Eggplant Pests: 7 Powerful Solutions for Higher Yields
Meta Description: Eggplant pest management is crucial for higher yields and quality produce. Explore integrated pest strategies, innovative solutions like Bt eggplant, and effective control methods for sustainable brinjal cultivation.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Eggplant Pest Management
- Common Eggplant Pests and Their Impact
- 7 Powerful Eggplant Pest Management Strategies
- Integrated Pest Management in Eggplant: An Innovative Approach
- Technology & Biotech Solutions: The Role of Bt Eggplant
- Farmonaut: Advancing Precision in Eggplant Pest Management
- Eggplant Farming Best Practices for Pest Control
- FAQ: Eggplant Pests and Pest Management
- Conclusion: Achieving Sustainable High Yields in Brinjal Cultivation
“Bt eggplant can increase brinjal yields by up to 42% by effectively controlling fruit and shoot borer pests.”
Introduction to Eggplant Pest Management
Eggplant (Solanum melongena), widely recognized as brinjal in many regions of Asia, stands among the world’s most cultivated vegetables due to its remarkable versatility and nutritional value. Whether you enjoy its tender flesh grilled, curried, or baked, this primary crop is an essential component in global cuisines. Yet, eggplant farming is persistently challenged by a host of pests capable of severely impacting yield and produce quality.
The management of eggplant pests and diseases is therefore critical. Without effective controls, infestations can devastate crops, causing several varieties of brinjal to experience significant yield losses. This comprehensive guide explores the most powerful pest management strategies, with a focus on integrated pest management in eggplant, cutting-edge biotechnology like Bt brinjal, and evidence-based practices to ensure sustainable farming and improved profits.
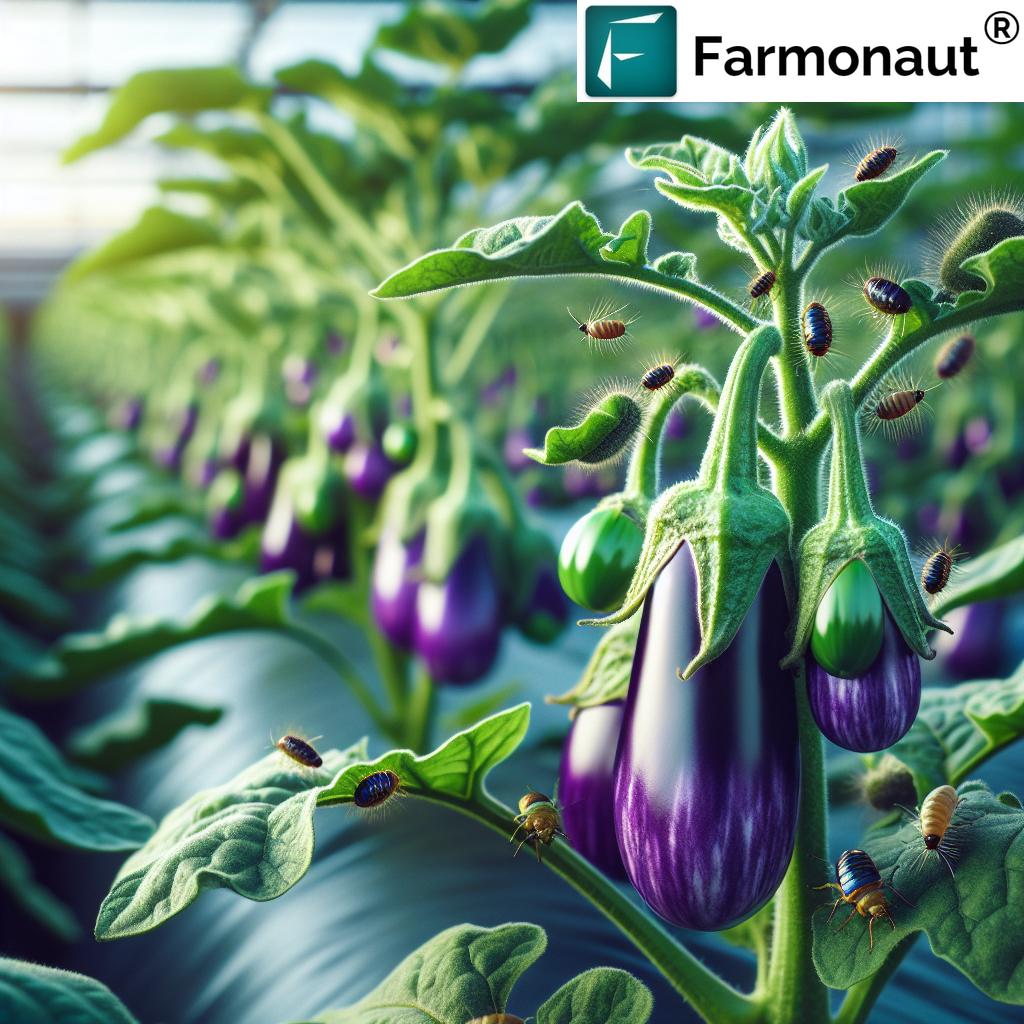
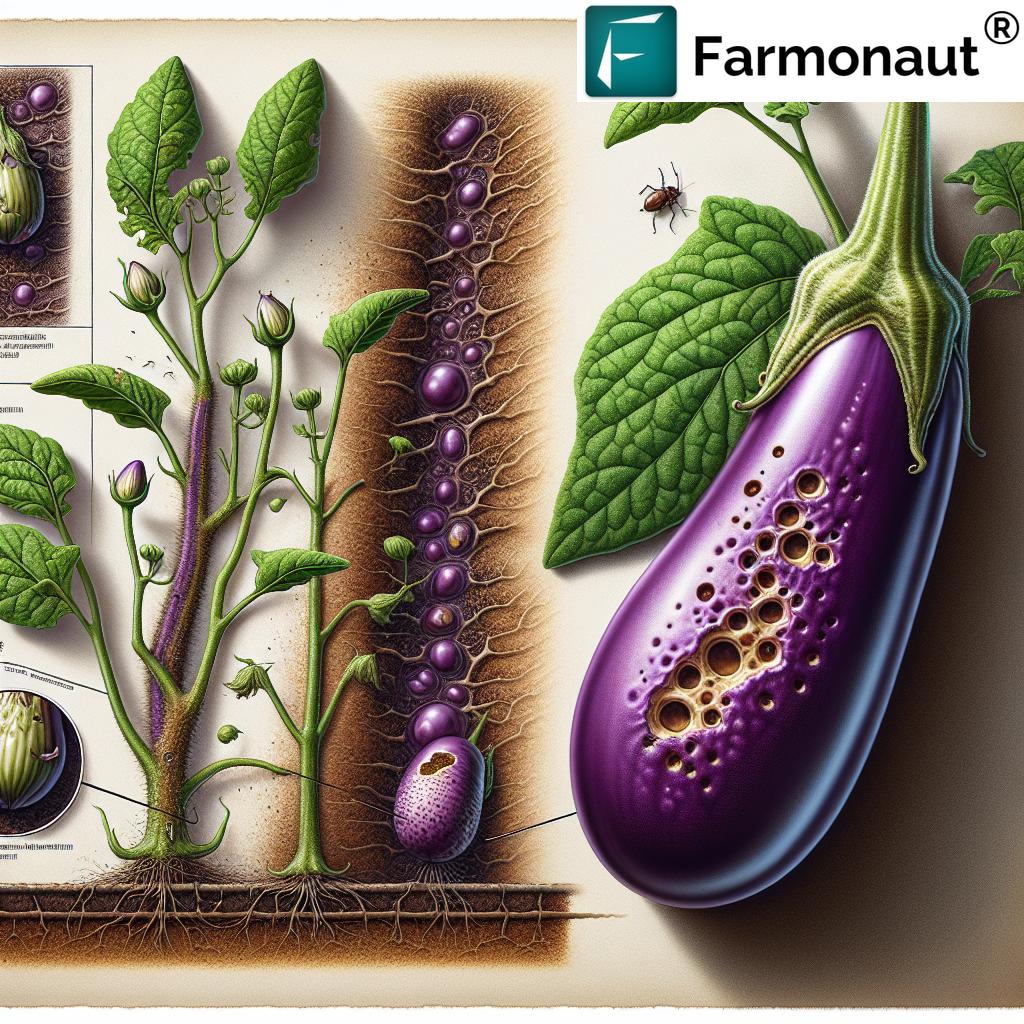
Common Eggplant Pests and Their Impact on Yield and Quality
Proper identification of eggplant pests is the foundation for effective management. Below, we detail major insects and species that threaten eggplant fields globally, with special attention to their impact on yields, plant growth, and fruit quality.
