Cotton Leaf Hopper: Identifying, Managing, and Preventing Hopper Burn in Your Cotton Crop

As agricultural technology experts at Farmonaut, we understand the challenges that cotton farmers face when dealing with pests like the cotton leaf hopper. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about this destructive pest, from identification to management strategies, and how our satellite-based farm management solutions can help you protect your cotton crops.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Cotton Leaf Hopper
- Identifying Cotton Leaf Hopper Damage
- The Impact of Hopper Burn in Cotton
- Management Strategies for Cotton Leaf Hopper
- Farmonaut’s Role in Pest Management
- Preventing Cotton Leaf Hopper Infestations
- FAQs
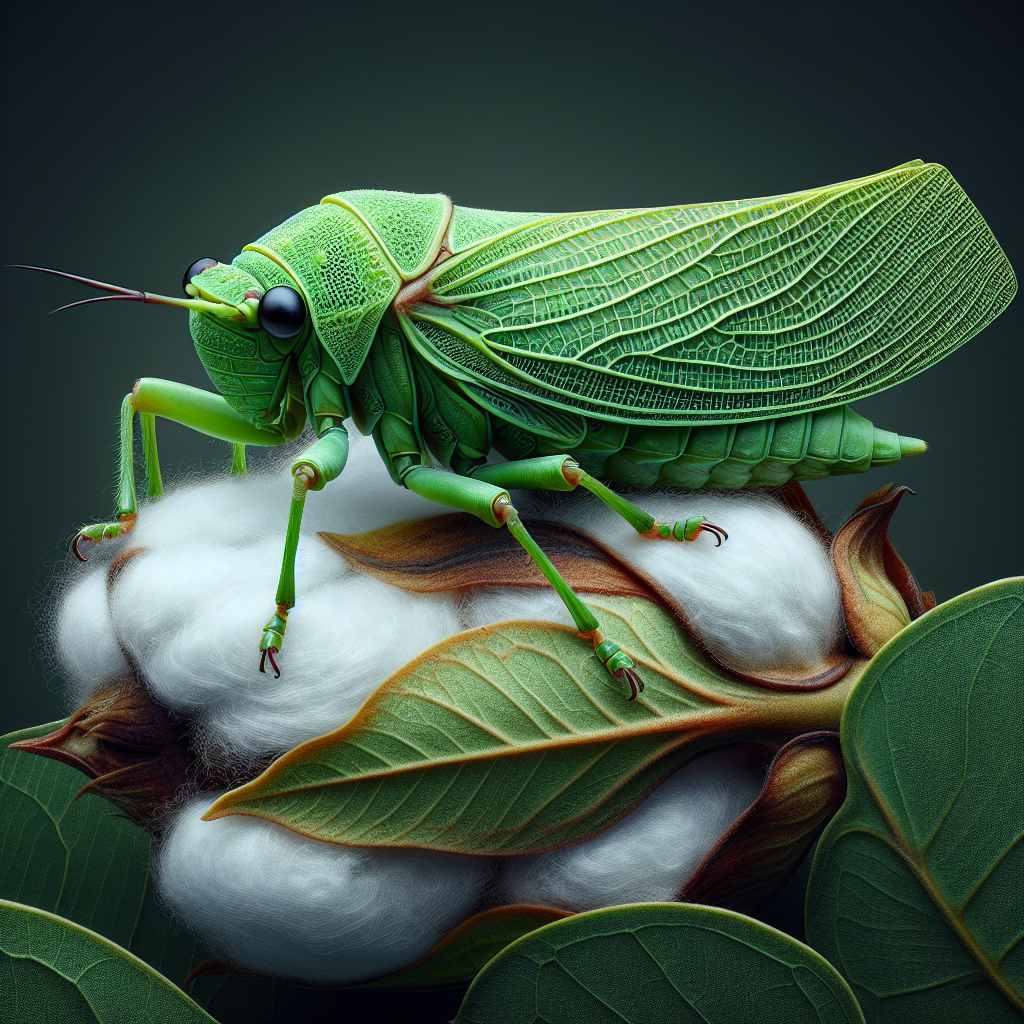
1. Understanding the Cotton Leaf Hopper
The cotton leaf hopper, also known as the cotton hopper or simply leaf hopper in cotton, is a small but formidable pest that can cause significant damage to cotton crops. To effectively manage this pest, it’s crucial to understand its characteristics and behavior.
