“Over 50% of global crop losses from anthracnose can be prevented with timely fungicide application and resistance management.”
Best Fungicide for Anthracnose: Powerful Strategies & Tips
Summary:
Understanding and Managing Anthracnose in Agriculture: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to anthracnose management, timely implementation of solutions can mean the difference between a thriving harvest and major yield losses. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the best fungicides for anthracnose, their application strategies, integrated control measures, and essential resistance management practices for a proactive and sustainable approach.
Understanding Anthracnose Disease in Crops
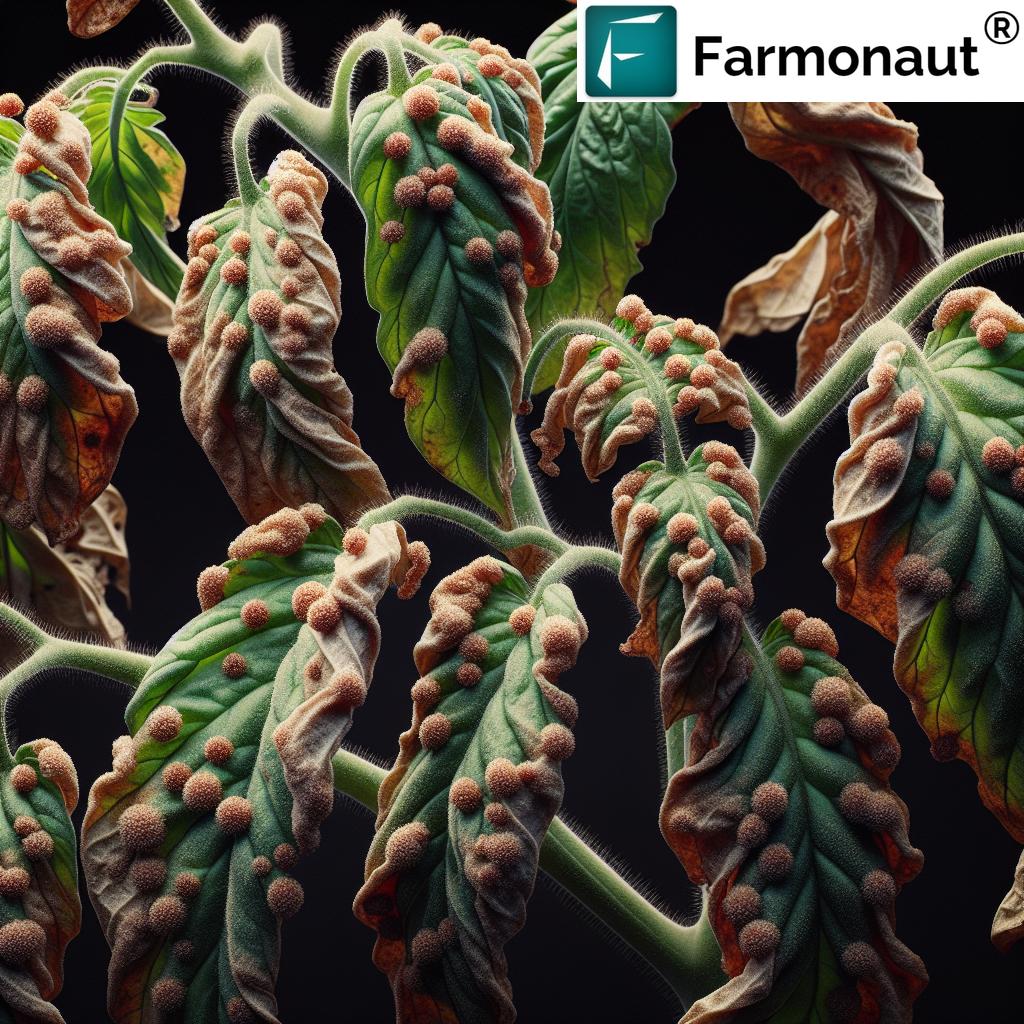
Anthracnose is a prevalent and destructive fungal disease that affects a broad range of crops, including fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants. The disease is primarily caused by various Colletotrichum species, leading to considerable yield reductions and compromised crop quality. In agriculture, the impact of anthracnose can be particularly severe in crops like strawberries, almonds, mangoes, turfgrass, bananas, and many other plant species.
