Internet of Things Smart Farming: 7 Ways IoT Transforms Ag
“Over 75 million IoT devices are projected to be used in agriculture worldwide by 2025, transforming data-driven farming.”
Summary: The Role of Internet of Things Smart Farming
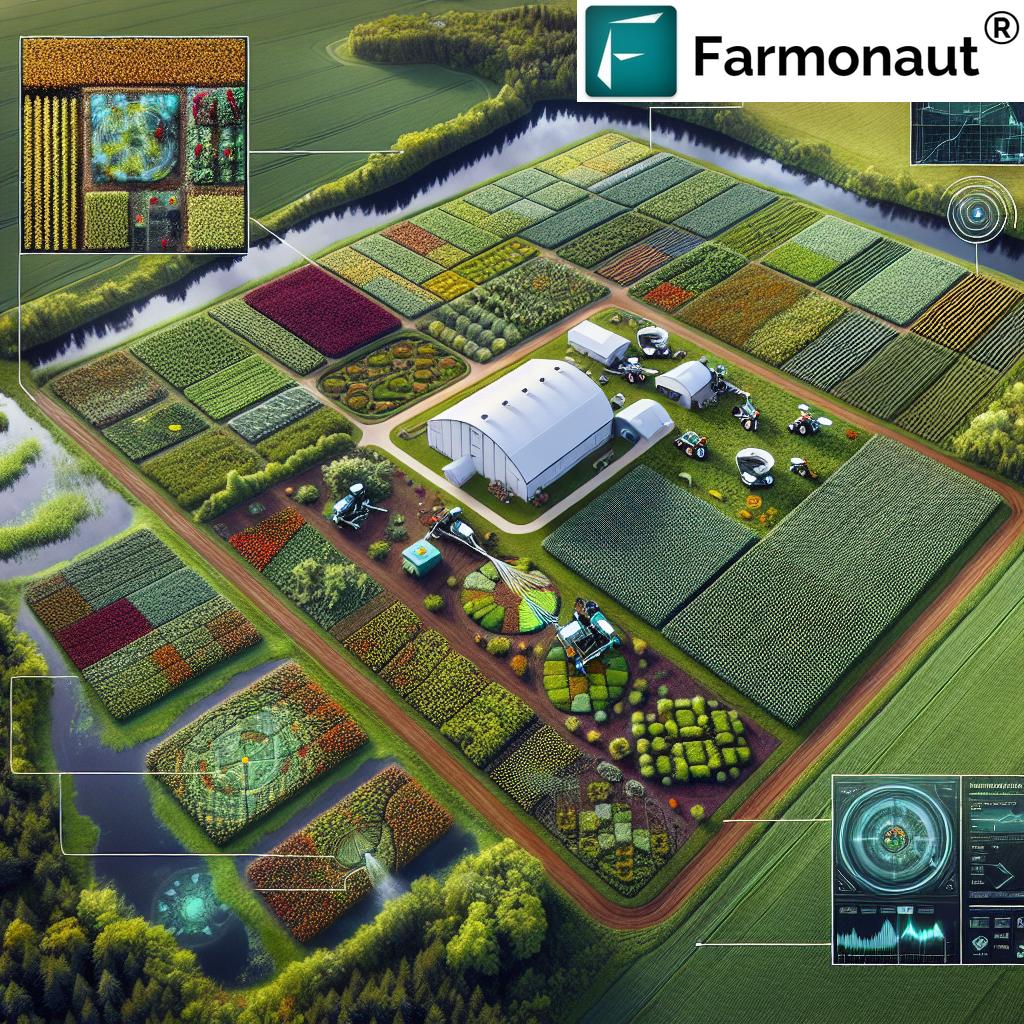
Internet of Things smart farming is transforming agriculture and forestry into sophisticated, data-driven industries. Through interconnected devices, precision monitoring, and intelligent analytics, farmers and foresters now manage their operations with unprecedented accuracy, efficiency, and sustainability. By leveraging IoT sensors, smart agriculture internet of things platforms, and innovative solutions, the industry is witnessing a shift from traditional methods towards connected, automated, and climate-resilient practices. In this article, we explore the applications, benefits, challenges, and future prospects of IoT in smart farming and forestry, delving deep into how this technology is revolutionizing the global farming industry.
