Agriculture Technology and Management: Top 7 Innovations
Agriculture technology and management have witnessed significant transformations in recent decades, driven by the rising challenges of climate change, the growing global population, and the urgent need for sustainability. Farmers and agribusinesses across the world are adopting innovative technologies and management practices to ensure improved productivity, resilience against shocks, and better environmental stewardship. This evolution encompasses state-of-the-art systems such as precision agriculture, integrated pest management (IPM), farm management software (FMS), crop monitoring systems, climate-smart agriculture (CSA), and other emerging technologies in agriculture.
In this comprehensive guide, we break down the top seven agricultural innovations transforming modern farming efficiency, crop yields, and sustainability. If you are a farmer, agri-business, or industry stakeholder seeking to optimize your operations or simply learn about the future of agriculture technology and management, you are in the right place.
- Introduction: The Evolution of Agricultural Technology and Management
- 1. Precision Agriculture
- 2. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
- 3. Climate-Smart Agriculture (CSA)
- 4. Emerging Technologies in Agriculture
- 5. Farm Management Software (FMS) and Crop Monitoring Systems
- 6. Mobile Agriculture (mAgri) and Digital Advisory
- 7. Sustainable Practices and Resource Management
- Comparison Table: Top 7 Agricultural Innovations
- Adoption Challenges and Future Outlook
- Farmonaut: Pioneering the Future of Agricultural Technology
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Agriculture Technology and Management
- Conclusion
Introduction: The Evolution of Agricultural Technology and Management
The landscape of global agriculture has undergone a dramatic evolution in recent decades. Constantly rising food demand, erratic weather patterns, soil degradation, and the threat of pests and diseases have challenged traditional farming practices. In response, innovative technologies and management strategies have emerged, redefining how farmers monitor, manage, and optimize their fields.
The integration of data-driven agricultural technology is not just about boosting productivity or reducing costs; it’s about building resilience into the food system, ensuring environmental sustainability, and securing better livelihoods for farmers. Below, we explore the top seven innovations propelling this transformation.
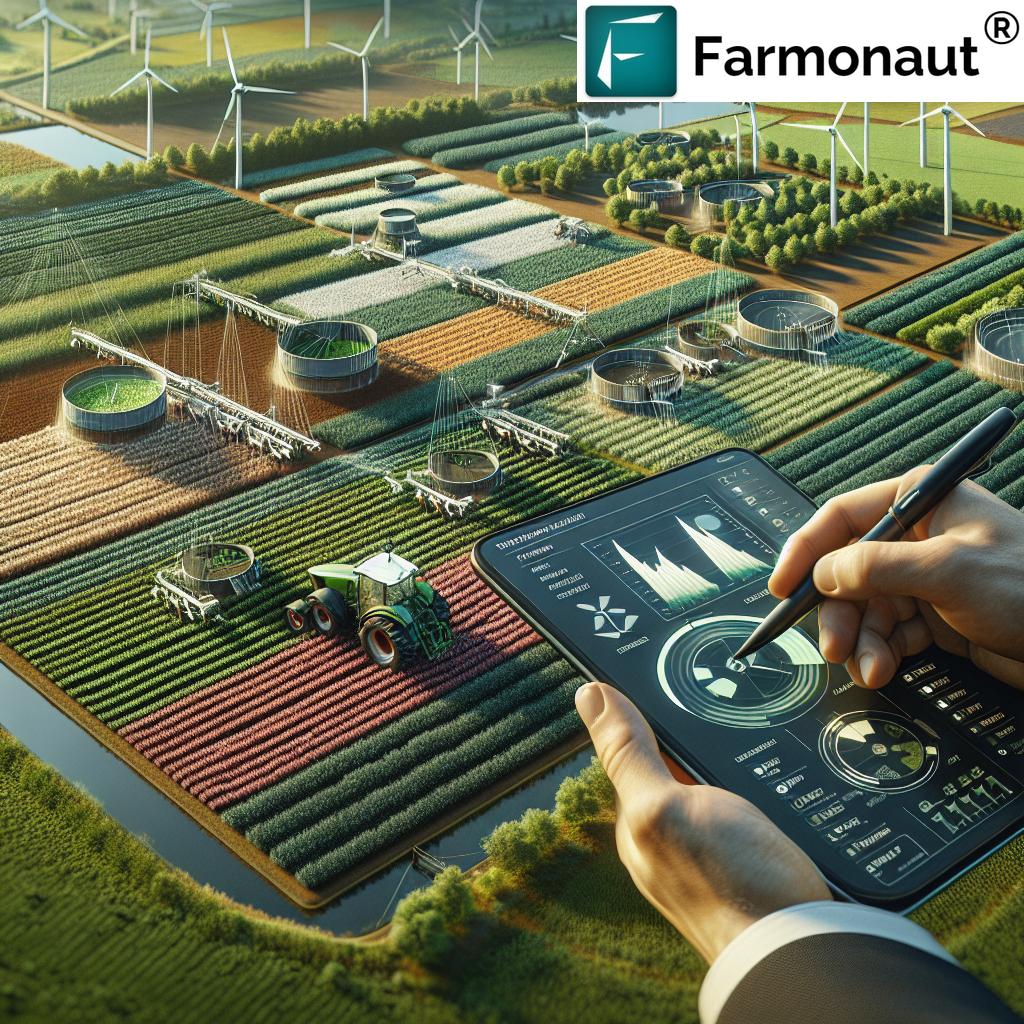
1. Precision Agriculture: Optimizing Productivity Through Technology
Precision agriculture (precision farming) represents a paradigm shift in how farmers approach management of their fields. Instead of uniform application of inputs, precision farming techniques leverage data and advanced technologies to analyze variability within and between fields. This enables far more targeted, efficient, and sustainable use of resources.
