Agriculture Drought Stress: Arizona Crop Drought 2025 – Challenges, Impacts & Sustainable Solutions
“Arizona’s 2025 drought threatens over 60% of its croplands, risking state-wide food supply stability.”
Agriculture Drought Stress: Arizona’s 2025 Outlook
Agriculture drought stress, often termed as crop drought, represents one of the most significant challenges facing Arizona’s agricultural sector in 2025. As the arizona drought 2025 continues, water scarcity, rising temperatures, and diminishing groundwater reserves have deeply impacted crop production, posing a threat to the livelihoods of farmers and the stability of the broader food supply chain in the region.
Understanding the nature and implications of drought stress is crucial for strategizing more resilient farming practices in a climate marked by increasing unpredictability. In this blog, we explore the scientific foundations of drought stress in agriculture, its transformative effects on crop health and output, and the most promising adaptive solutions emerging across Arizona in 2025 and beyond.
The Nature and Causes of Crop Drought in Arizona
In agricultural terms, drought refers to the condition where water scarcity limits crop growth and productivity. For Arizona in 2025, this is not merely a seasonal phenomenon—it is a prolonged, severe event resulting from a combination of environmental factors:
- Rising temperatures: With Arizona’s average temperatures increasing over the past decade, crops now undergo more water loss through evapotranspiration resulting in reduced soil moisture.
- Declining snowpack: The snowpack in surrounding mountain ranges feeds rivers and groundwater reserves that are vital during dry months. In 2025, snowpack levels have diminished significantly, reducing water inflow to agricultural regions.
- Reduced rainfall: The current drought is characterized by scarce rainfall and erratic precipitation patterns, delaying the recharge of critical water stores.
- Over-draft of groundwater: Increased water demand for agriculture and urban use, coupled with inadequate replenishment, has led to rapidly declining groundwater levels—a trend that continues in 2025.
These conditions have converged to create one of the most severe drought episodes in recent memory, affecting soil, plants, and the entire farming sector statewide.
How Drought Stress Affects Crop Health and Productivity
Agriculture drought stress manifests when crops do not receive adequate water, disrupting key physiological processes required for optimal growth and yields. Here’s how it negatively impacts agriculture in Arizona:
- Photosynthesis is hindered: Water limitations reduce chlorophyll production, stalling photosynthesis, the key process where plants convert sunlight to energy.
- Nutrient uptake and cell expansion: Crops need moisture to absorb soil nutrients and for cell expansion. Without sufficient water, cellular growth is stunted.
- Wilting and delayed flowering: Crops wilt and flowering is delayed, resulting in poor fruit development and fewer seeds, directly affecting yield stability.
- Poor soil health: Dry soils can become compacted and more prone to erosion, reducing fertility and making it harder for roots to grow.
- Susceptibility to pests and diseases: Stressed plants are more susceptible to pests and diseases, which compounds losses.
The combined effects often lead to reduced yields, stunted plant growth, and—in severe cases—crop failure. These shifts not only affect individual farms, but also pose systemic risks for Arizona’s broader agricultural output and food supply chain.
Arizona Crops Most Vulnerable to Drought Stress
Arizona’s key crops—such as cotton, alfalfa, wheat, and lettuce—form the backbone of the region’s agricultural production. In 2025, these crops are particularly vulnerable due to:
- High water needs: Crops like alfalfa and wheat require considerable irrigation. When soil moisture declines, their productivity limits become evident.
- Growth cycle dependence on regular water: Lettuce and many fruits & vegetables need consistent water for optimal development, and stress during flowering or fruit set severely limits yields.
- Exposure to intense heat: Crops are increasingly exposed to rising temperatures and heatwaves that exacerbate evaporation and demand for water.
Estimates for 2025 indicate that over 60% of croplands are at risk due to prolonged drought episodes. More than 70% of farmers report experiencing yield reductions and quality losses on a scale not seen in recent memory.
“Over 70% of Arizona farmers report crop yield losses due to severe drought stress in 2025.”
Effects of Drought Stress on Nutritional Quality, Market Value, & Food Supply Chain
The impacts of agriculture drought stress and crop drought aren’t limited to quantities produced; they extend to the nutritional quality, taste, and market value of Arizona produce.
- Nutrient and carbohydrate reduction: Drought often reduces carbohydrate accumulation and disrupts nutrient balance within plants, diminishing the nutritional content and taste of fruits and vegetables.