Cotton Leaf Hopper Scientific Name
The cotton leaf hopper scientific name is Amrasca biguttula biguttula (Ishida). This species belongs to the family Cicadellidae and is commonly found in cotton-growing regions across Asia and parts of Africa.
Physical Characteristics
- Size: Adults are typically 2-3 mm long
- Color: Pale green to yellowish-green
- Wings: Transparent wings folded tent-like over the body
- Movement: Quick, often moving sideways when disturbed
Life Cycle
Understanding the life cycle of the cotton leaf hopper is essential for implementing effective control measures:
- Eggs: Females lay eggs inside the leaf tissue, typically along the leaf veins.
- Nymphs: After hatching, nymphs go through five instars over 10-14 days.
- Adults: The adult stage lasts for about 30-40 days.
The entire life cycle from egg to adult takes approximately 15-25 days, depending on environmental conditions. This rapid life cycle allows for multiple generations within a single cotton growing season, making early detection and management crucial.
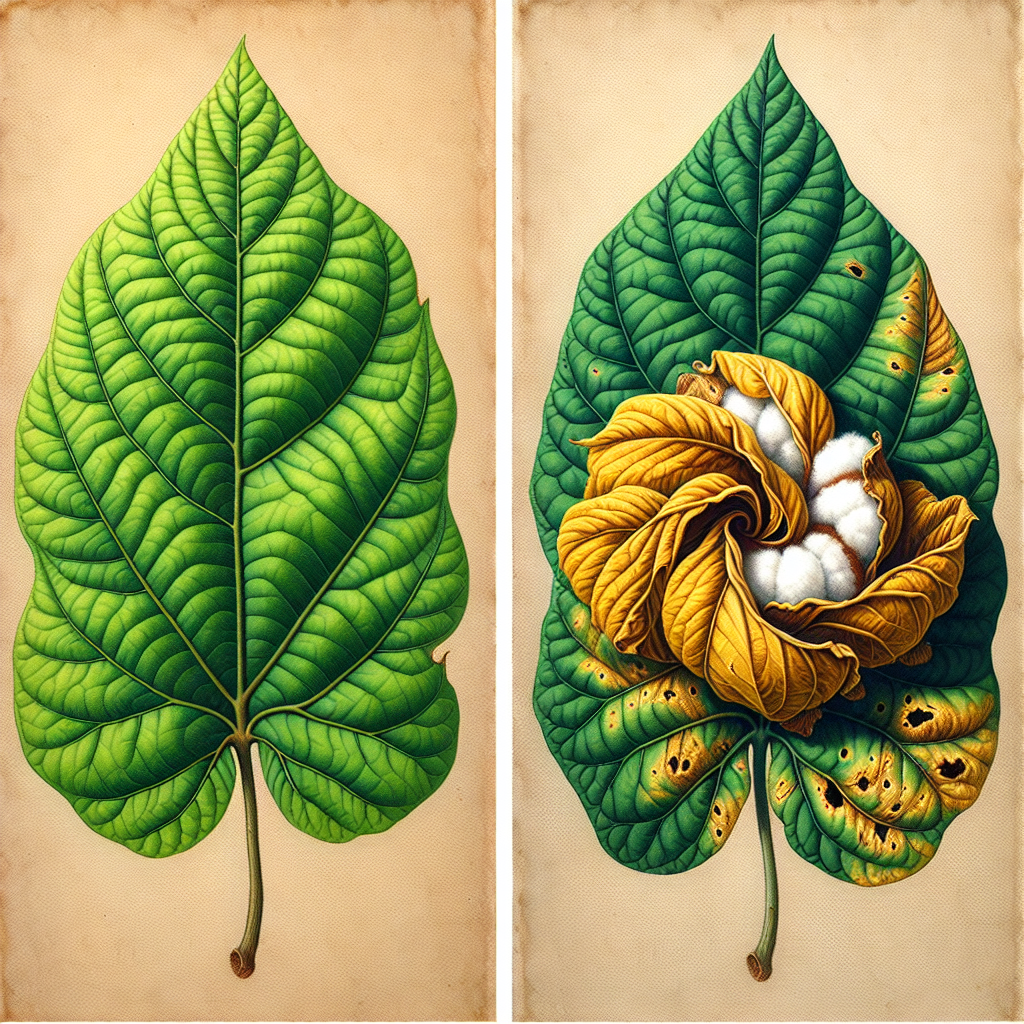
2. Identifying Cotton Leaf Hopper Damage

Recognizing the signs of cotton leaf hopper infestation is the first step in effective pest management. Here are the key indicators to look out for:
Visual Symptoms
- Leaf Curling: Infested leaves curl downwards and inwards, giving them a cup-like appearance.