Major Eggplant Pests: Identification and Damage
-
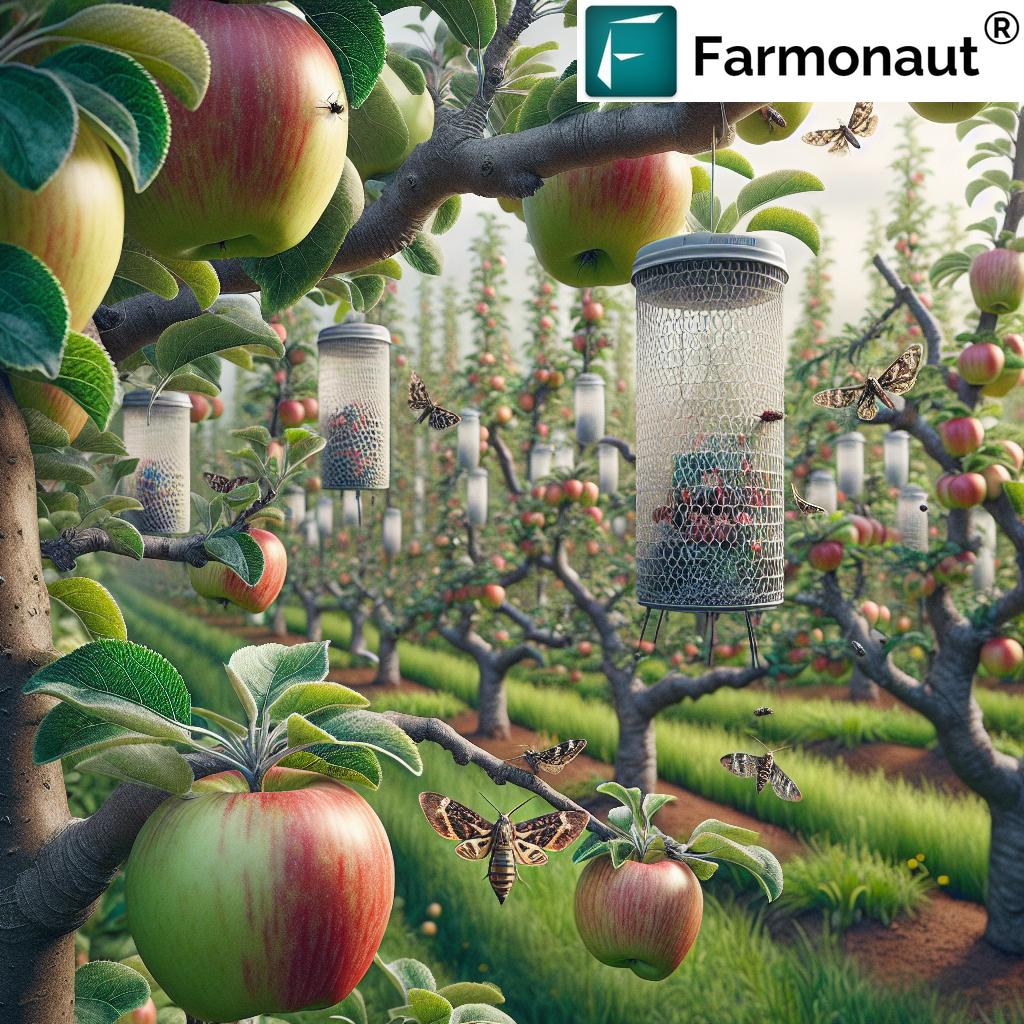
Eggplant Fruit and Shoot Borer (Leucinodes orbonalis)
Key Features: A notorious moth pest in South and Southeast Asia. Adults lay eggs beneath leaves, on flower buds, or on fruit calyces.