- Poor shelf life: Produce from drought-stressed crops tends to have a shorter shelf life and a lower market value.
- Pest and disease susceptibility: These plants are more susceptible to pests and diseases, further threatening yield stability and quality.
- Food price increases: Reduced output and quality put upward pressure on food prices and increased volatility in the supply chain.
This cascade of reduced productivity, lower nutritional value, and supply chain stress radiates throughout Arizona’s economy, rural communities, and even international export markets.
How Farmers & Managers Are Adapting to Crop Drought Stress in Arizona 2025
In the face of these pressing concerns, Arizona farmers and agricultural managers are pioneering adaptive strategies to mitigate drought impacts and ensure sustainable food production:
-
Precision irrigation: Methods such as drip irrigation and sensor-based soil moisture monitoring have become increasingly adopted. These approaches deliver water directly to the root zone, reducing waste and conserving limited supplies.
- Shifts in crop selection: Increasingly, drought-tolerant varieties are being chosen. Crop rotations and changes in planting schedules aim to align key growth phases with periods of higher water availability.
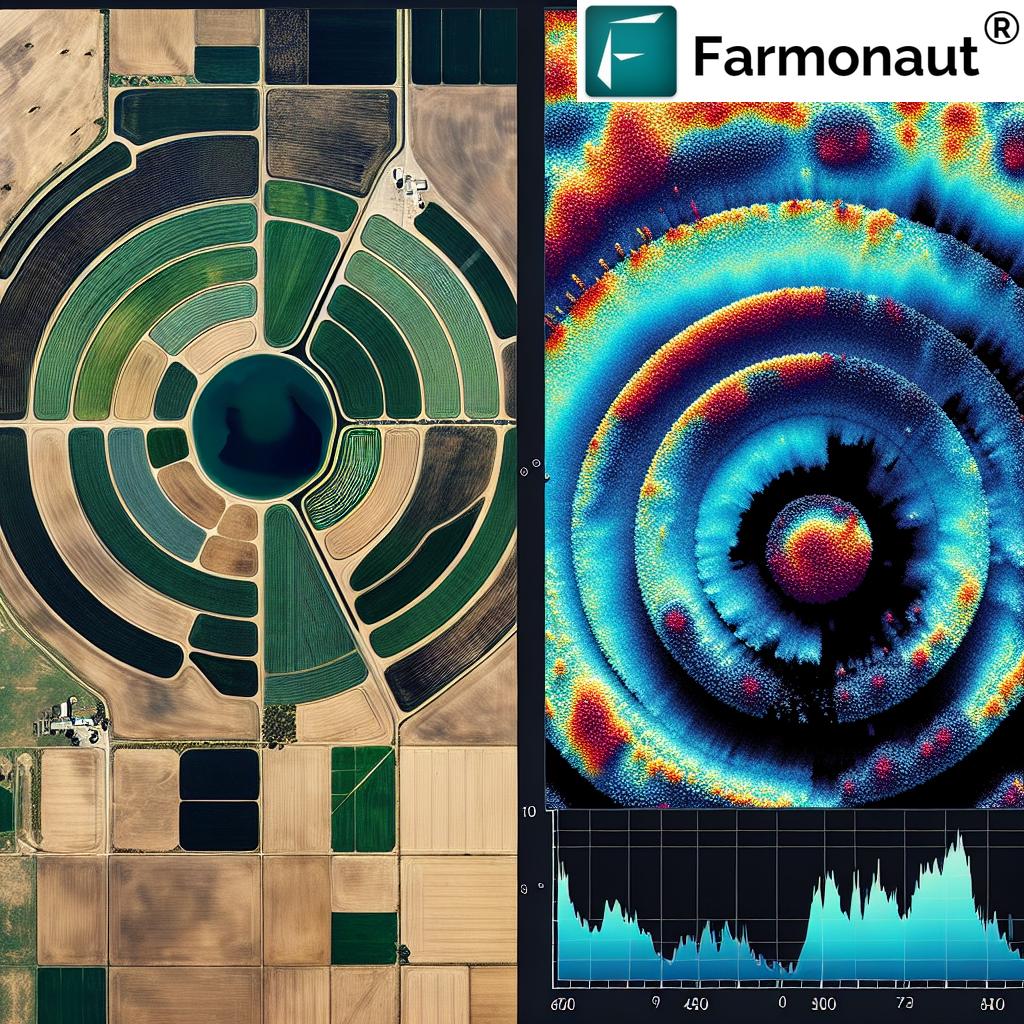
- Real-time data and remote sensing: Platforms like Farmonaut provide affordable, satellite-driven insights into crop health, soil moisture conditions, and irrigation needs—empowering smarter decision-making for farms of any scale.
