Viticulture Secrets: 7 Hacks for Sustainable Vineyards
Summary: The Cornerstone of Modern Viticulture
Viticulture, at its core, is more than just grape cultivation—it is an interplay between nature, science, and artistry. As a cornerstone of agriculture and wine production, particularly across the temperate regions of the world, its success relies on understanding and optimizing numerous factors. Climate, soil, site selection, and evolving vineyard management practices are crucial. Today, we must also embrace sustainable viticulture and digital solutions to maintain environmental balance and achieve consistently high wine quality.
In this comprehensive post, let us explore the secrets behind thriving, eco-conscious vineyards. We’ll delve into climate impact on wine quality, the puzzle of soil composition in vineyards, strategies for grape vine irrigation, the role of terroir, and the power of precision viticulture technology in ensuring our vines stay healthy and productive.
Climate and Terroir: Shaping Grape Quality
Climate defines the potential of every vineyard. Most of the world’s finest wines emerge from vineyards located between the 30° and 50° latitudes in each hemisphere. These regions offer temperate climates—and an annual mean temperature of 10°C to 22°C—which is critical for ideal grape growth. The presence of large bodies of water, like lakes and rivers, as well as nearby mountain ranges, can positively moderate day-night temperature swings. At night, stored heat in water bodies is gently released, reducing drastic temperature drops that can stress the vines.
