Table of Contents
- Introduction: Why Lemon Trees Attract Insects
- Common Pests Affecting Lemon Trees
- Pest Identification and Management Strategies Table
- Integrated Pest Management for Citrus Trees
- Top 7 Tips: How to Get Rid of Bugs on Lemon Tree
- Detailed Pest-Specific Control Strategies
- Farmonaut Tools for Pest Management
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
“Up to 90% of lemon tree pest infestations are caused by aphids and mealybugs.”
How to Get Rid of Bugs on Lemon Tree: Top 7 Tips
Lemon tree pests can turn our beautiful citrus havens into battlegrounds of wilting leaves and diminished fruit. Whether we are cultivating lemon trees for lush landscaping in our garden or aiming for a bounty of tangy fruits, these citrus trees often face relentless attacks from insects like aphids, mealy bugs, scale insects, and more.
Understanding how to get rid of bugs on lemon trees is crucial—not only does it protect the health and productivity of our trees, but it also enhances fruit quality and ensures long-term enjoyment of our citrus harvests. With integrated pest management for citrus trees, we can manage, control, and often prevent these common insects affecting lemon trees.
In this ultimate guide, we’ll help you identify, manage, and control a variety of lemon tree pests—from tiny aphids sucking plant sap to root weevil larvae causing wilting at the roots. We’ve integrated modern techniques and time-tested solutions in this educational, step-by-step resource, optimized for all home gardeners, orchard managers, and commercial citrus growers alike.
Common Pests Affecting Lemon Trees
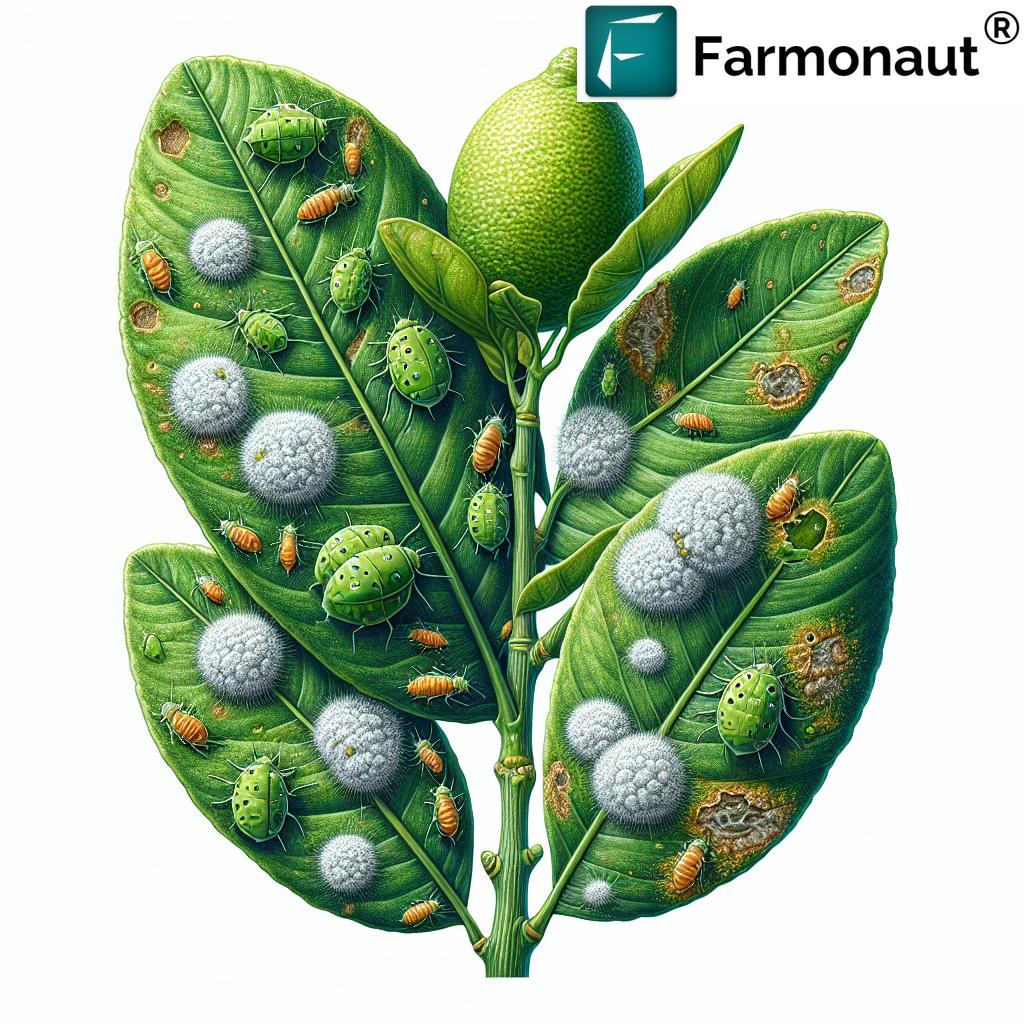
Lemon trees, like other citrus plants, are susceptible to a diverse array of pests. Knowing how to identify these insects at an early stage can be a game-changer in maintaining a healthy, thriving tree. Below, we overview the eight most common pests threatening citrus trees worldwide:
- Aphids: Soft-bodied pests feeding on plant sap, causing leaf distortion and potentially spreading disease.
