Palm Tree Farm: 10 Sustainable Practices for Success
“Precision agriculture can boost palm oil yields by up to 20% through targeted nutrient and water management.”
Palm Tree Farming: Summary
Palm tree cultivation, especially oil palm farming (Elaeis guineensis), stands at the heart of the global agricultural landscape, supplying over 40% of world-traded vegetable oil. Our journey through this comprehensive guide explores not only the how-tos of palm cultivation, but also advanced palm oil plantation management, climate resilience in palm oil production, and the crucial role of technologies like satellite-based monitoring.
From site selection to sustainable practices, integrated pest and disease management, and the impact of precision agriculture in palm farming, we will uncover the roadmap to higher yields, healthier palms, and environmentally responsible farming. Whether you are establishing or managing a large oil palm plantation or starting a smaller farm, the steps and strategies here will guide you to sustainable success.
1. Sustainable Site Selection and Preparation
Establishing a thriving palm tree farm begins with making informed choices about location, terrain, soil requirements for oil palm cultivation, and site readiness. Let’s explore what makes the perfect site for sustainable palm tree farming:
Understanding Key Climate & Soil Factors
- Climate: Elaeis guineensis flourishes in tropical regions with average temperatures of 24–30°C and annual rainfall of 1,800–2,500 mm, distributed year-round.
- Soil: Rich in organic matter, well-draining, with pH 6.0–7.0 (as emphasized in soil tests).
- Topography: Slopes of less than 12° are preferable to reduce erosion risks and facilitate infrastructure development.
- Flood risk: Choose areas that are not susceptible to flooding for healthy farm growth and to prevent palm disease outbreaks.
Site Assessment and Preparation Steps
- Soil Sampling & Testing: Before planting, we always conduct detailed soil tests. This assesses nutrient levels, texture, pH, and presence of pathogens to guide amendments and fertilization.
- Clearance & Land Preparation: Remove unwanted vegetation carefully, minimizing environmental impact. Adhering to best environmental practices and reducing deforestation is vital. Where possible, retain buffer zones along waterways and integrate natural habitat corridors.
- Layout & Infrastructure: Plan for access roads, drainage, irrigation channels, and transport connections. Good infrastructure supports efficient farm management and timely harvest transport to markets.
- Soil Amendments: Depending on initial soil analysis, apply needed organic matter, lime, gypsum, or compost to correct pH and boost soil fertility. Mulching helps conserve moisture and prevent weed competition.
2. Innovative Palm Tree Planting Techniques
Our palm tree planting techniques build healthy, productive plantations from day one. Let’s break down the core steps:
Selecting Seeds and Managing Nurseries
- Seed Selection: Always opt for certified, high-yielding, disease-tolerant seeds or seedlings from established nurseries. Superior genetics set the foundation for profitable oil palm plantation management.
- Nursery Practices: Germinate seeds in shaded beds or polybags with nutrient-optimized soil mixes. Maintain consistent moisture with regular misting, adequate shade (particularly in hot climates like Southeast Asia), and routine disease monitoring to prevent early loss.
- Seedling Development: Over 9–12 months, prioritize root establishment and solid stem growth. Remove weak or stunted seedlings—early selection ensures stronger, healthier palms in the field.
Field Planting for Optimal Productivity
- Timing: Field planting should coincide with the onset of rains and stable temperatures to minimize water stress.
- Spacing & Layout: Standard commercial spacing is 9m x 9m in a triangular (equilateral) pattern, allowing for proper air circulation and full canopy development by year 4–5.
- Planting Pits: Dig deep, wide holes (~60 x 60 x 60 cm), fill with enriched topsoil, compost, and organic amendments. This supports robust early root growth.
- Transplanting: Carefully handle the seedlings, avoiding root damage. Water thoroughly after transplant, and mulch around each palm to conserve moisture and prevent weed competition.
Initial Care: Ensuring Establishment Success
- Temporary Shade: Erect shade nets or use intercropping with fast-growing cover crops to reduce sun stress during early development.
- Weed Management: Manual removal or organic mulching can reduce competition without resorting to harsh chemicals. This aligns with sustainable palm oil farming practices.
- Watering: Frequent, light watering helps new seedlings establish, especially in drier climates or after transplant shock.
