Advanced Soil Technologies: 7 Powerful Ways to Boost Yields
“Precision soil mapping can increase crop yields by up to 20% using advanced sensor technologies.”
Introduction: The Evolution of Advanced Soil Technologies
Soil forms the foundation of agriculture, supporting every crop and farm managed across continents. As global food demand grows amidst resource constraints, innovative soil management technologies are critical for sustainable farming practices, optimizing yields, and safeguarding environmental health. Modern advanced soil technologies integrate tools like precision agriculture, digital soil mapping, real-time monitoring with sensors, smart irrigation systems, nanotechnology, biochar application, remote sensing, and artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance soil health, fertility, and overall crop productivity.
These innovations empower farmers to manage their fields efficiently, adapt to climate variability, optimize nutrient use, and reduce inputs—delivering food security while minimizing negative environmental impact. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the seven most powerful ways advanced soil technologies are transforming modern agriculture and how adopting these techniques is not just about increasing yields, but about ensuring the future of our planet’s soils.
Why Soil Health Management Matters More Than Ever
Advanced soil health management goes beyond traditional farming—it’s about addressing challenges like nutrient depletion, erosion, water scarcity, declining organic matter, and inconsistent yields, especially in regions facing volatile weather. Today’s technologies provide farmers with real-time data, actionable insights, and precision tools to manage soil conditions more efficiently and sustainably. Let’s explore the 7 most powerful advancements in soil technology, underpinned by practical solutions and measurable results.
1. Precision Agriculture and Digital Soil Mapping: Transforming Soil Health Management
Optimizing Inputs and Increasing Field Efficiency
Precision agriculture employs cutting-edge technologies to analyze and manage within-field variability, ensuring that areas of your farm receive the right amount of inputs at the right time. Leveraging digital soil mapping (DSM), farmers can visualize high-resolution maps of soil properties like organic matter, nutrient levels, moisture content, and more.
How Digital Soil Mapping Works
- Geospatial Data Integration: DSM utilizes remote sensing, geostatistics, and soil sampling to create detailed maps of key soil characteristics.
- Customized Field Insights: These maps help farmers apply inputs such as fertilizers, lime, and water efficiently, targeting nutrient-depleted or moisture-deficient zones.
- Waste and Environmental Impact: By reducing over-application, precision agriculture minimizes nutrient leaching and environmental harm.
Studies highlight that precision soil mapping can increase crop yields by up to 20% using advanced sensor technologies (source).
The integration of precision agriculture and digital soil mapping is at the core of platforms like Farmonaut. We harness satellite data and AI to deliver custom insights, optimize resource management, and offer these valuable tools via web, Android, iOS apps, and API access.
To further enhance large field operations, explore our Large Scale Farm Management solution, designed for efficient plantation and crop advisory at scale.
2. Soil Sensors and Real-Time Monitoring: Enhancing Decision-Making and Yield
Introduction to Real-Time Soil Monitoring
The adoption of soil sensors for farming has transformed soil health monitoring into a precise, responsive practice. Deploying in-field sensors to measure ph, moisture content, temperature, and nutrient levels provides real-time data on soil conditions and informs immediate decisions.
- Capacitive Sensors: Non-destructive and provide reliable readings ideal for commercial fields.
- Resistive Sensors: Cost-effective—suitable for smaller farms and quick soil checks.
- Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR) Sensors: High accuracy for research and precise field management.
With continuous monitoring, farmers can optimize irrigation and application of nutrients, directly reducing waste and improving crop performance.
Learn more from thefarminginsider.com.
For example, pairing soil sensors with satellite data enables plants to be watered only when necessary—conserving up to 30% of total water used (smart irrigation systems), thus reducing nutrient leaching and encouraging balanced plant growth.
3. Nanotechnology in Soil Management: Efficiency, Monitoring & Sustainability
Precision Nutrient Delivery and Soil Health Insights
Nanotechnology in agriculture introduces engineered nano-sized materials to improve soil management. The two most impactful applications in soil health management are:
- Nanofertilizers: These enhance nutrient uptake efficiency, increasing plant bioavailability and reducing nutrient leaching into water systems. Smaller particle sizes allow more nutrients to reach plant roots and cells.
- Nanosensors: Hyper-sensitive devices for real-time soil monitoring—measuring parameters like nitrate, phosphate, ph, and pesticide content. For example, graphene-based nanosensors rapidly detect nutrient levels and changes in soil conditions.
Benefits: Increases in fertility and crop productivity, reducing environmental impact by minimizing runoff, and paving the way for sustainable farming.
Smart soil amendments have reduced fertilizer use by 15% while maintaining productivity in tech-driven farms.
