Soil Preparation Secrets: Boost Yields with 7 Hacks!
“Conservation tillage can reduce soil erosion by up to 60%, significantly preserving topsoil and boosting long-term yields.”
Introduction
Soil preparation is the foundation of every successful agricultural venture. Whether we’re engaged in modern farming, sustainable agriculture, or forestry management, how we prepare the soil directly impacts crop yields, plant health, and environmental sustainability. Soil preparation techniques—ranging from tillage to organic amendments—are designed to create optimal conditions for seed germination, healthy root development, improved water retention, and resilient plant growth.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll uncover the secrets behind soil preparation, explain major conservation tillage methods, reveal how to improve soil fertility, and present actionable hacks for boosting productivity while protecting the environment. From the science of soil health and structure to the operational details for forestry and large-scale farming, we leave no stone unturned. Utilizing the latest technology, such as Farmonaut’s satellite-powered advisory and resource management tools, we can revolutionize soil management through precision, data, and sustainability.
Understanding Soil Preparation
Soil preparation refers to the systematic set of activities aimed at improving the physical, chemical, and biological properties of soil before planting. The main objectives are to create a suitable seed bed, control weeds, incorporate necessary nutrients and organic materials, and maintain optimal structure for water infiltration and root growth. This process is critical in both agriculture and forestry, as it establishes the root environment that defines all subsequent plant growth and productivity.
Key soil preparation techniques include:
- Tillage (primary and secondary): Mechanical soil manipulation for aeration and weed control
- Organic amendments: Incorporating compost, green manure, and residues to improve fertility
- Conservation methods: Tillage minimization, contour farming, and cover cropping to protect soil health and structure
The soil’s health, structure, and fertility hinge on how effectively these techniques are applied, how organic and crop residues are incorporated, and how water retention in soil is optimized.
Tillage Practices and Soil Preparation Techniques
Tillage remains a core component of soil preparation worldwide. Its primary purpose is to aerate soil, break up compacted layers, incorporate organic materials, and create a fine-textured, weed-free seed bed suitable for effective planting. However, the intensity, timing, and frequency of tillage should vary with soil type, climatic conditions, and sustainability objectives.
Types of Tillage for Soil Preparation
- Primary Tillage – Deep, mechanical tilling performed after the previous crop’s harvest. Objectives include:
- Breaking up compacted soil, facilitating root penetration
- Incorporating previous crop residues and organic waste
- Boosting soil aeration and drainage
- Secondary Tillage – Refines the seed bed after primary tillage, typically carried out using shallower implements. Goals are:
- Further breaking clods, leveling the soil surface
- Integrating fertilizers and organic matter
- Controlling weeds to ensure optimal planting conditions
While necessary for creating favorable conditions for seeds and young plants, excessive or untimely tillage can cause damage—such as structural breakdown, erosion, surface crusting, and soil compaction. This makes understanding alternative, conservation-oriented techniques even more crucial.
Conservation Tillage Methods: Minimizing Disturbance, Maximizing Sustainability
Conservation tillage methods have emerged as sustainable alternatives to traditional, intensive tillage. Their core principle is to minimize soil disturbance while maximizing surface cover and maintaining the integrity of soil structure. These methods aim to prevent soil erosion, retain organic matter, and promote long-term soil fertility—critical goals for sustainable agriculture.
Major Conservation Tillage Techniques
- No-Till Farming
- Seeds are planted directly into undisturbed soil.
- Crop residues remain on the surface, reducing erosion and improving water retention.
- Promotes soil organic matter accumulation, increases biodiversity, and improves fertility.
- Reduced Tillage
- Only part of the soil is disturbed; selected areas are tilled, leaving significant residues on the surface.
- Protects against erosion, helps maintain soil health, and reduces operational costs.
- Strip-Till
- Tills only narrow strips for seed rows, keeping the rest of the field protected by crop residues.
- Combines the benefits of no-till and conventional tillage techniques.
These approaches significantly reduce compaction, minimize erosion, and help mitigate adverse environmental impacts of excessive tillage.
Why Choose Conservation Tillage?
- Reduces labor and fuel costs (less mechanical equipment needed)
- Promotes soil biodiversity by maintaining natural habitats for soil organisms
- Supports water retention in soil, reducing irrigation needs
- Encourages carbon sequestration, improving overall environmental sustainability
Organic Soil Preparation Techniques: Building Fertility Naturally
Organic soil preparation focuses on incorporating natural materials, avoiding synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, and nurturing soil health naturally. Improving soil fertility through organic methods enhances not only yields but also supports long-term sustainability by preventing soil erosion and degradation.
Key Organic Soil Preparation Techniques
- Composting
- Involves decomposing organic waste (crop residues, manure, kitchen scraps) into nutrient-rich compost
- Boosts soil fertility and improves physical structure and water retention
- Green Manuring
- Growing cover crops, especially legumes, and incorporating them back into the soil before flowering
- Fixes atmospheric nitrogen, improves soil organic matter, and reduces need for synthetic fertilizers
- Cover Cropping
- Planting non-commercial crops specifically to protect the soil surface during off-seasons
- Reduces erosion, suppresses weeds, and adds organic matter upon decomposition
Cover cropping benefits include reducing soil erosion, improving soil structure, and increasing long-term soil fertility. Effective organic soil preparation practices are foundational for sustainable farming practices worldwide.