Lifecycle Impact: Once the eggs hatch, young larvae bore into shoots and fruits, causing sudden wilting, internal decay, and production of unmarketable brinjal. Peak infestations can reduce yields by up to 100%.
(Reference) -
Flea Beetles (Epitrix spp., especially Epitrix fuscula)
Key Features: Small, shiny beetles that hop when disturbed.
Damage: Characteristic “shot hole” feeding trails on leaves. Intense feeding reduces foliage area, stunts growth, and impedes fruit development.
(Reference) -
Aphids (Aphis spp.)
Key Features: Small sap-sucking insects clustered along stems or the undersides of leaves.
Damage: Weakens plants, retards growth, causes leaf curling and yellowing. Also responsible for the transmission of viral diseases, further reducing yields.
(Reference) -
Two-Spotted Spider Mite (Tetranychus urticae)
Key Features: Tiny arachnids, often on the undersides of eggplant leaves.
Damage: Causes bronzed, speckled leaf appearance, leaf drop, weakened plant vigor, and possible yield reduction during hot, dry seasons.
(Reference) -
Root-Knot Nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.)
Key Features: Microscopic worms that attack eggplant roots.
Damage: Creates root galls, disrupts water/nutrient uptake, leads to overt yellowing, wilting, stunted growth, and poor yields.
(Reference) -
Colorado Potato Beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata)
Key Features: Striped beetle, attacks both potatoes and eggplants.
Damage: Heavy feeding by adults and larvae defoliates plants, resulting in severe yield decrease and poor crop quality. Notoriously resistant to many standard pesticides.
(Reference) -
Cutworms (Various species)
Key Features: Larvae of various moth species, hidden in the soil line.
Damage: Severs young seedlings at base, leading to immediate loss of emerging plants.
(Reference) -
Whiteflies (Bemisia tabaci)
Key Features: Tiny winged insects forming clouds on eggplants when disturbed.
Damage: Feeds on plant sap, causes yellowing of leaves, stunted shoots, viral disease transmission, drastically affects yield and fruit quality.
(Reference)
“Integrated pest management reduces pesticide use in eggplant fields by nearly 50%, promoting safer and more sustainable cultivation.”
7 Powerful Eggplant Pest Management Strategies for Higher Yields
Managing eggplant pests for high-yield, sustainable brinjal farming requires a blend of traditional wisdom and tech-powered practices. Let’s examine the top 7 eggplant pest management solutions — each offering a strategic combination of effectiveness, yield impact, and sustainability.
1. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
- An integrated approach blending cultural, biological, and, when necessary, chemical methods.
- Key Tactics: crop rotation, field sanitation, resistant varieties, pest monitoring, threshold-based intervention, targeted biopesticides, and judicious pesticide use.
- Benefits: Maximizes yield, reduces pesticide load, slows development of pest resistance, promotes minimal environmental impact.
2. Bt Eggplant (Genetically Engineered Brinjal)
- Eggplant engineered to express Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) Cry1Ac gene offers in-plant protection against fruit and shoot borer.
- Impact: Reduces need for external insecticides, offers up to 42% yield improvement, Reference.
- Sustainability: Reduced chemical residues, eco-friendly, especially valuable in regions where Leucinodes orbonalis is rampant.
3. Cultural Control Methods
- Tactics like crop rotation, field hygiene, use of pest-free seedlings, destruction of infested debris, and adjusting planting time to avoid peak pest periods.
- Interrupts pest life cycles, minimizes initial infestation risk, and boosts plant health for better pest resistance.