Explore more at en.wikipedia.org
4. Biochar Application for Soil Fertility and Carbon Sequestration
Biochar: Building Soil Structure and Climate Resilience
Biochar application for soil fertility is a regenerative technology that involves adding stable, carbon-rich charcoal to soils. Produced via pyrolysis of organic matter under low oxygen, biochar offers numerous benefits:
- Improves Soil Structure: Enhances porosity and water retention, supporting plant resilience to drought.
- Increases Nutrient Holding Capacity: Reduces fertilizer leaching and optimizes nutrient management.
- Reduces Soil Acidity & Promotes Microbial Diversity: Supports healthy root development and diverse soil biology.
- Sequesters Carbon: Acts as a long-term carbon sink, offsetting CO2 emissions and supporting climate goals.
Farmers adopting biochar application report higher yields, enhanced organic matter levels, and a tangible reduction in fertilizer costs—all while promoting environmental sustainability.
Learn more at growerbusiness.com
5. Smart Irrigation Systems: Efficient Water and Nutrient Management
The Future of Water Conservation in Farming
Smart irrigation systems use sensors, AI algorithms, and cloud-based data to tailor water delivery exactly to crop and soil needs. A modern smart irrigation system can reduce water usage by up to 30% compared to traditional methods.
- Sensor Integration: Soil moisture, temperature, and ph sensors monitor real-time conditions.
- Remote Sensing: Satellite and drone data gauge field variability and weather patterns.
- Automated Control: Irrigation is adjusted instantly via cloud-connected valve systems—saving water and limiting nutrient leaching.
Farmonaut’s platform incorporates smart irrigation monitoring, helping users receive AI-driven irrigation recommendations based on satellite-detected soil moisture and crop stage.
Discover these benefits with our precision farming services.
For multi-farm businesses, you may also benefit from Farmonaut’s fleet management tools for efficient resource movement—see Fleet Management Solution.
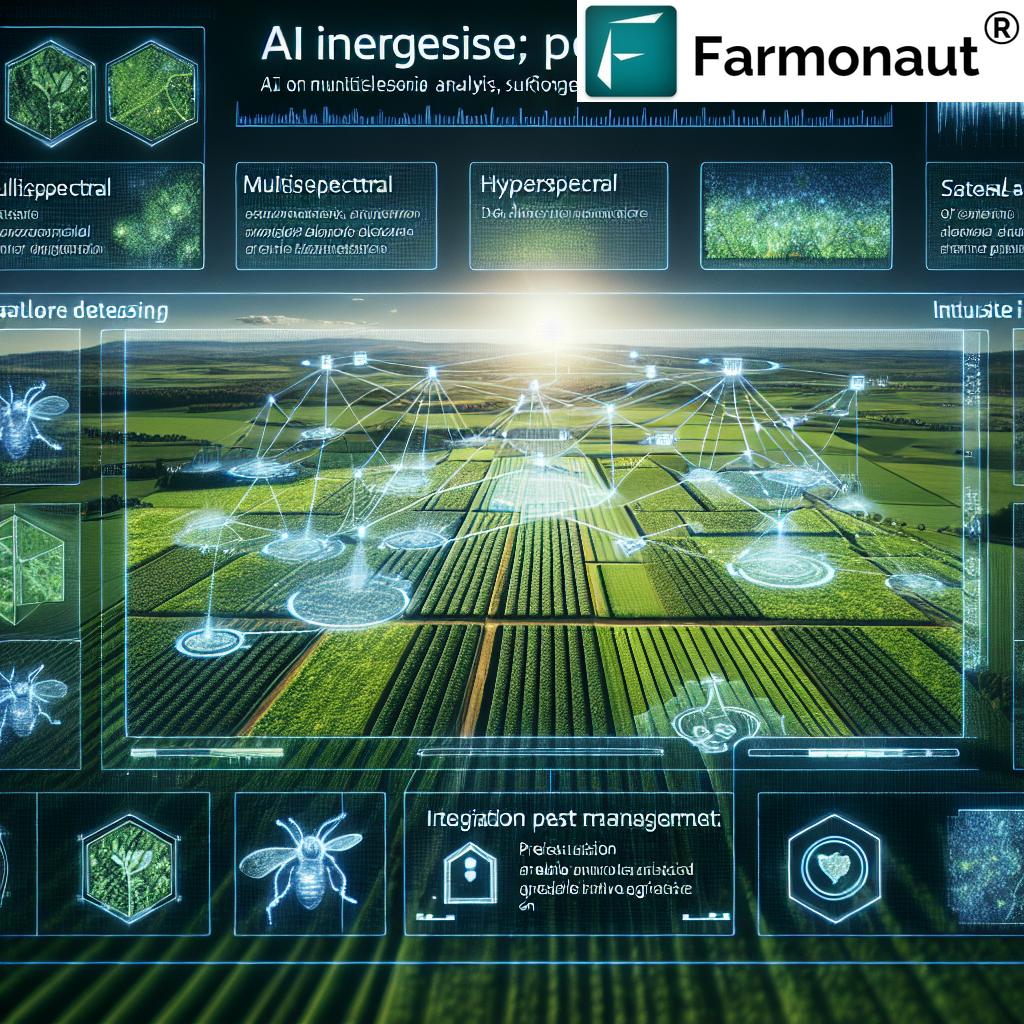
6. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Soil Management
From Data to Actionable Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) now underpin cutting-edge soil health management systems. These technologies synthesize large data sets—from sensors, satellites, past crop records, and weather feeds—to:
- Predict Soil Health Parameters: Spot potential soil degradation or contamination risks before they impact productivity.