“Adding organic matter increases soil fertility, raising crop productivity by as much as 30% in sustainable farming systems.”
Conservation Agriculture for Soil Health and Structure
Modern conservation agriculture synthesizes various best practices to maintain optimal soil health and structure while focusing on long-term productivity and environmental resilience.
- Minimum Soil Disturbance: Relying on no-till or reduced tillage methods to protect existing biological processes
- Permanent Soil Cover: Maintaining constant organic surface cover (using crop residues or cover crops) to prevent erosion, buffer against extreme temperatures, and enhance water retention
- Diversification of Plant Species: Utilizing crop rotation and intercropping to increase biodiversity, break pest/disease cycles, and stimulate healthy soil microbiota
These methods are proven to promote strong, resilient soil structure and optimize nutrient cycling, ultimately enhancing crop yields in a sustainable way.
Soil Conservation and Erosion Prevention
Soil erosion is a major environmental and agricultural concern, causing nutrient loss, reduced fertility, and poor water retention. Preventing soil erosion demands both sound soil preparation techniques and landscape-level conservation methods.
Top Techniques for Soil Conservation
- Contour Plowing: Plowing along the contours of slopes slows water runoff, minimizes soil removal, and protects topsoil. Learn more.
- Terracing: Reshaping slopes into flat, stepped levels to reduce water velocity and prevent soil loss
- Agroforestry: Integrating trees and shrubs into fields to anchor soil and foster biodiversity
These strategies, when combined with mulching and maintaining constant residues on the soil surface, are effective at both preventing erosion and restoring soil health. Incorporating the right materials (like mulch or compost) will further strengthen water retention in soil and improve nutrient cycling.
Soil Preparation in Forestry: Ensuring Robust Tree Establishment
In forestry, optimized soil preparation is critical for the establishment and sustained growth of trees. Complex landscapes, competition from weeds or unwanted vegetation, and the need for long-term biodiversity demand careful planning.
Key Forestry Soil Preparation Techniques
- Site Preparation: May involve prescribed burning to reduce excessive plant growth, recycle nutrients, and create favorable conditions for seedling survival. (Learn more about prescribed burning and tillage.)
- Mechanical Scarification: Using specialized equipment to disturb the soil surface, remove competing vegetation, and encourage germination of natural or planted tree seeds.
- Minimal Chemical Use: Targeted herbicides occasionally applied for weed control, always under careful management to preserve soil health.
Effective soil preparation ensures young trees have optimal conditions for root penetration, nutrient uptake, and long-term resilience, contributing to richer, more diverse forest systems.
Comparison Table: Soil Preparation Techniques for Yield and Sustainability
| Technique | Estimated Yield Boost (%) | Soil Fertility Impact | Environmental Sustainability | Best for These Crops |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conservation Tillage | 10–30% | High | Very High | Wheat, maize, soybean, cotton |
| Cover Cropping | 7–22% | High | Very High | Vegetables, cereals, orchards |
| Crop Rotation | 10–20% | Medium–High | High | Cereal–legume systems |
| Mulching | 5–15% | High | Very High | Fruits, vegetables, plantation crops |
| Organic Amendments (Compost, Manure) | 15–30% | Very High | High | Vegetables, cereals, fruit trees |
| Deep Plowing | 5–10% | Medium | Medium–Low | Root crops, cereals |
| No-Till Farming | 8–21% | High | Very High | Maize, soybean, wheat |
Benefits of Proper Soil Preparation
A well-prepared soil is the backbone of thriving crops and resilient ecosystems. By adopting the most suitable methods, we reap several transformative benefits, including:
- Enhancing Crop Yields – Targeted soil conditioning leads to faster germination, robust growth, and higher productivity per hectare.
- Soil Erosion Control – Conservation-inspired approaches and mulching preserve precious topsoil and prevent loss due to water or wind.
- Improving Soil Fertility – Organic amendments and green manures increase soil carbon, nitrogen, and essential nutrient availability.
- Water Conservation – Techniques like cover cropping, no-till, and mulching improve water retention in soil, reducing irrigation needs.
- Biodiversity Promotion – A variety of cover crops, rotation, and agroforestry support microorganisms, wildlife, and long-term sustainability.
It’s clear: optimizing soil preparation combines agronomic success with positive environmental and economic impacts.
Learn how to monitor and reduce your farm’s carbon footprint with Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting dashboard for greater sustainability.
Ensure supply chain transparency and food authenticity with farm-to-table traceability by Farmonaut.
