Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Trivia: Precision Agriculture & Soil Management
- The Process of Farming: Overview
- Step 1: Planning and Preparation in Farming
- Step 2: Soil Preparation and Health Management
- Step 3: Planting—Modern Techniques and Crop Rotation
- Step 4: Crop Management—Integrated Pest Management, Monitoring & More
- Step 5: Efficient Crop Harvesting Methods
- Step 6: Post-Harvest Handling and Storage
- Step 7: Marketing, Distribution & Reaching Consumers
- Sustainable Farming Practices and Environmental Conservation
- Modern Agricultural Technology & Precision Tools
- How Farmonaut Empowers Sustainable Farming
- Sustainable Farming Process: Steps, Key Actions, and Estimated Benefits
- Challenges and Future Directions in Sustainable Agriculture
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Sustainable Farming Practices
- Conclusion: Optimizing the Process of Farming for Sustainable Success
The Process of Farming: 7 Steps for Sustainable Success
Farming is more than a tradition—it’s a science, an art, and a series of evolving steps aimed at producing food, fiber, and agricultural products sustainably for our world. In the modern era, sustainable farming practices, soil health management, efficient crop harvesting methods, modern agricultural technology, and precision agriculture tools are all interwoven to ensure robust yields, environmental conservation, and food security for future generations. This comprehensive guide explores each stage in the process of farming, incorporating technological advancements, eco-friendly methods, and expert strategies for sustainable success.
“Precision agriculture can increase crop yields by up to 20% while reducing fertilizer use by 15%.”
The Process of Farming: Overview
Effective farming is built on an intricate process. Seven primary steps—planning, soil preparation, planting, crop management, harvesting, post-harvest handling, and marketing—work together to produce high-quality crops, maintain soil health, conserve resources, and fulfill market demand. Each step encompasses a blend of traditional wisdom and cutting-edge advancements, like precision agriculture tools offered by Farmonaut, designed to optimize every part of the agricultural journey.
Step 1: Planning and Preparation in Farming (Focus Keyword: planning and preparation in farming)
Assessing and Laying the Foundation
Every successful farming season begins with thorough planning and preparation. Farmers assess factors such as local climate, soil type, and market demand to determine the most suitable crops or livestock to cultivate. This initial phase is critical and includes strategic actions such as:
- Selecting appropriate seeds or breeds for targeted climate and soil conditions.
- Designing crop rotation techniques to maintain soil fertility and reduce pest cycles.
- Budgeting for resources—ensuring optimal allocation for labor, equipment, and agricultural inputs.
- Setting the foundation for sustainability, profitability, and optimal resource utilization.
Smart planning and preparation not only sets up the process of farming for success but also underpins the sustainability of the food production system. Incorporating market research into planning ensures alignment with consumer demand and maximizes profitability.
Related Resource: For streamlined, data-driven planning based on satellite-data insights, try the Farmonaut Large-Scale Farm Management App—empowering users to plan operations with precision and confidence.
Step 2: Soil Preparation and Health Management
Unlocking Yield Potential through Soil Science
Soil is the heartbeat of agriculture, underpinning the entire process of farming. Soil health management merges traditional techniques with conservation agriculture methods for sustainable, long-term productivity. Here’s how effective soil preparation unlocks yield and resilience:
- Tilling and Plowing: Preparing the field by breaking up compacted soil layers, improving aeration, and incorporating organic matter.
- Incorporating Organic Matter: Adding compost or farmyard manure to enhance soil structure, nutrient cycling, and retention.
- Minimal/No-Till Techniques: Using no-till farming to minimize soil disturbance, reduce erosion, and improve water retention, which supports both yields and climate resilience.
- Maintaining Permanent Cover: Using cover crops and mulch to shield soil, promote biodiversity, and reduce weed pressure.
- Contour Plowing and Terracing: Strategic land shaping to reduce surface runoff and protect against erosion, especially on slopes.
Utilizing technologies like Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting solutions allows for measured improvement in soil organic carbon and overall environmental stewardship.
“Healthy soil management can cut water usage in farming by nearly 30%, supporting sustainable agriculture.”
Step 3: Planting—Modern Techniques and Crop Rotation
Precision Sowing and Enhanced Germination
The planting stage truly brings farming to life. Here, the main aim is the precise placement of seeds or transplanting of healthy seedlings. Advancements in agricultural machinery have revolutionized this stage, enabling:
- Direct Seeding: Mechanical planters help evenly distribute seeds at correct depths and spacing.
- Transplanting: Specialized equipment ensures healthy establishment of crops that benefit from early indoor growth (such as rice, tomatoes, peppers).