Terroir is the French term for the unique blend of soil, climate, and topography that shapes a vineyard’s output. The terroir imparts distinctive characteristics—aroma, structure, even color—to grapes and, consequently, the wines produced. Preserving terroir is crucial for maintaining wine identity and authenticity.
- Key takeaway: Understanding climate impact on wine quality and terroir and grape quality is essential for every viticulturist aiming for excellence.
Soil Composition in Vineyards & Site Selection
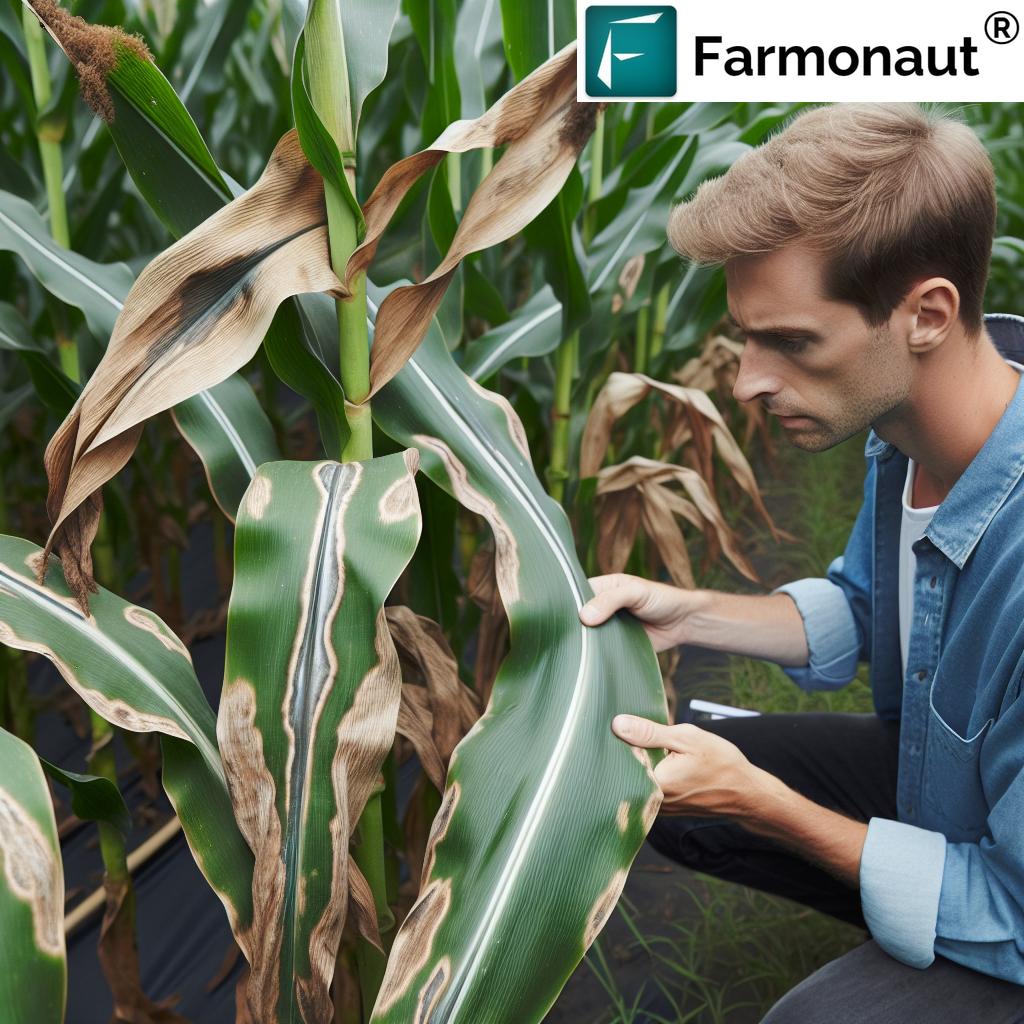
The soil beneath our feet is as vital as the vines above. Top-performing vineyards carefully consider soil composition and overall site selection. The best soils for viticulture are well-drained, aerated, and only moderately fertile. Excessive fertility triggers too much vine growth, risking unbalanced grape development and diluted wine quality.
Sloping sites, often elevated above their surroundings, help minimize frost risk and ensure strong air flow—critical in disease prevention. In cooler zones, south-facing slopes maximize sunlight exposure, while north-facing slopes help reduce excessive heat in warm regions.
- Effective vineyard site selection aligns topography, soil structure, and exposure to sunlight for more healthy grape vines and balanced wine characteristics.
Key Vineyard Management Practices for Sustainable Success
Excellence in viticulture is rooted in smart vineyard management practices. We marry traditional knowledge with innovations and data-driven technology. Controlling growth, managing disease risk, and optimizing resource use are essential elements of sustainable vineyard management.
Essential Practices Include:
- Pruning: Annual or seasonal pruning of our vines regulates their growth, improves air flow, and ensures better grape quality by managing sunlight exposure and reducing disease risk.
