Mastering Leaf Hopper Control: Effective Strategies to Prevent Leaf Rot and Identify Common Types
At Farmonaut, we understand the challenges farmers face when dealing with pests like leaf hoppers and the subsequent issues they can cause, such as leaf rot. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about leaf hoppers, including how to kill leaf hoppers, prevent leaf rot, and identify various types of leaf hoppers. Our satellite-based farm management solutions can help you detect and manage these issues more effectively, ensuring healthier crops and better yields.
Understanding Leaf Hoppers and Their Impact
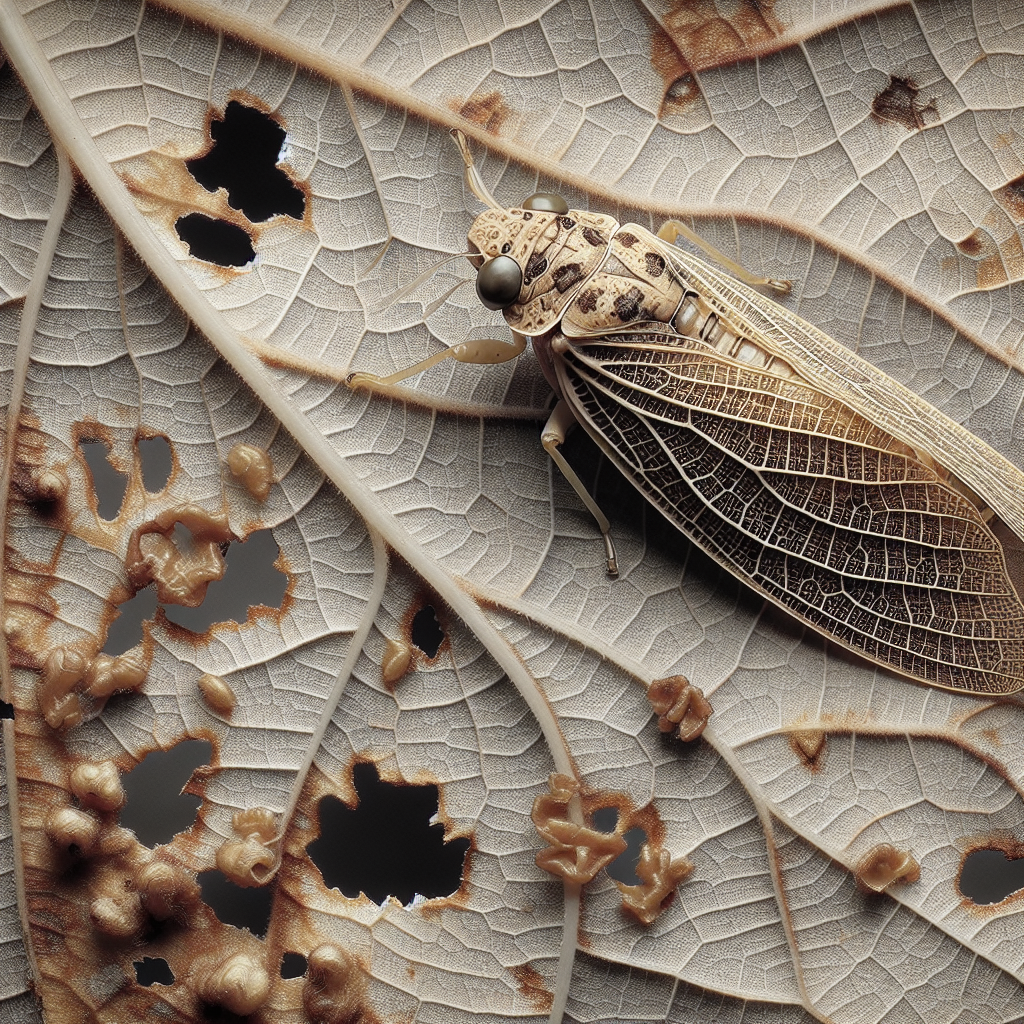
Leaf hoppers are small, wedge-shaped insects that can cause significant damage to crops. They feed on plant sap and can transmit various plant diseases, including those that lead to leaf rot. Understanding these pests is crucial for effective management.