- Smart Planting Tools: Precision agriculture tools help optimize seed density and germination rates, leading to robust crop stands.
- Crop Rotation Techniques: Rotating crop species from season to season helps to interrupt pest cycles, reduce disease pressure, and maintain nutrient balance.
Planting is directly enabled by accurate field mapping, weather prediction, and soil health data—empowering decisions around timing, method, and inputs for optimal establishment.
Did you know? Farmonaut provides Fleet Management Tools for large and small-scale farmers to coordinate planting operations efficiently, maximizing labor and equipment utilization while reducing costs and waste.
Step 4: Crop Management—Integrated Pest Management, Monitoring & More
Nurturing Growth for Sustainability and Yield
Ongoing crop management is at the heart of healthy agriculture. Sustainability, yield, and food safety all depend on how well we monitor, manage, and nurture crops. Keys to effective crop management include:
- Monitoring for Pests and Diseases: Early detection and accurate identification through regular scouting and data-driven surveillance.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): A holistic approach that combines biological controls (beneficial insects), cultural practices (crop rotation), physical barriers, and minimal/targeted chemical inputs to keep pests in check, reduce resistance, and safeguard the environment.
- Optimizing Fertilizer Application: Soil testing and precision agriculture tools target nutrient application for improved uptake and reduced waste.
- Irrigation Scheduling: Matching water supply to crop need using soil moisture sensors and weather data, reducing water use and stress.
- Using Technology for Management: Tools like those from Farmonaut provide real-time crop health monitoring, supporting informed decisions throughout the crop cycle.
With sustainable practices such as cover cropping, minimum tillage, and integrated pest management, modern crop management becomes less reliant on chemical interventions—ensuring produce quality, system resilience, and long-term profitability.
Step 5: Efficient Crop Harvesting Methods
Maximizing Yield and Minimizing Losses at Harvest
A season of diligent management, monitoring, and nurturing culminates in the harvest. Efficient crop harvesting methods ensure that the effort invested during earlier stages is fully realized as top-quality, market-ready product. Highlights of the harvesting process include:
- Timely Harvesting: Using crop maturity indicators, predictive weather data, and technological alerts to harvest at peak quality, avoiding both under- and overripeness.
- Modern Machinery: Combines, harvesters, and specialized equipment allow for large-scale harvesting with reduced labor needs and lower losses. For certain high-value fruits and delicate crops, manual harvesting preserves product quality.
- Reducing Waste: Smart logistics and resource management, such as Farmonaut Fleet Management, optimize transport and minimize the time between harvest and storage.
By tailoring harvesting techniques to specific crop and climate conditions, farmers can maximize yield, reduce waste, and ensure the highest possible product quality for market distribution.
Step 6: Post-Harvest Handling and Storage
Preserving Quality & Minimizing Losses After Harvest
Once crops leave the field, they enter another critical process of farming: post-harvest handling and storage. Losses at this stage directly impact farmer livelihoods and food security. Priority practices include:
- Cleaning and Sorting: Removing debris and separating by size or quality grade for optimal sale and reduced spoilage.
- Packaging: Using protective, food-safe materials to extend shelf-life, prevent contamination, and retain product quality.
- Storage Solutions: Cold rooms, controlled/modified atmosphere storage, and refrigerated containers slow ripening and reduce spoilage.
- Waste Minimization: Monitoring inventory and using technology to rotate stock efficiently, limiting perishables’ time in storage.
Farmonaut helps modern farms optimize this phase through features such as Blockchain-Based Traceability—securing the integrity, transparency, and trustworthiness of agricultural product movement from field to end-consumer.
Step 7: Marketing, Distribution & Reaching Consumers
Bringing Farm Fresh Produce to the Market
The final stage in the process of farming is connecting the harvested product to consumers. Effective marketing and distribution ensures profitability and the sustainability of agricultural livelihoods. This stage emphasizes:
- Understanding Market Demand: Analyzing trends and consumer preferences to align product offerings with demand.
- Channels of Distribution: Farmers can sell via direct-to-consumer models like farmers’ markets or community-supported agriculture programs, or work with wholesalers and retailers.
- Branding & Value Addition: Employing storytelling, certifications, and traceability (like that enabled by Farmonaut’s Product Traceability) to build trust and achieve premium prices.
- Smart Marketing: Utilizing digital platforms and real-time supply data to manage pricing, forecast demand, and minimize unsold inventory.
With robust product quality, efficient logistics, and transparent traceability, farms can meet modern consumer expectations while improving their profitability.