Understanding IoT in Agriculture and Forestry
The Internet of Things in agriculture refers to a vast network of interconnected physical devices—including sensors, automated machinery, and software—embedded across fields, barns, and forests to collect, process, and exchange data via the internet. In this ecosystem, sensors monitor variables like soil moisture, crop health, weather conditions, and machinery status. These insights empower precision agriculture, where every input and intervention is optimized for maximum productivity and minimal waste.
- Key Goal: Enable farmers and foresters to make informed, timely, and accurate decisions that optimize resources and reduce risks.
- How It Works: IoT devices capture real-time data which is transmitted via stable networks (Wi-Fi, 4G/5G, LPWAN, or satellite) to cloud platforms. There, advanced analytics and AI algorithms analyze it, delivering actionable recommendations.
Key Components of IoT in Smart Farming
The backbone of smart agriculture internet of things systems comprises various technologies and infrastructure elements. Let’s break them down:
1. Sensors and Devices
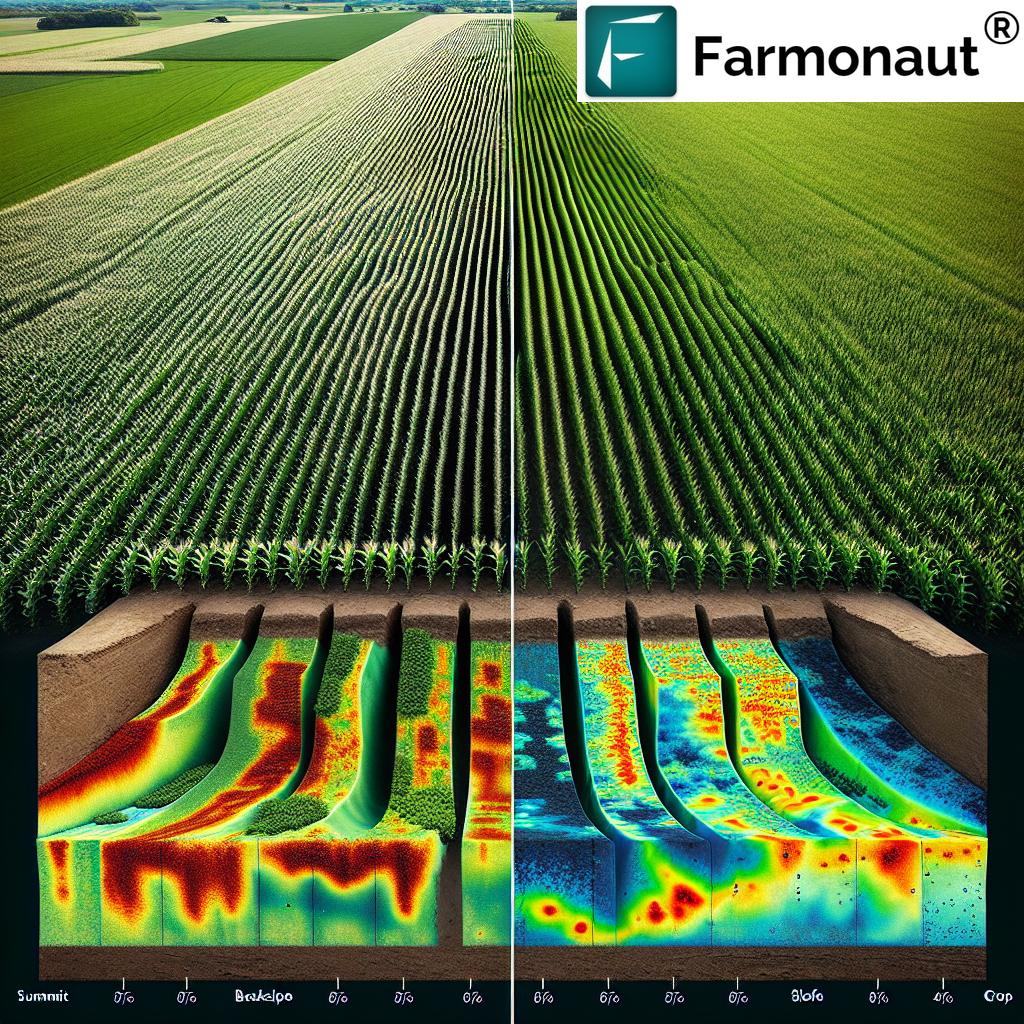
- Soil Moisture Sensors: Continuously measure soil water content, providing data for automated irrigation systems.