- Scale Insects: Appear as small bumps on stems and leaves, leading to yellowing and stunted growth.
- Mealybugs: White, cottony masses on plants feeding on sap, thus weakening the citrus tree.
- Spider Mites: Tiny arachnids inducing leaf stippling and drop in severe infestations.
- Citrus Leaf Miners: These moth larvae leave winding trails and cause leaf distortion and reduced photosynthesis.
- Whiteflies: Small, winged insects that excrete honeydew, thus promoting sooty mold and causing yellowing leaves.
- Thrips: Feeding on a variety of plant parts, these insects create silver streaks impacting fruit and leaf growth.
- Citrus Root Weevils: Beetle larvae feasting on roots, leading to wilting and poor growth.
It’s important for us to regularly inspect our trees, as early detection and action can make a remarkable difference in pest control, including helping prevent yellowing leaves on lemon trees. Let’s see how to distinguish these invaders and what we can do to defend our citrus assets.
Pest Identification and Management Strategies Table
| Pest Name | Appearance | Common Symptoms | Infestation Severity | Recommended Control Methods |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aphids | Green, yellow, or black soft-bodied, 1–3mm | Deformed, curled leaves; sticky residue (honeydew) | High |
|
| Scale Insects | Brown/tan bumps on stems/leaves | Yellowing, stunted growth, sticky leaves | Medium |
|
| Mealybugs | White, cottony masses on stems/leaves | Sticky honeydew, leaf yellowing, weak growth | High |
|
| Spider Mites | Tiny red/yellow/green mites, form webs | Leaf stippling/yellowing, leaf drop | Medium |
|
| Citrus Leaf Miners | Tiny moth larvae, white trail in leaves | Winding silvery trails, leaf curling/distortion | Low–Medium |
|
| Whiteflies | Tiny white, flying insects underneath leaves | Yellowing, sticky honeydew, sooty mold | Medium |
|
| Thrips | Tiny, slender yellow-brown insects | Silver streaks on leaves, deformed fruit | Low–Medium |
|
| Citrus Root Weevils | Black/brown beetles; larvae in soil | Wilting, poor growth, roots chewed | Low–Medium |
|
Integrated Pest Management for Citrus Trees: The Smart Approach
To keep our citrus trees robust and prolific, integrated pest management (IPM) is a proven, eco-friendly strategy. IPM combines cultural, biological, physical, and, where needed, chemical control methods—all aimed at reducing pest populations with minimal risk to people and the environment.
By implementing these integrated approaches, we’re not just responding to outbreaks, but actively preventing them. Let’s break down IPM for lemon trees step by step:
- Cultural Controls: Maintain healthy soil, remove weeds, and prune infested branches to naturally discourage pests.
- Biological Controls: Encourage or introduce natural enemies like ladybugs and beneficial nematodes.
- Physical Controls: Use barriers, traps, and direct removal techniques.
- Chemical Controls: Employ insecticidal soaps, oils, or targeted pesticides only if cultural, biological, and physical controls are insufficient.
IPM requires regular inspection and monitoring—which is where advanced tools like Farmonaut’s real-time crop health monitoring can be invaluable. Farmonaut leverages satellite-based observations and AI-driven insights to help us identify infestations early, manage resource use, and time interventions precisely. Discover Farmonaut’s Crop Plantation and Advisory solutions for better pest and disease management at scale.
For advanced users and developers, Farmonaut also offers robust API access and API developer documentation for satellite-driven crop monitoring, making integration with existing farm management systems a breeze.
“Proper pruning can reduce lemon tree pest populations by as much as 60%.”
