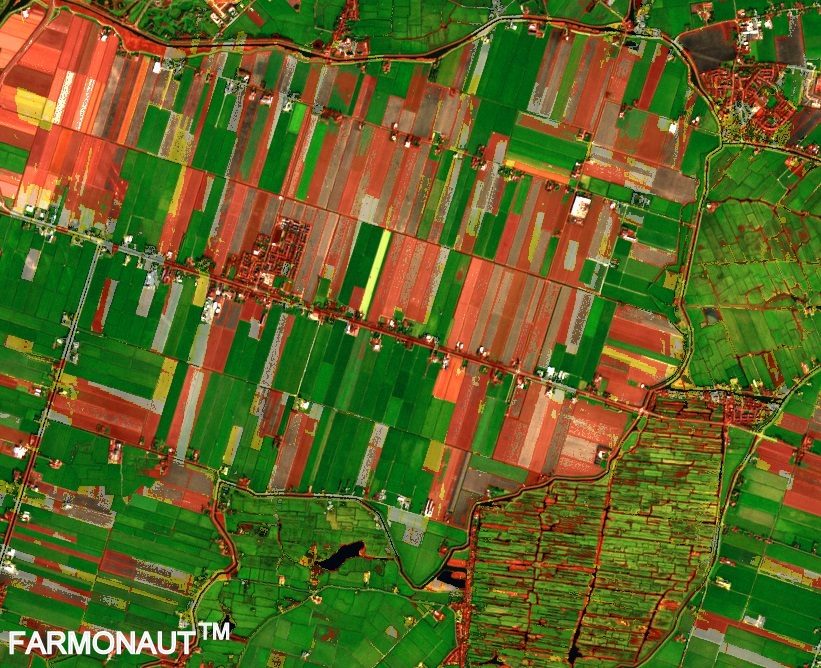
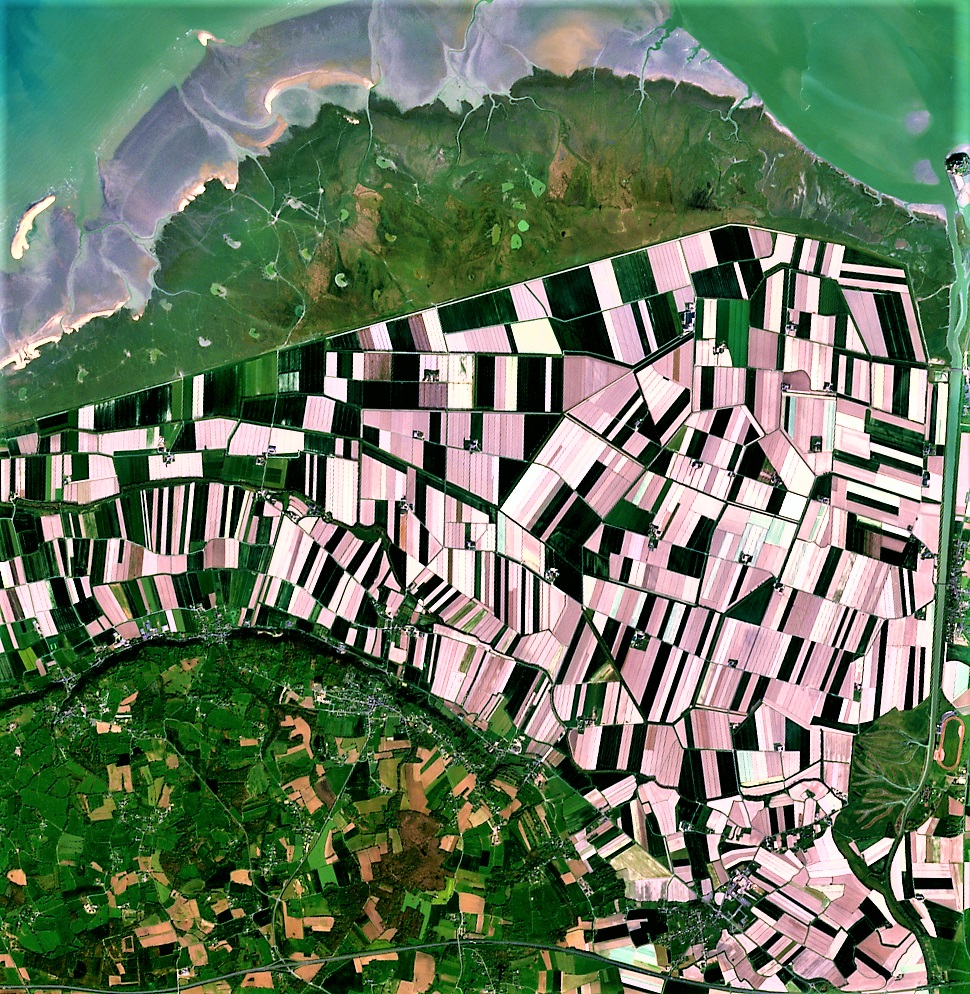
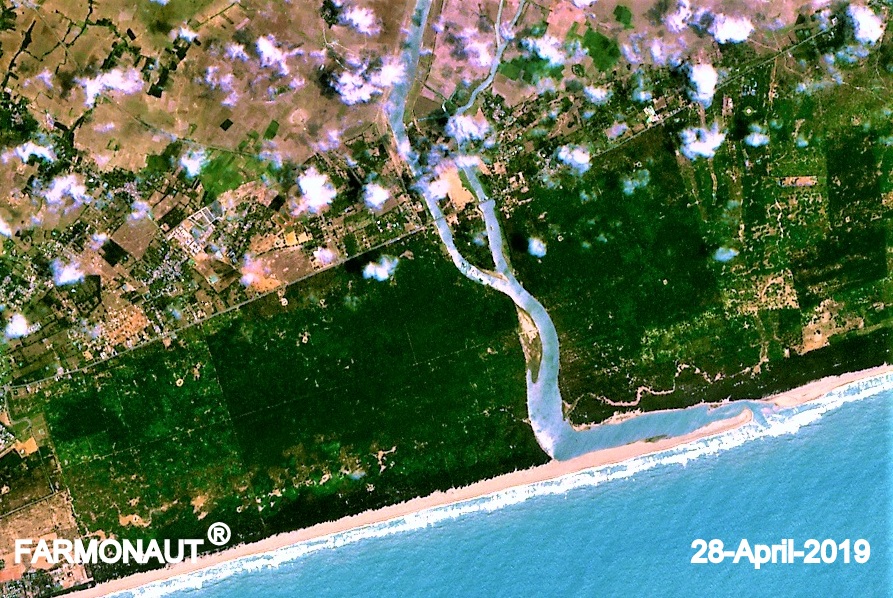
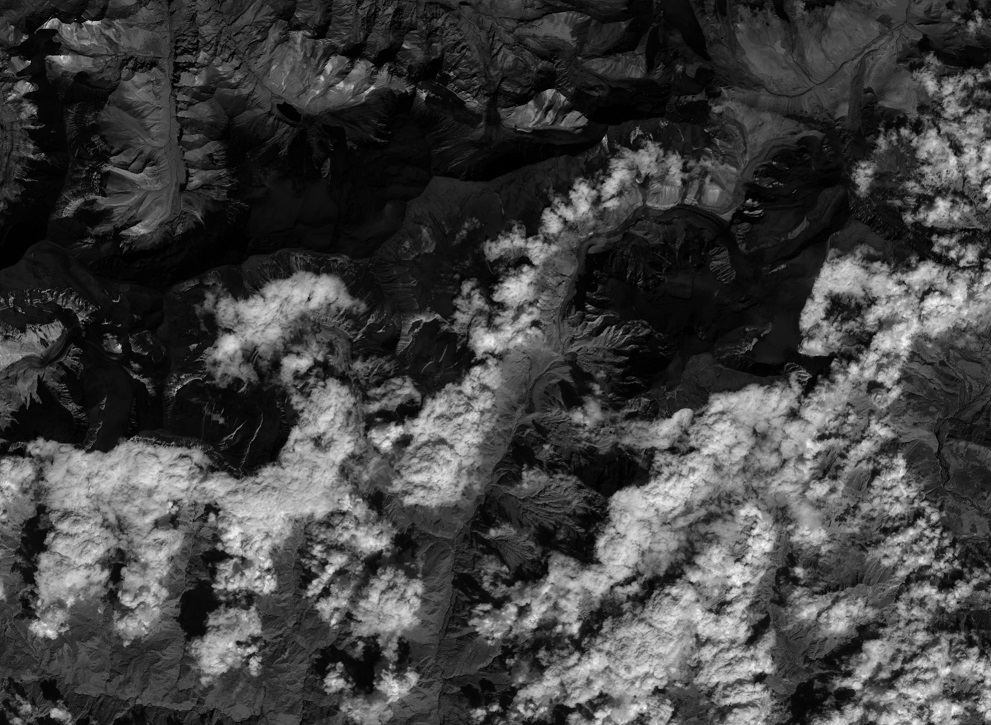
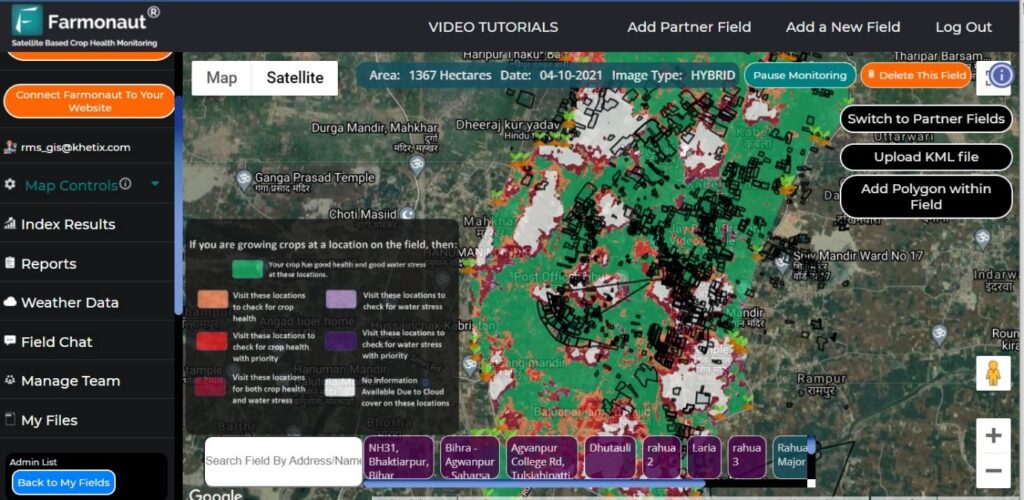
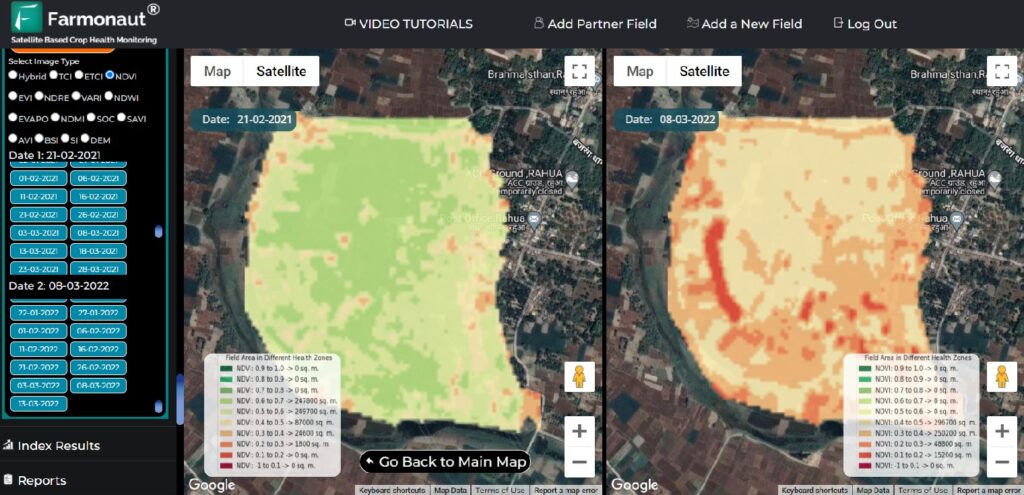
Land Classification in India: A Comprehensive Guide to Land Use Categories and Management

In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the intricate world of land classification in India, delving into its significance, categories, and management strategies. As experts in remote sensing and agricultural technology, we at Farmonaut understand the crucial role that proper land classification plays in sustainable development and efficient resource management.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Land Classification in India
- The Importance of Land Use Classification
- Major Categories of Land Classification in India
- Land Use Classification Systems in India
- Challenges in Land Classification
- Modern Technologies in Land Classification
- Farmonaut’s Role in Land Classification and Management
- Future Trends in Land Classification
- FAQs
1. Introduction to Land Classification in India
Land classification in India is a complex and multifaceted process that involves categorizing land based on its characteristics, uses, and potential. This system is crucial for effective land management, urban planning, agricultural development, and environmental conservation.