- Resource prioritization: In many cases, farmers prioritize high-value or profit-critical crops for irrigation and other drought mitigation efforts.
These adaptive practices, while essential, represent just one axis of a much broader, systemic response to crop drought in Arizona.
Adaptive Agricultural Practices & the Farmonaut Advantage
As agriculture drought stress becomes a permanent feature of Arizona’s climate, moving toward a more resilient & sustainable agricultural system is imperative.
-
Satellite Monitoring & AI: Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring provides real-time, multispectral imagery to assess crop health, soil moisture, and resource management. These insights empower farmers to deployment irrigation, fertilization, and pest controls only where needed—helping mitigate stress and reduce inputs.
- Jeevn AI Advisory: Using real-time climate and satellite data, AI-based platforms like Jeevn AI deliver timely advisories, optimize irrigation schedules, and guide responses to emerging drought stress, improving both short-term output and long-term farming resilience.
- Blockchain Traceability for Food Security: Farmonaut’s blockchain-powered traceability ensures transparent supply chains, increasing consumer trust and minimizing fraud during periods of supply volatility.
- Fleet & Resource Management: With automated fleet tracking and resource management tools, farms can optimize the use of machinery, reduce costs, and lower emissions even when operational hours or routes increase during drought mitigation responses.
- Carbon Footprinting & Sustainability: Advanced solutions like carbon footprint tracking help monitor environmental impact, fostering adoption of sustainable practices and compliance with regulatory changes in agriculture.
- Insurance & Financial Access: For financial institutions and farmers, satellite-based loan and insurance verification supports risk reduction and ensures that support reaches those actually impacted by drought.
All these practices are critical for building both immediate responses to drought and long-term, systemic resilience.
Systemic Water Management: Policy Shifts & Integrated Responses
Arizona’s 2025 drought underscores the urgency of a multi-level water management response:
- Integrated Water Resource Management: This involves cooperation between farmers, water districts, and state agencies to develop long-term strategies for groundwater recharge and surface water allocation.
- Recharge & storage: Efforts are underway to recharge groundwater basins using surplus runoff during occasional wet periods, creating a buffer against future drought years.
- Water-use efficiency incentives: Changing policies encourage agricultural users to adopt precision irrigation and conservation practices, sometimes through subsidies or credits.
- Adoption of innovative tech: With data-driven tools like Farmonaut’s APIs (API access here; developer documentation), water allocations and drought responses are becoming more targeted and scalable.
As these policies and systems continue to evolve, they form the foundation for ensuring resilient food production and supply chain stability despite ongoing climate uncertainty.
Wider Environmental and Economic Ramifications of Drought Stress
Sustained arizona drought 2025 trends have ramifications well beyond individual crops and farms:
- Food price volatility: Reduced agricultural output leads to food price spikes and food deserts, threatening the stability of rural economies.
- Land degradation: Persistently dry soil conditions contribute to erosion, salinity, and eventual soil infertility.
- Ecological risk: Extended drought increases wildfire risk and affects natural forests, pollinators, and biodiversity on and around farmlands.
- Migration and community impacts: As livelihoods are deeply impacted, there’s a risk of depopulation and increasing social challenges across vulnerable communities.
Comparative Impact and Adaptation Measures: Arizona’s Key Crops (2025 Projections)
The above table provides an overview of projected impacts and adaptive solutions for the main crops in Arizona under continued drought stress in 2025. These measures are essential for ensuring resilient agricultural output and sustainable food production.
The Role of Technology & Innovation in Addressing Agriculture Drought Stress
Innovation remains critical for Arizona agriculture in 2025 and the years ahead:
- Satellite-Driven Data: Enables macro-scale monitoring of drought episodes, soil moisture, crop stress, and water loss, facilitating faster, more targeted interventions.
- AI & Real-Time Climate Analytics: Providers like Farmonaut offer artificial intelligence tools that analyze changing climate data and recommend adaptive actions for crops most at risk.
-
Remote-Sensing and Drone Tech: Drones increasingly deliver field-by-field crop health checks and assist with precision irrigation, fertilization, and pest management.
