Mastering Water Detection: MNDWI vs NDWI for Accurate Open Water Feature Delineation
At Farmonaut, we’re constantly pushing the boundaries of agricultural technology to provide farmers with the most accurate and useful data. Today, we’re diving deep into the world of water detection in satellite imagery, specifically comparing two powerful indices: the
Modified Normalized Difference Water Index (MNDWI) and the
Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI). Understanding these indices is crucial for accurate water resource management, flood monitoring, and agricultural planning.
Introduction to Water Detection Indices
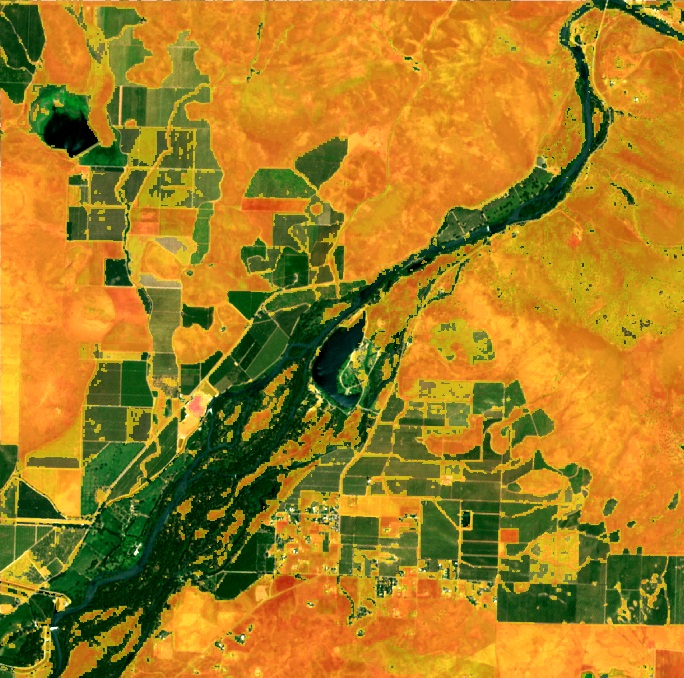
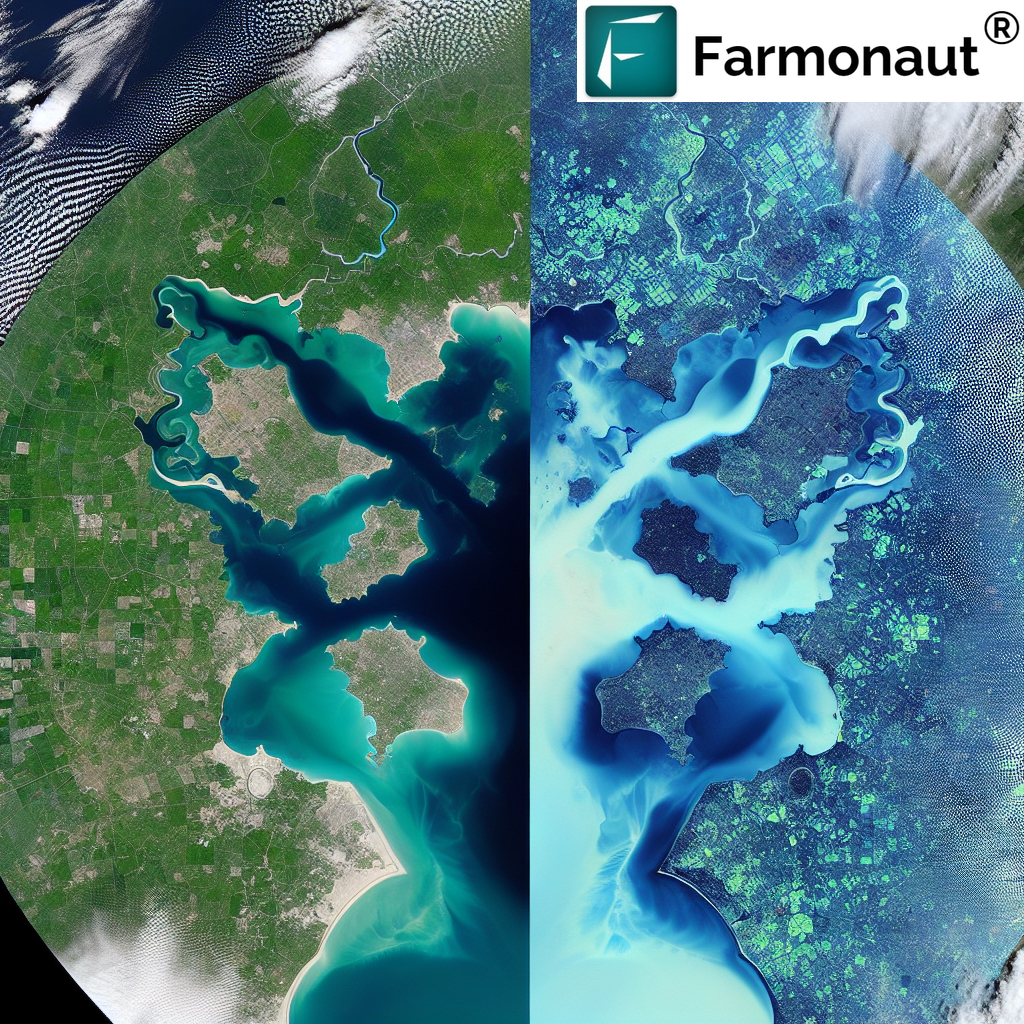
Water detection in satellite imagery plays a vital role in various applications, from agriculture to disaster management. Two of the most widely used indices for this purpose are the NDWI and MNDWI. Let’s explore these indices in detail and understand their significance in
the delineation of open water features.
Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI)
The
Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) was introduced by McFeeters in 1996. It’s designed to:
- Maximize reflectance of water by using green wavelengths
- Minimize the low reflectance of NIR by water features
- Take advantage of the high reflectance of NIR by vegetation and soil features
The formula for NDWI is:
NDWI = (Green – NIR) / (Green + NIR)
Where:
- Green = reflectance in the green band
- NIR = reflectance in the near-infrared band