- Canopy Management: Carefully adjusting leaf density and shoot positioning helps achieve balanced sunlight and air circulation, driving even ripening and disease prevention.
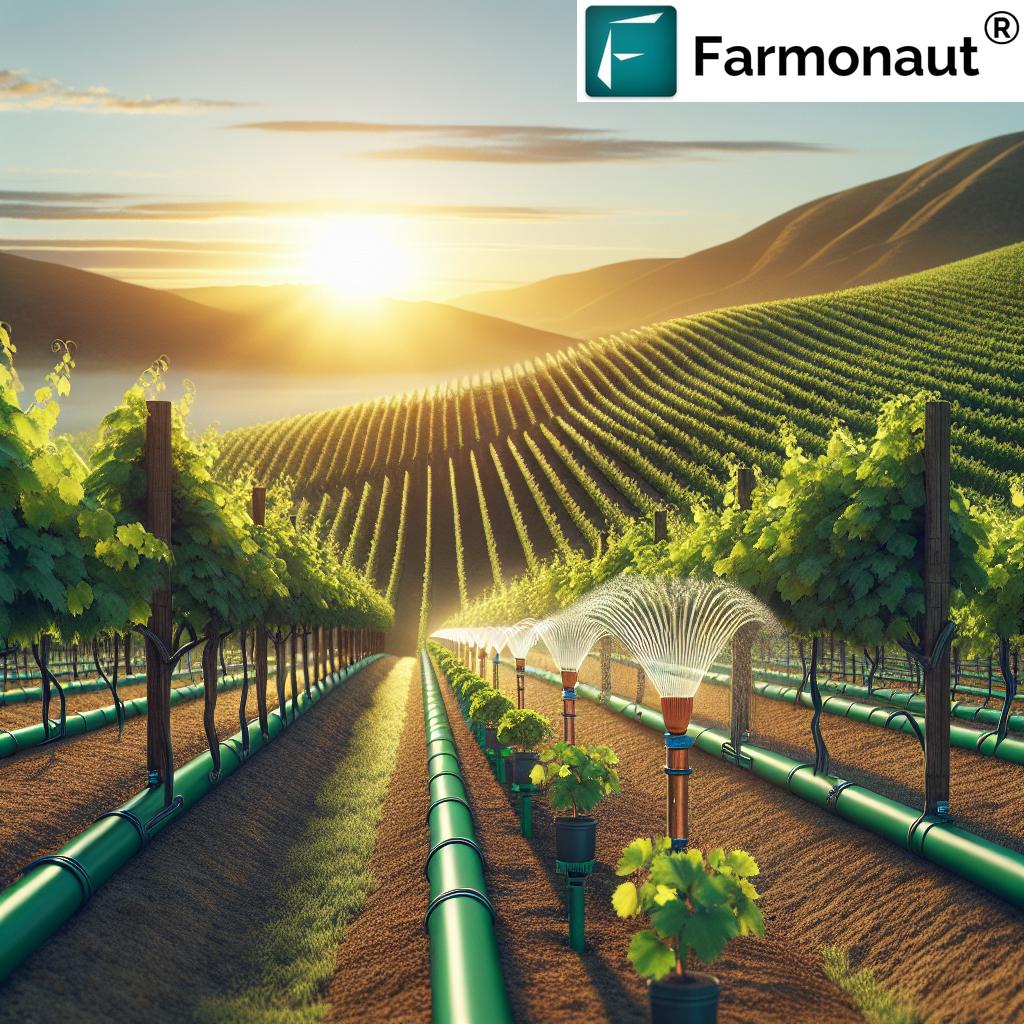
- Irrigation: Implementing efficient grape vine irrigation techniques like drip irrigation ensures our grape vines receive adequate water without wastage—crucial for quality in both dry and humid regions.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Employing IPM keeps pests at bay using sustainable approaches, reducing chemical reliance and promoting overall ecosystem health.
- Soil Health Monitoring: Regularly assessing soil structure, nutrients, and microbiology is vital for balanced vine growth and top-tier wine production.
Viticulture Secrets: 7 Hacks for Sustainable Vineyards
Let’s unlock the power of sustainable viticulture. These seven vineyard management hacks will protect our environment, boost yield and grape quality, and ensure our vines thrive despite evolving challenges.
-
1. Precision Irrigation for Maximum Water Conservation
Water scarcity and climate variability have made smart irrigation an absolute necessity. By implementing drip irrigation and soil moisture sensors, we deliver water directly to roots—conserving up to 40% more water than traditional surface or overhead methods. Precision irrigation enables:
- Efficient grape vine irrigation tailored to real-time needs
- Reduced risk of disease from overwatering or standing water
- Better wine quality and more consistent fruit development
Modern satellite monitoring platforms, like those from Farmonaut, support real-time soil moisture tracking and resource optimization for all vineyard scales.
