Table of Contents
- Summary: Moisture Mapping and Its Importance
- Did You Know?
- Why Moisture Mapping is Essential for Agriculture & Forestry
- Moisture Mapping: 7 Powerful Ways to Boost Crop Yields Fast
- 1. Deploying Soil Moisture Sensor Networks
- 2. Satellite Soil Moisture Mapping & Remote Sensing
- 3. Ground-Penetrating Radar (GPR) for Precise Sensing
- 4. Time-Domain Reflectometry (TDR) for Real-Time Data
- 5. Cosmic-Ray Neutron Sensing (CRNS) for Large Areas
- 6. GeoAI & Machine Learning for High-Resolution Soil Moisture Maps
- 7. Integrating Moisture Maps with Crop Irrigation Management Systems
- Comparative Table: Moisture Mapping Technologies & Impact
- How Farmonaut Enables Next-Gen Precision Agriculture Solutions
- Applications: Improving Crop Yields, Sustainability, and Forest Management
- Key Challenges & Future Directions of Moisture Mapping
- Moisture Mapping FAQ
- Farmonaut Subscriptions & Get Started
- Conclusion
Moisture Mapping: 7 Powerful Ways to Boost Crop Yields Fast
Summary: Moisture Mapping and Its Importance
Moisture mapping is a vital technique in modern agriculture, farming, and forestry. It involves the measurement and visualization of soil and plant moisture levels across different areas of a field or forest. By generating detailed moisture maps, we empower farmers and land managers to make smarter decisions about irrigation, fertilization, crop selection, and overall resource management.
With advancements in satellite imagery, soil moisture sensors, and machine learning, moisture mapping now enables real-time monitoring and predictive analytics—transforming agricultural productivity while promoting sustainability. Accurate assessment of soil moisture leads to optimized irrigation, higher yields and quality, water conservation, prevention of waterlogging, and tailored management practices that improve both farming and forest management.
Moisture mapping stands at the intersection of technology, innovation, and food security.
Why Moisture Mapping is Essential for Agriculture & Forestry
The importance of moisture mapping cannot be understated for anyone concerned with optimizing yields, conserving water, and building more sustainable agriculture systems. Here’s why understanding moisture at a granular level is fundamental:
- Optimized Irrigation Scheduling: By utilizing accurate, real-time soil moisture data, we can tailor irrigation to the actual needs of crops, preventing overwatering, underwatering, and associated stress or disease.
- Increased Crop Yield and Quality: Maintaining optimal soil moisture levels is proven to promote healthy plant growth, resulting in higher yields and improved crop quality.
- Water Conservation in Farming: Efficient water use directly reduces waste and ensures this vital resource is conserved for future generations.
- Prevention of Waterlogging: Consistent monitoring allows us to avoid waterlogging conditions that can damage plant roots and severely reduce yields.
- Better Informed Decisions: High-resolution moisture data supports decisions on crop selection, planting dates, and smart fertilizer application.
- Drought Monitoring Technology: Early detection of soil moisture deficits enables us to act proactively and reduce crop losses.
When we implement precision agriculture solutions, moisture mapping forms the backbone of actionable, data-driven farm management.
Moisture Mapping: 7 Powerful Ways We Can Boost Crop Yields Fast
Our approach combines advanced technology with practical field applications. Let’s explore the top 7 innovative ways to leverage moisture mapping for rapid improvement in crop yields, water efficiency, and sustainability. These methods optimize every part of the agriculture & forestry value chain.