4. Biological Control for Eggplant Pests
- Release or conservation of beneficial insects (ladybugs, lacewings), and deployment of biopesticides (trichogramma wasps, predator nematodes, and Bacillus thuringiensis products).
- Highly effective against soft-bodied pests like aphids and early-instar larvae.
5. Use of Insecticides and Insecticidal Soaps/Oils
- Targeted, label-compliant application of chemical pest controls when infestations break threshold limits.
- Effective for rapid knockdown but must be used alongside monitoring to prevent resistance and minimize impact on beneficial species.
6. Resistant and Tolerant Eggplant Varieties
- Choosing eggplants bred for resistance to major pests and diseases (reference).
- Reduces input costs, offers natural immunity, and supports longer-lasting field health.
7. Physical and Mechanical Controls
- Implementing row covers, sticky traps, hand-picking beetles/larvae, and mulching to directly reduce pest populations.
- Especially effective for small-scale brinjal cultivation and seedling protection against cutworms and flea beetles.
Comparative Solutions and Yield Impact Table for Eggplant Pest Management
| Solution Name | Pest(s) Targeted | Method/Technology Used | Estimated Yield Increase (%) | Sustainability Impact | Implementation Difficulty | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Integrated Pest Management (IPM) | Multiple (all major pests) | Cultural, biological, targeted chemical controls | 25–40% | High | Moderate | Moderate |
| Bt Eggplant | Fruit and shoot borer (Leucinodes orbonalis) | Genetically engineered Cry1Ac protein expression | 35–42% | High | Moderate/Hard* | Medium |
| Cultural Controls | All pests (varies by practice) | Rotation, sanitation, seedling selection, timing | 15–25% | High | Easy | Low |
| Biological Control Agents | Aphids, borers, mites, beetles | Beneficial insects, biopesticides (Bacillus thuringiensis, nematodes, etc.) | 15–30% | High | Moderate | Low–Medium |
| Insecticides (Synthetic/Organic) | Broad-spectrum | Chemical sprays, insecticidal soaps/oils | 20–30% | Low–Medium | Easy | Medium |
| Resistant Varieties | Specific pests/diseases | Select eggplant breeds with natural resistance | 18–22% | High | Easy | Low/Medium |
| Mechanical/Physical Barriers | Cutworms, flea beetles, whiteflies, borer eggs | Row covers, traps, hand-picking, mulching | 12–18% | High | Easy | Low |
Integrated Pest Management in Eggplant: An Innovative Approach
Integrated pest management (IPM) in eggplant (brinjal) is an adaptive, knowledge-based system that merges monitoring, decision-support, and a tactical blend of controls. It is essential for farmers aiming not only for higher yields, but also sustainable resource use and reduced chemical residues in their produce.
Key Components of IPM in Eggplant Cultivation
- Regular Pest Monitoring: Early identification and quantification of pest presence (e.g., weekly scouting, pheromone traps)
- Setting Economic Thresholds: Implementing controls only when pest numbers reach levels likely to cause economic yield loss
- Cultural Practices:
- Crop rotation with non-hosts (e.g., cereals)
- Field sanitation: removal of infested plant material and debris
- Good nursery practices and certified, disease/pest-free seedlings
- Biological and Biorational Controls: Conservation or augmentation of natural enemies, e.g., lady beetles, Trichogramma wasps, lacewings
- Selective Use of Chemical Controls: Minimal use of targeted, rotation-ready insecticides to slow development of pest resistance
How IPM Leads to Sustainable Yields
- Consistently reduces pesticide input by up to 50% without sacrificing productivity
- Improves plant resilience, enhances fruit quality, and prevents soil ecosystem disruption
- Slows resistance development in major pests
Technology & Biotech Solutions: Bt Eggplant and Modern Innovations
Modern biotechnology has redefined eggplant pest management in the last decade — particularly with the advent of Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) brinjal. Let’s review how these genetic and digital advancements offer sustainable, scalable, and resource-efficient pest control.
