Farming Netherlands 2025: Innovation & Sustainability
Meta description: Farming in the Netherlands leads the world in innovation and sustainability in 2025. Explore Dutch agriculture’s cutting-edge practices, precision farming, and global leadership for a resilient future.
Introduction to Farming in the Netherlands: Innovation, Sustainability, and Global Leadership in 2025
When discussing farming in the Netherlands, words like innovation, sustainability, and precision agriculture immediately come to mind. As of 2025, the Dutch agricultural sector continues to solidify its position as a global leader, leveraging advanced technology and data-driven solutions to maximize yields, minimize environmental impact, and ensure food security.
The Netherlands has managed to achieve substantial agricultural output despite its relatively small land area—only 1.8 million hectares (less than 20% of total land). This remarkable efficiency is made possible by highly intensified, precision farming systems, sustainable methodologies, and constant innovation. The result? A roadmap for the future of global agriculture that the world is eager to emulate.
Highly Intensified and Precision Farming Netherlands
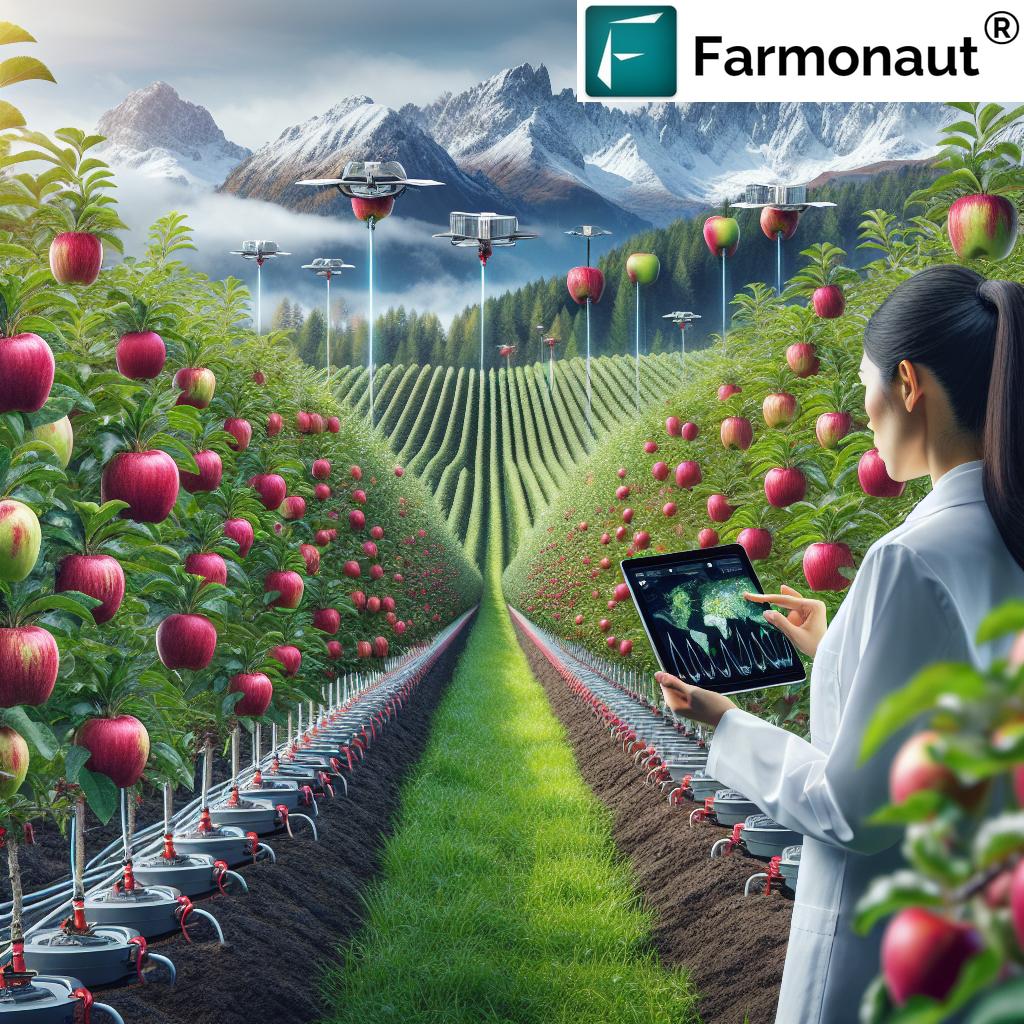
One of the defining characteristics of farming in the Netherlands in 2025 is its shift towards highly intensified, precision agriculture systems. Given the scarcity of arable land and the increasing challenge of climate change, Dutch farmers have adopted meticulous planning, technology integration, and real-time data to maximize yield and reduce environmental impact.