Top 7 Tips: How to Get Rid of Bugs on Lemon Tree
Every citrus enthusiast inevitably asks: How do we control pests on lemon trees—effectively and sustainably? Here, we share our 7 most powerful, integrated tips for managing and defeating lemon tree pests.
-
Regular Inspection and Early Identification
- Inspect trees weekly—look for curled, sticky, or yellowing leaves, and visible bugs on stems and fruits.
- Use a magnifying glass to spot tiny insects like spider mites and aphids on lemon tree leaves.
-
Healthy Soil and Watering Practices
- Use well-drained, nutrient-rich soil to support robust tree growth, making trees less susceptible to pests.
- Avoid overwatering, which invites pests and diseases to flourish around roots.
-
Pruning and Sanitation
- Prune out infested or unhealthy branches immediately to reduce lemon tree pest populations.
- Regularly remove fallen leaves, branches, and fruit to prevent pest life cycles from continuing undisturbed.
-
Weed and Companion Plant Management
- Keep weed growth in check; many weeds are a hiding spot for pests affecting citrus trees.
- Plant pest-repelling companions like basil and marigolds nearby as natural pest control for lemon trees.
-
Biological Pest Control for Lemon Trees
- Attract and protect beneficial insects (ladybugs, lacewings, predatory wasps) that feed on aphids, mealybugs, and whiteflies.
- For soil-dwelling pests, release beneficial nematodes to target larvae and root weevils.
-
Physical Pest Controls: Traps, Water, and Mulches
- Apply strong water sprays to dislodge soft-bodied pests like aphids and spider mites.
- Set up yellow sticky traps to capture and monitor adult whiteflies and some thrips.
- Use reflective mulches to deter sap-sucking insects from landing on the citrus tree foliage.
-
Chemical Controls: Last Resort, Not First Response
- Opt for insecticidal soaps and oils that target soft-bodied insects (aphids, mealybugs), minimizing harm to beneficial species.
- For severe infestations, use citrus-safe systemic insecticides or miticides, always following label directions and safety precautions.
Lemon Tree Pest Control: In-Depth Strategies for Each Pest
Let’s dive deeper into specific pests and outline our stepwise management methods using the principles of integrated pest management for citrus trees:
Aphids on Lemon Tree Leaves
- Typically cluster on new growth and tender leaves, aphids suck sap, distorting and curling foliage, often leaving a sticky residue (honeydew).
- Natural controls: Spray with water, introduce or conserve ladybugs, keep plants weed-free to minimize insect hiding spots.
- Physical/chemical: Apply insecticidal soap or neem oil. For severe issues, use systemic insecticide—but only as a last resort.
- Tip: Honeydew attracts sooty mold, leading to further stress and yellowing.
Mealybugs on Citrus Trees
- These pests resemble white, fluffy spots (“cottony masses”) on stems, foliage, and sometimes fruit.
- Control: Remove visible clusters with alcohol-soaked cotton swabs, encourage lacewings and ladybugs, apply horticultural oils.
- Ensure good air circulation and avoid excessive nitrogen fertilizer—which encourages rapid, soft growth attractive to mealybugs.
- Tip: Cleanliness and prompt action are essential to reduce mealybug populations.
Scale Insects
- Appear as hard or soft dome-shaped brown bumps attached to stems and leaves, sucking sap directly from the plant.
- Control: Prune and dispose of heavily infested parts to break the lifecycle, apply horticultural oils/soaps during crawler stage.
- Beneficial predatory insects like parasitic wasps aid in population reduction.
- Tip: Dormant oils in winter can help manage hidden scale eggs.
Spider Mites and Thrips
- Mites are tiny arachnids causing leaf stippling, browning tips, and sometimes webbing. Thrips create silver streaks and leaf markings.
- Physical control: Wash undersides of leaves regularly; maintain humidity to discourage mite outbreaks.
- Biological and chemical: Introduce predatory mites; apply miticides or approved soaps/oils if necessary.
- Tip: Inspect during hot, dry weather when mite populations peak.
Citrus Leaf Miners
- These are the larvae of tiny moths that feed under the skin of leaves, causing twisting, curling, and silvery “trails” across new growth.
- Control: Remove damaged leaves, use pheromone traps for adults, avoid over-fertilization which stimulates flushes of new, susceptible growth.
- Tip: Leaf miner infestations seldom seriously harm mature trees but can weaken young transplants.
Whiteflies on Lemon Tree
- Congregate on the undersides of leaves, causing yellowing, wilting, and often leaving honeydew leading to sooty mold.
- Control: Deploy yellow sticky traps, encourage natural predators, apply neem oil or insecticidal soaps as directed.