- Blockchain for Traceability and Market Access: By ensuring transparent transactions, technology like Farmonaut’s supports broader food supply chain stability during times of uncertainty.
- API Integration: Open APIs allow developers, agencies, and agribusinesses to blend satellite, weather, and farm data into their own platforms, supporting custom risk models and supply chain optimization.
These technologies together enhance drought response and create a more efficient, transparent, and climate-resilient agricultural sector.
Farmonaut: Empowering Arizona’s Transition to Resilient, Sustainable Agriculture
As a satellite technology leader, Farmonaut offers a comprehensive suite of satellite imagery, AI, and blockchain tools ideal for addressing agriculture drought stress. Our mission is to make advanced, actionable insights accessible to farmers, agribusinesses, and government stakeholders in Arizona and worldwide.
Key Farmonaut Solutions for Drought-Prone Regions:
- Satellite-based crop health and soil monitoring: Get affordable, actionable maps for crop stress, water needs, and soil conditions.
- AI Advisory and Fleet Management: Our Jeevn AI system provides in-depth, real-time advisories to maximize both productivity and water conservation. Meanwhile, fleet management tools optimize equipment logistics for farms of any scale.
- Blockchain Traceability & Carbon Footprinting: Our traceability services and carbon monitoring foster transparent, sustainable supply chains.
-
API and Large-Scale Management: For developers and enterprise users, the Farmonaut API and large scale management platform provide scalable integration for system-wide crop and resource tracking.
Explore developer documentation here.
The Farmonaut Difference: Real-time, reliable data for managing drought risk, optimizing productivity, and supporting sustainability—at costs accessible to farms of all sizes.
Ready to Enhance Your Farm’s Drought Resilience?
FAQ: Arizona Crop Drought 2025 & Drought Stress Solutions
What is agriculture drought stress and why is it severe in Arizona in 2025?
Agriculture drought stress refers to the limitations on crop growth and productivity that occur when crops do not receive enough water. In Arizona, 2025 is marked by a combination of scarce rainfall, rising temperatures, and declining groundwater supplies—making the drought especially severe compared to previous years.
Which crops in Arizona are most affected by drought stress?
Crops like cotton, alfalfa, wheat, and lettuce are particularly vulnerable due to their high water requirements. The projected yield losses range from 20% to 50%, depending on drought severity and the crop’s adaptive measures.
How does drought stress affect the nutritional and market value of crops?
Drought stress often leads to reduced carbohydrate and nutrient accumulation in plants, lowering the nutritional value, taste, and shelf life of produce. Drought-stressed crops are also more prone to pests and diseases, further undermining their market value.
What adaptive solutions help manage or mitigate crop drought stress?
Adaptive strategies include precision irrigation, adoption of drought-tolerant crop varieties, mulching, soil health improvements, shifting planting schedules, and deploying remote-sensing technologies for real-time monitoring.
How can technology and innovation support Arizona’s response to drought stress?
Technology such as satellite imagery, AI-driven analysis, blockchain traceability, and sensor-based monitoring optimize resource use, improve decision making, and build greater resilience against recurring drought conditions. Platforms like Farmonaut make these tools affordable and accessible.
Is policy support evolving in Arizona to combat the impacts of the 2025 drought?
Yes. Water management policies are focusing on integrated resource management, better data use, recharge of groundwater basins, and incentives for farmers who adopt efficient irrigation and conservation practices.
Where can I access Farmonaut for real-time agriculture monitoring?
Access the Farmonaut app via desktop or mobile, or explore the API documentation for integration in large-scale systems.
Conclusion – Navigating Arizona’s Crop Drought Stress in 2025… and the Future
The arizona drought 2025 is a turning point for both the region’s agriculture sector and the broader food supply chain. The ongoing severe drought threatens not only farmers’ livelihoods, but also the nutritional health and food security for millions relying on Arizona’s output.
Addressing drought stress demands a combination of:
- Technological innovation (satellite imagery, AI, blockchain traceability)
- Systemic, data-driven water management
- Adaptive on-farm practices (precision irrigation, resilient crops)
- Sustainable agriculture policies
As 2025 unfolds and the impacts of climate uncertainty continue, Arizona’s experience becomes a critical case study in resilience, sustainability, and innovation.
Farmonaut is committed to supporting all stakeholders—farmers, managers, policymakers, and communities—in crafting an agriculture future that is robust, sustainable, and climate-ready.
Start your journey to sustainable, climate-smart agriculture with Farmonaut today.