How Technology is Redefining Dutch Farming
- Satellite imagery and Drones: These tools help monitor crop growth and generate accurate data for fertilizer application, water usage, and early pest detection. Implementation of satellites and AI-backed imaging has resulted in a drastic reduction in resource usage and waste.
- Soil Sensors & IoT Devices: By embedding sensors in the soil, Dutch farmers are able to closely monitor moisture, nutrients, and temperature. This data enables precise fertilizer application and irrigation, customizing inputs to each field’s needs and reducing input waste.
- Greenhousing & Horticulture: The Netherlands is famous for its greenhouses, which now dominate its horticulture landscape. These state-of-the-art structures use integrated solar panels, geothermal heating, and closed-loop water systems to cultivate vegetables, fruits, and flowers all year round while minimizing environmental footprint.
Year-Round Production and Resource Efficiency
Vertical farming and hydroponics have become increasingly mainstream in farming Netherlands, enabling urban food production and achieving up to 90% water usage reductions compared to traditional methods. This not only leads to higher yields but also aligns with the EU’s sustainability targets.
Data-Driven Practices Boosting Sustainability
Precision farming in the Netherlands is underpinned by advanced crop data, imagery, and predictive analytics.
– Example: Satellite data enables farmers to apply water only where and when it’s needed. This smart application of resources significantly reduces fertilizer and pesticide runoff, benefiting both yields and environmental health.
Investments in automation and AI software allow for real-time monitoring and rapid response to emerging pest or disease threats.
Precision farming Netherlands unlocks actionable insights for farmers to reduce wastage, optimize inputs, and promote sustainable growth, all while ensuring maximum food security for future generations.
Sustainability and Circular Agriculture: The Cornerstone of Dutch Farming
In 2025, sustainability remains a cornerstone in the Dutch approach to agriculture. Policy incentives and consumer demand have inspired a large-scale transition to circular practices—closing resource loops and reducing waste. Circular agriculture in the Netherlands is not just a buzzword, but a reality that is transforming soil management, livestock, and resource use.
Circular Resource Loops
- Manure Recycling: Animal waste is converted into organic fertilizer, returning vital nutrients to the soil and significantly reducing dependence on synthetic alternatives.
- Crop Residue Utilization: Stems, leaves, and other agricultural byproducts are repurposed for bioenergy, animal feed, or compost, contributing to circularity and sustainability.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Dutch farms increasingly use solar panels, biogas installations, and geothermal heating to power operations, further reducing carbon footprints.
Organic Growth & EU Compliance
Organic farming continues to gain ground in the Netherlands, with increasing market share and robust consumer trust in ethically produced, pesticide-free food. Stringent EU targets, such as the Farm to Fork strategy, require Dutch agriculture to reduce nitrogen emissions, promote biodiversity, and improve soil health. The commitment is yielding:
- Fewer chemical inputs via integrated pest management and organic alternatives.
- Greater biodiversity through buffer strips, wildflower margins, and rotational planting.
- Increased soil organic matter via cover cropping and ecological farming practices.
The Dutch approach to sustainable farming blends advanced technology with deep-rooted environmental stewardship, offering valuable lessons to global markets struggling with resource scarcity, food security, and climate risk.
Livestock Farming, Animal Welfare and Dairy in the Netherlands
Livestock farming is integral to Dutch agriculture, with high-value outputs in dairy, pork, and poultry. Dutch dairy is globally recognized for its exceptional efficiency and commitment to animal welfare. The Netherlands has crafted a model where productivity and humane animal treatment not only coexist, but enhance each other.
