Dark Aphids: Identifying and Managing These Pesky Pests in Your Crops

As farmers and agricultural experts, we at Farmonaut understand the challenges that pests pose to crop health and yield. Among these pests, dark aphids are particularly troublesome due to their rapid reproduction and ability to cause significant damage. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about dark colored aphids and dark green aphids, including identification, management strategies, and how our satellite-based technology can help you combat these tiny invaders.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Dark Aphids
- Identifying Dark Aphids in Your Crops
- The Lifecycle of Dark Aphids
- Damage Caused by Dark Aphids
- Natural Predators of Dark Aphids
- Integrated Pest Management Strategies
- Chemical Control Methods
- Organic Control Methods
- Preventing Dark Aphid Infestations
- How Farmonaut Can Help in Aphid Management
- FAQs About Dark Aphids
1. Understanding Dark Aphids
Dark aphids, including dark colored aphids and dark green aphids, are small, soft-bodied insects that belong to the superfamily Aphidoidea. These pests are a common problem for farmers and gardeners worldwide, affecting a wide range of crops and ornamental plants.
While there are thousands of aphid species, those with darker coloration are often more challenging to spot and can cause significant damage before they’re noticed. Some common species of dark aphids include:
- Black bean aphid (Aphis fabae)
- Black cherry aphid (Myzus cerasi)
- Dark green peach aphid (Myzus persicae)
- Black citrus aphid (Toxoptera aurantii)
Understanding the characteristics and behavior of these pests is crucial for effective management and control.
2. Identifying Dark Aphids in Your Crops

Identifying dark aphids can be challenging due to their small size and ability to blend in with plant structures. However, there are several key characteristics to look out for:
- Size: Dark aphids are typically 1-3 mm in length.
- Color: As the name suggests, they range from dark green to black.
- Body shape: Pear-shaped bodies with long antennae.
- Cornicles: Two small tubes projecting from the rear of the abdomen.
- Wings: Most are wingless, but some develop wings for migration.
- Clustering: They often gather in dense groups on plant stems and leaves.
To effectively spot dark aphids, we recommend regular inspection of your crops, paying close attention to the undersides of leaves, young shoots, and flower buds. Using a magnifying glass can help in identifying these tiny pests.
3. The Lifecycle of Dark Aphids
Understanding the lifecycle of dark aphids is crucial for implementing effective control measures. These pests have a complex life cycle that can vary depending on the species and environmental conditions.
- Egg stage: In colder climates, some species of dark aphids overwinter as eggs on host plants.
- Nymph stage: Eggs hatch into nymphs, which are smaller versions of adult aphids.
- Adult stage: Nymphs molt several times before reaching adulthood.
- Reproduction: Most dark aphids reproduce asexually through parthenogenesis, giving birth to live young.
- Population explosion: Under favorable conditions, aphid populations can increase rapidly.
- Winged forms: When populations become too dense or food sources are depleted, some aphids develop wings to migrate to new host plants.
The rapid reproduction rate of dark aphids makes early detection and control crucial for preventing widespread infestations.
4. Damage Caused by Dark Aphids
Dark colored aphids and dark green aphids can cause significant damage to crops through various mechanisms:
- Sap feeding: Aphids use their piercing-sucking mouthparts to extract plant sap, leading to weakened plants and reduced yields.
- Leaf distortion: Feeding can cause leaves to curl, wilt, or become deformed.
- Stunted growth: Heavy infestations can stunt plant growth and reduce overall crop productivity.
- Honeydew production: Aphids excrete a sticky substance called honeydew, which can lead to the growth of sooty mold on leaves.
- Virus transmission: Many dark aphid species are vectors for plant viruses, spreading diseases as they move from plant to plant.
- Quality reduction: Aphid damage can reduce the marketability of fruits and vegetables.
The extent of damage can vary depending on the crop type, aphid species, and infestation level. Early detection and management are key to minimizing crop losses.
5. Natural Predators of Dark Aphids
Nature has provided several natural enemies that help control dark aphid populations. Encouraging these beneficial insects in your fields can be an effective part of your pest management strategy:
- Ladybugs (Coccinellidae): Both adults and larvae feed voraciously on aphids.