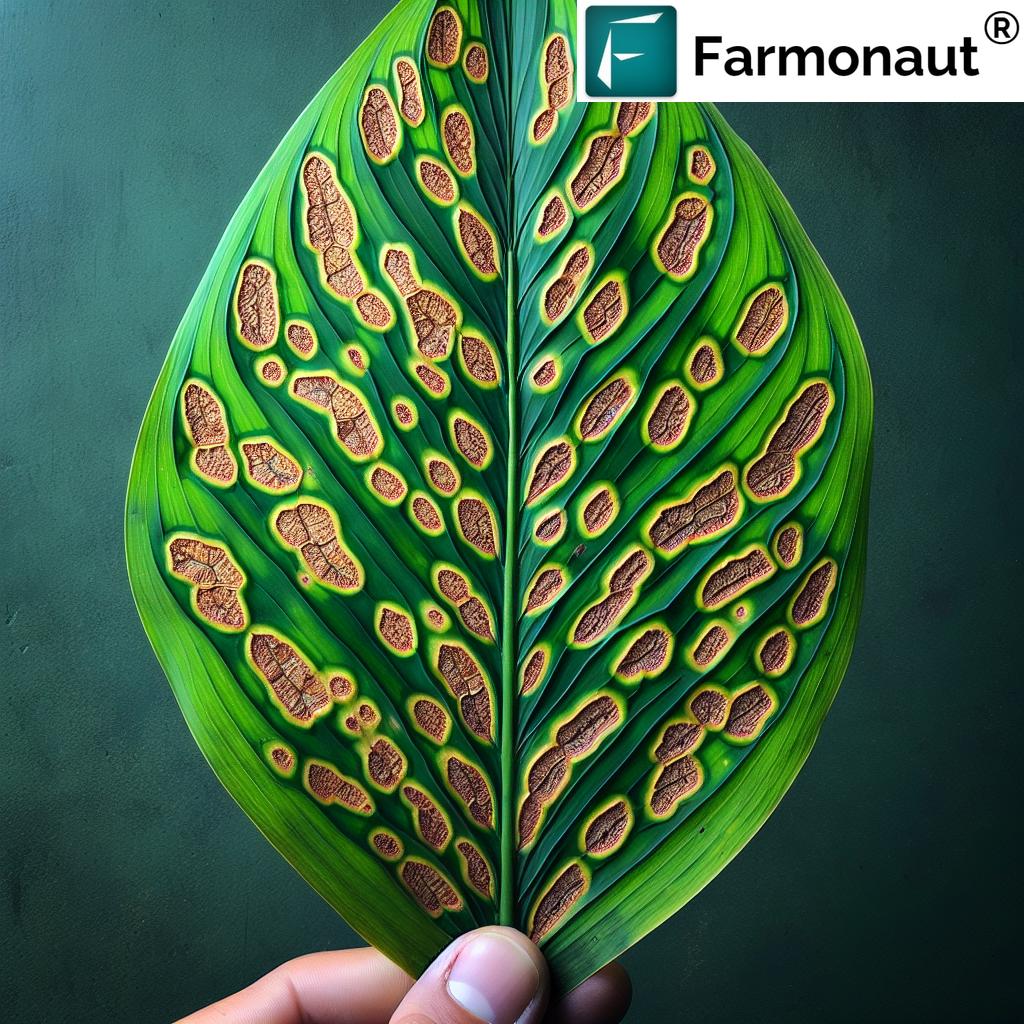
The symptoms often present as dark, sunken lesions on fruit, stems, leaves, and flowers. Early detection and understanding of the pathogen’s lifecycle are essential for effective management. The disease thrives under warm, humid conditions, making prompt control practices a necessity, especially in areas with conducive environmental conditions.
