Tractor Farming Techniques: Best & Poor Methods 2025
Introduction: Tractor Farming in 2025
The world of tractor farming techniques is undergoing a revolutionary transformation in 2025. The rapid integration of smart machinery, automation, and data-driven systems is marking a new era in agriculture worldwide. These advancements are not only enhancing productivity but are also pivotal for sustainability—addressing the dual challenges of feeding a growing population and maintaining environmental health.
Tractors, once limited to traditional plowing and tilling, are now equipped with electronic guidance, GPS precision, real-time sensors, and automated controls. This evolution is moving farming beyond labor-heavy tasks and individual guesswork towards a landscape where data, science, and practical experience converge.
The Evolution of Tractor Farming Techniques
The concept of using tractors in agriculture stretches back over a century, but the last decade has seen unprecedented advancements. Today, the integration of precision tools, smart sensors, eco-friendly fertilizers and pesticides, and real-time monitoring have enabled farmers to make highly informed management decisions.
From Traditional to High-Tech
- Traditional plowing and tilling techniques—labor-intensive, fuel-consuming, and often causing soil compaction and erosion.
- Modern tractors use GPS, automated steering, and AI-based sensors to reduce input costs and maximize efficiency.
- Innovative farming methods now emphasize resilient agricultural systems by combining mechanized efficiency with sound ecological practices.
Modern Tractor Farming Techniques: The Best Practices for 2025
Modern tractor farming techniques are designed to blend high output with sustainability. Let’s delve into the features that are setting apart the best practices in 2025:
1. Precision Agriculture with GPS & Sensor Integration
- GPS-Guided Systems: Tractors equipped with automated steering deliver seed, fertilizer, and pesticides with unmatched accuracy, significantly lowering input costs.
- Real-Time Soil Monitoring: Advanced sensors monitor soil moisture, fertility, and organic matter—optimizing irrigation, fertilizer application, and reducing wastage.
- AI-Based Analysis: Data collected from sensors feeds into AI models, providing actionable insights for field operations, and improving efficiency and yield.
2. Reduced Tillage & Conservation Practices
- Minimal soil disturbance: Reduced tillage methods maintain soil structure, decrease erosion, and preserve beneficial organisms.
- Cover cropping and residue management: Retain moisture, boost organic matter, and shield against nutrient depletion.
3. Autonomous & Electric Tractors
- Autonomous operation: Tractors use AI and machine learning for unmanned fieldwork—reducing labor dependency.
- Electric-powered tractors: Reduce fuel consumption, emissions, and operational costs while supporting eco-conscious farming goals.
4. Data-Driven Crop Management
