Organic Grape Protection: A Comprehensive Guide to Controlling Mite Infestations and Gall Pests on Vines
As advocates for sustainable agriculture, we at Farmonaut understand the challenges grape growers face when it comes to protecting their vines from pests, particularly mites and gall-causing organisms. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore organic and conventional methods for controlling these persistent pests, ensuring the health and productivity of your grape vines while maintaining environmental integrity.
Understanding Mites and Gall Pests in Grape Vineyards
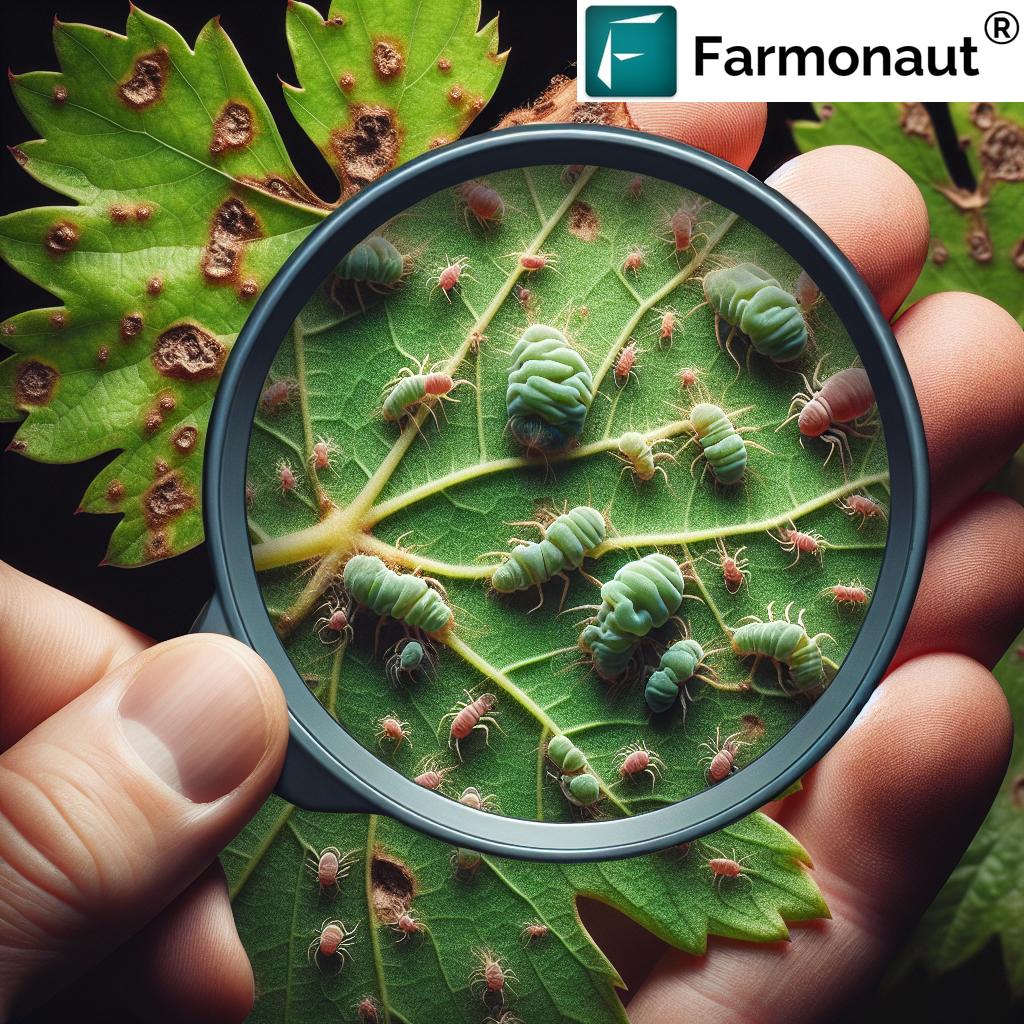
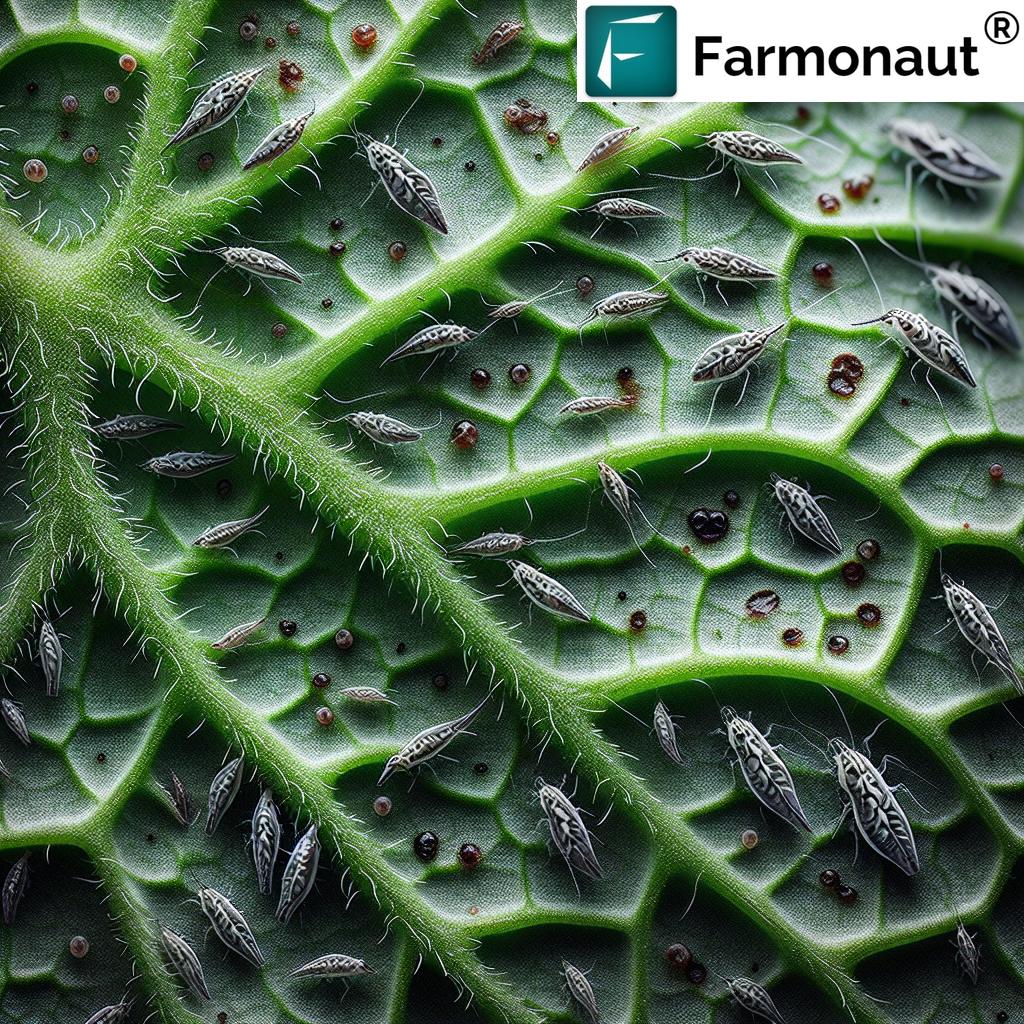
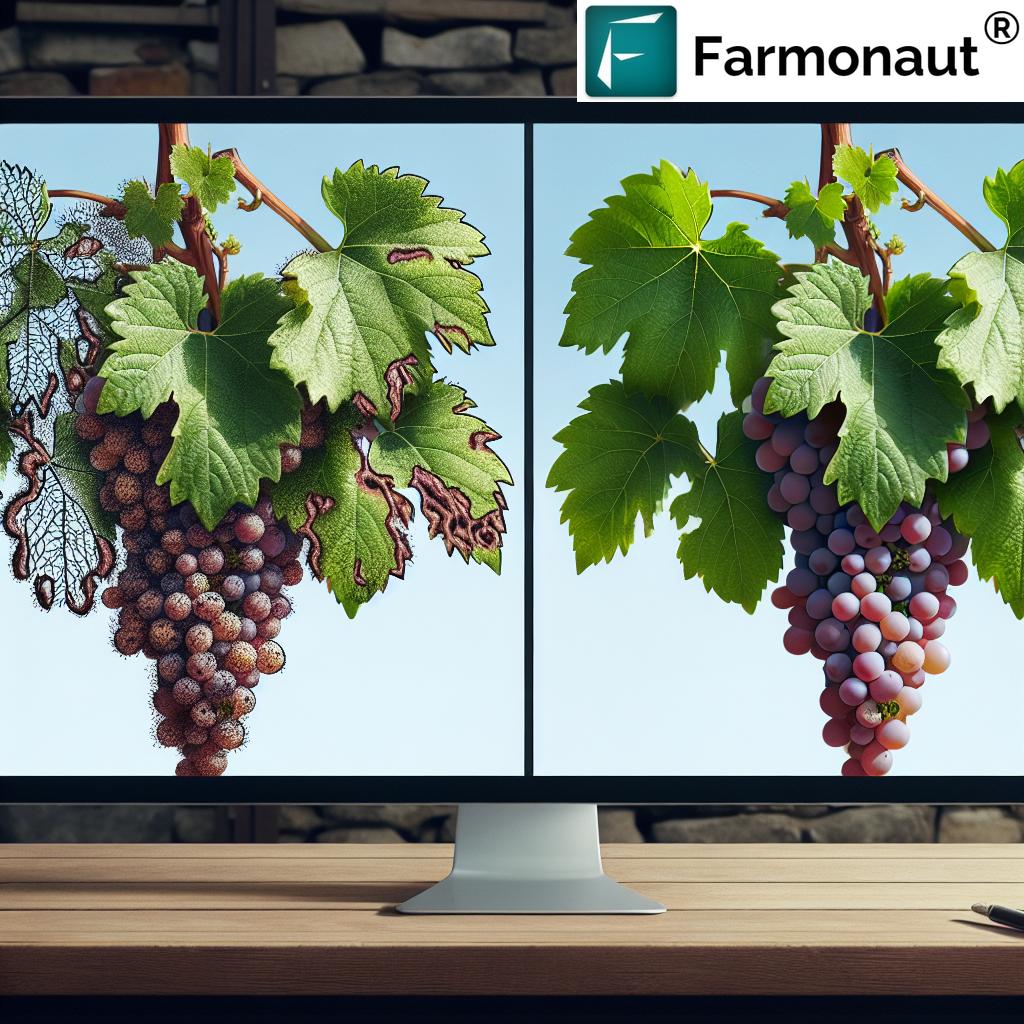
Before delving into treatment options, it’s crucial to understand the nature of mites and gall pests that commonly affect grape vines. These tiny yet destructive organisms can cause significant damage to leaves, stems, and buds, impacting both the vegetative growth and fruit production of your vines.