3. Effective Palm Tree Maintenance and Growth Management
Consistent maintenance underpins every successful farm. Healthy palm trees mean higher yields, better resistance against diseases and pests, and an extended productive lifespan.
Fertilization Strategies
- Soil Testing: Annual soil tests guide precise fertilization. Focus on nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, and boron—vital for production and soil health.
- Balanced Inputs: Use organic compost plus site-specific mineral fertilizers (if needed). Avoid over-application to prevent nutrient runoff or leaching.
- Timing: Split fertilizer applications between wet and dry seasons to match growth cycles and maximize uptake.
Irrigation and Water Management Systems
- Supplemental Irrigation: While palms tolerate drought, supplemental irrigation during prolonged dry periods maintains optimal yields.
- Efficient Systems: Drip or micro-sprinkler systems reduce water wastage and help prevent water-logging (linked to root rot diseases).
- Monitoring: Satellite imagery from platforms like Farmonaut supports remote soil moisture monitoring, helping us optimize irrigation schedules.
Regular Pruning and Canopy Management
- Remove Dead/Diseased Fronds: Key to improving air circulation, reducing pest infestations, and minimizing disease spread.
- Sanitary Collection: Properly dispose of all pruned materials to prevent harboring of pests and pathogens.
Strategic Replanting and Under Planting
- Replanting: Oil palms remain productive for about 25 years. Afterward, yields decline and replanting becomes a farm management necessity.
- Under Planting: Planting young palms beneath the aging canopy allows continued harvest, but requires careful shading and input management. Reference: sustainable palm oil replanting strategies.
Common Palm Tree Maintenance Pitfalls (to Avoid!)
- Ignoring soil health and organic matter levels
- Neglecting routine pruning leading to disease outbreaks
- Overwatering or poor drainage (rot risk!)
- Uncoordinated fertilizer application, causing resource waste
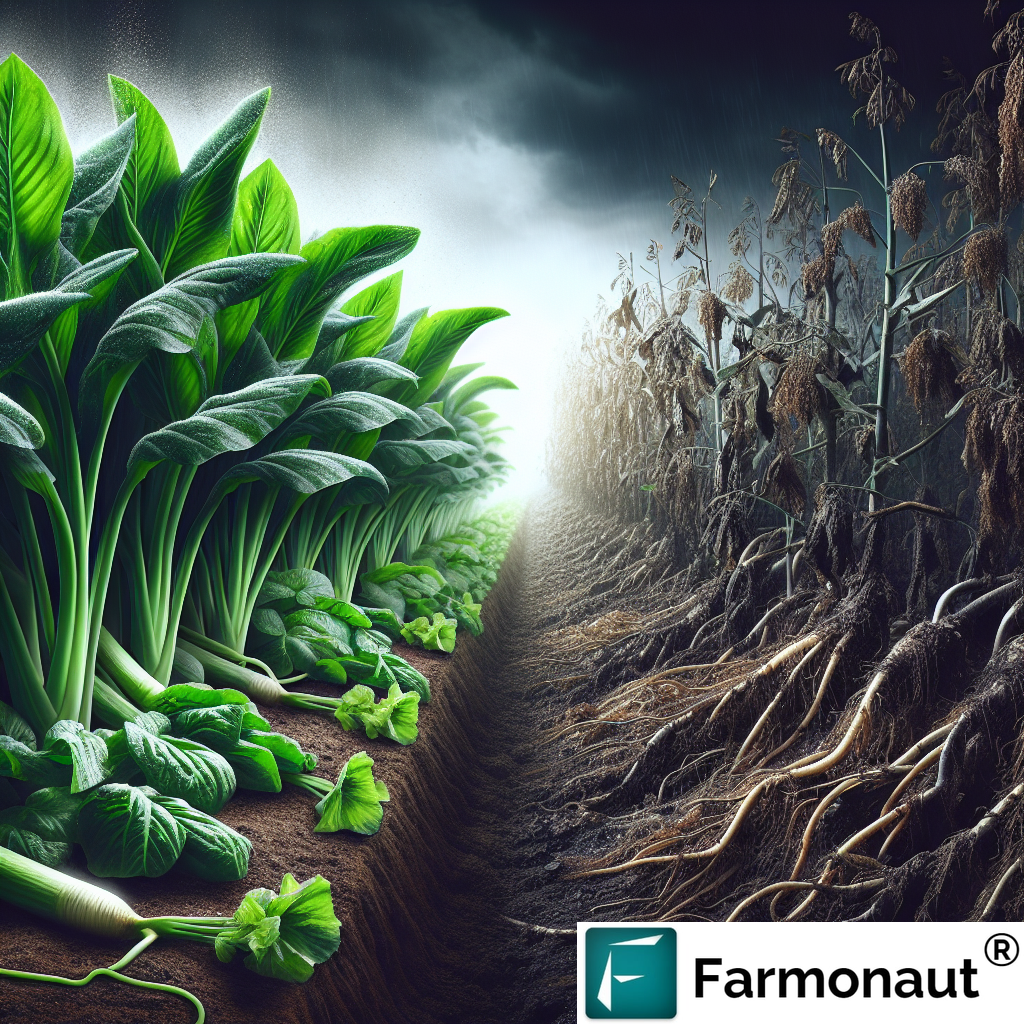
“Climate-resilient planting techniques reduce palm tree disease incidence by approximately 30% in sustainable plantations.”