- Yellowing: Leaves may develop a yellowish tinge, particularly around the edges.
- Stunted Growth: Affected plants often show reduced growth and may appear smaller than healthy plants.
- Reduced Flowering: Severe infestations can lead to fewer flowers and, consequently, reduced cotton yield.
Hopper Burn in Cotton
One of the most distinctive signs of cotton leaf hopper infestation is hopper burn in cotton. This phenomenon occurs due to the feeding behavior of the pest:
- Initial Damage: Leaf hoppers inject their saliva into the plant while feeding, which contains toxins.
- Physiological Response: The plant’s vascular system reacts to these toxins, leading to impaired nutrient transport.
- Visible Symptoms: Leaves begin to show reddish-brown discoloration, starting from the edges and progressing inwards.
- Advanced Stages: In severe cases, entire leaves may dry up and fall off, significantly impacting the plant’s ability to photosynthesize.
Hopper burn is not just a cosmetic issue; it significantly impacts the plant’s health and productivity. Early detection of these symptoms is crucial for implementing timely control measures.
3. The Impact of Hopper Burn in Cotton
The effects of hopper burn extend far beyond visible leaf damage. Let’s delve into the comprehensive impact of this pest on cotton crops:
Physiological Effects
- Reduced Photosynthesis: Damaged leaves have a decreased ability to perform photosynthesis, leading to reduced energy production for the plant.
- Nutrient Deficiency: The impaired vascular system struggles to transport nutrients effectively throughout the plant.
- Water Stress: Leaf damage can lead to increased water loss, making plants more susceptible to drought stress.
Economic Impact
The economic consequences of cotton leaf hopper infestations can be severe:
- Yield Reduction: Severe infestations can lead to yield losses of up to 50% in untreated fields.
- Quality Degradation: The fiber quality of affected plants may be compromised, leading to lower market prices.
- Increased Production Costs: Managing infestations often requires additional pesticide applications and labor, increasing overall production costs.
- Long-term Effects: Repeated infestations can weaken plants, making them more susceptible to other pests and diseases in subsequent seasons.
Environmental Considerations
While the immediate focus is often on crop protection, it’s important to consider the broader environmental implications:
- Pesticide Use: Increased reliance on chemical controls can impact beneficial insects and soil health.
- Ecosystem Disruption: Large-scale infestations can disrupt local ecosystems, affecting other plant and animal species.
- Resistance Development: Overuse of certain pesticides can lead to resistance in leaf hopper populations, making future management more challenging.
Given these wide-ranging impacts, it’s clear that effective management of cotton leaf hoppers is not just about protecting current crops, but also about ensuring sustainable cotton production for the future.
4. Management Strategies for Cotton Leaf Hopper
At Farmonaut, we advocate for an integrated pest management (IPM) approach to controlling cotton leaf hoppers. This strategy combines various methods to effectively manage pest populations while minimizing environmental impact and preserving the long-term productivity of your cotton fields.
Cultural Control Methods
- Crop Rotation: Alternating cotton with non-host crops can break the pest’s life cycle.
- Planting Dates: Adjusting planting dates to avoid peak leaf hopper activity periods.
- Field Sanitation: Removing crop residues and weeds that can harbor leaf hoppers.
- Water Management: Proper irrigation practices can help plants withstand pest pressure.
Biological Control
Encouraging natural predators can help keep leaf hopper populations in check:
- Predatory Insects: Ladybugs, lacewings, and predatory wasps feed on leaf hoppers.