Common Mite Species Affecting Grapes
- Spider mites (Tetranychus urticae)
- European red mite (Panonychus ulmi)
- Rust mites (Calepitrimerus vitis)
- Blister mites (Colomerus vitis)
Gall-Causing Pests in Grape Vineyards
- Grape phylloxera (Daktulosphaira vitifoliae)
- Grape leaf gall midge (Janetiella oenophila)
- Grape tumid gallmaker (Janetiella brevicauda)
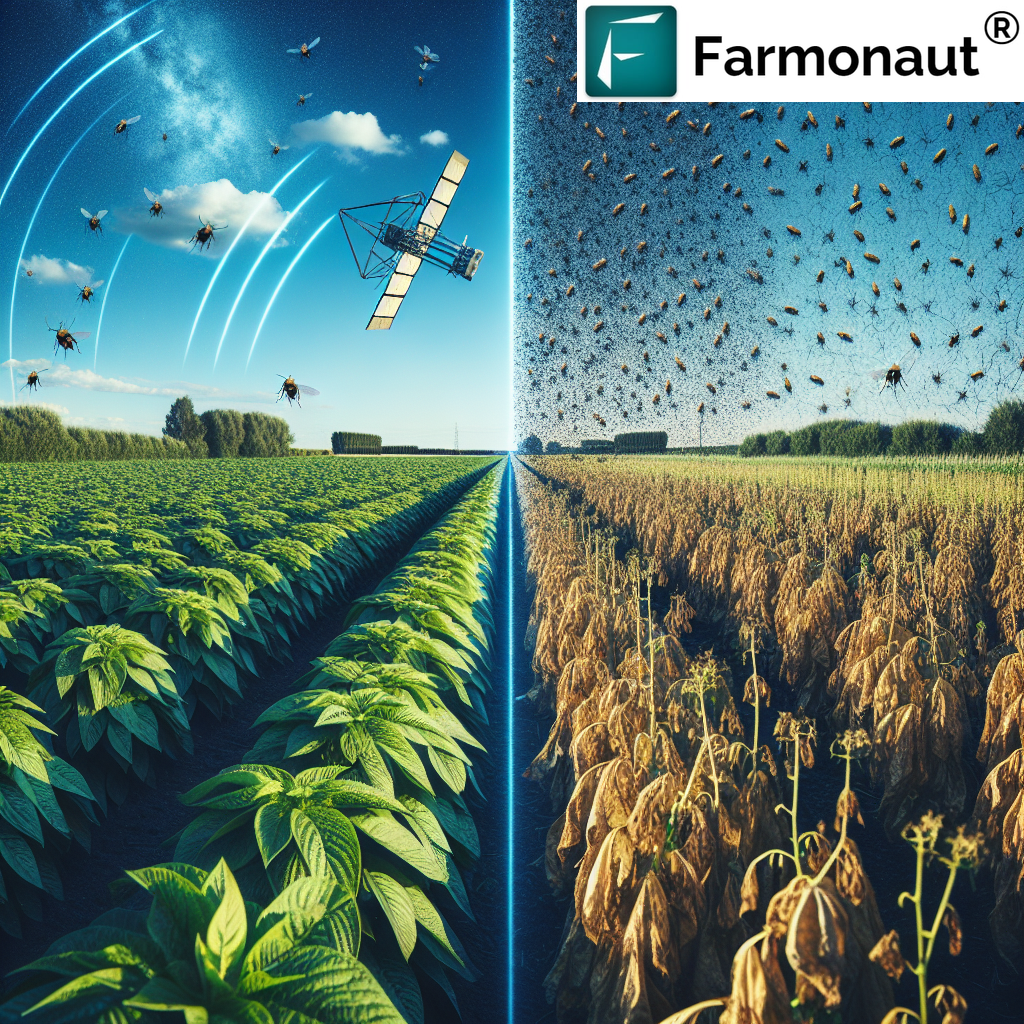
These pests can cause various types of damage, including:
- Leaf discoloration and stippling
- Reduced photosynthesis
- Defoliation
- Stunted growth
- Reduced fruit quality and yield
- Formation of galls on leaves, stems, and roots
Early Detection: The Key to Effective Pest Control
Identifying pest infestations early is crucial for implementing timely and effective control measures. At Farmonaut, we leverage advanced satellite technology to assist grape growers in early pest detection. Our satellite-based crop