- Weather Stations: On-field or connected via satellite, these monitor temperature, humidity, rainfall, wind, and more, supplying crucial context for farm management.
- Drones Equipped with Cameras: Conduct aerial surveys for crop health assessment, detecting pests and disease risks early.
- GPS Collars for Livestock: Enable real-time tracking of animal health, grazing patterns, and location.
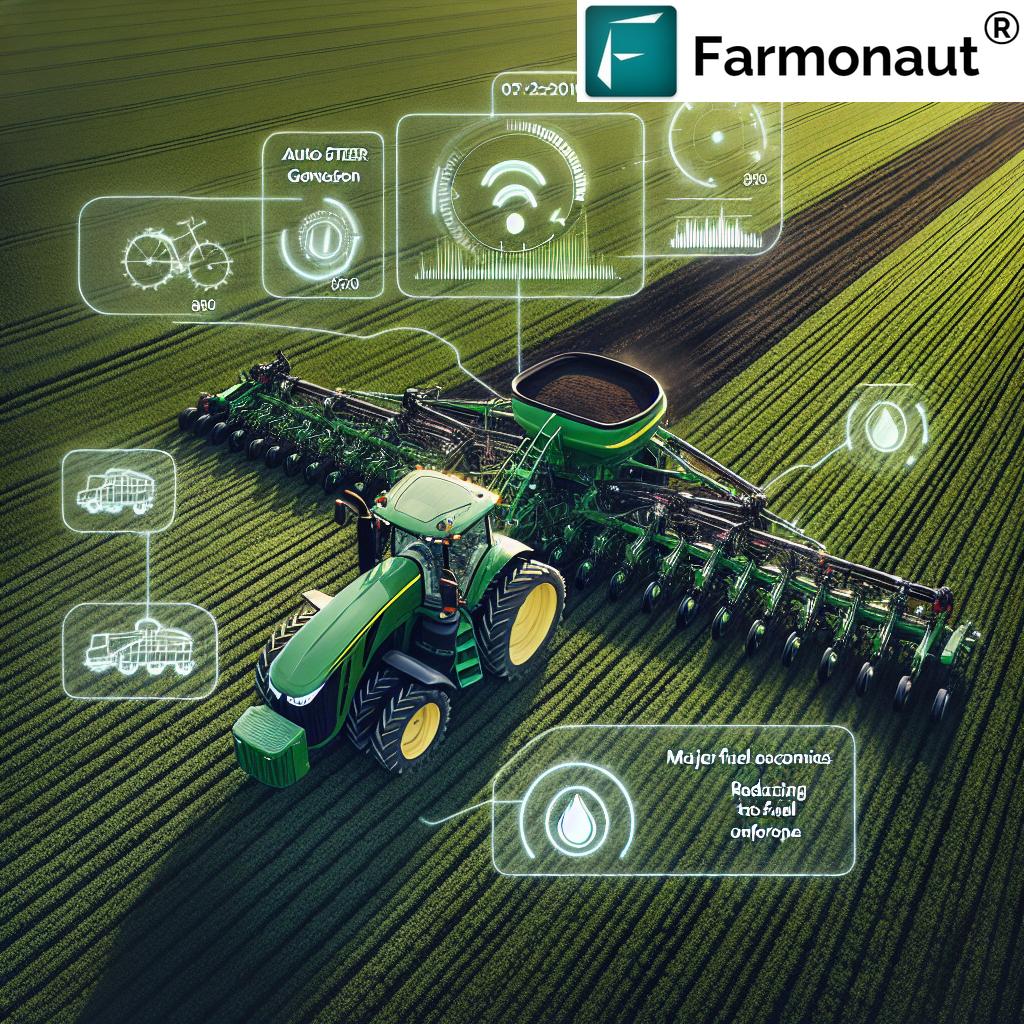
- Automated Machinery: Autonomous tractors, robotic equipment, and precision sprayers execute tasks based on IoT data.