- AI & Remote Sensing: Real-time crop health monitoring and yield prediction based on satellite and drone data.
- Resource Traceability: Blockchain-based traceability creates transparency in crop and input usage, helping manage food safety and sustainability.
For those seeking to further automate and streamline farm operations, our Fleet Management tools facilitate efficient oversight of farm vehicles and equipment—optimizing usage, reducing downtime, and lowering operational costs.
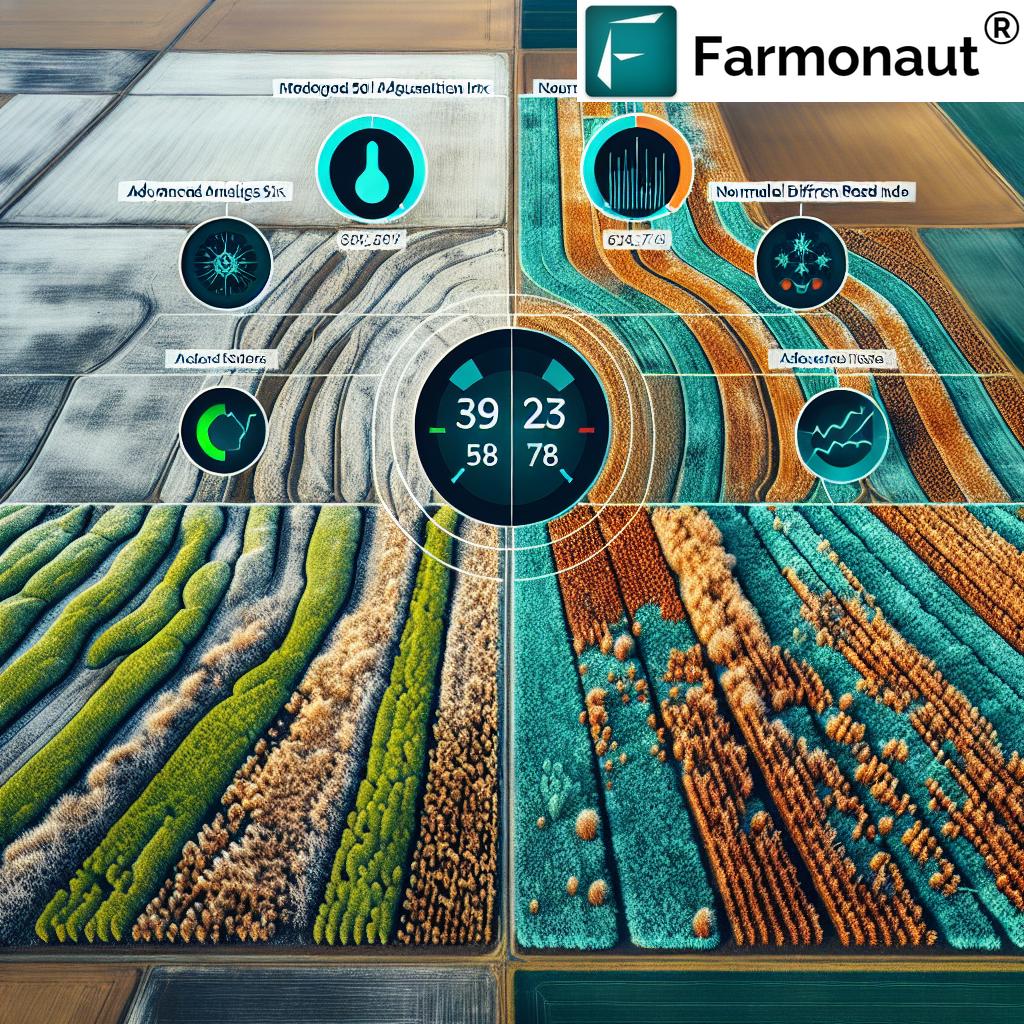
Comparative Features Table: Best vs Poor Tractor Farming Techniques (2025)
The comparison below highlights the transformative potential of modern techniques versus outdated methods in tractor-based farming. This visual guide illustrates core benefits, sustainability metrics, and practical impacts relevant for 2025 and beyond.
| Technique Type | Description | Estimated Efficiency (%) | Fuel Consumption (L/ha) | Environmental Impact | Suitability for Apples/Forestry | Expected Yield Improvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision Farming with GPS | Automated steering, sensor-based input application, and real-time monitoring. | 85-95 | 9-11 | Low | Yes | 15-22 |
| Autonomous Tractors | Self-driving tractors using AI and robotics for unmanned field operations. | 90-98 | 6-10 (or electric equivalent) | Low | Yes | 20-27 |
| Conventional Plowing | Manual or basic mechanized plowing for seedbed preparation; heavy soil inversion. | 55-65 | 14-18 | High | Limited | 2-6 |
| Traditional Tilling | Frequent, deep soil tillage operations with outdated machinery. | 50-62 | 18-22 | High | No | -5 to 0 (may decrease yield due to soil degradation) |
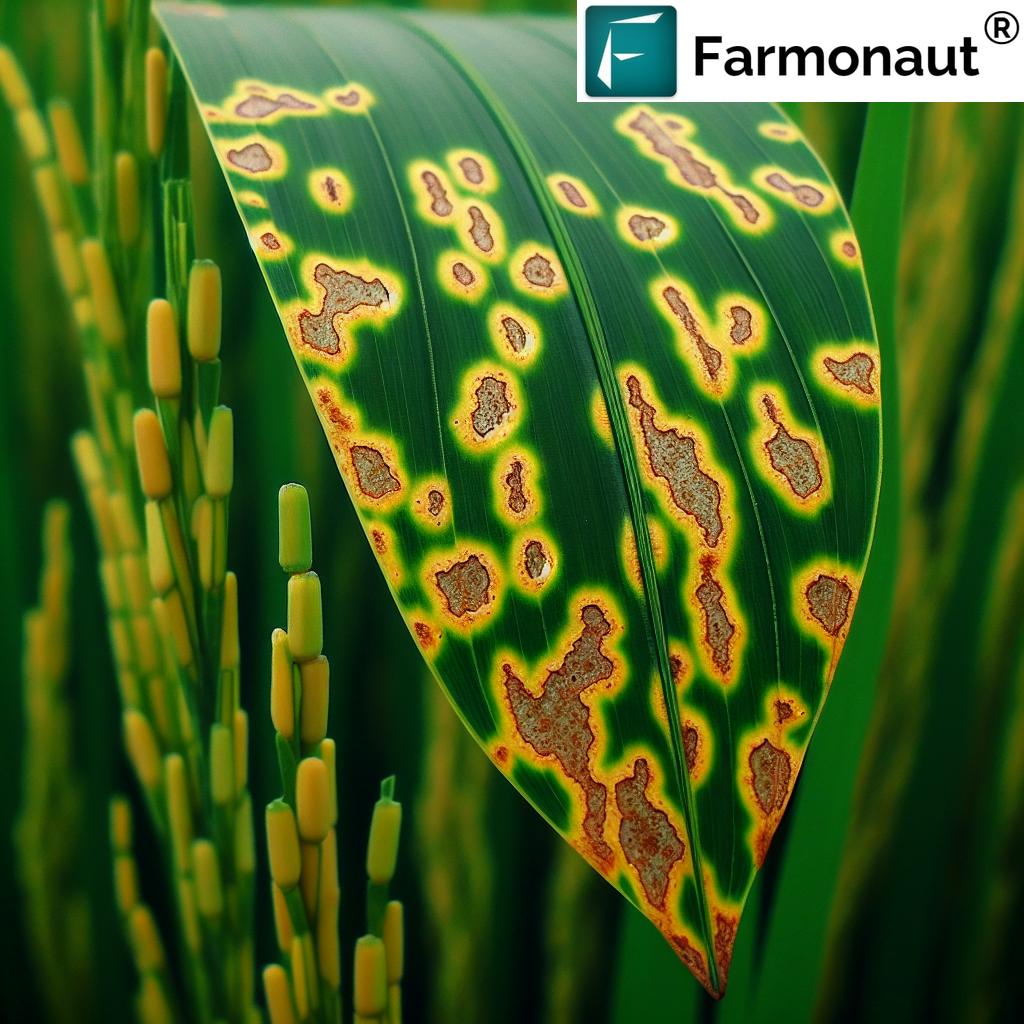
Poor Tractor Farming Techniques: Outdated Methods to Avoid
Not all farming methods keep pace with technological advancements. Several poor tractor farming techniques continue to threaten agricultural output and environmental health, particularly in regions where education and infrastructure support lag behind.
Key Outdated Methods
- Excessive tillage: Deep, repeated tilling disrupts soil structure, lowers fertility, and accelerates erosion.
- Monoculture without rotation: Growing the same crops year after year depletes nutrients and leads to higher dependency on synthetic fertilizers.
- Poor input management: Overuse of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides increases costs and pollutes water bodies.
- Inefficient equipment: Outdated machinery increases fuel consumption and cannot perform precise tasks required for modern crops like apples or forestry plantations.
The contrast is clear: while best tractor farming techniques conserve resources, minimize environmental impact, and foster resilience, poor practices threaten the viability of agriculture in the face of climate variability.
Good Farming Techniques for Enhanced Productivity & Sustainability
The agricultural landscape of 2025 demands good farming techniques that not only focus on productivity but also sustainability and resilience:
