how this disease develops and its consequences for farming communities.
- Species and Crops Affected: Key crops impacted include tomatoes, potatoes, carrots, cucurbits, brassicas, onions, cereals, legumes, apples, and pears.
- How Infection Spreads: Fungal spores are dispersed through wind, water, insects, and contaminated equipment. Infected debris is a major inoculum source.
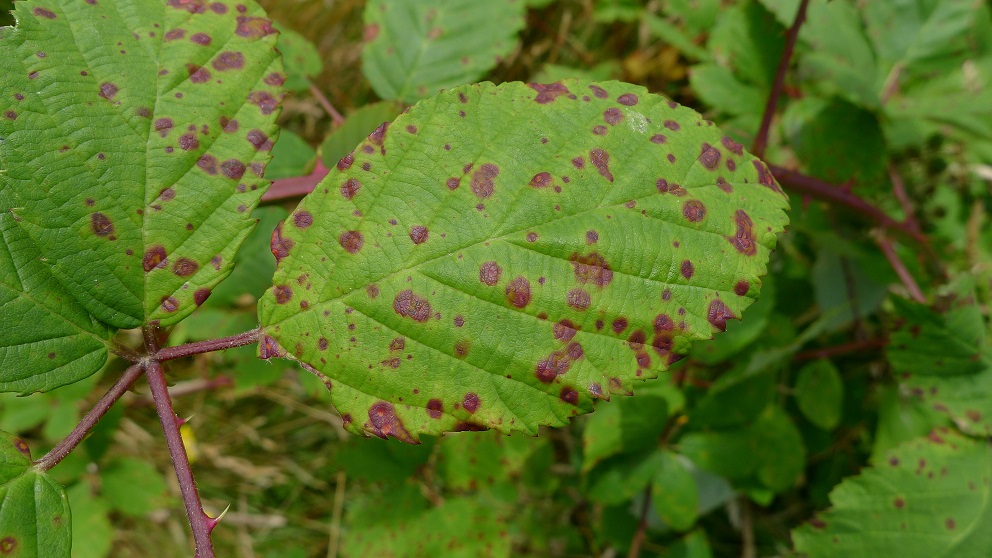
- Main Symptoms: Dark, concentric spots on leaves, often with yellow halos. Lesions coalesce, causing premature leaf drop and lowered photosynthetic capacity.
- Yield and Quality Losses: Both quantitative (yield) and qualitative (marketability, appearance) losses occur, harming profits throughout the supply chain.
- Secondary Impacts: Blemished produce lowers export and market value. Severe infection exposes tubers and fruits to secondary pathogens.
Economic and Environmental Implications
The economic implications of uncontrolled alternaria leaf spot are massive, affecting both farmers and input suppliers. Direct losses can exceed 30% in untreated fields, while secondary infections and post-harvest rot further erode returns. As consumers and markets demand sustainable food production, there’s a clear shift towards sustainable, integrated management approaches for long-term farm viability.
[Alternaria leaf spot treatment: Impact Snapshot]
- Total annual losses for tomatoes alone: Up to $3 billion globally
- Untreated outbreaks: Yield losses >30% depending on crop and region
- Current regulatory pressure: Limits on chemical residue in food and water
- Upcoming trend: Widespread adoption of best treatment for alternaria leaf spot that emphasizes environmental sustainability and reduced chemical input.
Recognizing Alternaria Leaf Spot: Key Symptoms Across Crops
Diagnosing Alternaria leaf spot accurately is crucial before adopting any alternaria species treatment. Bookmark this quick visual checklist for your fields:
- Symptoms on Leaves: Small, circular to angular spots, brown to black with concentric rings, characteristic of “target” pattern.
- Necrotic Lesions: These lesions often extend with age, sometimes merging together (coalesce).
- Yellow Halos: Faint yellow coloring or “halo” sometimes surrounds the spot.
- Foliage Drop: Severely infected leaves often yellow and drop prematurely; fruits/tubers become more vulnerable.
- Location: Commonly begins in older, lower leaves due to splashing water or soil contact.
- Crop-Specific Examples:
- Tomatoes: Dark brown spots, solani often causes rapid yellowing/dropping after extensive lesion formation.
- Potatoes: Large, sunken lesions with dark borders on leaves and tubers; can cause secondary tuber rot.
- Cucurbits, Brassicas, Onions, Fruits: Lesions of varying color and size (brown-black to grayish), rapid leaf decline under optimal disease conditions.