- Parasitoids: Certain wasp species parasitize leaf hopper eggs and nymphs.
- Conservation Practices: Maintaining diverse vegetation around cotton fields can provide habitat for beneficial insects.
Chemical Control
While we emphasize sustainable practices, chemical control may be necessary in severe infestations:
- Selective Insecticides: Choose products that target leaf hoppers while minimizing impact on beneficial insects.
- Timing: Apply insecticides when leaf hopper populations reach economic threshold levels.
- Rotation: Alternate between different classes of insecticides to prevent resistance development.
Resistant Varieties
Planting cotton varieties with natural resistance to leaf hoppers can be an effective long-term strategy:
- Hairy Leaf Varieties: Cotton plants with hairy leaves are less attractive to leaf hoppers.
- Tolerant Cultivars: Some cotton varieties can withstand higher leaf hopper populations without significant yield loss.
- Ongoing Research: Plant breeders are continually developing new varieties with enhanced pest resistance.
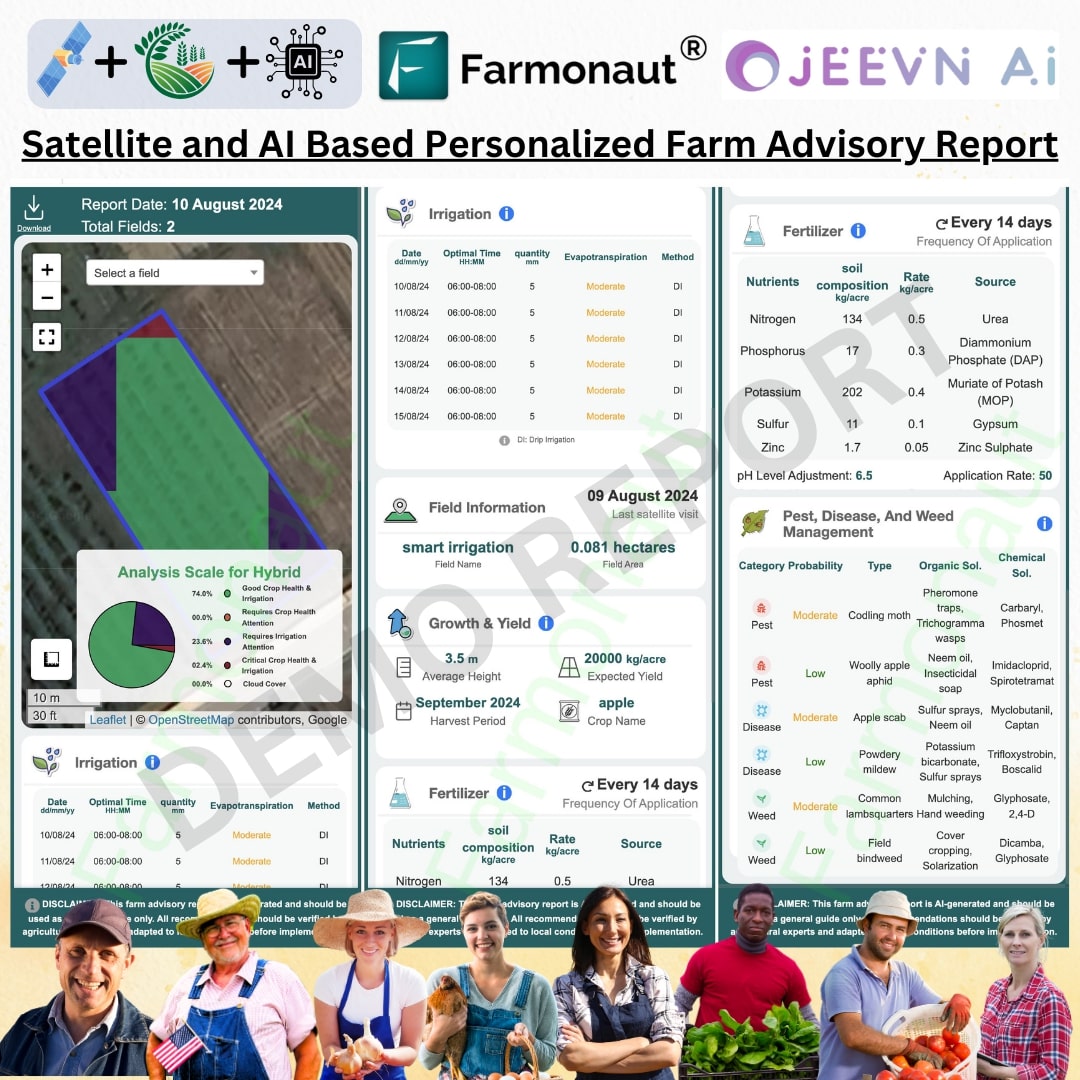
5. Farmonaut’s Role in Pest Management
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to empowering farmers with cutting-edge technology to enhance pest management strategies. Our satellite-based farm management solutions offer several advantages in the fight against cotton leaf hoppers:
Early Detection
- Vegetation Health Monitoring: Our satellite imagery can detect changes in crop health before visible symptoms appear.