Characteristics of Leaf Hoppers
- Size: Generally 3-15 mm long
- Shape: Wedge-shaped body
- Mobility: Excellent jumpers and flyers
- Feeding habits: Pierce plant tissues and suck sap
Damage Caused by Leaf Hoppers
- Direct feeding damage
- Transmission of plant pathogens
- Excretion of honeydew, leading to sooty mold growth
- Stunted plant growth
- Reduced crop yield
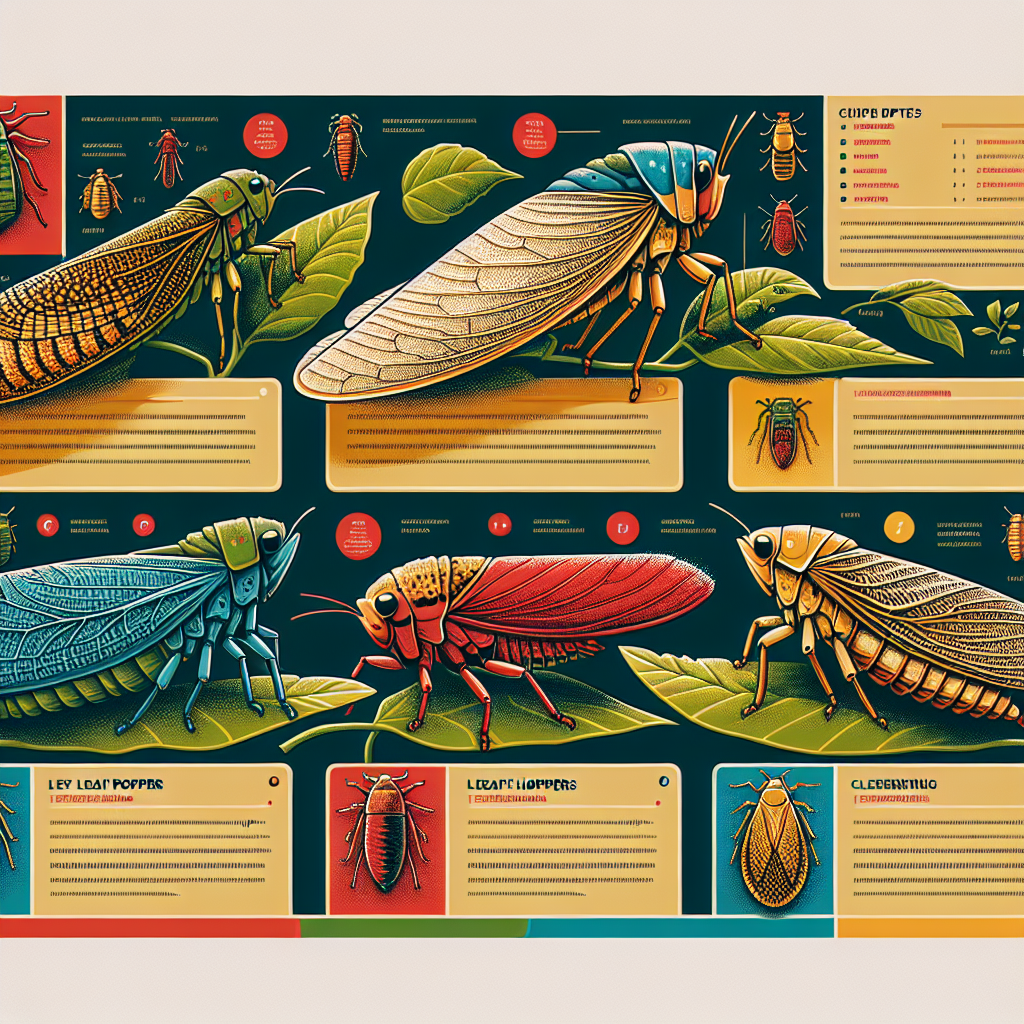
Types of Leaf Hoppers
Understanding the types of leaf hoppers affecting your crops is essential for targeted control measures. Here are some common species:
1. Potato Leafhopper (Empoasca fabae)
This species is a major pest of potatoes, alfalfa, and other crops. They cause “hopperburn,” a yellowing and curling of leaf edges.