Bt Eggplant (Bt Brinjal): A Game-Changer in Pest Control
- Mechanism: Engineered to express Cry1Ac protein from Bacillus thuringiensis, toxic to Leucinodes orbonalis larvae but harmless to humans and most beneficial insects.
- Yield Impact: Studies show yield boosts up to 42% due to effective fruit and shoot borer control and lower crop loss rates.
- Environmental Impact: Substantially reduces the frequency and volume of chemical pesticide applications—protecting beneficial insect populations and soil health.
- Practical Considerations: Adoption is subject to local regulations; widely implemented in Asia, especially Bangladesh, where traditional methods failed to check borer infestations.
Advantages of Bt Eggplant for Brinjal Cultivation Pest Control
- Reduces farmer exposure to hazardous chemicals
- Improves farm profitability through higher marketable yields and lower input costs
- Protects field biodiversity and pollinators
Read more about Bt Eggplant advantages and safety here.
Farmonaut: Advancing Precision in Eggplant Pest Management
At Farmonaut, we believe that technology and data-driven insights are the keys to tackling challenges like eggplant pest management at scale. By deploying a blend of satellite-based farm management, artificial intelligence, and blockchain, our platform supports both smallholder and commercial farmers with timely pest detection and yield optimization.
How Farmonaut Technology Empowers Eggplant Farming Best Practices:
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Using NDVI and similar indices, we detect early stress signals — including pest, disease, or water-related issues — before visible symptoms manifest in eggplant fields.
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: Our AI delivers real-time, personalized pest management advice and yield improvement strategies, integrating local weather risk, crop stage, and farm history.
- Blockchain-Based Traceability: Our traceability solution secures every stage of the brinjal supply chain — enhancing trust and transparency for exporters, retailers, and consumers.
- Resource Optimization Tools: Our large-scale farm management suite tracks machinery, labor, and fleet resources, ensuring efficient field operations during pest control activity peaks.
- Insurance and Loan Verification: By verifying fields with up-to-date imagery and health data, our crop loan/insurance module helps farmers access credit quickly and confidently mitigate pest-induced crop losses.
- API Integrations: We support external developers and enterprise customers via Farmonaut’s RESTful Satellite & Weather API — with detailed API documentation for seamless integration.
- Carbon Footprinting: Our carbon footprint tracking tool helps farmers and businesses measure and reduce the ecological impact of pest management practices.
By lowering costs, delivering real-time crop insights, and supporting sustainable practices, we equip farms—big and small— to maximize eggplant yields while maintaining ecological balance.
Eggplant Farming Best Practices for Pest Control and Higher Yields
Effective eggplant pest control depends on a holistic approach — where pre-season preparation, field hygiene, precision monitoring, and timely intervention work together to outsmart pest cycles. Here are actionable steps every brinjal grower should adopt:
Pre-Planting Strategies
- Soil Preparation: Deep plowing and solarization help disrupt soil pest/nematode populations.
- Seed & Seedling Quality: Use certified seeds and raised, insect-proof nurseries; regularly inspect for early pest/disease symptoms.
Field Management During The Season
- Row and Plant Spacing: Wider spacing and raised beds improve airflow (lessens fungal/viral outbreaks) and allows for easier pest scouting/intervention.
- Intercropping & Crop Rotation: Alternate eggplant with non-host crops (corn, pulses); enriches soil and disrupts pest life cycles, especially for nematodes and beetles.
- Trap Cropping: Plant solanaceous decoys or trap crops to attract and dispose of major pests like flea beetles.
Monitoring, Early Detection, and Threshold-Based Intervention
- Frequent Scouting: At least weekly, inspect for eggs, larvae, and leaf damage; monitor for aphids, whiteflies, and signs of viral diseases.
- Broadcast Sticky & Pheromone Traps: Useful for monitoring and trapping borer adults and whiteflies.
- Record Thresholds: Deploy controls when pest counts approach region-specific action thresholds (e.g., >2 borers per 5 plants, 10% leaf area loss, etc.)