- Lacewings (Chrysopidae): Lacewing larvae, known as “aphid lions,” are particularly effective aphid predators.
- Hoverflies (Syrphidae): The larvae of these flies consume large numbers of aphids.
- Parasitic wasps: Various species lay their eggs inside aphids, eventually killing them.
- Birds: Many bird species feed on aphids, helping to control populations in orchards and gardens.
- Predatory mites: Some mite species prey on aphids, particularly in greenhouse environments.
At Farmonaut, we encourage farmers to create habitats that support these beneficial insects as part of an integrated pest management approach. This can include planting flowering strips or maintaining diverse vegetation around crop fields.
6. Integrated Pest Management Strategies
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a holistic approach to pest control that combines various strategies to manage dark aphids effectively while minimizing environmental impact. Here are key components of an IPM strategy for dark aphid control:
- Monitoring: Regular crop inspections and use of yellow sticky traps to detect aphid presence early.
- Cultural controls: Implementing crop rotation, adjusting planting dates, and maintaining plant health to reduce susceptibility.
- Biological controls: Encouraging natural predators and using commercially available beneficial insects.
- Physical controls: Using reflective mulches or row covers to deter aphids.
- Chemical controls: Applying insecticides only when necessary and choosing selective products that minimize harm to beneficial insects.
- Resistant varieties: Planting crop varieties that are less susceptible to aphid infestations.
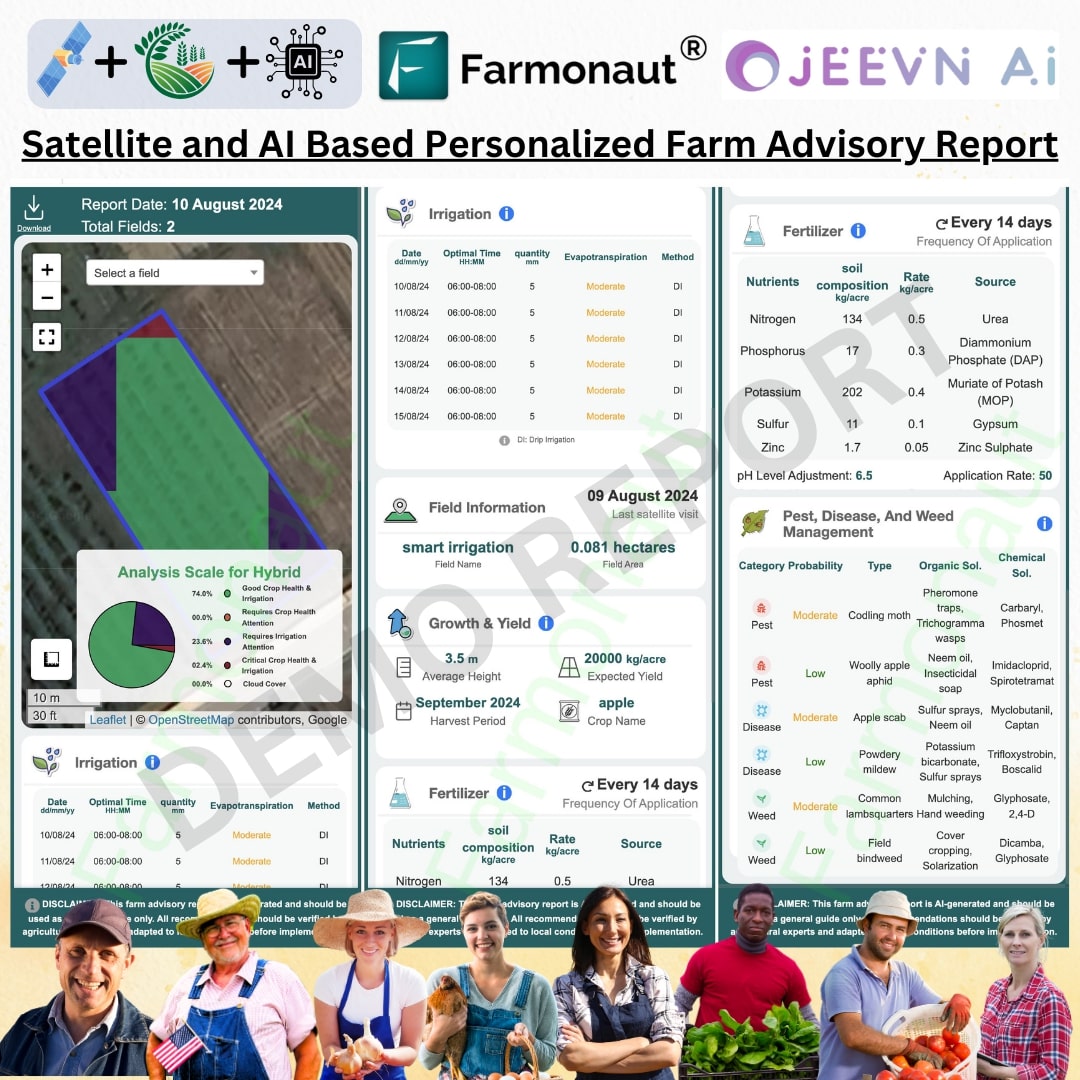
Our satellite-based monitoring system at Farmonaut can significantly enhance your IPM strategy by providing early detection of crop stress, which may indicate aphid infestations. To learn more about how our technology can support your pest management efforts, visit Farmonaut’s App.
7. Chemical Control Methods
While we advocate for integrated pest management, there are situations where chemical control of dark green aphids and other dark-colored species becomes necessary. When using insecticides, consider the following:
- Selective insecticides: Choose products that target aphids while minimizing harm to beneficial insects.
- Systemic insecticides: These are absorbed by the plant and can be effective against sap-feeding pests like aphids.
- Contact insecticides: These kill aphids on contact but may require thorough coverage and repeated applications.
- Insecticidal soaps and oils: These can be effective against aphids and are often considered more environmentally friendly options.