2. Beet Leafhopper (Circulifer tenellus)
Known for transmitting curly top virus in sugar beets and other crops.
3. Grape Leafhopper (Erythroneura comes)
Primarily affects grapevines, causing stippling on leaves.
4. Aster Leafhopper (Macrosteles quadrilineatus)
Transmits aster yellows phytoplasma to various vegetable and ornamental plants.
5. Rice Leafhopper (Nephotettix spp.)
A significant pest in rice cultivation, known for transmitting rice tungro virus.

How to Kill Leaf Hoppers: Effective Control Strategies
Now that we’ve identified the problem, let’s discuss how to kill leaf hoppers and prevent their damage. At Farmonaut, we recommend an integrated pest management (IPM) approach that combines various control methods for the best results.
1. Cultural Control
- Crop rotation to break the pest lifecycle
- Removal of weeds and alternative host plants
- Use of reflective mulches to repel leaf hoppers
- Proper irrigation to maintain plant health
2. Biological Control
Encourage natural predators of leaf hoppers, such as:
- Ladybugs
- Lacewings
- Parasitic wasps
- Predatory mites
3. Chemical Control
When necessary, use insecticides as part of your IPM strategy. Some effective options include:
- Pyrethroids
- Neonicotinoids
- Organophosphates
Note: Always follow label instructions and local regulations when applying pesticides.
4. Physical Barriers
- Use row covers to protect young plants
- Install sticky traps to monitor and reduce populations
5. Biotechnological Approaches
Consider using genetically modified crops resistant to leaf hoppers, where available and permitted.
Preventing Leaf Rot: A Crucial Step in Crop Protection
Leaf rot is often a secondary issue resulting from leaf hopper damage. Here’s how to prevent it:
1. Maintain Plant Health
- Ensure proper nutrition through soil testing and balanced fertilization
- Implement proper irrigation practices to avoid water stress
- Prune and thin plants to improve air circulation
2. Practice Good Sanitation
- Remove and destroy infected plant material
- Clean tools and equipment regularly to prevent disease spread
3. Use Fungicides Preventatively
Apply fungicides before disease onset, especially during high-risk periods.
4. Monitor Crop Health Regularly
Use Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop health monitoring to detect early signs of stress or disease. Our advanced technology can help you spot potential issues before they become severe problems. Learn more about our crop monitoring services.
Farmonaut’s Role in Leaf Hopper and Leaf Rot Management
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to helping farmers tackle challenges like leaf hoppers and leaf rot effectively. Our satellite-based farm management solutions offer several advantages:
1. Early Detection
Our multispectral satellite imagery can detect changes in crop health before they’re visible to the naked eye, allowing for early intervention against leaf hopper infestations and leaf rot.
2. Precision Application
By identifying specific areas of infestation or disease, we help you target your treatments more precisely, reducing costs and environmental impact.
3. Continuous Monitoring
Our system provides regular updates on crop health, allowing you to track the effectiveness of your control measures over time.
4. Data-Driven Decision Making
With our AI-powered Jeevn AI Advisory System, you’ll receive personalized recommendations for managing leaf hoppers and preventing leaf rot based on real-time data and expert insights.