4. Integrated Pest and Disease Control in Palm Plantations
Pest and disease control in palm plantations is vital to maintaining long-term productivity and ecosystem balance.
Key Pests and Threat Mitigation
-
Red Palm Weevil (Rhynchophorus ferrugineus):
- Infests stems and can cause extensive damage or palm collapse.
- Utilize early detection technologies—IoT-based monitoring for tunneling sounds, pheromone traps.
-
Caterpillars and Beetles: Defoliators or fruit borers; monitor for leaf damage and drill holes.
- Introduce natural predators and employ targeted biological control methods wherever possible.
Major Diseases and Preventive Strategies
-
Ganoderma Basal Stem Rot: Caused by soil-borne fungi, this is the primary killer of mature palms.
- Practice crop rotation, remove and destroy infected plants, and avoid excessive soil disturbance.
-
Phytophthora Crown Rot: Humid or poorly drained soils are at greatest risk.
- Improve drainage, select resistant varieties, and keep palms well-spaced.
Integrated Pest Management for Palms (IPM)
- Regular Monitoring: Systematic scouting, traps, and digital surveillance (Farmonaut’s real-time crop health monitoring) help detect early infestations and disease outbreaks.
- Cultural Controls: Field sanitation, rotation, promoting natural enemy habitats, and diversified cropping patterns.
- Mechanical/Physical Controls: Hand-picking, traps, or barriers where appropriate.
- Biological Controls: Release of beneficial insects or use of entomopathogenic fungi/bacteria.
- Chemical Controls: Apply only after all other strategies have failed, always favoring targeted, minimal-risk chemical use to preserve beneficial soil life.
By blending IPM, digital monitoring, and modern technologies, we build resilient oil palm plantations with sustainable, reduced input management.
5. Technological Advancements in Palm Cultivation
Modern farming is data-driven and technology-enabled. Incorporating technological advancements in palm cultivation maximizes yields, optimizes input use, and supports real-time decision-making.
Precision Agriculture in Palm Farming
- GPS-Enabled Machinery: Ensures precise field operations, reducing overlaps and minimizing wasted fertilizer, seed, or water.
- Drones: Used for aerial mapping, pest scouting, and targeted foliar application.
AI and IoT Integration
- Remote Crop Health Analysis: Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI Advisory System combines satellite imagery with weather and growth data to offer bespoke palm management insights. This aids in detecting nutrient deficiencies and predicting diseases before visual symptoms appear.
- IoT Sensors: Monitor soil moisture levels, air temperature, rainfall patterns, and even detect early pest activity via acoustic or pheromone sensors.
Consider integrating Farmonaut Carbon Footprinting for tracking and managing the environmental impact of your farm, supporting sustainability compliance and carbon credit applications.
Satellite Monitoring and Digital Platforms
- Real-Time Monitoring: Satellite platforms, such as Farmonaut, deliver regular updates on vegetation health (NDVI), enabling remote management of vast or hard-to-reach plantations.