- Guide Crop Decisions: Real-time, AI-driven analytics recommend optimal fertilization, irrigation, and soil restoration methods.
- Continuous Improvement: Algorithms learn and adapt, ensuring long-term accuracy of soil health management advice.
- Farmonaut Jeevn AI Advisory: Our platform’s advisory engine delivers customized insights via app/portal—transforming data into direct actions on your farm fields.
According to research, AI/ML optimizes crop yields by up to 15% compared to traditional advisory alone.
If you’re focused on environmental impact, learn more about Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting module—track farm emissions, reach compliance, and improve sustainability outcomes with real-time analytics.
7. Remote Sensing and Drones: Mapping, Monitoring, and Data-Driven Decisions
Accessibility Meets Precision in Soil and Crop Analysis
Remote sensing has revolutionized the monitoring of vast agricultural fields by combining satellite imagery and drones equipped with multi-spectral sensors. Now, farmers can:
- Survey Fields Effortlessly: Drones generate real-time, high-resolution maps showing moisture content, organic matter, and areas at risk of erosion.
- Spot Variability: Identify areas that need targeted nutrient or water application.
- Create Data Layers: Integration with GIS mapping enables historical and comparative analysis for smart field management.
- Act Early: Identify pest or disease outbreaks before visible symptoms appear—intervening earlier to protect yields.
Drones reduce costs compared to legacy field-mapping, making detailed soil and crop analysis accessible for small and large farms alike.
Read more at CropWatch.
Interested in automating crop insurance and monitoring for your business? Check Crop Loan & Insurance Solutions—satellite-based verification for secure, efficient claims and lending.
“Smart soil amendments have reduced fertilizer use by 15% while maintaining productivity in tech-driven farms.”
Comparative Table: Advanced Soil Technologies at a Glance
| Soil Technology | How It Works | Key Benefits | Estimated Yield Increase (%) | Sustainability Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision Agriculture & Digital Soil Mapping | Analyzes soil variability with geospatial data, sensors, and mapping tools | Reduces input waste, customizes field interventions | 15–20% | Optimizes resources, lowers environmental footprint |
| Soil Sensors & Real-Time Monitoring | Deploys sensors for pH, moisture, and nutrients, delivering instant data | Enables precise irrigation/fertilizer timing | 5–12% | Saves water, reduces fertilizer leaching |
| Nanotechnology in Soil Management | Uses nanofertilizers & nanosensors for accurate nutrient delivery & monitoring | Boosts fertilizer efficiency, cuts leaching | 8–18% | Reduces runoff, supports eco-friendly practices |
| Biochar Application | Applies pyrolyzed biomass to build soil carbon and improve structure | Increases fertility, carbon sequestration | 6–15% | Sequesters CO₂, fosters biodiversity |
| Smart Irrigation Systems | Combines sensor, weather, and AI data for automated watering | Prevents drought/overwatering, saves water | 6–12% | Minimizes water waste, maintains soil structure |
| Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning | Analyzes multi-source data, recommends optimal actions | Customizes management, increases ROI | 10–15% | Improves long-term soil sustainability |
| Remote Sensing & Drones | Aerial/satellite imaging and GIS produce actionable maps | Faster responses to variability and field problems | 7–14% | Limits erosion, enables conservation |
Further Advancements in Soil Health Management: Beyond the Seven
Conservation Tillage Practices
Conservation tillage practices—including no-till and reduced till operations—support sustainable soil management by minimizing soil disturbance, preserving soil structure and organic matter, and drastically reducing erosion loss.
- No-Till Farming: Keeps residual plant material on fields, protecting topsoil and improving moisture retention.
- Economic & Environmental Impact: Studies show erosion reduction by up to 97% and potential net income increases by up to 77% over time, benefiting both the farm and the planet.