- Timing: Apply insecticides when aphid populations are just beginning to increase for maximum effectiveness.
- Resistance management: Rotate between different classes of insecticides to prevent the development of resistance.
Always follow label instructions and local regulations when applying any chemical control measures. Our Farmonaut system can help you optimize the timing of insecticide applications by providing real-time crop health data.
8. Organic Control Methods
For organic farmers or those looking to reduce chemical use, there are several effective organic methods for controlling dark aphids:
- Neem oil: A natural insecticide that disrupts aphid feeding and reproduction.
- Pyrethrin: Derived from chrysanthemum flowers, this natural insecticide is effective against many pests, including aphids.
- Diatomaceous earth: This fine powder can be dusted on plants to deter aphids and other soft-bodied insects.
- Garlic and chili pepper sprays: Homemade solutions can repel aphids when sprayed on plants.
- Companion planting: Growing plants like marigolds, nasturtiums, or alliums near susceptible crops can help repel aphids.
- Strong water spray: A forceful jet of water can dislodge aphids from plants, disrupting their colonies.
These organic methods can be particularly effective when combined with other IPM strategies and regular monitoring of crop health.
9. Preventing Dark Aphid Infestations
Prevention is often the best strategy when it comes to managing dark colored aphids. Here are some preventive measures you can implement:
- Crop rotation: Rotating crops can disrupt aphid life cycles and reduce overwintering populations.
- Healthy plants: Well-nourished, stress-free plants are more resistant to aphid infestations.
- Weed management: Many weeds can serve as alternate hosts for aphids, so keep areas around crops weed-free.
- Barrier crops: Planting tall barrier crops can help prevent winged aphids from reaching susceptible plants.
- Proper spacing: Adequate spacing between plants improves air circulation and makes it harder for aphids to spread.
- Regular inspection: Early detection through frequent crop monitoring is crucial for preventing large-scale infestations.
By implementing these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of severe aphid outbreaks in your crops.
10. How Farmonaut Can Help in Aphid Management
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to helping farmers manage pests like dark aphids more effectively through our advanced satellite-based technology. Here’s how our system can support your aphid management efforts:
- Early detection: Our satellite imagery can detect changes in crop health that may indicate aphid infestations before they become visible to the naked eye.