Sustainable Farming Process: Steps, Key Actions, and Estimated Benefits
| Farming Step | Key Actions/Technologies Used | Sustainable Practice Incorporated | Estimated Environmental Benefit | Expected Yield Improvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Planning & Preparation | Satellite data analysis, digital mapping, climate forecasting, resource allocation tools | Strategic crop planning, crop rotation, optimized input use | Resource savings up to 20% | 10%-15% |
| Soil Preparation | Soil testing, conservation tillage, compost addition | No-till, cover cropping, contour plowing | Erosion reduction up to 75% | 12%-20% |
| Planting | Precision planters, drone seeding, transplanting | Optimal spacing, intercropping, crop rotation | Reduced seed wastage by 13%-20% | 10%-15% |
| Crop Management | Remote sensing, soil sensors, IPM, AI-advisory | Reduced chemical inputs, pest biocontrol, precise irrigation | Chemical use lowered by 30%-50% | Up to 20% |
| Harvesting | Combine harvesters, GPS mapping, labor management apps | Minimized grain loss, reduced labor intensity | Labor reduction 30%-50% | 5%-12% |
| Post-Harvest Handling & Storage | Cold storage units, sorting/cleaning tech, traceability platforms | Low-energy cooling, biodegradable packaging | Post-harvest loss reduced by 25%-50% | 10%-15% |
| Marketing & Distribution | Digital marketing, demand forecasting, blockchain traceability | Direct sales, transparent sourcing, efficient logistics | Transport emissions lowered by 15%-30% | 5%-10% |
Sustainable Farming Practices and Environmental Conservation
The principle of sustainability in agriculture is to strike a balance between production, resource conservation, environmental stewardship, and profitability. Leading sustainable farming practices include:
- Conservation agriculture methods: Using no-till, minimal disturbance, permanent organic soil cover, and crop rotations to improve soil health, reduce erosion, and increase water retention.
- Integrated pest management (IPM): Reducing chemical use and building resilient cropping systems through ecological pest suppression.
- Agroforestry and Intercropping: Integrating trees, shrubs, and diverse species to promote biodiversity, carbon sequestration, and microclimate regulation.
- Optimized Resource Use: Precision irrigation, targeted fertilization, and advanced field monitoring lowers environmental impact and operating costs.
- Reduced Inputs and Waste: By using biodegradable packaging and precision application of chemicals and water, we cut down on agricultural pollution and loss.
These sustainable farming practices are key to preserving our planet while feeding an increasing population.
Modern Agricultural Technology & Precision Tools
Revolutionizing Farming with Innovations
The integration of technology in agriculture is reshaping every stage of the farming process. Modern agricultural technology is characterized by:
- Precision Agriculture Tools: Utilize GPS-guided equipment, variable-rate technology (VRT), and drones for exact application of water, fertilizers, and crop protection agents.
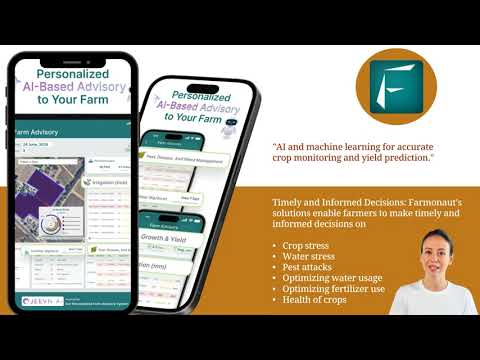
- Remote Sensing & Satellite Imagery: Farmonaut’s platform provides real-time crop health monitoring so that interventions are targeted where they’re needed most—reducing resource wastage and maximizing yields.
- AI-Based Farm Advisory: Tools like Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI system deliver actionable guidance and weather forecasts for effective, data-driven farming decisions.
- Blockchain-Based Traceability: Critical for modern food systems, this innovation ensures that all agricultural products can be verified back to their source, building consumer trust and supply chain security.
- IoT Sensors for Smart Management: Soil sensors and automated irrigation controllers provide feedback on real-time field conditions, enabling precise resource management.
Adopting these breakthroughs translates into substantial improvements in efficiency, quality, environmental impact, and profitability across every step of the farming process.
How Farmonaut Empowers Sustainable Farming
Enabling Precision, Sustainability and Success Globally
As a pioneering agricultural technology company, Farmonaut is committed to making precision agriculture affordable and accessible with satellite-based farm management solutions for farmers and agribusinesses worldwide. Our services, available via Android, iOS, web, and API, help users monitor crops, optimize resource use, and reduce environmental footprint. Here’s how:
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Get real-time insights into soil health, crop vigor (NDVI), and moisture conditions—empowering timely, informed farming decisions for optimal yields.