- Data-Driven Decisions: By collecting and analyzing soil, crop, and weather data, farmers make informed choices about planting, irrigation, fertilization, and harvesting.
- Reducing Waste: Applying inputs (like fertilizer and water) only where needed minimizes waste, protecting both the environment and farm budgets.
- Increasing Efficiency: Technologies such as GPS-guided equipment, variable rate technology (VRT), and remote sensing (satellite imagery and drones) maximize operational efficiency.
Why is Precision Agriculture Essential?
Farms experience significant variability in soil conditions, moisture, and crop health due to natural or human-induced differences. Traditional methods treat all areas the same, often resulting in resource inefficiencies, reduced yields, and environmental harm (runoff of pesticides and fertilizers). Precision agriculture empowers farmers to optimize each step for maximum output and sustainability.
Key Precision Agriculture Tools & Techniques
- GPS-Guided Tractors & Equipment: Ensure precise field operations (e.g., apply fertilizers and seeds exactly where needed).
- Satellite Crop Monitoring Systems: Real-time imagery helps monitor health, soil moisture, detect pest outbreaks, and track growth patterns for informed decisions.
- Variable Rate Technology (VRT): Adjusts input rates based on location—fertilizers, pesticides, and water applied only where necessary.
For those interested in affordable, AI-powered satellite-based crop health monitoring, we at Farmonaut offer an advanced platform that delivers real-time field data, custom advisories, and simple farm management tools available via Android, iOS, and web Apps, as well as developer-friendly APIs.
Resource: Explore carbon footprinting and sustainability tracking for agriculture—an integrated part of our satellite suite that helps reduce environmental impact.
2. Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Reducing Chemical Dependency for Sustainable Crop Protection
Integrated pest management (IPM) is an ecological, systematic approach to pest control that combines biological, cultural, physical, and chemical tools. IPM maximizes crop resilience and productivity while reducing environmental impact and cutting excessive pesticide use.
- Monitor pest populations and fields regularly to detect problems early.
- Set action thresholds—only take action when pest levels threaten crop yields or quality.
- Combine strategies: Encourage beneficial insects, use disease-resistant varieties, rotate crops, and if necessary, apply pesticides as a last resort with precision.
How IPM Works: A Practical Approach
- Prevention: Select resistant plant varieties; rotate crops; improve field hygiene.
- Monitoring: Use field scouting, remote sensing, and digital crop monitoring systems to detect pests and outbreaks.
- Decision Making: Set economic injury thresholds to guide interventions.
- Implementation: Use biological controls (e.g., beneficial insects), precision chemical application, and physical barriers.
- Assessment: Continuously evaluate results and adapt strategies.
According to recent studies, integrated pest management practices can reduce pesticide use by up to 50% without sacrificing yield—resulting in greater sustainability and enhanced food safety.
Digital IPM is gaining traction thanks to AI-based advisory systems and real-time monitoring tools. For example, Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI advisory provides instant, field-specific recommendations for IPM and controlled pesticide application, directly equipping farmers anywhere with expert guidance (learn about Jeevn AI in the app).
Furthermore, Fleet and Resource Management by Farmonaut supports large-scale and small farms by managing field operations, monitoring fleet logistics, and reducing operational costs through optimized scheduling and equipment usage.