Discover large-scale vineyard management with Farmonaut’s precision monitoring tools →
-
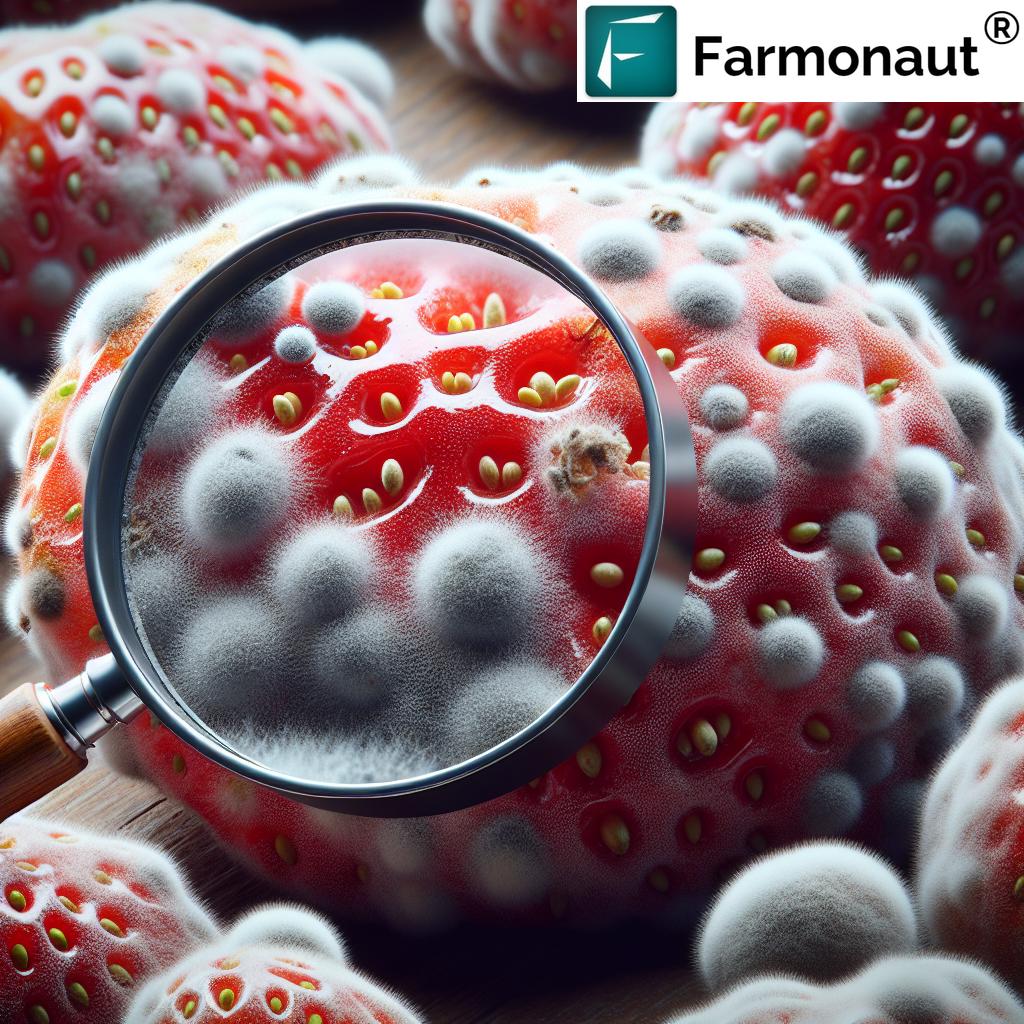
2. Organic & Integrated Pest Management in Vineyards
Protecting our vines from pests and diseases—from powdery mildew to phylloxera—is essential for consistent grape production. With IPM, we combine biological control, cultural strategies, and selective use of chemicals to contain pests while reducing environmental harm:
- Beneficial insects (e.g., ladybugs, parasitoids)
- Organic sprays and ecological habitat management
- Real-time pest pressure monitoring via digital tools
Farmonaut’s AI-advisory system empowers proactive integrated pest management in vineyards by predicting outbreaks and providing science-backed action steps.
Optimize pest control with smart fleet management solutions →
-
3. Cover Cropping and Biodiversity Enhancement
Planting robust cover crops between vineyard rows offers a myriad of environmental and agronomic benefits, including:
- Soil conservation by reducing erosion on slopes
- Suppression of weeds and support for beneficial insects
- Increase in organic matter, improving soil structure and water-holding capacity
Strategic use of native flowers and grasses protects our terroir and amplifies the unique qualities of our wines.