- Crops affected: Strawberries, mangoes, turfgrass, almonds, bananas, grapes, tomatoes, peppers, beans, cucurbits, and more.
- Primary Pathogen: Colletotrichum species (e.g., C. gloeosporioides, C. acutatum, C. capsici).
- Disease spread: Through infected plant debris, splashing water, tools, and sometimes insect vectors.
- Key symptoms: Sunken fruit spots, leaf necrosis, stem cankers, premature fruit drop, and reduced market value.
Why Anthracnose Management Requires an Integrated Approach
With the disease’s ability to adapt and develop resistance to chemical fungicides, relying solely on one tactic proves ineffective. Instead, a comprehensive guide to anthracnose control practices must involve:
- Choosing proven fungicides for anthracnose, tailored for specific crops
- Optimizing application strategies (rates, timing, and rotation)
- Applying integrated cultural practices and using resistant cultivars
- Monitoring disease pressure and adjusting management accordingly
Fungicides for Anthracnose: Types, Modes of Action, and Efficacy
Effective anthracnose disease control starts with understanding the best fungicides for crops and how they work. Fungicides may be systemic or contact and act through multiple modes of action—key in preventing resistance development. Let’s delve into the most commonly applied fungicide classes for anthracnose management.
1. Strobilurin Fungicides for Agriculture
- Azoxystrobin—A systemic, broad-spectrum fungicide that inhibits mitochondrial respiration in fungi. Widely used in turfgrass, strawberries, and cereals.
- Trifloxystrobin—Also a strobilurin; acts similarly to azoxystrobin, often used in combination for crops like mangoes and turfgrass.
- Pyraclostrobin—Shows excellent efficacy in strawberries and a range of fruits and vegetables.
2. Triazole (DMI) Fungicides
- Propiconazole—A demethylation inhibitor (DMI) that disrupts fungal cell membrane synthesis. Trusted for use in almonds, cereals, and turfgrass.
- Other DMI fungicides—Examples include tebuconazole and difenoconazole, providing control through similar mechanisms.
3. SDHI Fungicides
- Fluopyram—A succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor, often used in combination with other actives for anthracnose control in almonds.
- Fluxapyroxad—Another SDHI, commonly combined with strobilurins or others, effective in strawberries and assorted fruit/vegetable crops.
4. Natural & Botanical Fungicides
- Timorex Gold—A natural fungicide derived from Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree). Demonstrates efficacy in bananas, mangoes, and vegetables.
How Do These Fungicides Work?
Fungicides feature different modes of action such as:
- Mitochondrial respiration inhibitors—Block energy production in fungal cells (e.g. strobilurins like azoxystrobin and trifloxystrobin).
- Cell membrane synthesis disruptors—Halt ergosterol production, an essential sterol for fungal membranes (e.g. propiconazole).
- Succinate dehydrogenase inhibitors (SDHIs)—Target the fungal respiratory chain at the succinate dehydrogenase enzyme (e.g. fluopyram, fluxapyroxad).
- Natural compounds—Inhibit spore germination, hyphal growth, and infection processes by various mechanisms (Timorex Gold).
Key Crops & Situational Examples
- Turfgrass & Lawns: Azoxystrobin and propiconazole are the most recommended for preventive and curative control.
- Strawberries: Pyraclostrobin, fluxapyroxad, and propiconazole are proven effective, especially as part of a combination or rotation program.
- Almonds: Propiconazole and fluopyram are frequently used, typically with careful application timing and rotation.
- Mangoes & Bananas: Trifloxystrobin and Timorex Gold are valued for their efficacy and safety profiles.