3. Climate-Smart Agriculture (CSA): Building Resilience for a Changing Planet
Climate-smart agriculture (CSA) is an integrated approach that aims to increase agricultural productivity, enhance resilience to climate change, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions from farming. As unpredictable weather patterns, more frequent droughts, and extreme events challenge traditional agriculture, CSA has become vital for food security.
- Adaptive Practices: Use drought-resistant crop varieties and alter planting dates.
- Efficient Water Management: Implement smart irrigation systems and rainwater harvesting to conserve resources.
- Soil and Water Conservation: Apply techniques such as mulching, cover cropping, and reduced tillage to protect soil and retain water.
- Climate Data Integration: Data on weather forecasts and soil moisture help farmers make adaptive, informed decisions.
- Carbon Footprinting: Track and reduce carbon emissions from farming operations to ensure long-term environmental sustainability.
Farmonaut provides advanced carbon footprinting tools so agribusinesses and farmers can actively monitor their environmental impact, meeting sustainability objectives and regulatory requirements.
Real-life Example: A farm integrates satellite-based soil moisture monitoring, adopts smart irrigation controls, and chooses heat-tolerant crops. As a result, it withstands a severe drought while maintaining yields—showcasing the power of climate-smart agriculture.
To further bolster food security and climate resilience on a national scale, government agencies often utilize large-scale farm monitoring platforms powered by remote sensing, such as those we offer at Farmonaut.
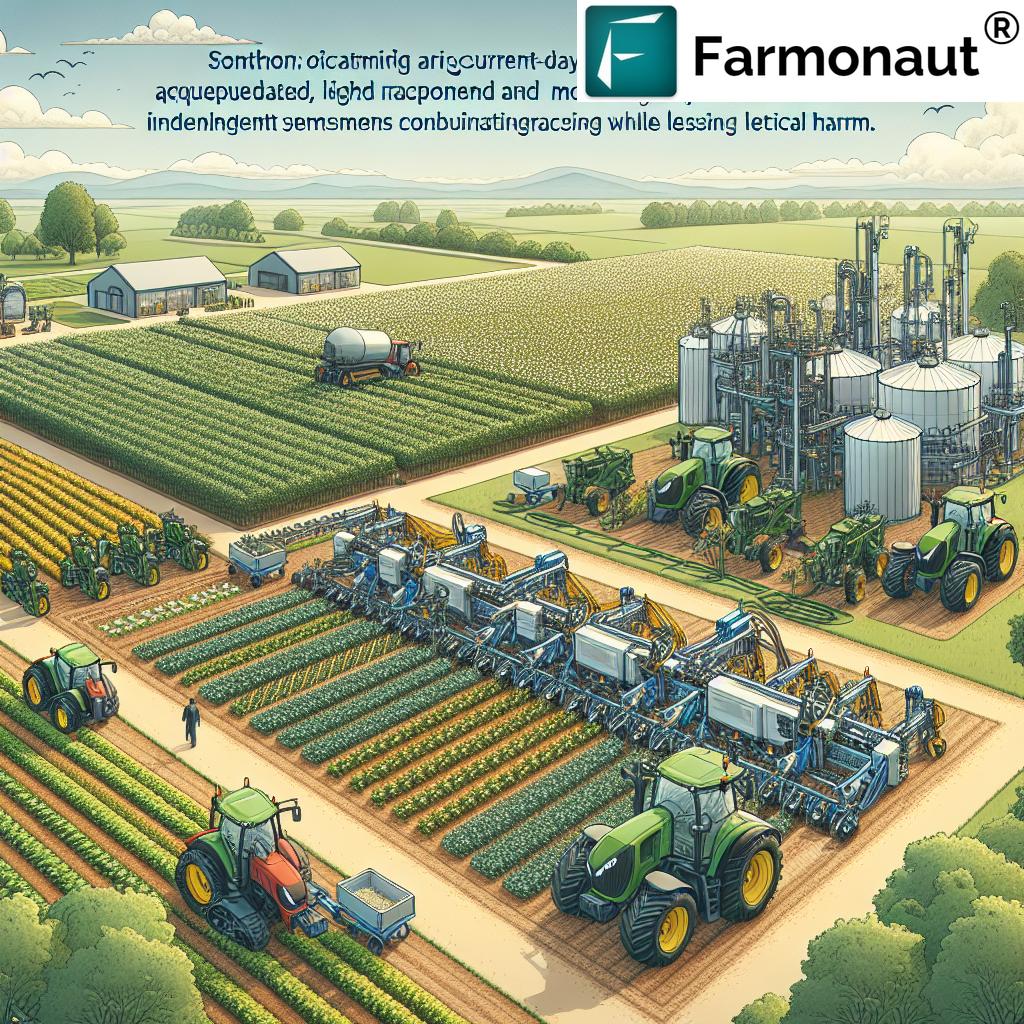
4. Emerging Technologies in Agriculture: Drones, Robotics, and Beyond
The rapid integration of emerging technologies in agriculture—including Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) or drones, robots, and the Internet of Things (IoT)—is revolutionizing farming operations and management.