-
4. Vineyard Canopy Management for Sunlight and Airflow
The canopy is like a shield for the fruit—but too much or too little leaf cover can lead to issues. Meticulous canopy management ensures:
- Balanced exposure to sunlight for even sugar and phenolic ripening
- Reduction of fungal disease risk, especially mildew
- Improved grape quality and flavor intensity
Fine-tuning must suit each variety, region, and vintage—precision is key!
-
5. Soil Health Improvement for Robust Vines
Consistent investment in soil health is foundational to successful viticulture. Methods include:
- Applying composts or green manures
- Minimal tillage to preserve structure and reduce carbon loss
- Regular soil microbiome testing
Monitoring tools provided by Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting system help us track the environmental and productivity gains of these practices.
Healthy, living soil supports stronger, less disease-prone grapevines. -
6. Smart Vineyard Pruning & Training Techniques
Systematic pruning and vine training have a direct impact on grape production, vine health, and disease prevention. Benefits include:
- Improved air and sunlight penetration
- Controlled and balanced yield
- Reduction in pest and disease habitats
Digital farm management apps, such as Farmonaut, help log pruning dates and visualize long-term growth impacts on production via time-lapse records.
Try smart vineyard monitoring for pruning and training guidance →
-
7. Embracing Precision Viticulture Technology
The future of viticulture lies in harnessing precision technology for targeted, data-driven actions. This includes:
- Satellite-based crop health monitoring to identify variability in grape vine health
- AI advisory systems for farm-specific recommendations
- Blockchain traceability to guarantee wine authenticity
Explore how blockchain-based traceability enhances vineyard product trust →
Access Farmonaut API for satellite and weather monitoring in your own vineyard app →
Explore Farmonaut API developer docs →
Comparison Table of Sustainable Practices vs. Traditional Methods
| Practice/Technique | Sustainable Method (Description) | Traditional Method (Description) | Impact on Yield (%) | Water Savings (%) | Environmental Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision Irrigation | Drip system, soil moisture sensors, water scheduling | Flooding, overhead sprinklers, fixed schedules | Up to +10% More uniform quality |
Up to 40% saved | Reduces run-off and salinity, conserves water |
| Organic & Integrated Pest Management | Biological controls, IPM, organic sprays | Broad-spectrum chemical pesticides | +5–10% avg. | N/A | Less chemical residue, preserves beneficial insects |
| Cover Cropping | Native plants, legume covers, insect habitat | Bare soil, herbicide usage | Stable/increase | 10–20% (via better retention) | Prevents erosion, boosts soil biodiversity |
| Canopy Management | Strategic leaf thinning, shoot positioning | Minimal canopy adjustment | +10–15% higher quality | N/A | Less disease, better grape ripeness |
| Soil Health Improvement | Composting, reduced tillage, microbiome inputs | Deep tillage, heavy fertilizer | +5–15% over time | 5–10% | Enhanced soil life, sequesters carbon |
| Smart Pruning & Training | Timed, data-driven cutting, disease prevention | Calendar-based, generic cutting | +10–20% consistency | N/A | Healthier vines, lower disease risk |
| Precision Technology | Satellite monitoring, AI advisories, blockchain traceability | Manual observation, paper records | Up to +15% (less loss, higher value) | Varies with application | Data-driven, transparent, reduces resource wastage |
Farmonaut: Digital Farming for Precision Viticulture
The era of precision viticulture technology is here—and Farmonaut is empowering grape growers to harness the power of satellites, AI, and blockchain without breaking the bank. Our platform delivers robust, actionable insights on crop health, soil moisture, and resource management directly to your fingertips, on Android, iOS, or web.
Main Features for Vineyards:
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Evaluate NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) for rapidly detecting stress or variability in your vineyards.
- Soil Moisture Insight: Plan irrigation more efficiently using real-time soil moisture data.
- AI-Based Advisory: Personalized, instant guidance for disease, pest management, and seasonal activities.
- Blockchain Traceability: Secure every bottle’s journey from vine to table, building trust with consumers and regulators.
- Resource & Fleet Management: Streamline labor and input allocation—lowering costs without sacrificing quality.