Core Principles of Good Farming Techniques
- Crop rotation: Alternating legumes with cereal crops like wheat or corn naturally replenishes nitrogen and reduces disease cycles, lowering the need for synthetic nutrients.
- Cover cropping: Planting cover crops (such as clover or vetch) prevents soil erosion, improves organic matter content, and enhances moisture retention in dry spells.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Using beneficial insects, biological treatments, and targeted pesticide use for effective pest management while minimizing environmental impact.
- Soil health monitoring: Utilizing sensors and AI models, like those available via Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting solutions, enables farmers to track and reduce their environmental impact for regulatory compliance and long-term soil fertility.
- Water management: Precision irrigation systems, informed by real-time data, save water and ensure uniform rations across fields.
The Role of Technology
Modern tractors and Farmonaut-powered platforms ensure that these good practices are measurable, traceable, and scalable thanks to satellite monitoring and AI-driven analytics. This leads to cost effective and sustainable agriculture systems that can withstand market and climate fluctuations.
Innovations in Apple Farming Techniques
Apple farming techniques are being redefined by the adoption of high-efficiency systems uniquely suited to orchards. With 2025 technologies, the focus is on quality, yield, and environmental stewardship.
High-Efficiency Orchard Management
- Trellis and Dwarf Rootstock Systems: Support high-density plantings and improved light penetration, leading to better fruit quality and easier mechanized harvesting.
- Precision Irrigation: IoT sensors and AI models monitor soil moisture and apply water exactly as needed, reducing water usage and promoting optimal fruit sizing.
- Targeted Nutrient Delivery: Microdosing based on real-time soil nutrient data optimizes fertilizer application and lowers costs.
- Integrated Pest Management for Apples: Use of pheromone traps, beneficial insects, and targeted organic sprays to manage major apple pests with minimal chemical input.
- Blockchain Traceability: Enhance food safety and premium market access with product traceability for apples—from orchard to shelf.
Our Farmonaut solutions further strengthen apple farming by providing NDVI-driven orchard health monitoring and remote advisory for improved input management.
Forestry Techniques: Mechanized Precision for Sustainable Timber
Forestry techniques have made leaps in both productivity and ecological soundness—particularly as new tools allow precise, large-scale tracking and management of forest plantations.
Cutting-Edge Methods in Forestry
- Precision Forestry: Drones and satellites monitor forest health, assess carbon sequestration, and guide resource allocation—enabling selective logging and replanting.