Regular and thorough scouting is the cornerstone of effective disease management—allowing for timely application of alternaria treatment fungicide or biocontrol measures.
Best Treatment for Alternaria Leaf Spot: Integrated and Sustainable Approaches
To ensure sustainable crop protection and reduce dependency on chemical fungicides, alternaria leaf spot treatment in 2025 emphasizes integrated management strategies that blend cultural practices, optimized use of fungicides, effective biological agents, and cutting-edge technologies. Here’s an overview of the most reliable and sustainable approaches for alternaria species treatment this year:
1. Cultural Practices: Prevention is the Cornerstone
- Crop Rotation: Alternate with non-hosts (e.g., cereals after solanaceous crops) to break the inoculum cycle.
- Sanitation: Remove infected crop debris and volunteer plants at season end.
- Improving Air Circulation: Maintain proper plant spacing, perform rational pruning, and avoid dense planting.
- Watering Strategy: Use drip irrigation to avoid prolonged leaf wetness; water early to allow drying.
- Resistant Varieties: Whenever possible, choose disease-resistant or tolerant cultivars. Breeding advances in 2025 have significantly expanded the seed options for major crops.
- Soil Health: Rotate crops and use cover crops/organic matter to enhance microflora that suppresses alternaria development.
Cultural methods alone can reduce disease pressure before any fungicide or biological agent is applied—making them crucial for sustainable agriculture.
2. Fungicides: Intelligent Use & Rotational Programs
-
Broad-Spectrum Protectants:
Chlorothalonil, mancozeb, and copper-based formulations remain widely used for their high efficacy against Alternaria leaf spot in many crops. -
Systemic Fungicides:
Modern strobilurins (like azoxystrobin), triazoles (like difenoconazole), and SDHIs offer strong curative and preventive activity, often at lower doses. -
Fungicide Formulation Advances (2025):
- Microencapsulation for controlled release and minimal drift.
- Lipid-based and water-dispersible granules for targeted coverage and lower human/ecological risk.
- Resistance Management: Rotate fungicides with different modes of action, and avoid repeated single-product application.
- Mixtures: Combine protectants and systemics for broader spectrum and lower resistance development potential.
- Application Timing: Begin spraying at first sign of infection or when weather conditions favor Alternaria development. Adhere strictly to re-application intervals and harvest safety intervals.
With increased regulatory scrutiny, always check local restrictions—and consider integrating biological or low-residue options into your program where possible.
3. Biological Control: Sustainable Alternatives
- Bacillus subtilis: Competes with alternaria, produces antifungal metabolites, and is approved for use in organic agriculture.
- Trichoderma harzianum: Highly effective mycoparasite that colonizes plant surfaces and inhibits alternaria spore germination.
- Pseudomonas fluorescens: Induces systemic resistance in plants against a range of fungal pathogens.
- Mode of Delivery: Typically as seed/soil treatments, foliar sprays, or in compost teas. Their use reduces chemical residues and avoids disrupting beneficial soil life.
- Fit Within Integrated Management: Best results observed when biocontrols are combined with reduced chemical or biochemical fungicide programs.
Consumers increasingly demand produce with low chemical residue, further accelerating adoption of biological agents for alternaria leaf spot treatment.
4. Integrated Disease Management: Optimized Alternaria Leaf Spot Treatment
Integrated programs combine cultural, chemical, biological, and monitoring strategies for the best treatment for alternaria leaf spot. The aim is not just to control the disease but to promote sustainable agriculture, improve resilience, and protect long-term production.
- Alternating Biologicals & Fungicides: Reduces risk of resistance, maintains efficacy, lowers residue and input cost
- Precision Spraying: Applies chemicals or biologicals only where and when needed (see Emerging Technologies below).
- Record Keeping: Use digital platforms (like Farmonaut’s Large-Scale Farm Management tools) for accurate tracking of intervention success, input use, and scouting.
“In 2025, eco-friendly fungicides are projected to reduce Alternaria leaf spot severity by up to 60% in field trials.”
Best Alternaria Treatment Fungicide Guide for 2025
With advances in agricultural science and product formulation, farmers today can choose from a wide array of alternaria leaf spot treatment fungicides. Here, we highlight leading families and application recommendations aligned with 2025 sustainability goals.
Top Fungicide Classes for Alternaria Disease Control
- Chlorothalonil (Broad-spectrum protectant): Excellent for early and late blight in vegetables and fruits; ensure compliance with residue limits.