2. Connectivity Infrastructure
- Robust internet-enabled networks are foundational for real-time data exchange between devices, farms, and cloud platforms.
- Rural infrastructure enhancements, such as LPWAN, satellite internet, and 5G, are increasingly bridging the connectivity gap for remote areas.
3. Data Analytics and Cloud Computing
- Data collected from various sources is transmitted to cloud platforms where it is analyzed using AI, machine learning, and advanced analytics.
- This layer delivers actionable insights for precision decision making, historical trend analysis, and predictive maintenance.
4. Automation Systems
- Based on IoT data and software platforms, automation allows for timely, precise interventions—from starting an irrigation cycle to deploying robotic weeders.
- Farm management systems integrate machine controls, field data, and schedules into a unified interface for farmers.
7 Ways Internet of Things Smart Farming Revolutionizes Agriculture
The Internet of Things smart farming paradigm introduces multiple advanced applications that revolutionize how we manage crops, livestock, forests, and agricultural resources. Here are seven transformative ways IoT is elevating the farming industry:
-
1. Precision Crop Monitoring and Management
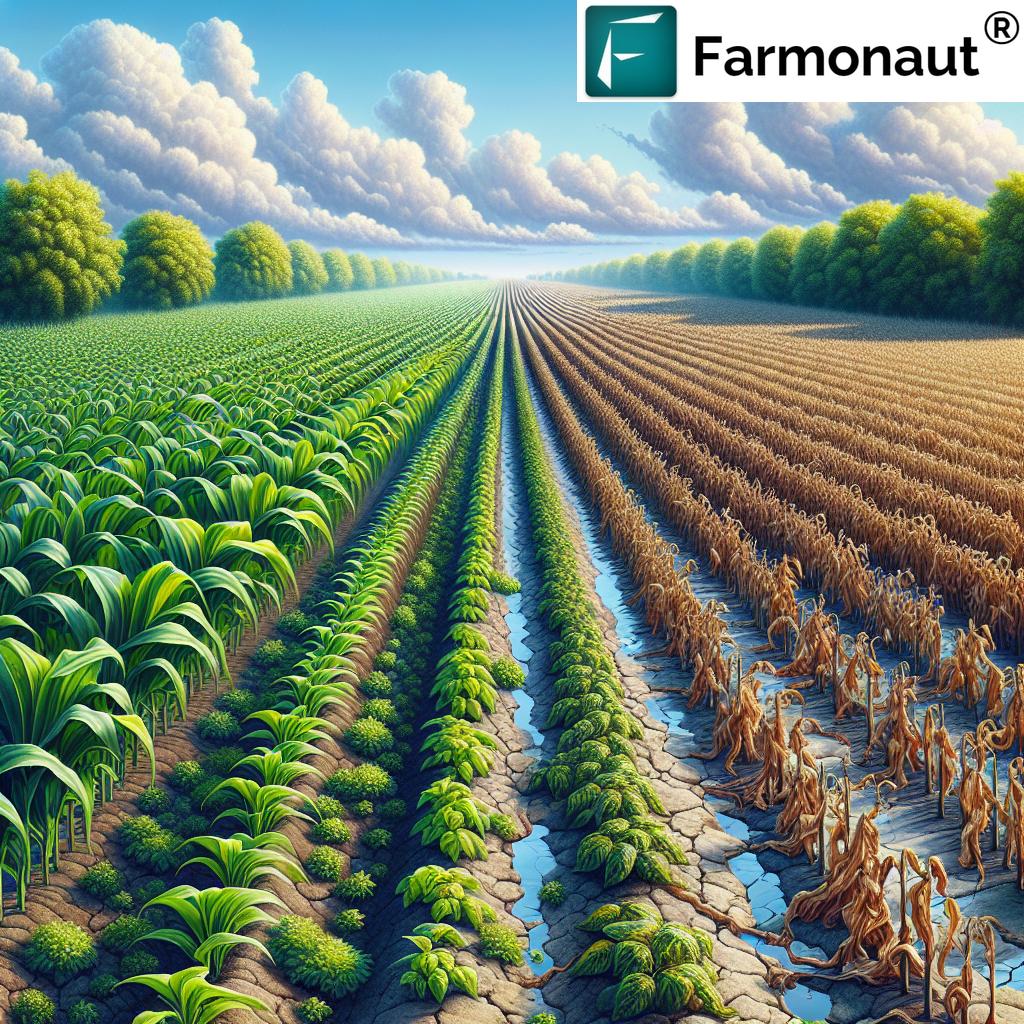
Sensors embedded in soil, crops, and environmental monitoring devices collect real-time data on moisture, nutrients, temperature, and overall crop health. This enables highly targeted use of water, fertilizers, and pest controls, helping to reduce waste and increase yields.