- Drones (UAVs): Perform aerial crop surveys, pest monitoring, mapping, and even biological pest control (releasing beneficial insects in the field). Their real-time imagery assists in precise crop monitoring and assessment of stress.
- Agricultural Robots: Handle tasks such as planting, weeding, and harvesting autonomously—saving on labor costs and increasing consistency.
- IoT Sensors: Deployed in fields, they capture soil conditions, moisture, and microclimate data to guide decisions on irrigation and fertilization in real time.
- Automated Machinery: Self-steering tractors and harvesters increase efficiency and allow farmers to manage larger areas.
- Blockchain for Traceability: Track food from farm to fork, ensuring safety and authenticity. We at Farmonaut support this via blockchain-based product traceability for agriculture commodities, addressing consumer trust and regulatory needs.
These emerging systems not only improve accuracy and yields but also create new data layers for advanced farm analysis, tying seamlessly into modern farm management software and digital decision-making.
Resource: For agriculture input businesses or developers wishing to build on top of Farmonaut’s satellite and weather-based APIs, check out: Farmonaut Satellite Weather API Developer Docs.
5. Farm Management Software (FMS) and Crop Monitoring Systems
Farm management software (FMS) brings together all aspects of farm operations into one digital hub. From tracking crop and livestock performance to managing finances, planning planting & harvesting schedules, and analyzing data, FMS makes management vastly more robust and transparent.
- Centralized data enables better scheduling, resource allocation, and rapid response to field conditions.
- Integration with crop monitoring systems (from satellites, drones, and sensors) automates field analysis and helps detect issues early.
- Platform-based advisory services (AI-driven) personalize farm recommendations for each field, crop, and season.
- Mobile and web accessibility ensures farmers can manage operations anytime, anywhere.
At Farmonaut, we deliver satellite-based FMS tools via Android, iOS, and web Apps that empower individual farmers and large agribusinesses to maximize yields and profitability while reducing input waste.
Learn more about dedicated satellite crop verification for crop loans and insurance—a crucial feature ensuring access to finance and transparency for both farmers and financial institutions.
6. Mobile Agriculture (mAgri) and Digital Advisory: Empowering Decision-Making on the Go
Mobile agriculture (mAgri) taps into the proliferation of mobile devices to connect farmers with market, weather, and agriculture technology services—even in the most remote regions.
- Instant Access: Weather updates, price alerts, digital market linkages, and expert advice delivered to mobile phones.
- Inclusivity: Lowers the entry barrier for smallholder farmers by making digital management services affordable and accessible.
- Smart Apps: Apps like those provided by us at Farmonaut (Download Now) deliver crop health alerts, real-time soil and water conservation insights, and more directly to mobile devices.
When combined with field sensors and remote crop imagery, mAgri creates a powerful digital extension, substantially improving the efficiency of farming operations and resilience to changing climate and market conditions.
7. Sustainable Practices and Resource Management: Meeting Future Food Demands
True sustainable farming practices balance present food needs with the future capacity of the earth to regenerate. This involves maximizing output while safeguarding soil health, water, and biodiversity for generations to come.
- Smart Irrigation Systems: Auto-regulate water use based on soil moisture, weather, and crop demand; drastically reduce waste.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Solar-powered pumps and equipment for sustainable energy use and reduced carbon footprint.
- Soil Conservation: Reduced tillage, organic amendments, and conservation agriculture techniques prevent erosion and foster soil fertility.
- Resource Management: Remote crop monitoring systems and data analytics enable precise resource allocation and increase overall efficiency.
Farmonaut’s focus on sustainability is evident through our carbon tracking, resource management tools, and precise field-level recommendations available in our app ecosystem.