Technological Advancements in Dutch Livestock Farming
- Robotic Milking Systems: Automation in milking not only reduces labor needs but improves animal health monitoring, detects early signs of illness, and delivers individualized care to increase milk yields.
- Precision Feed Management: AI-powered dietary planning and genetic research ensure herds receive balanced feed, reducing methane emissions and environmental impact per liter of milk produced.
- Animal Welfare Regulation: Dutch law now mandates larger living areas, environmental enrichment, and high standards of care, enabling Dutch farms to command premium prices in both national and international export markets.
These innovations are not limited to dairy: pork and poultry farms increasingly employ sensors, automation, and data analytics for optimal production efficiency and animal welfare. With continued investment in sustainable livestock production, the Netherlands is setting global benchmarks for ethical and profitable farming.
Dutch Global Leadership: Agricultural Exports and Technological Innovation
The Netherlands is a small country in terms of land area, yet it is the second-largest agricultural exporter in the world, surpassed only by the United States. This is made possible by:
- High-Value Exports: Products like vegetables, flowers, seeds, dairy, and meat dominate Dutch trade.
- Efficient Logistics: Advanced ports and cold-chain infrastructure ensure fresh produce and perishable goods reach global markets swiftly, with minimal food waste.
- Exporting Innovation: The Netherlands exports not just products, but technology: greenhouse design, sensor systems, automated machinery, and precision agtech are adopted worldwide.
As a pivotal player on the global agricultural stage, the Netherlands proves that sustainability and business growth can coexist. Its approach offers valuable lessons in addressing food security, resilience to climate uncertainty, and responsible environmental stewardship.
For Dutch agricultural exporters and supply chain managers, Farmonaut Product Traceability solutions are pivotal. Leveraging blockchain-based traceability, this tool ensures transparency, authenticity, and builds consumer trust for high-value agricultural products across global markets.
Challenges for Farming in the Netherlands in 2025 and Beyond
Despite the impressive progress, farming in the Netherlands faces several challenges:
- Climate Change Impact: More weather variability threatens traditional cropping cycles and increases the need for resilient systems and climate-smart crops.
- Water Management: The Netherlands must address declining groundwater levels, salinization, and drought risk. Investment in precision irrigation systems and water retention solutions is essential for future security.
- Reducing Nitrogen Emissions: New EU and national restrictions mandate the reduction of nitrogen runoff—a challenge for intensive livestock and fertilizer-dependent production systems.
- Soil Degradation & Biodiversity Loss: Intensified farming can deplete soil organic matter and harm biodiversity. Solutions include cover cropping, rotational planting, and enhanced monitoring.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Post-pandemic disruptions have highlighted the need for adaptable, transparent food supply chains.
To address these, Dutch farmers are:
- Developing climate-resilient crop varieties
- Enhancing water-efficient systems
- Applying digital tools for blockchain-based supply chain traceability and AI-driven risk assessment
- Experimenting with alternative proteins (e.g., plant-based, cultured meat) to diversify food systems
Satellite Technology & Farmonaut: Precision Insights for Dutch Farming
Innovative technology is the bedrock of efficient, sustainable agriculture in the Netherlands. At Farmonaut, we are proud to offer satellite-based solutions and real-time insights that support Dutch farmers, businesses, and policy makers in their pursuit of sustainability, productivity, and resilience.
Our technologies leverage satellite imagery, AI advisory systems, and blockchain traceability—all tailored to the needs of arable and horticultural farmers, livestock managers, and agri-businesses across the Netherlands.
- Satellite-Based Monitoring: Our platform empowers Dutch farmers to monitor crop health, soil quality, and environmental impact across every hectare, helping reduce fertilizer use and increase yields sustainably.
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI delivers real-time, field-specific recommendations—from weather forecasts to optimal irrigation windows.
- Blockchain Traceability: For Dutch exporters, our traceability tools provide a transparent chain of custody for agricultural products—boosting credibility in demanding global markets.
- Fleet and Resource Management: Operations managers in Dutch agribusiness use our tools to track vehicles, manage fuel, and optimize machinery workflows.