The classification of land in India has evolved over time, influenced by historical, cultural, and economic factors. Today, it incorporates modern scientific methodologies and technologies to provide a more accurate and detailed understanding of the country’s diverse landscape.
2. The Importance of Land Use Classification
Land use classification in India serves several critical purposes:
- Resource Management: It helps in the efficient allocation and use of land resources.
- Urban Planning: Guides the development of cities and towns.
- Agricultural Planning: Assists in identifying suitable areas for different types of crops.
- Environmental Conservation: Helps in protecting ecologically sensitive areas.
- Policy Formulation: Informs government policies on land use and development.
At Farmonaut, we recognize the significance of accurate land classification in optimizing agricultural practices. Our satellite-based crop health monitoring system utilizes this information to provide tailored insights to farmers and agribusinesses.
3. Major Categories of Land Classification in India
The classification of land in India is broadly divided into several categories:
3.1 Forest Land
Forest land includes areas with significant tree cover, whether natural or planted. It plays a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance and biodiversity.
3.2 Agricultural Land
This category encompasses land used for cultivation, including:
- Net sown area
- Current fallow land
- Other fallow land
3.3 Pastures and Grazing Land
These are areas used for livestock grazing and include both permanent pastures and meadows.
3.4 Land Under Miscellaneous Tree Crops
This category includes land under tree crops not classified as forests, such as orchards and plantations.
3.5 Culturable Waste Land
Land that is potentially suitable for cultivation but is currently not being used due to various reasons.
3.6 Fallow Land
Agricultural land that is temporarily not under cultivation.
3.7 Current Fallow
Cropland left uncultivated during the current agricultural year.
3.8 Other Fallow Land
Land left fallow for more than one agricultural year but less than five years.
3.9 Barren and Uncultivable Land
Land that cannot be brought under cultivation due to topography, climate, or soil conditions.
3.10 Land Put to Non-Agricultural Uses
This includes land used for settlements, industries, roads, railways, and other infrastructure.
4. Land Use Classification Systems in India
Several systems are used for land use classification in India:
4.1 Nine-Fold Classification
This is the most commonly used system, categorizing land into nine broad classes:
- Forests
- Area under non-agricultural uses
- Barren and uncultivable land
- Permanent pastures and other grazing lands
- Land under miscellaneous tree crops and groves
- Culturable wasteland
- Fallow lands other than current fallows
- Current fallows
- Net area sown
4.2 LULC Classification
The Land Use and Land Cover (LULC) classification is a more detailed system that includes:
- Built-up land
- Agricultural land
- Forest
- Wastelands
- Water bodies
- Others
4.3 NRSC Classification
The National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC) uses a hierarchical classification system with three levels:
- Level I: Broad land use/land cover classes
- Level II: Sub-classes of Level I
- Level III: Further sub-division of Level II classes
5. Challenges in Land Classification
Despite advancements in technology, several challenges persist in land classification in India:
- Dynamic Nature of Land Use: Rapid changes in land use patterns due to urbanization and development.
- Data Accuracy: Ensuring the accuracy and timeliness of land use data.
- Technological Limitations: Access to advanced remote sensing technologies in all regions.
- Diverse Landscape: India’s varied geography makes uniform classification challenging.
- Policy Implementation: Ensuring that land use policies are effectively implemented at the ground level.
6. Modern Technologies in Land Classification
At Farmonaut, we leverage cutting-edge technologies to enhance land classification and management:
6.1 Remote Sensing
Satellite imagery provides high-resolution data for accurate land classification. Our satellite-based crop health monitoring system utilizes this technology to offer real-time insights into agricultural lands.