Resistant Varieties & Crop Rotation
- Planting resistant/tolerant brinjal breeds reduces need for chemical intervention and ensures stable yield across seasons.
- Continuous rotation (avoid Solanaceae back-to-back) disrupts buildup of nematode, borer, and beetle populations.
Biological and Judicious Chemical Control
- Release natural enemies (parasitic wasps, predatory beetles) at appropriate crop stages.
- Apply biopesticides like neem-based sprays or Bacillus thuringiensis during vulnerable larval stages.
- If chemical controls are necessary, always rotate active ingredients and apply in late afternoon to protect pollinators and beneficial insects.
Sanitation and Post-Harvest Action
- Destroy or compost all infested plant debris immediately after harvest to minimize pest carryover.
- Clean field tools and equipment often to avoid mechanical transmission of pests, especially viral agents.
FAQ: Eggplant Pests and Eggplant Pest Management
Q1. What are the most common eggplant pests that reduce yield?
Major pests include the eggplant fruit and shoot borer (Leucinodes orbonalis), flea beetles (Epitrix spp.), aphids (Aphis spp.), two-spotted spider mite, root-knot nematodes, Colorado potato beetle, whiteflies, and cutworms. Each species affects eggplant crops differently—borers destroy shoots/fruits, aphids transmit viral diseases, flea beetles stunt plant growth, and so on.
Q2. What is integrated pest management in eggplant, and why is it recommended?
Integrated pest management (IPM) combines strategies such as cultural controls, biological methods, and selective chemical use. This system lowers pesticide dependency (by up to 50%), preserves beneficial insects, delays resistance, and delivers effective eggplant pest control for sustainable, profitable farming.
Q3. How does Bt eggplant work, and is it safe?
Bt eggplant expresses the Cry1Ac protein from Bacillus thuringiensis, which is toxic to the larvae of Leucinodes orbonalis (fruit and shoot borer), but harmless to humans, livestock, and most beneficial insects. Regulatory agencies have reviewed Bt brinjal safety. It is a breakthrough for yield improvement in regions plagued by borers.
Q4. Do I need to spray insecticides if I use resistant varieties or biocontrols?
While resistant eggplant varieties and biological control agents substantially reduce pest pressure, careful field monitoring is always needed. If pest outbreaks occur above action thresholds, selective, targeted chemical controls may be necessary. Rotate chemistries to prevent development of resistant pest populations.
Q5. What Farmonaut tools can support my brinjal pest management program?
Farmonaut provides a full suite of technologies:
Satellite crop health monitoring (for detecting early stress), Jeevn AI-based advisory system (for real-time best practices), resource management tools (for tracking pest control resources), and traceability solutions for secure supply chains. Get started via our web and mobile apps or check the API documentation for developer integration.
Q6. What cultural practices can help suppress eggplant pests naturally?
- Rotate eggplant with non-host crops
- Remove all infested plants/fruit immediately
- Use floating row covers/physical barriers early in the season
- Maintain weed-free field borders to discourage pest build-up
Q7. Can precision monitoring really increase eggplant yields?
Yes! Accurate, timely detection and intervention leads to early pest suppression, lower input costs, and higher marketable yields. Technologies like Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring tools are proven to elevate farm decision-making and optimize yield per hectare.
Conclusion: Achieving Sustainable High Yields in Brinjal Cultivation
Eggplant (Solanum melongena) offers immense value as a nutritious, versatile crop but does not come without challenges from aggressive pest communities. To safeguard yield and improve quality, modern eggplant farmers must transition from reactive spraying toward integrated pest strategies that combine cultural, biological, genetic, and technological solutions.
Innovations like Bt eggplant, satellite crop health monitoring, AI-powered advice, and blockchain traceability equip today’s grower to not only outsmart pests but also fulfill market and sustainability goals. By uniting ancient farming knowledge with precision agriculture, we can ensure that future eggplant cultivation remains productive, resilient, and resource-efficient worldwide.
Explore how Farmonaut can help you maximize your eggplant yield and protect your farm’s future here.