- Example: Soil moisture sensors trigger irrigation only when required, preventing overwatering and conserving resources.
- Impact: Significant improvement in productivity, resource efficiency, and overall sustainability.
-
2. Smart Irrigation Systems
IoT-powered automated irrigation utilizes real-time feedback from soil sensors and localized weather forecasts via connected weather stations or satellites. These systems optimize watering cycles, ensuring crops get precise amounts of moisture at the right times.
- Advantage: Drastically reduces water use (often by 20–50%) and ensures crop vitality, which is crucial in the face of climate variability and water scarcity.
-
3. Automated and Robotic Machinery Control
Internet of Things farming industry leverages sensors, GPS, and AI-driven software to automate machinery like self-driving tractors, robotic weeders, precision planters, and harvesters. These devices operate autonomously, receiving real-time commands based on field data—greatly boosting efficiency.
- Benefit: Significantly reduces labor dependency and operational costs while optimizing inputs and minimizing human error.
-
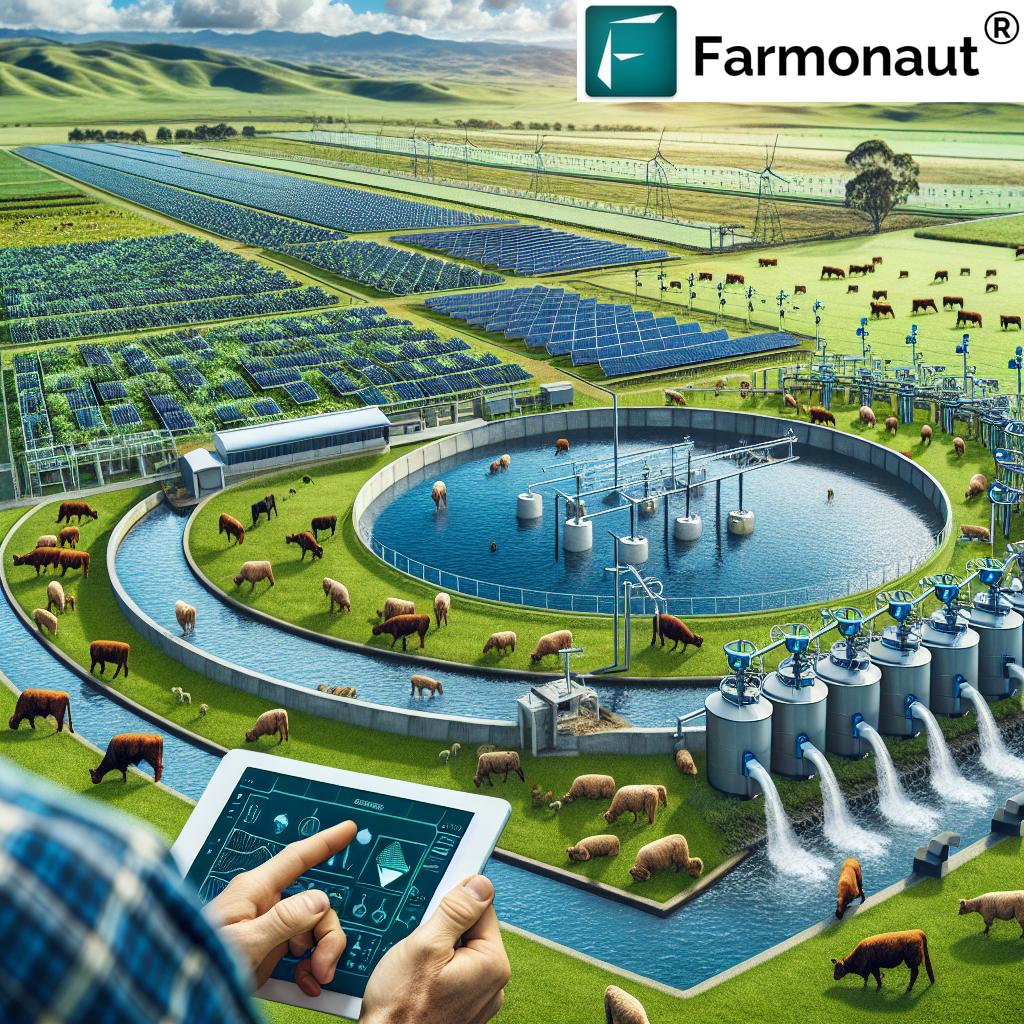
4. Livestock Monitoring and Management
GPS-enabled IoT collars and wearable biometric sensors track health, movement, and reproductive status of livestock. Automated systems can alert on deviations, enabling preemptive care and optimized feeding or breeding schedules.