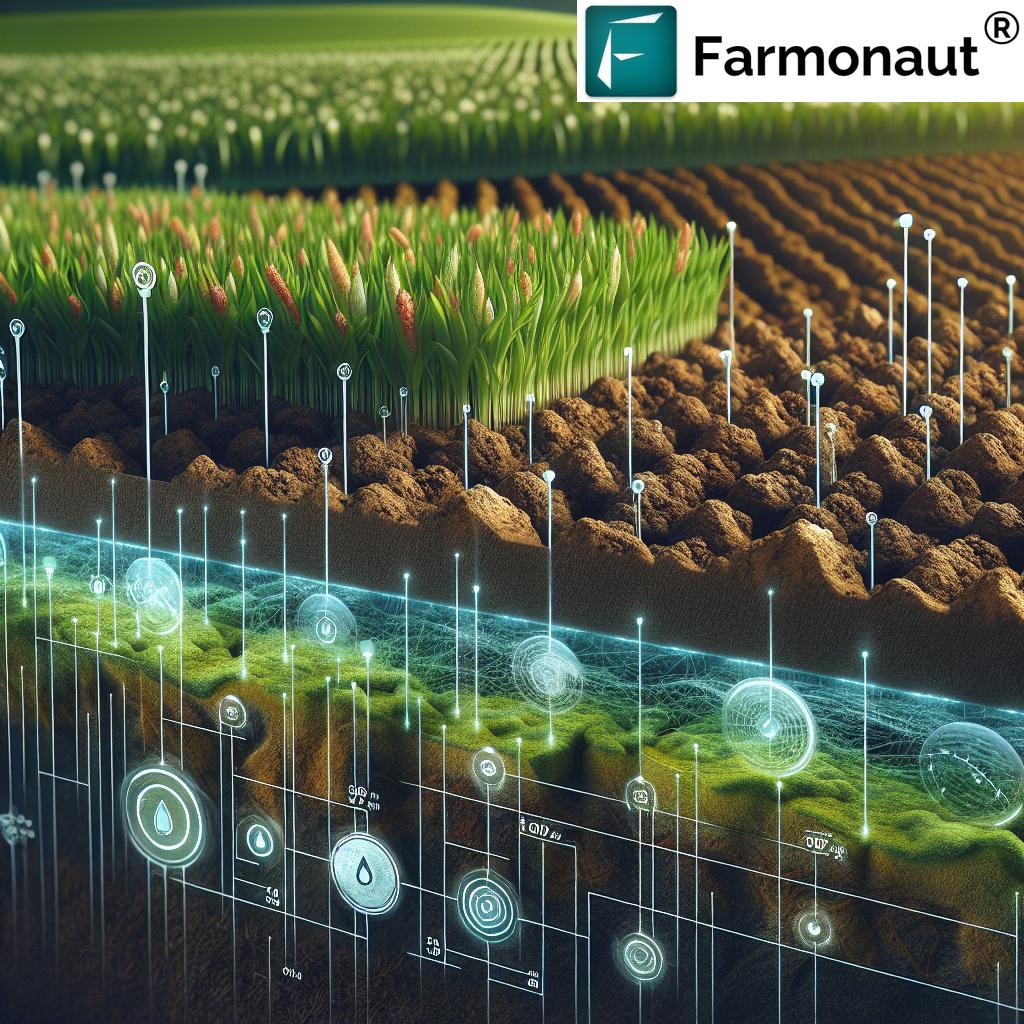
1. Deploying Soil Moisture Sensor Networks
One of the most effective and accessible techniques for real-time moisture measurement in agriculture is the use of soil moisture sensors.
What are Soil Moisture Sensors?
- TDR (Time-Domain Reflectometry) Sensors: Time-Domain Reflectometry (TDR) sensors work by sending electrical pulses through the soil; their speed and reflection indicate the amount of water present. These TDR soil moisture sensors are used due to their accuracy, reliability, and low maintenance in diverse soil conditions (Learn more).
- Capacitive & Resistive Sensors: Affordable, easy to deploy, and suited for grid-like distribution across fields—but less accurate than TDR.
When connected in networks, moisture sensors allow for continuous monitoring of soil moisture levels at different depths and locations, producing rich data maps that visualize dry and wet zones instantly.
Key Benefits:
- High accuracy for “point measurement”
- Supports precision irrigation via automation or alerts
- Prevents overwatering, underwatering, waterlogging
- Facilitates variable-rate fertilization
- Reduces waste and increases yields up to 20% in many field scenarios
Soil moisture sensors are at the heart of modern large scale farm management platforms. With Farmonaut, these can be integrated with satellite-based insights for even richer decision making.