Modified Normalized Difference Water Index (MNDWI)
The
Modified Normalized Difference Water Index (MNDWI) was proposed by Xu in 2006 as an improvement over the original NDWI. The key difference is the use of the middle infrared (MIR) band instead of the NIR band. The formula for MNDWI is:
MNDWI = (Green – MIR) / (Green + MIR)
Where:
- Green = reflectance in the green band
- MIR = reflectance in the middle infrared band
Comparing NDWI and MNDWI
Both NDWI and MNDWI have their strengths and applications. Let’s compare them:
| Aspect |
NDWI |
MNDWI |
| Bands Used |
Green and NIR |
Green and MIR |
| Water Feature Enhancement |
Good |
Better |
| Built-up Land Noise |
More susceptible |
Less susceptible |
| Soil Noise |
More susceptible |
Less susceptible |
| Vegetation Noise |
More susceptible |
Less susceptible |
The Use of NDWI in the Delineation of Open Water Features
The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features has been widely adopted in remote sensing applications. Here’s why it’s effective:
- NDWI enhances the presence of water features while suppressing the noise from soil and vegetation.
- It’s particularly useful for detecting surface water in areas with vegetation cover.
- NDWI values for water bodies are typically positive, while values for soil and vegetation are usually zero or negative.
- This clear distinction makes it easier to set thresholds for water detection.
However, NDWI has some limitations, particularly in urban areas where built-up land can produce positive values similar to water. This is where MNDWI comes into play.