- AI-Based Timber Management: Data-driven systems calculate optimal harvest time for timber, ensuring high yields while minimizing ecosystem disruption.
- Sustainable Site Preparation: Mechanized tractors prepare land for reforestation with minimal disturbance, boosting seedling survival and overall forest cover.
- Automated Tree Detection & Mapping: Platforms like Farmonaut provide advanced tools for automated tree counting and spatial mapping, simplifying timber inventory and compliance.
- Water Conservation: Integrating moisture sensors and AI forecasting ensures optimal irrigation in plantation forestry, reducing water consumption and fostering resilient systems even in dry spells.
Forestry operations can further benefit from Farmonaut’s crop plantation and forest advisory tools, accessible via web and mobile app (click here to get started), which support everything from growth monitoring to targeted intervention.
Leveraging Satellite Innovation: How Farmonaut Empowers Precision Farming
As satellite technology disrupts agriculture, Farmonaut makes advanced solutions accessible to all. By providing cost-effective, real-time monitoring, AI-based advisory, and blockchain traceability, we empower farmers, orchard managers, and foresters to make data-driven decisions.
Key Farmonaut Features for 2025:
- Satellite-Based Monitoring: Access multispectral imagery to evaluate soil health, vegetation index, and irrigation needs—perfect for precision farming techniques.
- AI Advisory (Jeevn): Receive customized, actionable recommendations for operational improvements.
- Blockchain Traceability: Instantly validate the movement and state of products and inputs, meeting market and regulatory standards.
- Resource Management: Track machinery, plan logistics, and cut costs through optimized fleet use (learn about fleet management).
- Environmental Impact Tracking: Monitor emission levels, carbon footprint, and compliance, supporting the shift to regenerative farming systems (see carbon tracking tools).
For developers and agribusinesses, our Farmonaut API and developer documentation enable seamless data integration.
Those managing large holdings can benefit from Agro Admin App, allowing multi-farm monitoring, resource allocation, and regulatory compliance—all from one dashboard.
Future Prospects: Resilient Agriculture & Forestry in 2025 & Beyond
By 2025, the convergence of tractor farming techniques, sound agronomic practices, and digital transformation is creating agriculture that is not just productive, but sustainable, transparent and resilient to climate change and market volatility.
What’s Next?
- Ultra-automation: Next-generation tractors will be fully autonomous, requiring minimal labor inputs even on vast farms and rugged terrain.
- Connected Systems: IoT smart devices, drones and on-field robots will form integrated networks for seamless data sharing.
- Widespread Adoption of Traceability: With growing consumer and regulatory demand, transparent traceability systems will be the new normal in high-value crops and forestry products.
- Climate Adaptation: Integrated forecasting models and adaptive management tools will ensure that farming and forestry techniques withstand increasingly erratic weather patterns.
Those who embrace these innovations will be best placed for productivity, profitability, and environmental sustainability in the years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary advantages of using modern tractor farming techniques in 2025?
Modern tractor farming techniques, especially with GPS and AI integration, increase efficiency, reduce input and labor costs, minimize fuel consumption, and support sustainability with lower environmental impacts. They also provide data-driven management for better yield and soil health.
How do poor tractor farming techniques impact production and the environment?
Poor tractor farming techniques—like excessive tillage, monoculture, and overuse of synthetic inputs—lead to degraded soil structure, increased erosion, higher production costs, reduced yield, and significant environmental pollution.
How can I integrate satellite monitoring and precision agriculture into my farming?
Using platforms such as Farmonaut, you can access real-time crop monitoring, AI-based advisory, and blockchain traceability for efficient and sustainable farm management. Start by registering through their web or mobile app.
Are these techniques suitable for small and medium-sized farms?
Absolutely. Farmonaut’s solutions and modern precision agriculture tools are scalable and cost-effective, making them accessible to small, medium, and large farm operations.
What future innovations should farmers expect beyond 2025?
Look forward to further automation (autonomous tractors and robots), even smarter sensor networks, wider adoption of blockchain traceability, and highly adaptive, real-time management in response to climate changes and market trends.
Farmonaut Subscription Pricing
Farmonaut offers a flexible, subscription-based pricing model to make satellite, AI, and blockchain-powered solutions accessible for all sizes of farms, forestry, and agricultural businesses. Benefit from real-time monitoring, remote advisory, and operational analytics designed to enhance your productivity and sustainability.
Conclusion: Tractor Farming Techniques in a Sustainable Era
As we look to 2025 and beyond, the synergy between modern tractor farming techniques, sustainable practices, and digital innovation is transforming the future of agriculture and forestry. By adopting best practices and leveraging solutions from providers like Farmonaut, farmers and producers are positioned to boost productivity, lower costs, and champion environmental stewardship in a rapidly changing world.