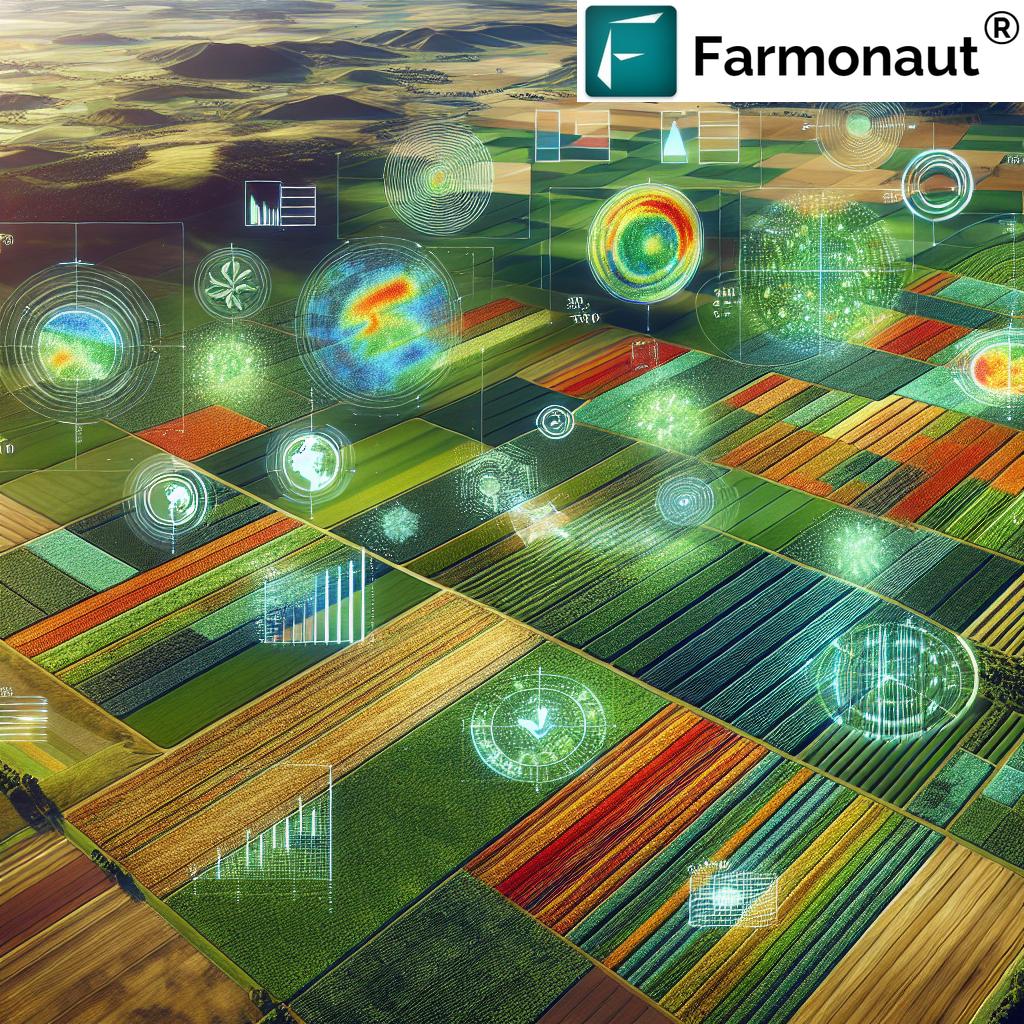
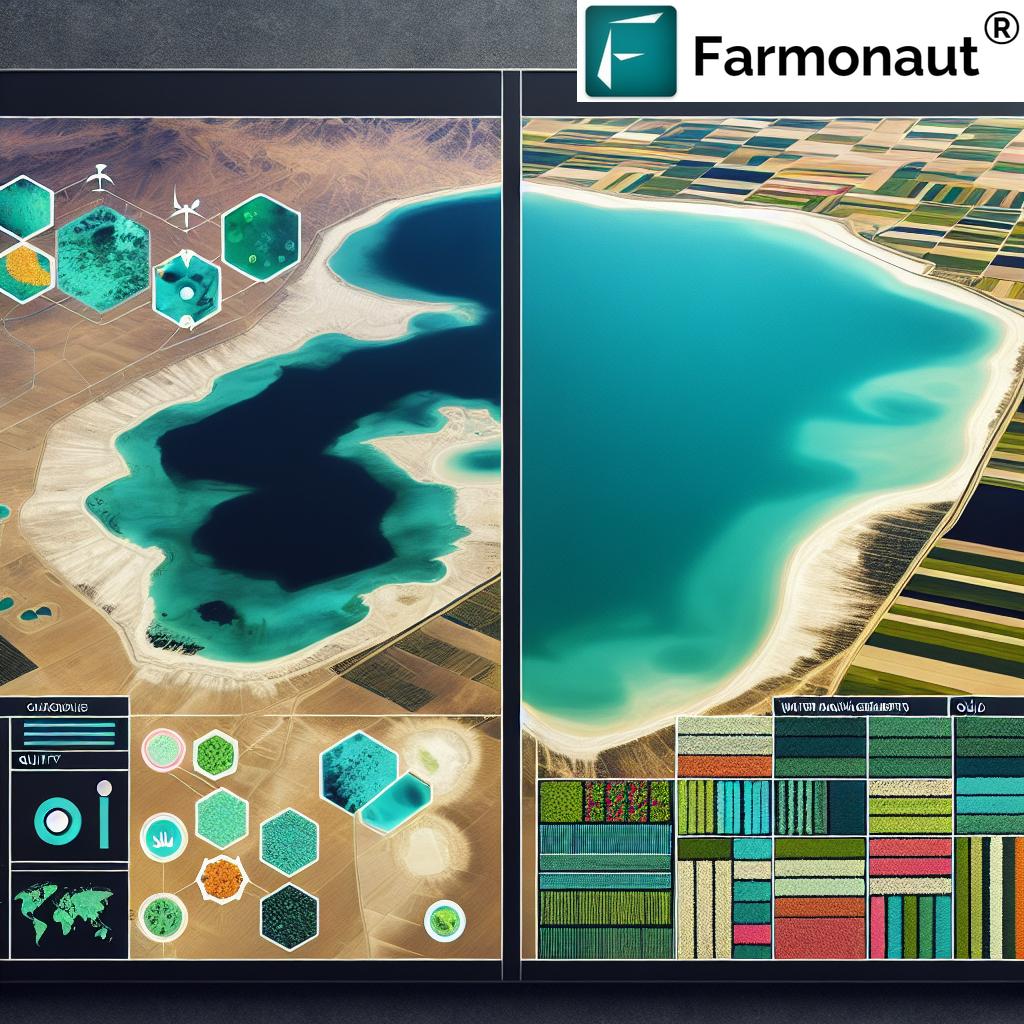
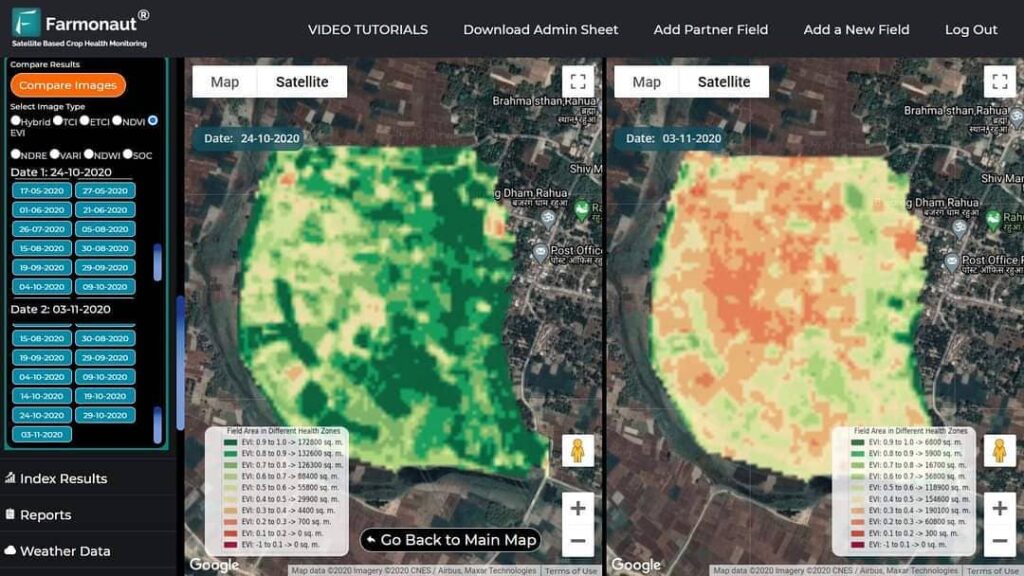
2. Satellite Soil Moisture Mapping & Remote Sensing in Agriculture
Advances in remote sensing in agriculture have made it possible for us to visualize and quantify soil moisture at field, state, or even country scale within hours. Satellite soil moisture data has become instrumental for both small farmers and large agricultural enterprises.