Estimated Efficacy Rates
Most top fungicides achieve efficacy rates between 80-95% when applied correctly and as part of an integrated management strategy.
“Did you know? Rotating at least 3 fungicide classes reduces anthracnose resistance risk by up to 70%.”
Fungicide Application Strategies & Timing for Anthracnose Disease Control
Maximizing efficacy in anthracnose management depends on precise application strategies. Several considerations—including timing, rates, combinations, and preventiveness—shape the overall success of disease control.
Optimal Fungicide Application Timing
- Preventive Applications: Most effective when applied before symptoms appear or at early disease pressure, e.g., starting in mid to late spring for turfgrass as soil temperatures rise above 65°F.
- Sequential Applications: In strawberries and some vegetables, sequential chloropicrin or 1,3-dichloropropene plus chloropicrin should be followed 7 days later by metam sodium or metam potassium for robust anthracnose control.
- Recommended Rates: Always follow label or official guidelines (e.g., propiconazole at 8.0 oz per acre for almonds; maximum two consecutive, four total sprays per season).
- Combination & Rotation: Over-reliance on one mode invites resistance. Rotating fungicide classes and using tank mixes is highly recommended.
Real-World Example: Anthracnose in Strawberries
For anthracnose in strawberries, using sequenced, rotated applications—combining fungicides such as pyraclostrobin, propiconazole, fluxapyroxad, and chloropicrin—offers prolonged control and minimized resistance risk.
Key Application Considerations
- Respect pre-harvest intervals and maximum number of applications.
- Ensure uniform coverage, especially on susceptible plant parts (fruits, leaves, stems).
- Integrate with cultural practices for anthracnose: Avoid over-irrigation or high humidity in greenhouses where possible.
- Always monitor disease pressure to guide timing and intensity of applications.
Anthracnose Resistance Management in Fungicides
Resistance management remains at the core of sustainable anthracnose disease control. Fungal pathogens like Colletotrichum species adapt rapidly, making integrated resistance strategies essential:
- Rotate fungicides with different modes of action/group numbers every application or block of 2-3 sprays.
- Use combination products, especially strobilurin-SDHI, DMI-strobilurin, or biologicals with chemicals.
- Combine with non-chemical approaches—use resistant cultivars and cultural practices for anthracnose.
- Monitor disease regularly; adjust the strategy if resistance is suspected or if control breakdowns occur.
- Do not exceed recommended rates or maximum number of applications per season.
Helpful Tip: Always follow the latest Integrated Pest Management (IPM) guidelines for your crop and region!
Comparative Fungicide & Management Strategies Table
| Fungicide Name | Active Ingredient | Estimated Efficacy (%) | Recommended Application Method & Timing | Resistance Risk | Supplementary Control Practices |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Azoxystrobin | Strobilurin (QoI) | 90-95 | Preventive; Begin at early symptom onset; Repeat every 14-21 days | High (if overused) |
Rotate with DMI/SDHI fungicides; Integrate with proper irrigation and mowing in turfgrass. |
| Propiconazole | DMI (Triazole) | 85-92 |
Curative & preventive; Apply at 8.0 oz/acre in almonds; Max 2 sequential, 4 total annually. |
Medium |
Use with crop sanitation and crop rotation; Monitor for resistance and tank-mix if possible. |
| Trifloxystrobin | Strobilurin (QoI) | 88-93 | Preventive; Tank-mix with other fungicides for mango, vegetables. | High |
Use resistant cultivars; Rotate classes; Enhance air circulation. |
| Pyraclostrobin | Strobilurin (QoI) | 91-95 | In strawberry: Preventive; Begin before expected outbreaks; rotate with SDHI/DMIs. | High |
Remove infected debris; Drip irrigation over overhead. |
| Fluopyram | SDHI | 85-90 | Preventive & early curative; Apply with compatible partner in almonds/other fruit crops. | Medium |
Rotate modes; Avoid back-to-back SDHI use. |
| Fluxapyroxad | SDHI | 88-91 |
Apply as part of rotation in strawberries and vegetables; Use in mix, monitor resistance. |
Medium |
Integrate with field hygiene; Regular scouting. |
| Timorex Gold | Natural botanical (Melaleuca alternifolia) | 80-87 |
Preventive/corrective; Start at first sign in banana, mango, tomato. Rotate with synthetic fungicides. |
Low |
Support with resistant varieties; Minimize field humidity. |
| Chloropicrin (fumigant) | Chloropicrin | Varies (high for soilborne phases) | Pre-plant; Sequential use as per local schedule; Followed by metam sodium/potassium. | Low |
Incorporate with solarization; Strict safety protocols. |
Integrated Anthracnose Management: Best Practices
Only through an integrated anthracnose strategy can we sustainably protect our crops and minimize both yield and quality losses. The best results stem from the synergy of chemical, cultural, and genetic approaches.