health monitoring system can detect subtle changes in plant health that may indicate the presence of mites or gall pests before visible damage occurs.
| Mite and Gall Pest Detection: Traditional vs. Farmonaut Satellite System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Aspect | Traditional Scouting | Farmonaut Satellite System |
| Efficiency | Time-consuming manual inspection | Rapid, automated analysis of entire vineyard |
| Accuracy | Subject to human error and oversight | High-precision spectral analysis for early detection |
| Coverage Area | Limited to accessible areas | Comprehensive coverage of entire vineyard |
| Early Detection | Often detects issues after visible damage occurs | Identifies potential infestations before visible symptoms appear |
| Data Analysis | Manual record-keeping and interpretation | AI-powered analysis with historical data comparison |
By utilizing our Farmonaut app, grape growers can access real-time data on their vineyard’s health, enabling them to take proactive measures against pest infestations.
Organic Treatment Options for Mite and Gall Pest Control
For those committed to organic grape production, there are several effective methods to control mites and gall pests without resorting to synthetic chemicals. These methods focus on enhancing the vineyard’s natural ecosystem and using organic products that are safe for both the environment and consumers.
1. Biological Control
Introducing and encouraging beneficial predators can significantly reduce mite and gall pest populations in your vineyard.
- Predatory Mites: Species like Phytoseiulus persimilis and Amblyseius californicus feed on pest mites, providing natural control.
- Ladybugs: These beneficial insects consume various pests, including mites and their eggs.
- Lacewings: Both adults and larvae feed on mites and other small pests.
- Predatory Thrips: Certain thrips species prey on pest mites and their eggs.