How Does Satellite Moisture Mapping Work?
- Multispectral Satellite Imagery: Specially calibrated satellites record electromagnetic signals from the earth’s surface, which change depending on soil moisture content, crop health, temperature, and more.
- Active-Passive Sensors (e.g., SMAP): NASA’s Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) satellite utilizes a combination of radar (active) and radiometer (passive) sensors for comprehensive, global soil moisture monitoring (details).
- Cloud Computing: Platforms like Farmonaut process these images into actionable soil moisture maps for decision support.
Key Benefits:
- Enables remote, large-scale monitoring—no physical installation required
- Rapid identification of dry, wet, and at-risk areas anywhere on earth
- Enhances crop irrigation management & drought monitoring technology
- Facilitates weather forecasting & resource allocation
- Integrates seamlessly with digital large scale farm management solutions
Satellite data opens new horizons for precision agriculture and is central to Farmonaut’s platform. Thanks to Farmonaut’s API Developer Docs, you can integrate live moisture data directly into your own farm apps and dashboards.
3. Ground-Penetrating Radar (GPR) for Precise Moisture Sensing
Ground-Penetrating Radar (GPR) systems revolutionize the non-invasive measurement of soil moisture and subsurface features. They emit high-frequency microwaves into the ground, which are then reflected back. The reflected signals are analyzed to estimate moisture content variation across depths and areas.
GPR’s precision and ability to detect moisture gradients make it valuable for:
- Mapping moisture in layered soils and varied terrain
- Forest moisture monitoring (for wildfire risk assessment and ecosystem health)
- Research plots and special conservation management zones
Pros & Cons:
- High accuracy and spatial coverage
- Requires specialized training for setup and data interpretation
- Performance can be influenced by certain soil types (e.g., clays) and stony ground
Read more: Ground-Penetrating Radar in Moisture Mapping.
4. Time-Domain Reflectometry (TDR) for High-Accuracy, Real-Time Monitoring
Time-Domain Reflectometry (TDR) soil moisture sensors have become a gold standard for near-instant, precise moisture content measurement. By measuring the dielectric constant of the soil—which depends on its moisture level—TDR provides data that directly informs irrigation scheduling and fertilizer management.
- Real-time, automated moisture logging: Connect to cloud-based precision agriculture systems like Farmonaut for easy visualization and alerts
- Industry-trusted for scientific research and monitoring
- User-friendly; integrates into both fixed-point and mobile platforms (TDR sensor info)
Tip: Combining TDR sensor grids with satellite maps offers unmatched data accuracy and coverage—delivering highly actionable insights for crop irrigation management.
5. Cosmic-Ray Neutron Sensing (CRNS) for Large-Area Soil Moisture Measurement
Cosmic-Ray Neutron Sensing (CRNS) leverages neutrons from cosmic rays that are slowed down by hydrogen in water molecules. By measuring the level of moderated neutrons at the soil surface, CRNS systems estimate moisture over several hectares from a single sensor point (More details).
- Ideal for non-invasive, large-area measurement
- Low maintenance; high value for large farming operations and forest management
- Excellent for tracking drought evolution and resource allocation at scale
CRNS complements point-based sensors and satellite data—offering a cost-effective way to bridge the gap between ground arrays and regional moisture mapping.
6. GeoAI & Machine Learning: High-Resolution Soil Moisture Mapping for Precision Agriculture
The integration of machine learning and GeoAI (Geospatial Artificial Intelligence) allows us to extract actionable soil and crop insights from massive satellite imagery and environmental data sets. Key innovations include:
- Predictive Moisture Mapping: AI analyzes historical and real-time data—satellite images, NDVI, land temperature, and more—to create hyper-local moisture maps that guide precision applications.
- Automated Drought & Flood Detection: Models can highlight risk areas weeks in advance.
- Variable Rate Irrigation Management: Irrigation is automatically tailored to spatial variation in soil moisture, reducing input costs and water waste.