- Choose resistant cultivars where available. Many breeders now offer varieties less susceptible to anthracnose.
- Practice field sanitation—Remove and destroy infected plant parts to reduce inoculum pressure.
- Optimize irrigation and canopy management. Wet, dense canopies and splashing water facilitate anthracnose spread.
- Apply rotations and sequences of effective fungicides, per local expert recommendations.
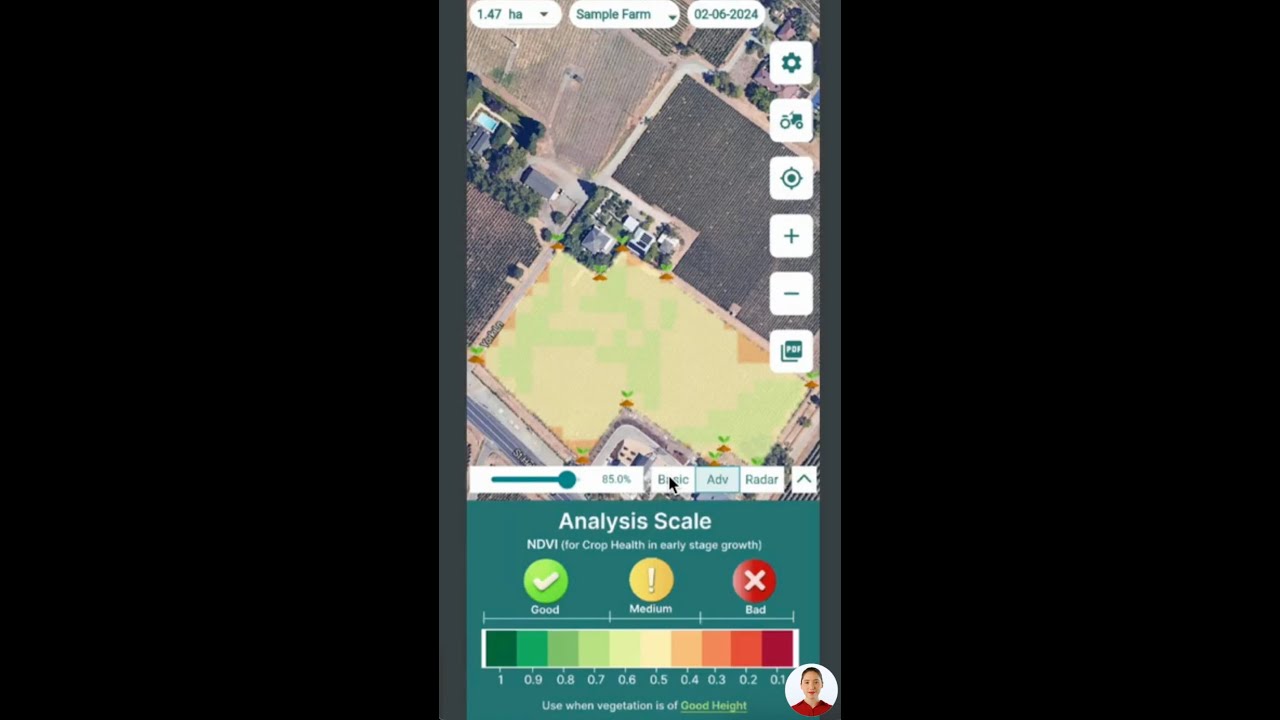
- Monitor fields with modern tools, such as Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop health monitoring, to anticipate outbreaks and guide in-field scouting.