6.2 Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
GIS tools help in analyzing and visualizing land use patterns, aiding in better decision-making for land management.
6.3 Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
These technologies enable automated classification of land use types from satellite imagery, improving accuracy and efficiency.
6.4 Blockchain Technology
Farmonaut’s blockchain-based traceability solutions ensure transparency in land use records and transactions.
7. Farmonaut’s Role in Land Classification and Management
At Farmonaut, we play a crucial role in enhancing land classification and management through our advanced technologies:
- Satellite-Based Monitoring: Our platform provides real-time data on crop health, soil moisture, and other critical metrics, aiding in precise land use classification and management.
- AI-Driven Insights: The Jeevn AI Advisory System offers personalized recommendations for land management based on satellite data and other inputs.
- Blockchain Traceability: Our blockchain solutions ensure transparent and secure recording of land use changes and transactions.
- Resource Optimization: Tools for fleet and resource management help in efficient utilization of agricultural lands.
- Sustainability Tracking: Carbon footprint monitoring aids in sustainable land management practices.
To experience the benefits of our advanced land management solutions, visit Farmonaut App or explore our API services.
Comparison: Farmonaut Satellite System vs. Drone and IoT-based Farm Monitoring
| Feature | Farmonaut Satellite System | Drone-based Monitoring | IoT-based Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage Area | Large scale (Global) | Limited (Local) | Limited (Local) |
| Data Collection Frequency | High (Daily updates) | Moderate | High |
| Initial Setup Cost | Low | High | Moderate to High |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Regular | Regular |
| Weather Dependency | Low | High | Moderate |
| Data Processing | Automated (AI-driven) | Semi-automated | Automated |
| Scalability | Highly Scalable | Limited Scalability | Moderate Scalability |
8. Future Trends in Land Classification
As we look to the future, several trends are shaping the landscape of land classification in India:
- Integration of Big Data: Combining multiple data sources for more comprehensive land classification.
- 3D Mapping: Incorporating elevation data for more accurate classification of urban and mountainous areas.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Continuous updating of land use data through advanced satellite technologies.
- Participatory Mapping: Involving local communities in the land classification process for more accurate and contextual data.
- Climate Change Adaptation: Incorporating climate change models into land use planning and classification.
At Farmonaut, we are at the forefront of these trends, continuously evolving our technologies to provide the most accurate and useful land classification and management solutions.
9. FAQs
Q1: What is the primary purpose of land classification in India?
A1: The primary purpose of land classification in India is to categorize land based on its characteristics and uses, aiding in efficient resource management, urban planning, agricultural development, and environmental conservation.
Q2: How does Farmonaut contribute to land classification and management?
A2: Farmonaut contributes through its satellite-based crop health monitoring system, AI-driven insights, blockchain traceability solutions, and resource optimization tools, providing comprehensive data for accurate land classification and efficient management.
Q3: What are the major categories in the classification of land in India?
A3: The major categories include forest land, agricultural land, pastures and grazing land, land under miscellaneous tree crops, culturable waste land, fallow land, barren and uncultivable land, and land put to non-agricultural uses.
Q4: How does satellite technology improve land use classification in India?
A4: Satellite technology provides high-resolution, real-time data on land cover, allowing for more accurate and up-to-date classification. It enables monitoring of large areas efficiently and helps in detecting changes in land use over time.
Q5: What challenges are faced in land classification in India?
A5: Challenges include the dynamic nature of land use, ensuring data accuracy, technological limitations in some regions, India’s diverse landscape making uniform classification difficult, and effective implementation of land use policies.
To learn more about how Farmonaut can assist in land classification and management, visit our website or download our app:
For developers interested in integrating our satellite and weather data into their systems, check out our API documentation.
Subscribe to Farmonaut Services
In conclusion, land classification in India is a vital process that underpins sustainable development and efficient resource management. As technology continues to evolve, the accuracy and utility of land classification systems will only improve, leading to better decision-making in urban planning, agriculture, and environmental conservation. At Farmonaut, we are committed to leveraging cutting-edge technologies to support this crucial aspect of land management, contributing to a more sustainable and productive future for India’s diverse landscape.