Farmonaut employs AI-driven crop advisories via its Jeevn AI Advisory System, offering predictive soil moisture analytics, farm-specific recommendations, and resource optimization for all users.
Learn more: Innovative Machine Learning for Soil Moisture Mapping.
7. Integrating Moisture Maps with Crop Irrigation Management Systems
The ultimate benefit of these moisture mapping methods is realized when they are directly linked to smart crop irrigation management systems. By combining current and forecasted soil moisture with weather, crop, and topographical data, we enable:
- Automated irrigation scheduling—water is supplied only where and when needed
- Integration with carbon footprinting tools—track water use efficiency and climate impact
- Reduction in manual oversight, freeing labor for high-value tasks
- Increased crop productivity and dramatically improved water conservation
Modern platforms like Farmonaut streamline this integration through mobile and web apps, resource planning, and satellite monitoring.
Comparative Table: Moisture Mapping Technologies and Their Impact on Crop Yields
| Technology/Method | Estimated Cost (per acre) | Installation Time (days) | Data Accuracy (%) | Estimated Yield Increase (%) | Scalability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Moisture Sensors (TDR/Capacitive) | $12–$50 | 2–7 | 85–95% | 8–20% | Medium |
| Satellite-Based Moisture Mapping (API Integration) | $3–$6 | 1–2 | 70–90% | 5–15% | High |
| Drone-Based Moisture Sensing | $18–$60 | 1–3 | 75–92% | 8–18% | Medium |
| Remote Sensing via IoT Devices | $8–$35 | 2–10 | 75–92% | 7–17% | Medium–High |
| GPR (Ground Penetrating Radar) | $50–$120 | 7–15 | 90–98% | 9–21% | Low–Medium |
| CRNS (Cosmic-Ray Neutron Sensing) | $70–$210 | 3–9 | 83–91% | 6–14% | High |
| Machine Learning & GeoAI Mapping | $6–$15 | 1–3 | 75–96%* | 8–19% | High |
*Accuracy depends on training data and sensor integration.
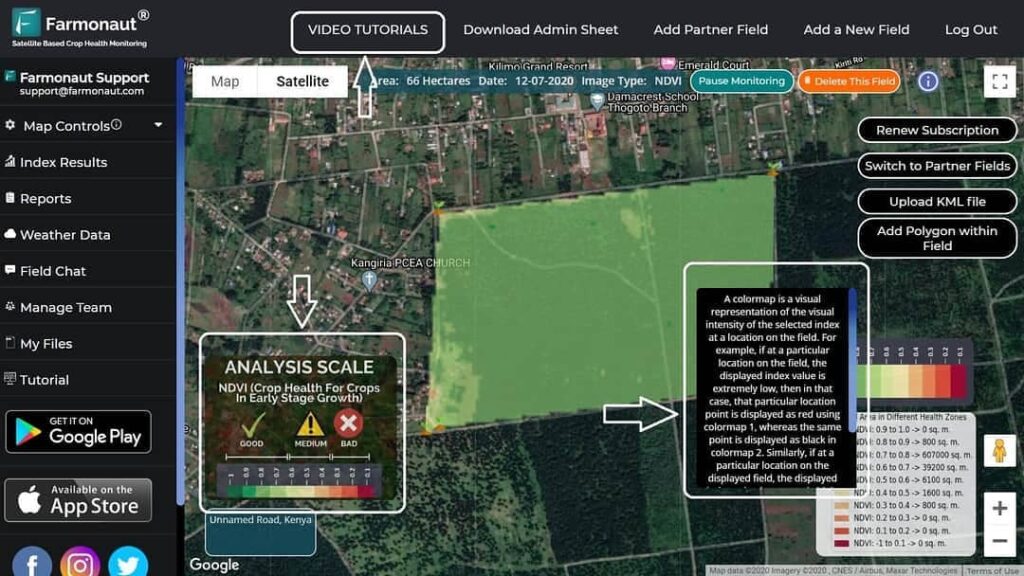
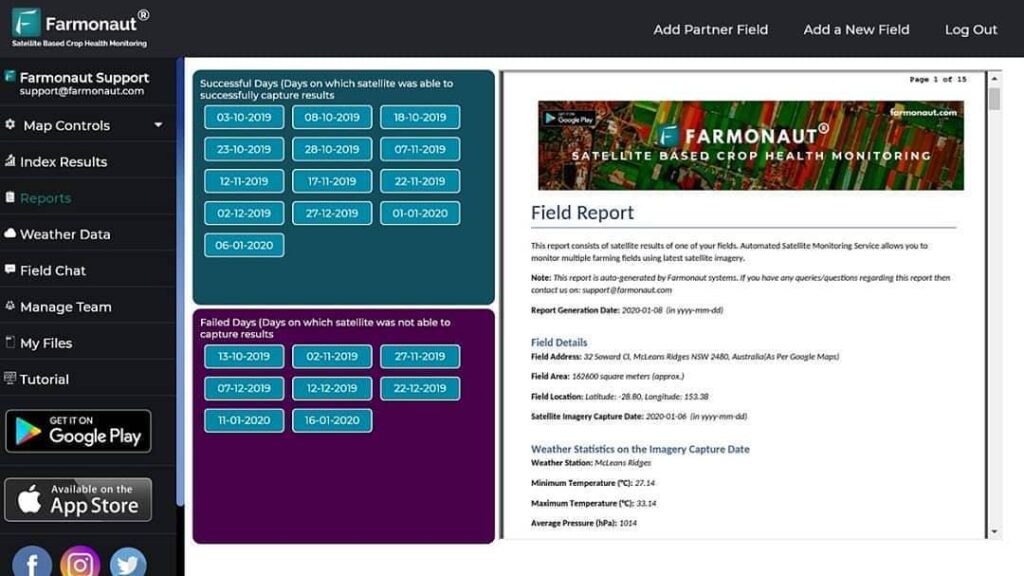
How Farmonaut Enables Next-Gen Precision Agriculture Solutions for Moisture Mapping
At Farmonaut, our mission is clear: democratize precision agriculture solutions and make moisture mapping accessible for every farmer, agribusiness, and land manager globally.
- Satellite-Based Crop Health & Moisture Monitoring: Get real-time moisture data from multispectral imagery to optimize crop health and irrigation.
- Jeevn AI Advisory: Leverage personalized, AI-driven recommendations that interpret soil moisture maps and climate data for smarter decisions.