- Resource Optimization: Pinpoint areas experiencing drought, nutrient deficiency, or pest attack before they escalate.
- Blockchain-Driven Traceability: Guarantee transparency and supply chain integrity with Farmonaut Product Traceability Solutions.
6. Commitment to Sustainability and Environmental Practices
As global scrutiny increases over palm oil production, sustainable palm oil farming is both an ethical and economic imperative. Here’s how we approach sustainability:
Regenerative Agriculture Approaches
- Intercropping: Planting legumes, cover crops, or shade trees between palms increases biodiversity, suppresses weeds, and improves overall soil fertility.
- Crop Rotation and Diversity: Decreases disease pressure and disrupts pest cycles, consistent with conservation goals.
- Mulching and Composting: Retain organic residues; use compost to build organic matter and reduce chemical fertilizer reliance.
Soil and Water Conservation Techniques
- Contour Planting/Terraces: On sloping land, prevents erosion and runoff.
- Mulch Application: Retains soil moisture, moderates temperature, and provides natural weed suppression.
- Efficient Irrigation: Prioritize drip or micro-sprinklers, use treated wastewater where regulations allow, and monitor for leaks or losses.
Explore how regenerative agriculture supports conservation and market access.
Social Responsibility and Certification
- Community Engagement: Involve local communities in decision-making, share benefits, and respect traditional land rights.
- Fair Labor: Uphold fair wages, safe working conditions, and eliminate exploitative practices—for both long-term productivity and social license to operate.
- Third-Party Certification: RSPO, ISCC, and similar certifications confirm compliance with both environmental and social standards, opening premium markets and benefiting long-term farm profitability.
For those operating large plantations, consider Farmonaut’s Large Scale Farm Management App for comprehensive operational and compliance management.
7. Understanding Economic Considerations and Market Dynamics
Palm oil is a cornerstone of the global edible oil trade. Understanding market dynamics and applying cost-effective practices are key to mitigating financial risks and maximizing returns.
- Market Demand: Monitor trends in established and emerging markets. Rapidly developing countries drive growth, but sustainability preferences are rising everywhere.
- Price Volatility: Weather swings, geopolitical shifts, and consumer pressure for certified, deforestation-free oils all influence price.
- Diversified Revenue Streams: Integrate intercropping, waste valorization (oil palm fronds for biomass), or carbon credits (useful for those leveraging Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting platform).
- Traceability and Premium Access: Sustainability certifications and traceable products win premium prices and access to export markets. Try Farmonaut’s blockchain-based traceability for supply chain transparency.
- Crop Insurance and Lending: Satellite-based farm verification tools, like those from Farmonaut, reduce loan fraud risk and improve access to finance and insurance.
8. Tackling Challenges and Embracing the Future in Palm Oil Production
Despite its potential, the palm industry faces significant hurdles—climate change, ethical debates, land disputes, and public scrutiny. We must proactively adapt with climate resilience in palm oil production and uphold responsible, adaptive management.
Key Risks and Adaptive Strategies
- Climate Change: Unpredictable weather, rising temperatures, and changing rainfall demand new, climate-resilient varieties and dynamic water/fertility management.
- Deforestation: Only establish new plantations on previously cleared or degraded land. Use robust land-use planning, and adhere to deforestation-free initiatives.
- Social & Ethical Concerns: Fairly negotiate land access, avoid displacement, and ensure transparent labor practices.
Adapting to these challenges requires ongoing education, community engagement, and adoption of both traditional knowledge and modern technological advancements in palm farming.