- Environmental Impact Monitoring: Our carbon footprinting tools help farmers and companies measure, track, and reduce CO₂ emissions, aligning Dutch agricultural businesses with EU sustainability regulations.
Access Farmonaut’s tools across platforms:
For API integrations and developer resources:
See our API |
API Developer Documentation
Farmonaut also supports Dutch agriculture with satellite-verified crop loan and insurance services, reducing fraud, streamlining financing, and improving access to essential credit.
For Dutch agronomists and farm managers, we offer robust digital tools for plot-level planning and large-scale farm management, making the day-to-day monitoring and reporting processes faster and more accurate.
Benefit Summary:
- Real-time field insights and NDVI monitoring for health and vigor
- Precise input management (water, fertilizer, pesticides)
- Comprehensive environmental carbon tracking for compliance and transparency
- Blockchain-based traceability for export credibility
- Subscription-based model for scalable, cost-effective access
Comparison Table: Key Dutch Farming Innovations and Impacts
| Innovation/Technology | Estimated Implementation Rate (2025) | Sustainability Impact (CO₂ Reduction %) |
Precision Yield Increase (%) | Adoption Cost (€/hectare, estimated) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical Farming | 25% | 60–80% | 100–250% | €1,000–€2,500 |
| Precision Irrigation Systems | 60% | 35–50% | 15–30% | €400–€900 |
| Autonomous Machinery (Drones/Robots) | 45% | 25–40% | 10–20% | €600–€1,200 |
| Smart Greenhouse Controls | 70% | 40–60% | 30–55% | €750–€1,400 |
| Blockchain Product Traceability | 30% | 5–12% | Indirect (Market Value ⬆) | €150–€350 |
| Carbon Footprinting Tools | 40% | 5–18% | 5–8% | €50–€150 |
*Estimates based on Netherlands’ sector-specific projections for 2025. Adoption cost varies with scale and technology provider. CO₂ reduction percentages are relative to conventional baseline practices per technology.
FAQ: Farming in Netherlands 2025
- Q1: How does farming in the Netherlands achieve such high yields with limited land?
- Farming Netherlands combines precision agriculture, advanced technology, and year-round greenhouse production. Dutch farmers use satellite imagery, IoT sensors, and robotics to maximize yields from every hectare while minimizing inputs and environmental impact.
- Q2: What makes Dutch agriculture a model for sustainability?
- The Netherlands has pioneered circular agriculture, investing in manure recycling, renewable energy, and integrated organic practices. This holistic approach addresses both carbon reduction and resource efficiency while meeting strict environmental standards.
- Q3: How important is animal welfare in Dutch farming?
- Animal welfare is integral, with robotic monitoring, genetic optimization, and improved living conditions now the standard—particularly in dairy. This results in both higher-quality products and premium market prices.
- Q4: What are the biggest challenges for the Netherlands’ agricultural sector in 2025?
- Key challenges include climate change, water management, nitrogen emissions, soil health, and supply chain resilience. The sector is tackling these with digital innovations, sustainable practices, and genetic research into resilient crops.
- Q5: How can Dutch farms manage their carbon footprint and traceability?
- Leveraging technology such as Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting and traceability solutions helps Dutch farmers and exporters measure and transparently report their environmental performance across global markets.
Conclusion: Dutch Agriculture as the Model for the Future
Farming in the Netherlands 2025 is a globally recognized leader in agricultural innovation, sustainability, and food security. Through advanced precision technology, intensified production systems, and a commitment to environmental stewardship, the Dutch model demonstrates how a small country with limited arable land can maximize yield, minimize environmental impact, and feed both local and global populations.
As climate change and resource scarcity challenge agriculture worldwide, farming Netherlands serves as a compelling blueprint for both present and future generations. Through continual technological innovation and sustainable practices, the Netherlands proves that progress, prosperity, and the planet can thrive together.
Dive deeper into precision farming and sustainable agriculture advancements through our YouTube video collection above.
For the most advanced, scalable and affordable satellite agriculture monitoring and environmental sustainability insights, explore Farmonaut’s suite of solutions today.
Explore:
Carbon Footprinting Tools |
Blockchain Traceability for Dutch Agriculture |
Crop Loan & Insurance Verification