- Mancozeb (Dithiocarbamate group): Popular for solanaceous crops; optimal when alternated with other classes.
- Azoxystrobin (Strobilurin): Systemic, long-lasting effect with lower environmental impact and broad crop registration.
- Difenoconazole (Triazole): Effective as a curative and preventive; rotate to prevent resistance.
- Copper-based (e.g., copper hydroxide, copper oxychloride): Suitable for organic usage but watch for copper accumulation.
- Bio-fungicides (Bacillus, Trichoderma, Pseudomonas-based): Generally safe, low-residue, with short pre-harvest intervals and organic certification.
- Plant Extracts/Essential Oils (e.g., thyme, neem): Gaining ground for use in integrated organic programs.
See the Comparative Sustainability & Efficacy Table below for a detailed side-by-side comparison of industry-leading options.
Comparative Sustainability & Efficacy Table: Leading Treatments & Fungicides 2025
| Treatment/Fungicide Name | Formulation Type | Estimated Efficacy (%) | Environmental Impact | Application Frequency | Residue Risk | Organic Certification Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorothalonil | Contact Protectant | 85-90% | Medium | 7–10 days, or as per label | High | No |
| Mancozeb | Contact Protectant | 75-90% | Medium | 7 days | Medium | No |
| Azoxystrobin | Systemic/Strobilurin | 90% | Low-Medium | 10–14 days | Medium | No |
| Difenoconazole | Triazole (Systemic) | 85-88% | Medium | 10–14 days | Medium | No |
| Copper Hydroxide/Oxychloride | Contact/Protectant | 70-80% | High (build-up hazard) | 7 days | Medium-High | Yes |
| Bacillus subtilis (Bio-fungicide) | Biological/Spore-based | 70-78% | Low | 5–7 days (foliar) | Low | Yes |
| Trichoderma harzianum | Biological/Mycoparasite | 68-75% | Low | Every 10–15 days | Low | Yes |
| Pseudomonas fluorescens | Biological (Bacteria) | 65-72% | Low | 5–7 days | Low | Yes |
| Essential Oil Formulations (e.g., thyme, neem) | Botanical Extract | 55–65% | Very Low | 5–7 days | Low | Yes |
Note: Efficacy percentages are estimated ranges based on 2025 research and field reports. Always check regional regulations and current resistance status for each fungicide. Full integration of biologicals plus protectants is recommended for best treatment for alternaria leaf spot with minimized residue and impact.
Emerging Technologies: Precision Agriculture, Monitoring, and AI Solutions
The future of alternaria leaf spot control is increasingly data-driven. Precision agriculture, real-time disease monitoring, and blockchain-based traceability reduce waste, lower costs, and maximize efficacy for every dollar spent. These are the technologies reshaping sustainable disease management for 2025 and beyond:
- Drones & Satellite Monitoring: The use of drones and satellite imagery enables rapid, non-invasive detection of disease hotspots. Satellite solutions—like those provided by Farmonaut—offer precise imagery, analysis, and environmental footprint tracking for farms and fields, helping growers fine-tune fungicide usage and minimize environmental runoff.
- AI-based Disease Prediction: Cutting-edge artificial intelligence models integrate weather data and historical outbreaks to predict optimal intervention points—facilitating timely alternaria treatment fungicide application.
- Blockchain Traceability: Digital tracking (see Farmonaut’s Traceability platform) ensures food products are authentic, sustainably sourced, and meet global standards for residue and ethical sourcing—improving access to premium export markets.
- Fleet and Resource Management: For large farms, optimized logistics provided by tools such as Farmonaut Fleet Management helps schedule spraying, harvesting, and post-harvest operations with efficiency and precision, ensuring resources are used only as needed.
- Loan and Insurance Access: Satellite-based verification from providers like Farmonaut Crop Loan and Insurance enhances smallholder and commercial farmer access to finance, essential during major disease outbreaks that threaten yields and income.
- APIs for Custom Solutions: Integrate real-time field and environmental monitoring into your systems using Farmonaut’s Satellite API or detailed guide at Farmonaut API Developer Docs to power tailored agri-digital solutions.
By embracing these technologies, agriculture stakeholders will realize higher productivity, improved disease outcomes, and better stewardship of environmental resources.