Comparison Table of Sustainable Palm Tree Farming Practices
| Practice Name | Description | Estimated Yield Improvement (%) | Resource Savings | Climate Resilience Rating | Implementation Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision Irrigation | Deploy drip or micro-sprinkler systems for targeted water delivery | Up to 15% | Saves 20% water annually | High | Medium |
| Intercropping | Grow compatible crops (e.g., legumes) between palm rows | 10–18% | Reduces fertilizer; enhances soil health | High | Medium |
| Cover Cropping | Establish ground cover plants to suppress weeds & improve soil structure | 5–12% | Cuts herbicide use by 40% | Medium | Easy |
| Compost Usage | Apply composted palm residues for organic nutrient supply | 8–14% | Cuts fertilizer needs by 25% | Medium | Easy |
| Disease-Resistant Varieties | Plant certified seed/varieties with improved tolerance to pests & diseases | up to 15% | Reduces pesticide applications | Very High | Medium |
| Digital Monitoring (Satellite & IoT) | Use remote sensing and AI for early issue detection and farm optimization | Up to 20% | Optimizes all inputs | Very High | Medium |
| Mulching | Apply organic matter to retain soil moisture, regulate temperature | 6–10% | Reduces irrigation & fertilizer use | Medium | Easy |
| Integrated Pest Management | Combine monitoring, biological control, and limited chemical use | 10–20% | Reduces pesticide costs | High | Medium |
| Recycling Palm Biomass | Convert fronds, shells, and empty fruit bunches to mulch or compost | 7–13% | Substitutes mineral fertilizers | Medium | Medium |
| Contour Planting | Follow land contours to reduce erosion and runoff | 5–8% | Prevents soil erosion | High | Medium |
Frequently Asked Questions on Palm Tree Farming
What are the best soils for oil palm cultivation?
The ideal soils are deep, well-draining, rich in organic matter, and have a pH range of 6.0 to 7.0. Periodic soil tests are crucial to adjust fertility and address deficiencies for healthy palm growth.
How do I prevent pest and disease outbreaks in palm plantations?
Adopt integrated pest management: monitor regularly using digital platforms, encourage natural predators, maintain field sanitation, and only apply chemical treatments as a last resort.
How can technology improve my palm tree farm management?
By leveraging satellite imagery, IoT sensors, and AI-powered advisory systems such as those offered by Farmonaut, you can monitor crop health, optimize input use, and detect problems before they escalate.
What are the main sustainability challenges in palm oil production?
Deforestation, loss of biodiversity, social and labor concerns, and climate change are primary challenges. Implementing regenerative agriculture, respecting land rights, and adhering to deforestation-free policies are vital.
Which certifications are important for sustainable palm oil farming?
The most recognized include the RSPO (Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil) and ISCC (International Sustainability and Carbon Certification), validating both environmental and social performance.
How does Farmonaut support palm tree growers?
Farmonaut delivers accessible precision agriculture tools—offering satellite crop health monitoring, AI advisories, traceability, and resource management through web/mobile apps and API for anyone managing oil palm plantations.
Farmonaut: Smart Solutions for Palm Tree Farm Management
Modern palm farming is inseparable from data-driven management. With Farmonaut, farmers and plantation managers access unparalleled technologies—satellite health tracking, real-time soil condition reports, AI-based pest prediction, and blockchain-based product traceability for supply chain transparency.
- Crop Health Monitoring: Get field-wide vigor and disease scans using NDVI and related indices for precise action.
- Jeevn AI Advisory: Receive personalized watering, nutrition, and pest control advice based on up-to-date field data.
- Traceability Solutions: Ensure authenticity and premium market access with blockchain-backed certification.
- Fleet and Resource Management: Streamline logistics with Farmonaut Fleet Management.
- Large Scale Farm Tech: Manage hundreds of hectares efficiently—from a single dashboard—with Farmonaut Admin Apps for plantations and agro-corporates.
- Crop Loan & Insurance: Get instant, satellite-enhanced verification for agricultural loans and insurance with Farmonaut’s verification platform.
- API Integrations: Build your own smart farm solutions or business tools using Farmonaut’s robust Satellite & Weather API.
Download Farmonaut on Android, iOS, or use the web app for immediate access to real-time palm plantation insights.
Farmonaut Subscription Options
Choose the subscription level that matches your farm size and data needs. Farmonaut offers flexible, scalable solutions to maximize both efficiency and returns in palm tree farming.
Conclusion
Success in palm tree farming requires more than planting high-quality seeds—it’s a continuous process of informed management, regular soil and crop monitoring, adaptive maintenance, and a deep commitment to social and environmental sustainability.
By integrating data-driven technological advancements from platforms like Farmonaut with the wisdom of regenerative agricultural practices, we can achieve productive, resilient, and sustainable palm oil plantation management—for today’s growers and future generations.
Leap into the future of precision palm farming. Download Farmonaut, explore the API, or learn more on our website for smarter, greener plantation success.