- Use blockchain-based traceability to maintain quality and transparency across the supply chain. Farmonaut’s traceability solutions can be integrated for efficient tracking and verification of disease-free produce.
- Incorporate AI and expert decision systems like Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI Advisory to receive customized crop protection guidance in real-time.
For large farms or plantations, real-time monitoring and area estimation are critical. Discover Farmonaut’s large-scale farm management tools to optimize inputs and proactively implement disease management strategies.
How Farmonaut Empowers Anthracnose Management
While effective anthracnose management starts in the field, emerging technologies now give us an unmatched advantage:
- Real-time satellite-based crop health monitoring tracks disease progression and locates hotspots before symptoms worsen.
- AI-powered advisory, such as Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI, delivers instant, location-specific guidance on fungicide selection, resistance management, irrigation, and fertilizer optimization.
-
Blockchain traceability ensures every produce batch is verifiable and disease-free, raising consumer trust and supply chain value.
Learn more about product traceability. - Fleet and resource management tools optimize application logistics and machinery, making timely and effective fungicide applications more efficient. Did you know Farmonaut supports fleet tracking for large farm operations?
-
Environmental sustainability is supported by carbon footprint monitoring, keeping disease control efforts eco-friendly and compliant.
Read about Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting benefits.
Agribusinesses, corporates, and governments can access Farmonaut via Web app, Android, iOS, or integrate satellite and weather data directly into their digital systems with our API and API documentation.
Farmonaut Subscription and Resources
Whether you are a smallholder farmer seeking precision agriculture or a large-scale producer managing thousands of hectares, we offer affordable, scalable subscription plans to suit your needs. All Farmonaut tools are available across Web, Android, and iOS platforms, making advanced agricultural intelligence accessible from anywhere.
For crop loan and insurance needs, Farmonaut’s satellite-based verification streamlines claims and approvals. Explore satellite-verified crop insurance solutions for extra security and peace of mind.
Ready to transform your anthracnose management? Start with our farm management app or learn more through our Plantation, Crop & Forest advisory.
FAQs: Anthracnose Fungicides & Management
What is the best fungicide for anthracnose in strawberries?
How can I prevent fungicide resistance in my crops?
- Rotate fungicides with different modes of action (e.g. strobilurin, SDHI, DMI).
- Do not exceed label rates or number of sprays per season.
- Combine fungicides when possible and support with cultural practices like sanitation and resistant varieties.
- Monitor disease regularly and adjust as needed.
What integrated methods control anthracnose besides fungicides?
Can I use natural fungicides for anthracnose?
How does Farmonaut help with disease monitoring?
Conclusion
Anthracnose remains a top threat to agricultural productivity and crop quality worldwide. However, with a full understanding of the best fungicides for anthracnose, precise application strategies, robust resistance management, and cutting-edge technology tools like those from Farmonaut, we can significantly reduce disease pressure, limit losses, and sustain healthy, profitable harvests.
We encourage every grower and farm manager, whether protecting strawberries, almonds, turfgrass, or any susceptible plant, to adopt integrated anthracnose strategies blending the power of modern fungicides, traditional cultural practices, disease-resistant genetics, and digital smart farming platforms for season-after-season success.
Empower your fields with data, stay vigilant with resistance management, and never underestimate the value of timely, informed decisions—your harvest and your bottom line will thank you.