Future Perspectives: Innovations & Advances in Alternaria Leaf Spot Management
The next decade will see transformation in how we approach alternaria leaf spot treatment. Here are forward-looking trends and breakthroughs to watch:
- Genetic Approaches: CRISPR-based editing and R-gene introgression are producing crops with built-in resistance to Alternaria species.
- Next-Gen Biologicals: Research is expanding on microbial consortia (blends of bacteria, fungi, and beneficial yeasts) delivering multi-pathogen control—and on plant peptides that prime immune signaling.
- Natural Fungicide Discovery: Screening of plant extracts for new antifungal actives continues apace, with several eco-friendly products set for regulatory approval in 2026 and beyond.
- Digital and Remote-First Farm Management: Apps and web platforms like those offered by Farmonaut Large Scale Farm Management are empowering larger numbers of growers to track and adapt disease management practices with near-real time insights.
- Blockchain-enabled Supply Chains: As global buyers prioritize traceable, certified produce, platforms with blockchain at their core ensure compliance and win new markets.
Farmonaut’s Role in Sustainable Crop Protection
At Farmonaut, we are committed to supporting sustainable agriculture by making advanced satellite-based monitoring, AI-driven advisory, and blockchain-enabled traceability accessible and affordable to farmers, businesses, and governments worldwide.
- Satellite-Based Monitoring: With multispectral imagery, we provide real-time insights on field health, disease outbreaks, and environmental impact—directly supporting alternaria leaf spot treatment decisions and overall crop protection.
- Jeevn AI Advisory: Our AI-powered platform delivers disease risk forecasts and tailored intervention guidelines based on satellite-data analytics—aligning treatment timing with weather and disease cycles to minimize unnecessary input use.
- Blockchain for Traceability: Our solutions enable farmers and agribusinesses to guarantee the sustainability and authenticity of their crops throughout the supply chain.
- Resource & Environmental Impact Tracking: Our carbon footprint monitoring feature empowers growers and organizations to meet strict environmental standards by tracking emissions and resource use.
- Fleet and Large-scale Management Tools: Web and mobile app access makes it easy for both individual and enterprise operations to optimize logistics and farm-wide disease control from anywhere.
By utilizing these tools, agricultural professionals can maximize yield and quality, minimize environmental footprint, and meet consumer and regulatory demands for eco-friendly crop protection.
FAQ: Alternaria Leaf Spot Treatment & Fungicide 2025
1. What is the best treatment for alternaria leaf spot in 2025?
The best approach is integrated management combining preventive cultural practices, alternaria treatment fungicides (like azoxystrobin, mancozeb, bio-fungicides), biological agents (e.g., Bacillus subtilis), and high-tech monitoring.
2. How can I reduce fungicide resistance in alternaria species?
Alternate fungicide modes of action, limit total number of chemical applications, integrate biologicals, and follow recommended application intervals.
3. Are eco-friendly or organic fungicides effective?
Yes, field trials in 2025 project up to 60% reduction in alternaria leaf spot severity using certified bio-fungicides or essential oil-based products as part of an integrated plan.
4. Which crops are most threatened by alternaria disease?
Tomatoes, potatoes, carrots, brassicas, onions, cucurbits, apples, and cereals are especially vulnerable in warm, humid regions.
5. Can remote monitoring help with alternaria leaf spot management?
Absolutely. Technologies like Farmonaut’s app platform deliver real-time disease alerts, crop health mapping, and environmental impact assessments for precise and timely interventions that save resources and reduce losses.
6. What resources are available for large-scale or enterprise farming?
Platforms such as Farmonaut’s Large-scale Farm Management offer advanced crop monitoring, logistical tools, and disease tracking for multi-field and cross-region operations.
Conclusion: Strategies for Effective Alternaria Control & Sustainable Agriculture
Alternaria leaf spot remains a significant threat to crop yield and quality in 2025, affecting a wide range of crops across all major growing regions. However, by adopting an integrated approach—merging best cultural practices, strategic fungicide application, biocontrol agents, and precision monitoring technologies—farmers and agricultural stakeholders can effectively protect crops, preserve environmental health, and ensure long-term resilience in a changing climate.
Our mission is to empower the global agriculture community with actionable insights and advanced digital tools to tackle alternaria leaf spot and other fungal diseases—driving both productivity and sustainability for generations to come.
Ready to implement the best practices for 2025? Start with precise disease monitoring, optimize your pesticide program, and unlock next-gen farm management and traceability with Farmonaut’s satellite-driven platform today.