To encourage these beneficial organisms, we recommend:
- Planting diverse cover crops and flowering plants to provide habitat and alternative food sources
- Minimizing broad-spectrum pesticide use, which can harm beneficial insects
- Releasing commercially available predators strategically throughout the growing season
2. Cultural Practices
Implementing proper cultural practices can significantly reduce the likelihood of severe mite and gall pest infestations:
- Proper Pruning: Maintain open canopies to improve air circulation and reduce humidity, creating less favorable conditions for mites.
- Water Management: Avoid over-irrigation, as water-stressed plants are more susceptible to mite infestations.
- Sanitation: Remove and destroy infested plant material to prevent the spread of pests.
- Cover Cropping: Plant cover crops that repel pests or attract beneficial insects.
- Crop Rotation: Where possible, rotate grape varieties or implement fallow periods to disrupt pest life cycles.
3. Organic Sprays and Treatments
Several organic products can effectively control mites and gall pests when applied correctly:
- Neem Oil: A natural insecticide that disrupts pest feeding and reproduction.
- Sulfur: Effective against many mite species, but use cautiously as it can harm beneficial insects.
- Horticultural Oils: Smother and suffocate mites and their eggs.
- Insecticidal Soaps: Disrupt the cell membranes of soft-bodied pests like mites.
- Diatomaceous Earth: A fine powder that physically damages the exoskeletons of pests.
- Garlic and Chili Pepper Sprays: Natural repellents that can deter pests.
Application Tips:
- Always follow label instructions for organic products.
- Apply treatments during cooler parts of the day to minimize plant stress.
- Ensure thorough coverage, especially on the undersides of leaves where mites often reside.
- Rotate different organic treatments to prevent pest resistance.
Conventional Chemical Control Methods
While our focus is on organic methods, we recognize that some situations may require the use of conventional chemical treatments. These should be used judiciously and as part of an integrated pest management (IPM) approach.
Common Chemical Miticides and Acaricides
- Abamectin
- Bifenazate
- Etoxazole
- Fenpyroximate
- Spiromesifen
Important Considerations for Chemical Use:
- Always adhere to local regulations and product labels.
- Rotate chemical classes to prevent resistance development.
- Be mindful of pre-harvest intervals and potential impacts on beneficial organisms.
- Use targeted applications rather than broad-spectrum treatments when possible.
Monitoring and Prevention Strategies
Effective pest management begins with vigilant monitoring and preventive measures. Our Farmonaut satellite system plays a crucial role in this process, providing early warnings of potential infestations.
1. Regular Scouting
While our satellite technology offers comprehensive coverage, it’s still important to conduct regular visual inspections:
- Examine leaves, stems, and buds for signs of mite damage or gall formation.
- Use a hand lens to look for mites and eggs on the undersides of leaves.
- Keep detailed records of pest populations and locations within the vineyard.
2. Weather Monitoring
Mite populations often surge during hot, dry conditions. Our Farmonaut Satellite Weather API provides accurate, localized weather data to help you anticipate potential pest outbreaks.
3. Stress Reduction
Healthy vines are more resistant to pest infestations. Minimize plant stress by:
- Ensuring proper irrigation and nutrition
- Protecting vines from environmental extremes
- Addressing other pest or disease issues promptly
4. Winter Management
Many mite species overwinter on grape vines. Implement these strategies during the dormant season:
- Apply dormant oils to smother overwintering mites and eggs
- Prune and destroy infested canes
- Clean up leaf litter and other debris that may harbor pests
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for Long-term Control
At Farmonaut, we advocate for an integrated approach to pest management that combines various control methods for sustainable, long-term results.
Key Components of an Effective IPM Strategy:
- Prevention: Implement cultural practices that discourage pest establishment.
- Monitoring: Utilize our satellite technology and regular scouting to track pest populations.
- Thresholds: Establish action thresholds based on pest levels and potential economic impact.
- Multiple Control Methods: Combine biological, cultural, and chemical (if necessary) control methods.
- Evaluation: Continuously assess the effectiveness of your IPM strategy and adjust as needed.
By leveraging our Android and iOS apps, grape growers can easily integrate satellite data into their IPM strategies, making informed decisions about when and how to intervene against mite and gall pest infestations.
The Role of Technology in Modern Pest Management
As we continue to face challenges in grape production, including climate change and evolving pest pressures, technology plays an increasingly vital role in effective pest management.