- NDVI Analysis: We use Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) to identify areas of stress in cotton fields, which could indicate pest infestations.
- Historical Data Comparison: By comparing current field conditions with historical data, we can identify anomalies that may signal pest problems.
Precision Application
Our technology enables more targeted and efficient pest control measures:
- Zone Management: We help identify specific areas within fields that require treatment, reducing overall pesticide use.
- Variable Rate Application: Our data can guide variable rate technology for more precise pesticide application.
- Timing Optimization: By analyzing weather data and pest life cycles, we can recommend optimal timing for control measures.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Farmonaut’s platform provides comprehensive data to inform your pest management strategies:
- Real-time Monitoring: Access up-to-date information on crop health and potential pest hotspots.
- Predictive Analytics: Our AI-powered system can forecast potential pest outbreaks based on environmental conditions.
- Integration with IPM: Our data seamlessly integrates with integrated pest management practices, enhancing their effectiveness.
Farmonaut vs. Traditional Monitoring Methods
| Feature | Farmonaut Satellite System | Drone-based Monitoring | IoT-based Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage Area | Entire fields at once | Limited by flight time and regulations | Dependent on sensor placement |
| Frequency of Data Collection | Daily to weekly updates | As needed, requires manual flights | Continuous, but localized |
| Weather Independence | Can operate in most weather conditions | Limited by wind and precipitation | Weather-resistant, but may have connectivity issues |
| Data Processing | Automated, AI-powered analysis | Often requires manual interpretation | Automated, but may require calibration |
| Cost Efficiency | High (no hardware investment required) | Moderate (equipment and operator costs) | Variable (depends on number of sensors) |
| Scalability | Easily scalable to large areas | Limited by equipment and manpower | Requires additional sensor deployment |
To experience the power of Farmonaut’s satellite-based farm management solutions, visit our app or explore our API services. Our platform is available on both Android and iOS devices.
6. Preventing Cotton Leaf Hopper Infestations
While effective management is crucial, preventing cotton leaf hopper infestations in the first place is the ideal scenario. Here are some proactive measures that can help reduce the risk of infestations:
Crop Planning and Field Preparation
- Crop Rotation: Plan a rotation schedule that includes non-host crops to break the pest cycle.
- Field Sanitation: Thoroughly clean fields after harvest to remove potential overwintering sites.
- Soil Health: Maintain good soil health to promote strong, resilient plants that can better withstand pest pressure.
Planting Strategies
- Resistant Varieties: Choose cotton varieties known for leaf hopper resistance or tolerance.
- Planting Dates: Time planting to avoid peak leaf hopper activity periods in your region.
- Plant Density: Maintain appropriate plant spacing to promote air circulation and reduce humidity.
Cultural Practices
Implement cultural practices that create an environment less favorable to leaf hoppers:
- Weed Management: Control weeds in and around cotton fields, as they can serve as alternate hosts for leaf hoppers.
- Intercropping: Consider intercropping with non-host plants that may repel or confuse leaf hoppers.
- Border Crops: Plant trap crops or repellent plants around field edges to intercept incoming leaf hoppers.
Monitoring and Early Detection
Regular monitoring is key to preventing severe infestations:
- Scouting: Implement a regular scouting program to detect leaf hoppers early in the season.