- AI-Powered Advisory: Our Jeevn AI system delivers tailored advice, weather forecasts, and crop management recommendations—improving productivity and responding to real-time challenges.
- Blockchain Traceability: Our product traceability solutions secure the entire crop journey, boosting transparency and reducing the risk of fraud.
- Fleet/Resource Management: Manage logistics, field operations, and machinery efficiently—lowering labor costs and emissions.
- Carbon Footprinting: Our carbon footprint tracking tools allow agribusinesses to monitor and reduce emissions, supporting regulatory compliance and environmental conservation.
Our offerings are flexibly priced, scalable for farms and organizations of all sizes, and accessible globally. We believe in transforming agriculture through technology, sustaining farmers and our shared planet for generations to come.
Ready to take your farm to the next level?
- Try the Farmonaut Web App for precision monitoring.
- Build custom solutions with our API (Developer Docs).
- Streamline paperwork with crop loan and insurance verification—reducing fraud and improving financing access.
Challenges and Future Directions in Sustainable Agriculture
While technology and innovation have greatly enhanced sustainable farming practices, future success will depend on our ability to respond flexibly and proactively to new and ongoing challenges, including:
- Climate Change: Erratic weather, droughts, and floods require resilient farming systems, drought-resistant crop breeds, and robust risk management strategies.
- Water Scarcity: With responsible soil management, precision irrigation, and water recycling, we can reduce water use and minimize waste.
- Soil Degradation: Continuous innovation in soil health management, nutrient cycling, and restoration is essential to ensure healthy future crops.
- Market Volatility: Digital platforms, demand forecasting, and supply chain tracking help farmers successfully navigate market uncertainty and pricing shifts.
- Knowledge and Technology Gaps: Expanding education, research, and affordable access to modern agricultural technology will empower even smallholder farmers.
- Data and Artificial Intelligence: Leveraging machine learning for targeted advisory, yield prediction, and automated resource management will further boost efficiency and productivity at scale.
By continuing to refine and innovate at every step—from planning and soil preparation to marketing and traceability—farming can evolve to meet the dual challenges of food security and environmental conservation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Sustainable Farming Practices
What are the main steps in the process of farming?
The seven essential steps are: planning and preparation, soil preparation, planting, crop management, harvesting, post-harvest handling and storage, and marketing/distribution.
What is meant by sustainable farming practices?
Sustainable farming practices aim to balance profitable food production with environmental protection, efficient resource use, and social responsibility. This includes using conservation agriculture, integrated pest management, proper soil health management, and modern precision technologies that minimize inputs and environmental footprint.
How does crop rotation help soil health?
Crop rotation techniques break pest and disease cycles, replenish soil nutrients, and reduce the need for chemical inputs—helping maintain soil fertility and structure for long-term productivity.
How can technology make farming more sustainable?
Through innovations like satellite monitoring, artificial intelligence, soil and weather sensors, and blockchain-based traceability, technology enables precision input use, real-time problem detection, waste reduction, and greater supply chain transparency—helping farms become more efficient, resilient, and environmentally sound.
Why is post-harvest handling important?
Proper post-harvest handling and storage reduce food losses, maintain quality, extend shelf life, and boost farmer incomes by ensuring crops reach market in optimal condition.
How does Farmonaut support sustainable farming?
Farmonaut provides affordable precision agriculture solutions—including real-time crop monitoring, AI-based crop advisory, carbon footprint tracking, fleet management, and blockchain traceability—driving sustainability, efficiency, and profitability for farmers globally.
Conclusion: Optimizing the Process of Farming for Sustainable Success
The future of farming lies in the intelligent integration of traditional practices with modern agricultural technology and a steadfast commitment to sustainability. By optimizing each stage—from planning and preparation through to crop management, efficient harvesting, post-harvest handling, and marketing—farmers can maximize yield, maintain environmental stewardship, and ensure lasting food security.
Adopting sustainable farming practices, leveraging precision agriculture tools, and embracing ongoing innovation are key—allowing us all to meet growing demand without compromising the health of our planet. With dedicated tools like Farmonaut, we now have the power and insight to make informed decisions at every turn of the farming process.
Begin your journey towards sustainable success in farming:
- Access powerful farm management via the Farmonaut Web and Mobile App.
- Empower research and development using the Farmonaut API.
- Ensure supply chain transparency with Blockchain-based Product Traceability.
Let’s build a more resilient, profitable, and sustainable world—one farm, one field, one step at a time.