- Outcome: Improved herd health, lower disease risks, increased productivity, and reduced operational costs.
-
5. Smart Supply Chain and Blockchain Traceability
IoT-integrated platforms track the movement and condition of crops and farm produce through the entire supply chain, from farm to consumer. When combined with blockchain technology, this offers transparent, tamper-proof traceability that builds trust and combats fraud.
- Key Result: Enhanced food safety, quality assurance, and rapid response during recalls or contamination events.
-
6. Forest and Environmental Monitoring
IoT-enabled sensors in forests detect early signs of pest outbreaks, illegal logging, or forest fires, as well as measure air quality and soil health. Satellite imaging and drones supplement ground sensors, providing comprehensive oversight for sustainable forestry management.
- Sustainability: Supports biodiversity, ecosystem health, and regulatory compliance, especially for regions prone to environmental risks.
-
7. Predictive Analytics and AI-Driven Advisory
By synthesizing vast amounts of IoT data—from weather trends, soil conditions, to livestock behavior—platforms powered by AI offer predictive forecasts. These inform crop schedules, risk management, fertilizer applications, and disease outbreak prevention.
- Value: Reduces guesswork, enhances farmers’ ability to make informed decisions, and maximizes resource use for best outcomes.
“IoT sensors can monitor soil moisture every 15 minutes, enabling precise irrigation and resource management in smart farming.”