- Traps: Use yellow sticky traps to monitor leaf hopper populations.
- Satellite Monitoring: Utilize Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring to detect early signs of crop stress that may indicate pest activity.
Biological Diversity
Encourage a diverse ecosystem that supports natural pest control:
- Beneficial Insects: Create habitats for predatory insects that feed on leaf hoppers.
- Plant Diversity: Maintain diverse vegetation around cotton fields to support a range of beneficial organisms.
- Minimal Pesticide Use: Limit broad-spectrum pesticide use to preserve natural enemy populations.
Water and Nutrient Management
Proper plant care can enhance resistance to pest pressure:
- Irrigation: Avoid over-irrigation, which can create favorable conditions for leaf hoppers.
- Balanced Nutrition: Ensure plants receive balanced nutrition to promote overall health and resilience.
- Foliar Sprays: Consider using nutrient foliar sprays to strengthen plant defenses.
Collaborative Efforts
Work with neighboring farmers and local agricultural agencies:
- Area-wide Management: Coordinate pest management efforts with nearby farmers to reduce overall pest pressure in the region.
- Information Sharing: Participate in local pest monitoring networks to stay informed about regional pest trends.
- Training Programs: Attend workshops and training sessions to stay updated on the latest prevention strategies.
By implementing these preventive measures and leveraging Farmonaut’s advanced monitoring capabilities, you can significantly reduce the risk of cotton leaf hopper infestations and protect your cotton crops more effectively.
7. FAQs
Q: What is the cotton leaf hopper scientific name?
A: The scientific name for the cotton leaf hopper is Amrasca biguttula biguttula (Ishida).
Q: How can I identify leaf hopper in cotton?
A: Look for small (2-3 mm), pale green to yellowish-green insects on the undersides of leaves. Signs of infestation include leaf curling, yellowing, and the characteristic “hopper burn” symptom.
Q: What causes hopper burn in cotton?
A: Hopper burn is caused by the feeding activity of cotton leaf hoppers. Their saliva contains toxins that disrupt the plant’s vascular system, leading to reddish-brown discoloration of leaves, starting from the edges.
Q: How can Farmonaut help in managing cotton leaf hoppers?
A: Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring system can detect early signs of crop stress, enable precise pest management, and provide data-driven insights for more effective integrated pest management strategies.
Q: Are there any natural predators of the cotton leaf hopper?
A: Yes, natural predators include ladybugs, lacewings, and certain species of predatory wasps. Encouraging these beneficial insects can help control leaf hopper populations.
Q: How often should I monitor my cotton fields for leaf hoppers?
A: Regular monitoring is crucial. We recommend weekly scouting during the growing season, with more frequent checks during peak pest activity periods or when environmental conditions favor leaf hopper development.
Q: Can resistant cotton varieties completely prevent leaf hopper infestations?
A: While resistant varieties can significantly reduce the risk and severity of infestations, they may not provide complete protection. They should be used as part of an integrated pest management approach.
Q: How does climate change affect cotton leaf hopper populations?
A: Climate change can potentially lead to expanded ranges for leaf hoppers, altered life cycles, and increased generations per season. This makes ongoing monitoring and adaptive management strategies even more important.
Q: Are organic control methods effective against cotton leaf hoppers?
A: Organic methods such as using neem-based products, introducing beneficial insects, and implementing cultural controls can be effective, especially when used preventively and in combination.
Q: How can I access Farmonaut’s services for my cotton farm?
A: You can access our services through our mobile app available on Android and iOS, or through our web platform. For developers interested in integrating our data, check out our API documentation.
Conclusion
Managing cotton leaf hoppers and preventing hopper burn in cotton requires a comprehensive, integrated approach. By combining traditional pest management techniques with advanced satellite monitoring from Farmonaut, cotton farmers can significantly improve their crop protection strategies. Remember, early detection and timely intervention are key to minimizing the impact of these destructive pests.
For more information on how Farmonaut can help you protect your cotton crops and optimize your farm management, explore our subscription options below:
By leveraging our satellite-based farm management solutions, you’ll be better equipped to tackle the challenges posed by cotton leaf hoppers and other pests, ensuring healthier crops and better yields for your cotton farm.