- Tip: Frequent inspection under warm, dry conditions will help to visually detect whiteflies early.
Citrus Root Weevils
- Adult beetles are rarely spotted, but larvae feed on roots, causing wilting and stunted growth above ground.
- Biological control: Apply beneficial nematodes to soil as a safe and highly effective solution.
- Practice proper watering to reduce attraction and improve overall tree resilience.
Interested in sustainable growing? Learn how to minimize environmental impact with Farmonaut Carbon Footprinting solutions.
For enhanced food safety, track the origin of your citrus fruits with blockchain-based supply chain traceability from Farmonaut.
For accessing agricultural loans or crop insurance with higher transparency, rely on satellite verification with Farmonaut’s crop loan and insurance verification technology.
How Farmonaut Technology Supports Modern Pest Management Practices
Digital transformation is revolutionizing agriculture—and lemon growers stand to benefit immensely from precision technologies. At Farmonaut, our satellite-based solutions empower you to monitor citrus crop health, detect stress caused by pest damage, track irrigation needs, and manage interventions with more accuracy than ever before. Here’s how our technology supports integrated pest management for citrus trees:
- Real-Time Crop Health Monitoring: Identify irregularities early—thanks to NDVI and other spectral indices reflecting pest or disease stress before visible symptoms appear.
- AI-Based Pest & Crop Advisory: Receive custom, data-driven recommendations for pest, disease, and nutrition interventions, saving both time and input costs.
- Blockchain Traceability: Ensure transparency from orchard to table—vital for food safety and market value.
- Resource Management: Optimize irrigation and fertilizer use, creating less favorable conditions for pests while boosting efficiency and sustainability.
Our platform is accessible to a global audience—available via Android, iOS, Web, and API—so whether you manage a small home garden or a large-scale citrus operation, you can always stay ahead of threats by regularly monitoring pest risks and receiving targeted pest control guidance.
Want affordable, real-time satellite crop monitoring for your citrus orchard?
Subscribe to Farmonaut and empower your crop pest management!
Frequently Asked Questions
How can we identify pests on lemon trees early?
Early identification involves regular inspection of leaves, stems, and fruit for visible signs of pests (tiny insects, cottony spots, trails, honeydew, webbing) and symptoms like leaf curling, yellowing, or stunted growth. Use a magnifier for tiny pests and consider remote monitoring technologies like Farmonaut for larger orchards.
What are safe, natural pest control options for lemon trees?
Natural pest control for lemon trees includes introducing beneficial insects such as ladybugs and lacewings; spraying with weak soapy water, neem oil, or horticultural oils; physically removing pests with a strong stream of water; and companion planting with pest-repellent herbs like basil and marigold.
Which lemon tree pests are most common?
Aphids and mealybugs are the most prevalent lemon tree pests, followed by scale insects, spider mites, citrus leaf miners, whiteflies, thrips, and citrus root weevils.
Are chemical controls necessary for lemon tree pest management?
Chemical controls are a last resort in integrated pest management for citrus trees. Try cultural, biological, and physical methods first; use citrus-safe insecticidal soaps or oils when populations are high, and only use systemic insecticides or miticides for acute, unmanageable outbreaks.
How does proper watering and fertilization impact pest control?
Proper watering and balanced nutrition promote strong, resilient tree growth, making lemon trees less appealing to pests and less vulnerable to disease transmission. Overwatering and excessive nitrogen should be avoided as they can attract pests or lead to root rot.
Can digital technology help with lemon tree pest management?
Absolutely. Platforms like Farmonaut provide satellite-driven crop health monitoring and AI-driven pest advisory, enabling precise, prompt intervention and more sustainable lemon orchard management.
Conclusion: Achieve Pest-Free Lemon Trees with Smart, Sustainable Strategies
Managing lemon tree pests is an ongoing process requiring vigilance, knowledge, and the right integrated approach. By combining regular inspection, cultural practices, biological controls, and—when needed—chemical interventions, we can maintain thriving citrus trees that reward us with bountiful fruit and vibrant growth.
Farmonaut’s advanced, precision agriculture solutions are designed to make crop health monitoring, pest detection, and resource management accessible and affordable worldwide. Whether you tend a single lemon tree or manage a commercial orchard, leveraging these insights and tools will empower you to make timely, informed decisions for healthy, productive citrus crops—naturally and sustainably.
Take charge of your lemon tree’s pest management with integrated methods, and enjoy the full beauty and bounty of your garden for years to come.