- Blockchain-Based Traceability: Evaluate sustainable irrigation and soil management actions with verifiable blockchain records.
- Fleet & Resource Management: Overlay moisture & crop data to direct machinery/fleet where it’s most needed for planting, watering, or harvesting—fully digitized on the Fleet Management Platform.
- Carbon Footprinting: Track water efficiency and environmental sustainability through real-time footprinting tools.
- Insurance & Financing: Use satellite-based moisture verification for crop loans and insurance.
- API & Developer Friendly: Integrate Farmonaut’s soil moisture and weather API—with full developer documentation.
- Mobile & Browser App Access: Use our solutions anywhere with responsive apps—see Farmonaut Crop, Plantation & Forest Advisory.
Farmonaut’s approach minimizes costs by harnessing satellite data—so there’s no need for expensive dedicated hardware. Our platform supports both smallholder farmers and large enterprises, and scales from a single plot to thousands of hectares instantly.
Applications of Moisture Mapping: Improving Crop Yields, Sustainability & Forest Management
Let’s see how these technologies and methods translate into actionable applications for agriculture, forestry, and sustainable resource management.
-
Precision Agriculture:
- Variable-rate irrigation and fertilization (using soil moisture & satellite maps)
- Reduction of (resource & input) costs and improving crop yields with data-driven strategy
- Early stress detection ensures healthy, uniform growth across every field segment
-
Drought Monitoring Technology:
- Continuous monitoring enables us to forecast, detect and mitigate drought impacts quickly
- Resource allocation supports prioritized irrigation scheduling (critical during crisis periods)
-
Forest Moisture Monitoring:
- Fire risk assessment and real-time alerts via satellite mapping
- Planning reforestation or conservation actions in moisture-stressed forest areas
- Supports long-term forest ecosystem health management
-
Soil Conservation & Erosion Control:
- Map and identify dry zones susceptible to erosion or degradation
- Enables targeted soil conservation practices and infrastructure planning
-
Efficient Crop Plantation & Forest Advisory:
- Optimize crop type, planting date, and establishment methods for each microclimate using Farmonaut’s Crop & Forest Advisory
Key Challenges & Future Directions of Moisture Mapping
Main Challenges
- Data Accuracy & Calibration: Soil heterogeneity (varied soil types, compaction, organic matter) can affect sensor output; frequent calibration and cross-validation are necessary.