Dive deeper at en.wikipedia.org
Biofertilizers for Sustainable Farming
The use of biofertilizers for sustainable farming is rapidly gaining momentum. These eco-friendly products contain beneficial microbes (e.g., nitrogen-fixing bacteria, phosphate solubilizers) that increase the availability of essential nutrients naturally, enhancing soil structure, health, and resilience.
- Benefits: Enhance soil health, increase crop yields, improve nutrient cycling, and reduce dependence on chemical fertilizers.
- Startup Innovations: Deliver these as foliar sprays or soil amendments—with both natural and synthetic sources, addressing sustainability and performance goals.
More at ttconsultants.com
Artificial Intelligence in Mobile Soil Analysis
New mobile analysis systems with AI and colorimetric paper sensors now offer instant chemical soil tests under field conditions. By integrating with smartphones and cloud platforms, farmers can generate high-resolution pH maps of their fields with experiences reaching 97% accuracy versus laboratory analysis—reducing waiting times from days to minutes.
Learn about this revolution at arxiv.org.
For transparent, secure food supply chains, explore Blockchain-Based Product Traceability—Farmonaut’s secure, satellite-verified traceability suite for agribusiness and food sector stakeholders.
Farmonaut: Powering Precision Agriculture Through Advanced Soil Technologies
At Farmonaut, we are committed to democratizing access to precision agriculture and advanced soil health management. Using a blend of satellite imagery, artificial intelligence, blockchain, and machine learning, our platform empowers farmers, agribusinesses, governments, and corporate clients to optimize soil conditions, enhance yields, and move towards true sustainability.
Key Farmonaut Capabilities:
- Satellite-Based Crop & Soil Monitoring: Instant insights on crop health, soil moisture, and field variabilities—reducing guesswork and resource waste.
- AI-Driven Advisory: Personalized, real-time recommendations for every field and crop.
- Blockchain Traceability: Transparent, tamper-proof records; trace products from farm to table.
- Carbon Footprinting: Track and reduce your operation’s carbon impact with accurate analytics.
- Fleet Management & Resource Tools: Optimize usage, improve safety, and cut operating expenses.
- Flexible Access: Use Farmonaut via Android, iOS, web browser, or API integration (for developers and enterprise systems).
- Affordable, Scalable Plans: For every farm size—see our pricing table below.
For step-by-step integration, review our API Developer Documentation.
Start Using Farmonaut: Click Here to Launch the App →
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is soil health management, and why is it important?
Soil health management is the use of modern agricultural practices and technologies to monitor, preserve, and enhance the physical, chemical, and biological health of soil. It is crucial for sustainable farming, higher yields, reduced input costs, and environmental protection.
How does precision agriculture differ from traditional farming?
Precision agriculture uses advanced tools—such as satellites, sensors, and AI—to analyze detailed variability within fields. Instead of treating the entire field uniformly, inputs like water and fertilizers are applied exactly where and when needed, increasing yield and resource efficiency.
Can smallholder farmers afford modern soil technologies?
Yes. Platforms like Farmonaut are specifically designed to make advanced technologies accessible and affordable for farms of any size, including smallholders. Cloud-based and mobile tools further reduce costs.
What are the main benefits of using soil sensors for farming?
Soil sensors provide real-time data on pH, moisture, temperature, and nutrient levels. This enables farmers to make instant, informed decisions about irrigation and fertilization, preventing waste and improving crop performance.
How does smart irrigation improve sustainability?
Smart irrigation systems use sensor and weather data to supply just the necessary amount of water, preventing overwatering and nutrient leaching, conserving water, and maintaining soil structure.
How does Farmonaut support traceability in the supply chain?
Farmonaut uses blockchain technology to create verifiable, tamper-proof records at every supply chain stage, ensuring transparency, food safety, and consumer trust.
Can these advanced soil technologies help me meet carbon neutrality or regulatory goals?
Absolutely. Techniques like biochar application, precision input management, and Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting tools enable farms and agribusinesses to track and actively reduce their environmental and carbon impact.
Conclusion: Advancements in Soil Technologies—A New Era for Farmers & Sustainability
The integration of advanced soil technologies is reshaping the future of agriculture, enabling farmers to not only maximize yields but also promote sustainable practices and mitigate the effects of climate change. By adopting tools and techniques such as precision agriculture, digital soil mapping, smart sensors, biochar, nanotechnology, AI-driven analytics, and remote sensing, agricultural stakeholders across the globe are prepared to meet tomorrow’s production and ecological demands.
Farmonaut stands at the forefront of this movement, offering comprehensive, affordable, and scalable solutions across all farm sizes and sectors. If you’re ready to take your fields and soils to the next level, start with advanced, data-driven agricultural management—empowering your journey to higher productivity and a resilient, sustainable planet.
Ready to revolutionize your farm? Get started with Farmonaut today!