Advantages of MNDWI over NDWI
The
Modified Normalized Difference Water Index (MNDWI) offers several advantages over the traditional NDWI:
- Enhanced water feature detection: MNDWI typically provides a greater contrast between water and non-water features.
- Reduced noise from built-up areas: The use of the MIR band helps to suppress noise from urban areas more effectively.
- Better performance in mixed environments: MNDWI is often more accurate in areas with a mix of water, vegetation, and built-up land.
- Improved shallow water detection: MNDWI can often detect shallow water bodies that NDWI might miss.
Practical Applications in Agriculture
At Farmonaut, we leverage these water detection indices to provide valuable insights for farmers and agricultural managers. Here are some key applications:
- Irrigation management: By accurately detecting water bodies and soil moisture, we help farmers optimize their irrigation strategies.
- Flood monitoring: Our satellite-based system can quickly identify flooded areas, allowing for rapid response and damage assessment.
- Water resource planning: Long-term tracking of water bodies helps in sustainable water resource management.
- Wetland conservation: Accurate delineation of wetlands supports conservation efforts and compliance with environmental regulations.
To explore how Farmonaut can help you leverage these technologies for your agricultural needs, visit our
application page.
Farmonaut’s Satellite System vs. Drone and IoT-based Farm Monitoring
While drones and IoT devices have their place in agriculture, Farmonaut’s satellite-based system offers unique advantages:
| Feature |
Farmonaut Satellite System |
Drone-based Monitoring |
IoT-based Monitoring |
| Coverage Area |
Large scale (entire farms) |
Limited by flight time and regulations |
Limited by sensor placement |
| Frequency of Data Collection |
Regular (based on satellite revisit time) |
On-demand, but labor-intensive |
Continuous, but localized |
| Initial Setup Cost |
Low |
High (equipment and training) |
Medium to High (sensors and network) |
| Maintenance |
Minimal (cloud-based system) |
Regular (drone maintenance) |
Regular (sensor maintenance) |
| Data Processing |
Automated with AI |
Often requires manual processing |
Automated, but limited to sensor data |
| Scalability |
Highly scalable |
Limited by operational capacity |
Requires additional hardware for scaling |
Integrating Water Detection in Farmonaut’s Platform
At Farmonaut, we’ve integrated advanced water detection algorithms into our satellite-based farm management platform. Here’s how we use this technology to benefit our users:
- Precision irrigation: By accurately detecting water bodies and soil moisture levels, we help farmers optimize their irrigation schedules, reducing water waste and improving crop yields.
- Flood risk assessment: Our system can identify areas prone to flooding, allowing farmers to take preventive measures and protect their crops.
- Water resource management: Long-term tracking of water bodies helps in sustainable water resource planning, crucial for areas facing water scarcity.
- Environmental compliance: Accurate delineation of wetlands and water bodies supports compliance with environmental regulations and conservation efforts.
To leverage these advanced features for your farm or agribusiness, consider subscribing to Farmonaut:
Future Developments in Water Detection Technology
As we continue to innovate at Farmonaut, we’re exploring new frontiers in water detection technology:
- AI-enhanced index refinement: We’re developing machine learning algorithms to automatically adjust water detection indices based on local conditions, improving accuracy across diverse landscapes.
- Fusion of multiple data sources: By combining satellite data with ground-based sensors and weather forecasts, we aim to provide even more accurate and timely water-related insights.
- Real-time flood monitoring: We’re working on systems to provide near-real-time flood alerts by analyzing rapid changes in water indices.
- Integration with climate models: By incorporating long-term climate data, we’ll be able to provide predictive insights on water availability and flood risks.
Accessing Farmonaut’s Water Detection Technology
We offer multiple ways to access and integrate our water detection technology:
- Farmonaut App: Available on both Android and iOS, our app provides easy access to water-related insights for your farm.
- API Integration: For developers and businesses looking to integrate our technology into their systems, we offer a robust API. Check out our API documentation for more details.