- Technology Cost & Accessibility: Some advanced moisture mapping technologies involve high initial costs or require specialized knowledge—limiting access for smallholders.
- Data Integration: Combining satellite data with ground sensors, meteorological records, and IoT inputs into a unified, actionable dashboard remains a data-processing challenge.
Where the Future is Heading
- Cost-effective Sensors: Next-gen low-cost, robust sensors will lower entry barriers even further.
- Open, Accessible Platforms: Farmonaut’s affordable, app-based approach sets the standard for wide adoption.
- AI-Powered Predictive Tools: Emerging machine learning algorithms will boost the accuracy, scope, and personalization of moisture mapping.
- Real-Time Integration with Irrigation Systems: Future-proof systems will automatically optimize irrigation based on live moisture map data.
- Global Data Initiatives: Collaboration on open soil moisture and crop sensing data will improve resilience, particularly in drought-prone zones.
By continually improving technology and accessibility, moisture mapping stands as a core driver for food security, sustainable land management, and climate adaptation strategies.
Moisture Mapping FAQ
Soil moisture mapping is the process of measuring and visualizing the distribution of water content within the soil at various depths and locations across a field, plantation, or forested area. It helps us identify dry or wet zones, optimize irrigation practices, and manage crops or forests efficiently.
How does remote sensing in agriculture measure soil moisture?
Remote sensing in agriculture uses satellite and aerial sensors to detect electromagnetic signals reflected from the earth’s surface. Differences in these signals, particularly in microwave and thermal bands, allow us to estimate soil moisture content over large areas quickly and accurately.
What technologies are used for moisture mapping?
Common technologies include soil moisture sensors (TDR, capacitive, resistive), satellite-based imagery, drone-based sensors, Ground-Penetrating Radar (GPR), Cosmic-Ray Neutron Sensing (CRNS), and AI-driven analytics such as machine learning and GeoAI models.
How does moisture mapping improve crop yield?
By providing accurate moisture data, farmers can optimize irrigation, avoid under/overwatering, reduce input waste, and ensure that each plant receives what it needs, resulting in optimal growth, improved crop quality, and higher yields.
Can I access moisture mapping on my phone?
Yes! With platforms like Farmonaut, you can view real-time satellite-based soil moisture maps, receive AI-powered crop advisories, and manage all your fields directly from your Android, iOS, or web browser app.
Is moisture mapping useful for forestry?
Absolutely. Forest moisture monitoring helps assess fire risk, plan reforestation, support ecosystem health, and ensure effective conservation practices.
How do I get started?
Sign up on the Farmonaut platform, choose your field/plot or forest, and begin receiving instant, updated moisture, crop, and advisory data tailored to your needs.
Farmonaut Subscriptions & Get Started
For access to real-time crop monitoring, satellite-based soil moisture mapping, blockchain traceability, fleet management, and AI advisories, explore Farmonaut’s simple subscription plans below:
Tip: Try the web app for a live demo or jump straight into the iOS/Android mobile app. Developers and large-scale operators can access the Farmonaut API and developer docs for custom integration.
Conclusion: Moisture Mapping—A Pillar for Productive and Sustainable Agriculture
Moisture mapping is the cornerstone of precision agriculture and sustainable forestry management in the 21st century. By embracing a range of technologies—from soil sensors and satellite imagery to machine learning—we unlock higher yields, protect the environment, and future-proof food production systems for generations to come.
Accessible, real-time, and highly actionable, moisture data empowers farmers, agribusinesses, foresters, and resource managers to maximize productivity while minimizing inputs and risk. Platforms like Farmonaut offer scalable, affordable, and technologically advanced tools that make these benefits available anywhere in the world—via mobile, web, and powerful APIs.
Investing in moisture mapping is not just about increasing farm income—it is a foundation for global food security, water conservation, and climate resilience. Join the moisture mapping revolution today with smart, data-driven decision-making!