Satellite-Based Monitoring
Our Farmonaut satellite system offers several advantages for pest detection and management:
- Early detection of stress patterns that may indicate pest activity
- Comprehensive coverage of large vineyard areas
- Historical data analysis to identify trends and recurring problem areas
- Integration with other farm management tools for holistic decision-making
AI-Powered Pest Identification
We’re continuously developing our AI capabilities to assist in pest identification and treatment recommendations. By analyzing satellite imagery and ground-level data, our system can:
- Distinguish between different types of pest damage
- Predict potential outbreaks based on historical patterns and current conditions
- Suggest targeted treatment options based on pest type and infestation severity
Precision Application Technologies
While not directly offered by Farmonaut, we support the integration of our data with precision application technologies:
- Variable-rate sprayers that adjust application based on pest pressure detected by our satellite system
- Drone-based spot treatments for localized infestations
- Smart traps that use AI to identify and count pest species, integrating with our data platform
Case Studies: Successful Mite and Gall Pest Management
While we don’t provide specific case studies, we can share general observations from our work with grape growers worldwide:
- Vineyards implementing IPM strategies supported by our satellite technology have reported up to 40% reduction in pest-related crop losses.
- Organic growers using our early detection system have successfully managed mite populations with timely releases of predatory insects, reducing the need for organic sprays by up to 60%.
- Conventional growers have optimized their chemical applications, reducing overall pesticide use by 30% while maintaining effective pest control.
Future Directions in Grape Pest Management
As we look to the future, several promising developments are on the horizon for managing mites and gall pests in grape vineyards:
1. Advanced Genetic Resistance
Researchers are working on developing grape varieties with enhanced natural resistance to mites and gall-forming pests. These varieties could significantly reduce the need for interventions while maintaining high-quality fruit production.
2. Pheromone Disruption Techniques
While currently more effective against insect pests, ongoing research is exploring the potential of pheromone-based disruption methods for mite control, which could offer a highly targeted and environmentally friendly approach.
3. Microbiome Management
Understanding and manipulating the vineyard microbiome may provide new avenues for pest control. Beneficial microorganisms could be introduced to enhance plant resistance or directly antagonize pest populations.
4. Nanotechnology in Pest Control
Nanoparticles are being studied for their potential in delivering pest control agents more effectively and with less environmental impact. This could lead to more precise and efficient treatment options.
5. Climate-Adaptive Strategies
As climate change affects pest populations and vine susceptibility, we’re working on predictive models that integrate climate data with pest life cycles to help growers adapt their management strategies proactively.
Conclusion
Effective management of mites and gall pests in grape vineyards requires a multifaceted approach that balances organic and conventional methods, leverages advanced technology, and adapts to changing environmental conditions. By combining time-tested cultural practices with cutting-edge solutions like our Farmonaut satellite monitoring system, grape growers can protect their vines, ensure healthy growth, and produce high-quality fruit while minimizing environmental impact.
We encourage growers to explore the full potential of our satellite-based crop health monitoring system and integrate it into their pest management strategies. By staying informed, adaptive, and proactive, we can work together to overcome the challenges posed by mites and gall pests in grape production.
FAQs
- Q: How often should I scout my vineyard for mites and gall pests?
A: We recommend weekly scouting during the growing season, with more frequent checks during hot, dry periods when mite populations tend to increase rapidly. - Q: Can organic methods effectively control severe mite infestations?
A: Yes, when implemented proactively and consistently, organic methods can effectively manage even severe infestations. However, it may take longer to see results compared to conventional chemical treatments. - Q: How does Farmonaut’s satellite system detect mite infestations?
A: Our system analyzes spectral data from satellite imagery to detect subtle changes in plant health that may indicate pest stress before visible symptoms appear. - Q: Are there any grape varieties that are naturally resistant to mites and gall pests?
A: While no grape variety is completely immune, some show higher tolerance. Consult with local agricultural extensions for varieties that perform well in your region. - Q: How can I integrate Farmonaut’s technology with my existing pest management practices?
A: Our system is designed to complement existing practices. Use our app to monitor overall vineyard health, set alerts for potential issues, and inform your scouting and treatment decisions.
For more information on how Farmonaut can support your vineyard management efforts, please visit our developer documentation or contact our support team.