Comparative Benefits Table: 7 Ways IoT Transforms Agriculture
| IoT Technology/Application | Description | Estimated Impact | Sustainability Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precision Crop Monitoring | Real-time soil/crop sensors for moisture, health, pest, and nutrient monitoring | Yield Increase: 10–20% Resource Use ↓ 20–40% |
Reduced fertilizer & water usage, higher land productivity |
| Smart Irrigation | Automated irrigation based on sensor & weather data | Water Use ↓ 20–50% | Major water conservation, better crop resilience |
| Automated Machinery | Robotic tractors, planters, and weeders guided by IoT & GPS | Operational Costs ↓ 15–35% | Lower fuel use, carbon footprint, efficient labor |
| Livestock Monitoring | GPS & biometric sensors for real-time livestock health & movement | Disease Incidence ↓ 10–30% Productivity ↑ 5–15% |
Less antibiotic use, healthier animals, waste management |
| Smart Supply Chain & Blockchain | IoT-tracked logistics & blockchain traceability | Food Waste ↓ 5–15% Recall Time ↓ 30–50% |
Supply chain efficiency, food safety |
| Forest & Environmental Monitoring | Sensors detect pest, fire, illegal logging in forests & natural areas | Biodiversity Preservation ↑ @Risk Area Coverage ↑ |
Climate resilience, ecosystem protection |
| Predictive Analytics & AI Advisory | Data-driven, AI-enhanced farm management systems | Decision Accuracy ↑ 70–90% Emergency Response Time ↓ 40% |
Optimal resource use, minimal environmental impact |
Key Benefits of Internet of Things Smart Farming
- Increased Productivity & Yields: Precision use of inputs and timely interventions boost crop and livestock productivity.
- Resource Efficiency: Smart automation systems reduce water, fertilizer, and energy wastage, promoting sustainable farming.
- Cost Reduction: Automation, predictive analytics, and reduced labor needs help cut operational and input costs for farmers and agribusinesses.
- Environmental Health: IoT-enabled farming minimizes overuse of chemicals, reduces emissions, and conserves natural resources.
- Enhanced Decision Making: Real-time data and AI-powered insights support better, more informed decisions throughout the crop or forest cycle.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Blockchain and logistics monitoring improve product authentication, food safety, and rapid traceability.
- Improved Food Security: Consistent, efficient farming practices result in higher, more stable outputs to meet global food demand.
- Sustainability and Biodiversity: Integrated monitoring supports ecosystem resilience, pollinator and wildlife health, and sustainable land use.
Start Smart Farming With Farmonaut: Apps & API Access
Farmonaut delivers advanced, satellite-based farm management solutions through our Android, iOS, and web apps as well as a robust API for businesses and developers. Our mission is to make precision agriculture and internet of things smart farming affordable and accessible for all, transforming data into actionable intelligence—without the need for expensive on-field hardware.
Challenges in the Adoption of Internet of Things in Agriculture
Despite its many benefits, several challenges stand in the way of rapid, universal adoption of IoT technologies within the farming industry. Let’s examine the key barriers:
- High Initial Costs: The upfront investment required for deploying IoT devices, sensors, and supporting infrastructure can be significant, especially for smallholder or traditional farmers.
- Connectivity Issues: Many rural and remote areas still experience unreliable internet connectivity, hindering real-time data transmission and system integration.
- Data Management Complexity: The large volumes of data generated require advanced cloud computing, analytics, and trained personnel for effective management and use.
- Interoperability Concerns: Integrating diverse devices and software platforms from different vendors can be technically challenging and may result in compatibility issues.
- Security and Privacy Risks: As with any connected system, IoT platforms can be vulnerable to cyber threats, potentially jeopardizing operations and data confidentiality.
- Resistance to Change: Many farmers may lack training or awareness regarding digital innovations, making them hesitant to transition from established, traditional practices.
Farmonaut: Empowering Affordable, Data-Driven Agriculture
Farmonaut stands at the intersection of technology innovation and smart agriculture internet of things adoption. By integrating satellite data, AI-powered advisory, blockchain traceability, and digital resource management into one unified platform, we empower individual farmers, agribusinesses, NGOs, and government institutions worldwide.
Unlike most traditional precision ag solutions that require costly on-site hardware, Farmonaut’s approach leverages satellite imagery and advanced analytics—delivered directly through user-friendly Web, Android, and iOS apps or our open API.
- Satellite Crop Health Monitoring: Via real-time, multispectral satellite imaging and indices like NDVI, farmers identify crop stress, pest, and irrigation needs immediately—optimizing resource use and minimizing loss.