Comparison Table: Top 7 Agricultural Innovations
| Innovation Name | Brief Description | Key Benefits | Estimated Increase in Productivity (%) | Sustainability Impact | Adoption Rate (%) | Example Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision Agriculture | Data-driven field management using sensors, maps, and analytics | Higher yields, reduced input costs, minimized waste | 10–20% | High | 35–40% | Cereals, oilseeds, vegetables |
| Integrated Pest Management (IPM) | Combining biological, cultural, and selective chemical pest controls | 50% less pesticide, improved crop resilience | 7–15% | High | 30–50% | Fruits, vegetables, cotton |
| Drones (UAVs) | Aerial crop monitoring, mapping, and targeted spraying | Faster scouting, early pest detection, precise input application | 5–12% | Medium | 10–20% | Rice fields, orchards, large-area crops |
| IoT Sensors | Networked soil, weather, and crop condition sensors | Optimal irrigation/fertilizer, disease outbreak alerts | 8–15% | Medium-High | 12–18% | Greenhouses, open vegetable fields |
| Satellite Monitoring | Remote crop health monitoring using satellite imagery | Wide-area, real-time insights, boost efficiency | 7–20% | High | 30–38% | Wheat, rice, sugarcane, large row crops |
| Automated Machinery | Self-steering tractors/harvesters, robots for field tasks | Lower labor costs, higher operational consistency | 10–18% | Medium | 6–14% | Corn harvest, large-scale row crops |
| Smart Irrigation | Sensor-driven water management systems, drip/trickle irrigation | Water savings, improved yields, drought resilience | 9–17% | High | 17–24% | Vegetables, fruit orchards, arid regions |
Adoption Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite the clear benefits, global adoption of advanced agriculture technology and management faces persistent challenges:
- Initial Costs: Many technologies require upfront investment, which is harder for smallholders or those without access to affordable financing.
- Technical Complexity: Modern systems need digital literacy and sometimes broadband coverage, posing accessibility hurdles.
- Knowledge Gap: Without training, farmers may not realize the full potential of their technology investments.
- Infrastructure and Connectivity: Rural areas may lack networks for remote crop monitoring systems or reliable app-based services.
- Data Privacy & Digital Divide: Some farmers remain cautious about data sharing; inclusion strategies are vital.
Closing these gaps calls for inclusive policies, financial support, robust extension services, and intuitive technology (like that delivered by us at Farmonaut).
Farmonaut: Pioneering the Future of Agricultural Technology
We at Farmonaut stand at the forefront of agricultural technology and management innovation, striving to make precision agriculture accessible and affordable for farmers globally. Our platform blends advanced satellite-based crop monitoring systems, AI-driven advisory tools, blockchain traceability, and robust resource management into one unified experience.
- Real-Time Satellite Crop Health Monitoring: Analyze NDVI, soil moisture, and much more for precisely informed decisions on irrigation, fertilization, and pest management.
- AI-Based Personalized Farm Advisory (Jeevn AI): Delivers field-specific, actionable guidance for crop management and maximizing productivity.
- Blockchain-Based Traceability: Sets a new standard for transparency in the food and textile supply chain (learn more on our Traceability Product Page).
- Fleet & Resource Management: Optimize equipment, logistics, and operations—especially valuable for large farming enterprises (details here: Farmonaut Fleet Management).
- APIs and Developer Tools: Extend satellite and weather insights into your own apps via our powerful APIs and API Docs.
Our mission is simple: empower farmers and agribusinesses—regardless of scale or location—to optimize every input, increase productivity, and champion sustainable farming practices for the future of food security worldwide.
Want to experience Farmonaut’s innovations? Try our platform or check subscription options below:
Check our dedicated digital advisory for forest, crop, and plantation management at: Farmonaut Crop Plantation & Forest Advisory
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Agriculture Technology and Management
Conclusion
Modern agriculture technology and management have ushered in a new era for global food production. With advances such as precision agriculture, integrated pest management, climate-smart agriculture, and farm management software, farmers now possess powerful tools to boost productivity, safeguard the environment, and meet the demands of a growing global population.
As innovative crop monitoring systems, emerging technologies like drones and IoT, and robust digital decision-making tools become more accessible, the future of farming is one of unprecedented efficiency, resilience, and sustainability.
At Farmonaut, our mission remains to democratize access to these innovations, making advanced agricultural technology affordable and actionable for every farmer, everywhere. It’s not just about technology—it’s about building a smarter, more resilient agricultural future together.
Ready to transform your farming operations? Download the Farmonaut Android App or the iOS App today, or access our web platform.
Together, let’s innovate, conserve, and build a sustainable future for agriculture.