- Precise monitoring: Our platform allows you to monitor large areas efficiently, helping you identify potential problem spots quickly.
- Data-driven decisions: By providing real-time data on crop health, soil moisture, and weather patterns, we help you make informed decisions about pest management strategies.
- Optimized resource use: Our system helps you target your pest control efforts more precisely, reducing unnecessary pesticide applications and saving resources.
- Integration with IPM: Farmonaut’s technology complements and enhances your integrated pest management strategies.
To experience how Farmonaut can revolutionize your approach to pest management, download our app:
Download Farmonaut for Android
Download Farmonaut for iOS
Farmonaut Satellite System vs. Drone and IoT-based Farm Monitoring
| Feature | Farmonaut Satellite System | Drone-based Monitoring | IoT-based Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage Area | Large scale (100s to 1000s of hectares) | Limited (10s of hectares per flight) | Localized (depends on sensor placement) |
| Frequency of Data Collection | Regular (every few days) | As needed (requires manual flights) | Continuous (real-time data possible) |
| Initial Setup Cost | Low (subscription-based) | High (equipment purchase required) | Moderate to High (sensors and network setup) |
| Operational Complexity | Low (automated data collection) | High (requires skilled operators) | Moderate (maintenance of sensors required) |
| Weather Dependency | Low (can penetrate cloud cover) | High (affected by wind, rain) | Low (most sensors work in all weather) |
| Data Analysis | Advanced AI and machine learning | Requires separate analysis software | Depends on integrated software capabilities |
| Scalability | Highly scalable | Limited by equipment and personnel | Scalable but requires additional hardware |
FAQs About Dark Aphids
- Q: How quickly can dark aphids reproduce?
A: Under favorable conditions, dark aphids can reproduce rapidly, with populations doubling in as little as a week. - Q: Can dark aphids survive winter?
A: Some species of dark aphids lay eggs that can overwinter, while others may survive on indoor plants or in greenhouses. - Q: Are dark aphids harmful to humans?
A: Dark aphids do not directly harm humans, but they can significantly damage crops and garden plants. - Q: How can I tell if my plants have dark aphids?
A: Look for clusters of small, dark insects on the undersides of leaves, curled or distorted leaves, and the presence of sticky honeydew on leaves or stems. - Q: Can dark aphids fly?
A: While most aphids are wingless, some develop wings when populations become dense or food sources are depleted, allowing them to migrate to new plants. - Q: What’s the best organic method to control dark aphids?
A: A combination of encouraging natural predators, using insecticidal soaps, and practicing good crop management is often the most effective organic approach. - Q: How does Farmonaut help in managing dark aphid infestations?
A: Farmonaut’s satellite-based technology provides early detection of crop stress, which can indicate aphid infestations, allowing for timely and targeted interventions. - Q: Are there any plants that repel dark aphids?
A: Yes, certain plants like marigolds, nasturtiums, and alliums can help repel aphids when planted near susceptible crops. - Q: How often should I monitor my crops for dark aphids?
A: Regular monitoring, at least weekly during the growing season, is recommended. Farmonaut’s system can provide continuous monitoring to complement your on-ground inspections. - Q: Can dark aphids develop resistance to insecticides?
A: Yes, aphids can develop resistance to insecticides over time, which is why an integrated pest management approach is recommended.
Conclusion
Managing dark aphids, including dark colored aphids and dark green aphids, requires a comprehensive approach that combines vigilant monitoring, preventive measures, and targeted interventions. By understanding the lifecycle and behavior of these pests, farmers can implement effective strategies to protect their crops and maintain healthy yields.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to supporting farmers in their pest management efforts through our advanced satellite-based technology. Our platform provides valuable insights that can enhance your integrated pest management strategies, helping you detect and address aphid infestations more effectively.
To learn more about how Farmonaut can revolutionize your approach to crop management and pest control, visit our API documentation or explore our satellite data services.
Ready to take your farm management to the next level? Subscribe to Farmonaut today:
Together, we can create more resilient and productive agricultural systems, ensuring food security for generations to come.