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: Delivers customized farm management suggestions, yield forecasts, and early risk alerts by analyzing satellite and environmental data intelligently.
-
Blockchain Traceability: Our solution offers transparent tracking for agri-products across supply chains, enhancing trust and combating food fraud.
Learn more: Farmonaut’s Product Traceability solution - Fleet and Resource Management: Automates logistics, improves machinery uptime, and enables large-scale coordination.
-
Carbon Footprinting: Real-time emissions tracking aids compliance with sustainability targets and carbon reduction.
Find details: Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting - API for Integration: Developers and agritech companies can integrate Farmonaut’s data directly into their platforms, accelerating digital transformation.
- Accessible Subscription Model: Farmers can choose the services and scale that fit their needs, paying only for what they use.
Getting started is easy—our web app, Android and iOS apps bring smart agriculture internet of things insights to farmers globally!
Future Prospects and Innovations: What’s Next for IoT in Agriculture?
The future of internet of things farming industry is even more promising as digital technologies, AI, and advanced infrastructure continue to mature:
- Deeper AI-Integration: Machine learning will drive precision advice on crop schedules, fertilizer use, and climate adaptation for every unique field.
- Edge Computing: On-device data processing reduces latency and internet dependency, expanding smart farming to previously inaccessible areas.
- Blockchain Supply Chains: Universal blockchain adoption will deliver transparent, tamper-proof monitoring from field to fork.
- Farmer-Friendly Automation: Ease-of-use in robotic machinery and accessible data visualization will lower barriers for traditional farmers.
- Focus on Sustainability: As climate change challenges intensify, integrated IoT solutions will help agriculture optimize resources, lower emissions, and support biodiversity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Internet of Things Smart Farming
What is Internet of Things smart farming?
Internet of Things smart farming is the use of connected sensors, devices, and software in agriculture to collect, transmit, and analyze data in real-time. It enables precision decisions on irrigation, crop health, livestock, and resource allocation.
What are the main applications of IoT in smart agriculture?
Core applications include precision crop monitoring, smart irrigation, automated machinery, livestock tracking, supply chain traceability, forest monitoring, and AI-based farm advisory systems.
How does IoT benefit smallholder and resource-limited farmers?
IoT reduces input costs, optimizes resource use, and increases yields by providing actionable insights and automation—even for small-scale farms, especially when digital tools eliminate the need for expensive on-field hardware.
Is Internet connectivity essential for IoT in agriculture?
Reliable connectivity ensures real-time data transfer, but with advances in edge computing and satellite technology, even remote regions can deploy smart agriculture internet of things solutions.
How does Farmonaut support IoT adoption in agriculture?
We provide affordable, satellite-driven data and AI insights via Android, iOS, web apps, and an open API, helping farmers, businesses, and governments adopt precision farming without heavy upfront investment.
What about data security and privacy?
IoT deployments require robust cybersecurity and privacy protocols; Farmonaut’s blockchain-enhanced traceability also assures data integrity and transparency throughout the supply chain.
How can I start using IoT solutions for my farm?
Download the Farmonaut app for instant access to satellite-based crop health monitoring, AI-driven advisory, and digital farm management tools.
Subscribe to Farmonaut’s Advanced Internet of Things Smart Farming Solutions
Experience the most comprehensive, affordable way to bring IoT and precision agriculture to your farm or agribusiness. Use our subscription options below.
Conclusion: The Internet of Things—Driving an Agricultural Revolution
The Internet of Things smart farming revolution is transforming agriculture and forestry, empowering farmers and foresters to harness the power of connected devices, real-time analytics, and automated systems. This shift is not just about increasing productivity—it’s fundamentally about advancing sustainability, resilience, and global food security. As we move towards a future where food and natural resource demands rise, embracing IoT-enabled, data-driven practices is no longer optional, but essential. By making these innovations accessible, affordable, and actionable, digital agriculture ensures both profitability and stewardship for today and generations to come.