- Custom Solutions: For large-scale projects or specific needs, we offer customized solutions. Contact our team to discuss your requirements.
Conclusion
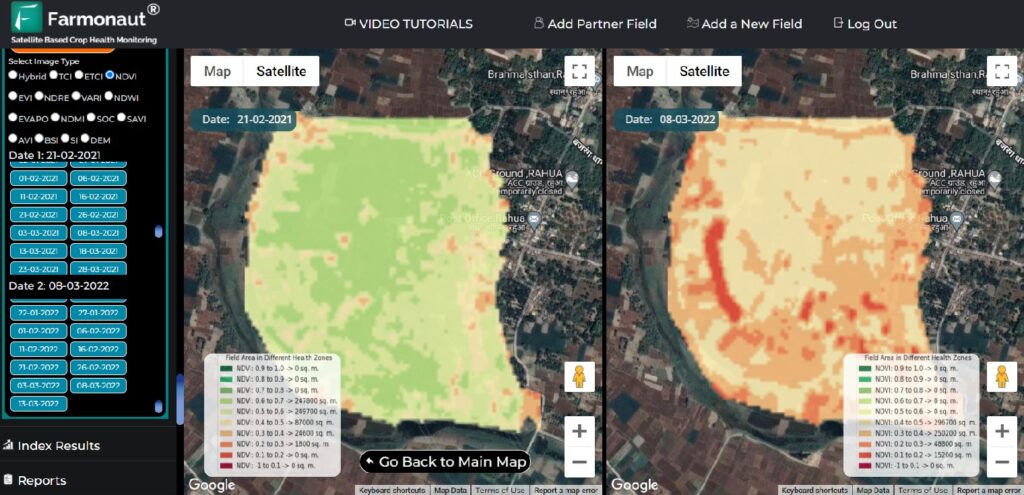
The accurate detection and monitoring of water bodies are crucial for modern agriculture and environmental management. While both NDWI and MNDWI have their strengths, the
Modified Normalized Difference Water Index (MNDWI) often provides superior results, especially in complex environments.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to leveraging the most advanced technologies to provide farmers and agricultural managers with the insights they need. By integrating these water detection indices into our satellite-based platform, we’re helping to optimize water usage, improve crop yields, and promote sustainable farming practices.
Whether you’re a small-scale farmer or managing large agricultural operations, Farmonaut’s technology can provide you with valuable insights for better water management. Visit our
application page to learn more about how we can help you optimize your agricultural practices.
FAQs
- Q: What is the main difference between NDWI and MNDWI?
A: The main difference is in the bands used. NDWI uses green and near-infrared (NIR) bands, while MNDWI uses green and middle infrared (MIR) bands. MNDWI generally provides better water feature enhancement and less noise from built-up areas and vegetation.
- Q: How accurate is satellite-based water detection compared to ground surveys?
A: Satellite-based water detection can be highly accurate, especially when using advanced indices like MNDWI. While ground surveys may provide more detailed information for small areas, satellite-based methods offer broader coverage and frequent updates, making them ideal for large-scale monitoring.
- Q: Can Farmonaut’s technology detect small water bodies like ponds or streams?
A: Yes, our technology can detect various sizes of water bodies, including small ponds and streams. The detection capability depends on the resolution of the satellite imagery used, which we continuously optimize for best results.
- Q: How often is the water detection data updated in Farmonaut’s system?
A: The update frequency depends on satellite revisit times and cloud cover. Typically, we provide updates every 5-7 days, but this can vary based on specific location and weather conditions.
- Q: Can your system differentiate between different types of water bodies (e.g., freshwater vs. saltwater)?
A: While our basic water detection doesn’t differentiate between water types, we’re developing advanced algorithms that can potentially distinguish different water qualities based on spectral signatures. This is an area of ongoing research and development.
For more information on how Farmonaut can help you leverage advanced water detection technology for your agricultural needs, please visit our website or contact our support team.