Farmonaut Satellite System vs. Drone and IoT-based Farm Monitoring
| Feature | Farmonaut Satellite System | Drone-based Monitoring | IoT-based Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage Area | Large scale (entire farms) | Limited by flight time and regulations | Limited by sensor placement |
| Frequency of Data Collection | Regular (as per satellite pass) | On-demand, weather dependent | Continuous |
| Initial Setup Cost | Low | High (drone purchase, training) | High (sensors, network infrastructure) |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Regular (drone maintenance, battery replacement) | Regular (sensor calibration, replacement) |
| Data Processing | Automated, AI-powered | Often requires manual processing | Automated, but limited to sensor data |
| Scalability | Highly scalable | Limited by operational constraints | Requires additional infrastructure for scaling |
Integrating Farmonaut into Your Pest Management Strategy
To make the most of our services in managing leaf hoppers and preventing leaf rot, consider the following steps:
- Sign up for Farmonaut: Visit our app page to get started with our satellite-based farm management solutions.
- Set up field boundaries: Define your farm areas within our system for accurate monitoring.
- Regular monitoring: Check your dashboard frequently for updates on crop health and potential pest issues.
- Implement recommendations: Follow the personalized advice provided by our Jeevn AI system to manage leaf hoppers and prevent leaf rot effectively.
- Track progress: Use our historical data feature to monitor the effectiveness of your management strategies over time.
Expanding Your Toolkit: Farmonaut’s Additional Resources
To further enhance your farm management capabilities, explore these additional Farmonaut offerings:
- API Access: Integrate our satellite and weather data directly into your existing systems. Learn more about our API.
- Mobile Apps: Access your farm data on the go with our mobile applications:
- Weather API: Get detailed weather forecasts and historical data for your farm location. Check out our Weather API documentation.
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Leaf Hopper Control and Crop Health
Managing leaf hoppers and preventing leaf rot requires a comprehensive approach that combines traditional farming practices with modern technology. By understanding the types of leaf hoppers affecting your crops, implementing effective strategies on how to kill leaf hoppers, and utilizing Farmonaut’s advanced satellite-based monitoring systems, you can significantly reduce crop damage and improve your overall yields.
Remember, prevention is always better than cure. Regular monitoring, early detection, and prompt action are key to keeping your crops healthy and productive. With Farmonaut by your side, you’re equipped with the tools and insights needed to stay ahead of pest problems and optimize your farm’s performance.
FAQs
Q1: How often should I monitor my crops for leaf hoppers?
A: We recommend weekly visual inspections during the growing season, complemented by daily checks of your Farmonaut dashboard for any anomalies in crop health that might indicate pest presence.
Q2: Are there any natural repellents for leaf hoppers?
A: Yes, some natural repellents include neem oil, garlic spray, and kaolin clay. These can be effective as part of an integrated pest management strategy.
Q3: How does Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring detect leaf hopper infestations?
A: Our satellite imagery can detect changes in plant health and vigor, which are often early indicators of pest infestations. While we can’t directly see the insects, we can identify patterns of stress in crops that are consistent with leaf hopper damage.
Q4: Can leaf hoppers develop resistance to pesticides?
A: Yes, like many pests, leaf hoppers can develop resistance to pesticides over time. This is why we recommend an integrated approach that doesn’t rely solely on chemical controls.
Q5: How does climate change affect leaf hopper populations?
A: Climate change can lead to milder winters and longer growing seasons in some areas, potentially increasing leaf hopper populations and extending their active period. Our weather forecasting and climate analysis tools can help you anticipate and prepare for these changes.
Subscribe to Farmonaut
Ready to take your farm management to the next level? Subscribe to Farmonaut today and gain access to our full suite of satellite-based monitoring and advisory services.
By leveraging our advanced technology and expert insights, you’ll be better equipped to tackle challenges like leaf hoppers and leaf rot, ensuring healthier crops and better yields. Join the Farmonaut community today and transform the way you manage your farm!