- Carbon Footprinting: Quantify and minimize your vineyard’s environmental impact with carbon tracking dashboard.
Ready to experience next-generation vineyard management tools?
Launch the Farmonaut App for Desktop or Mobile →
Learn how to optimize large vineyard plantations →
Challenges & Innovations in Vineyard Management
Major Challenges Facing Sustainable Viticulture
- Climate Change: Shifting weather, rising temperatures, and erratic rainfall patterns are rewriting growth and harvest calendars. Adaptation requires selecting heat-tolerant varieties and using technology for real-time crop health monitoring.
- Pest and Disease Pressure: Pests, fungi (mildew), and emerging pathogens require IPM strategies—monitoring, biocontrols, and resistant vines.
- Water Management: Water conservation in grape cultivation is paramount in drought-prone regions. Deficit irrigation, soil moisture analytics, and rainwater harvesting all play a role.
- Labor & Economic Pressures: Digitizing records and automating monitoring with platforms like Farmonaut reduce dependence on manual labor for optimal vineyard management.
Cutting-edge Innovations
- Remote Sensing & Satellites: Real-time health mapping pinpoints emerging issues and tailors field actions, boosting efficiency.
- Blockchain Traceability: Authenticate every bottle’s origin and journey with Farmonaut’s traceability systems, enhancing transparency from vineyard to consumer.
- AI and Machine Learning: Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI analyzes input data—satellite, local sensors, and weather—for bespoke suggestions on irrigation, pest control, and yield optimization.
- API Integration: Advanced users and agribusinesses can incorporate Farmonaut’s satellite/weather API to power proprietary management solutions.
Keeping up with these innovations is vital for maintaining vineyard health, protecting resources, and delivering stunning wine quality in the modern era.
FAQ: Sustainable Viticulture, Practices, and Technology
What is viticulture?
Viticulture refers to the cultivation of grape vines primarily for wine production, but also for table grapes and other products. It encompasses all activities from site selection and planting to harvest and vineyard management.
How do climate and terroir affect wine quality?
Climate impact on wine quality is profound—temperatures, rainfall, and seasonal patterns define grape ripening, acidity, and flavor. Terroir blends climate, soil composition, and topography to impart unique characteristics to grapes and the wines produced.
What are the top water-saving grape vine irrigation techniques?
Drip irrigation and the use of soil moisture sensors are the most effective. These systems deliver adequate water directly to the roots, reducing wastage and disease, and helping conserve resources—vital for sustainable viticulture.
How can we practice sustainable vineyard management?
Sustainable vineyard management includes cover cropping, integrated pest management (IPM), smart irrigation, renewable energy use, and adopting precision technology. Balancing yield, quality, and ecological health is key.
Why is precision technology important in modern vineyards?
Precision technology empowers us with real-time data on plant health, water status, and pest risk, enabling data-driven decisions. Platforms like Farmonaut make these capabilities accessible, increasing productivity, sustainability, and transparency in vineyard management.
Can Farmonaut help with regulatory compliance and product transparency?
Yes, Farmonaut’s traceability solution secures your supply chain with blockchain, ensuring accurate reporting and product verification from vineyard to bottle.
How do sustainable practices improve wine quality and yield?
By promoting healthy soils, conserving water, reducing chemical inputs, and optimizing grape maturity, these methods increase both the yield and distinctiveness of wines. Improved biodiversity also enhances natural plant resilience—leading to more consistent production and vibrant flavors.
Conclusion: Growing the Future of Wine
As caretakers of the land and architects of celebrated wines, our commitment to sustainable viticulture ensures a bright, resilient path forward for agriculture. By understanding the influence of climate, nurturing vibrant soil ecosystems, and embracing powerful precision technology—like those offered by Farmonaut—we can create vineyards that produce world-class wines while respecting environmental boundaries.
The journey requires ongoing learning, and Farmonaut will remain a vital ally as we navigate the dynamic range of viticultural challenges and opportunities across all global regions.