Challenges and Important Considerations in Soil Preparation
While modern soil preparation techniques offer unmatched potential, challenges exist in their adoption and ongoing management:
- Economic Factors
- Initial investment for advanced mechanical equipment, composting setups, or transitioning from traditional tillage to no-till systems
- Potential short-term yield dips during system transition periods
- Knowledge and Training
- Farmers and foresters require education on method selection, equipment calibration, and best practices for different soils and climates
- Access to unbiased, data-driven advice (such as Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI) is crucial for effective implementation
- Environmental and Local Conditions
- Topography, rainfall, and inherent soil properties dictate the appropriate preparation strategy
- Weed dynamics: Some conservation systems may require enhanced weed control measures (cover crops, rotation, or integrated pest management)
Smart planning, continuous adaptation, and leveraging technology (such as satellite monitoring and AI analytics) are essential for overcoming these hurdles and achieving the full promise of sustainable farming practices.
Boost Yields with 7 Soil Preparation Hacks!
-
Integrate Organic Matter Continuously
Regularly add compost, green manure, and crop residues to the soil. Composting accelerates the decomposition of organic waste, enriching the soil with vital nutrients, improving water retention, and enhancing soil structure for healthier root development.
-
Adopt Conservation Tillage Methods
Minimize soil disturbance by transitioning to no-till, reduced tillage, or strip-till approaches. These techniques help preserve soil health, prevent erosion, and foster resilient farming systems.
-
Leverage Cover Cropping Benefits
Grow cover crops during off-seasons or between main crop cycles to maintain surface cover, suppress weeds, and add organic material during decomposition. This simple step also improves water retention in soil and stabilizes temperatures for germinating seeds.
-
Rotate Crops for Improved Fertility
Alternate plant families every cycle to prevent pest/disease buildup, break nutrient depletion patterns, and increase biodiversity. Legume rotation, in particular, is effective at fixing nitrogen naturally.
-
Use Mulches Smartly
Apply organic mulch (straw, wood chips, or compost) on the soil surface to prevent evaporation, reduce erosion, and keep weeds at bay, thus supporting both soil health and yield.
-
Monitor Soil—Tech-Driven Decisions
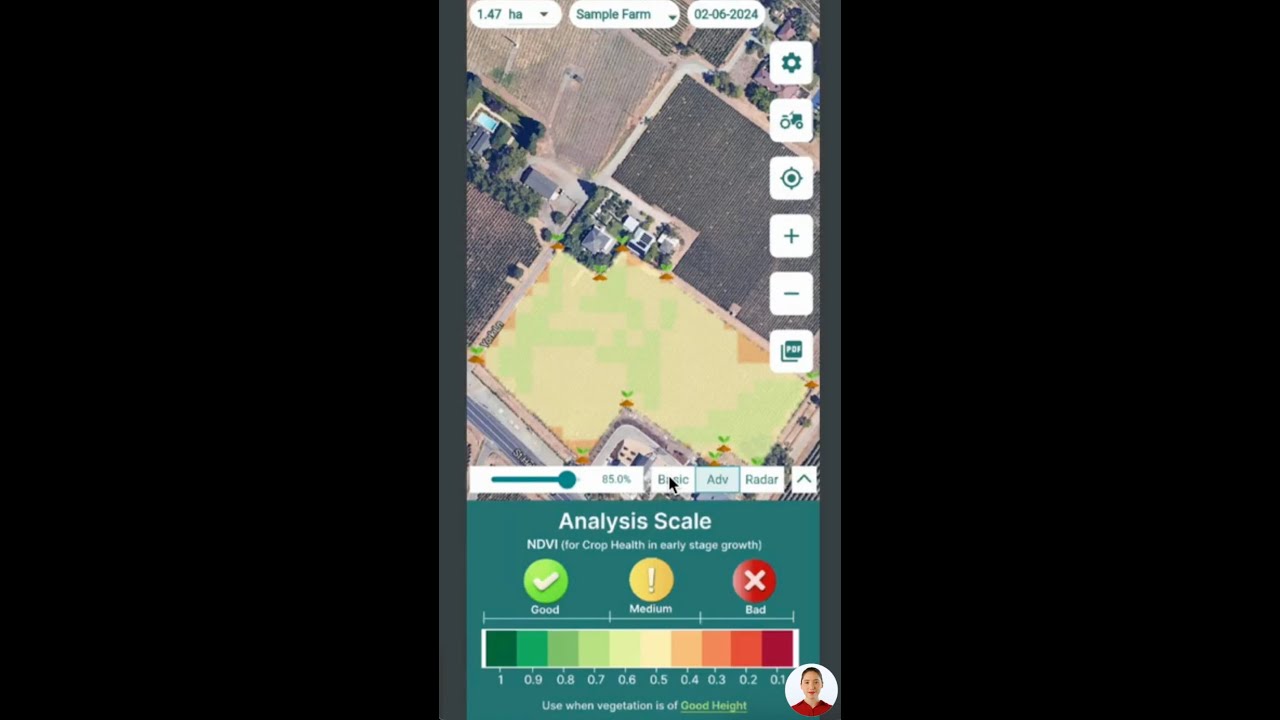
Utilize satellite-based monitoring and data tools (like Farmonaut) for real-time insights on vegetation health, soil moisture, and management decisions.
-
Invest in Site-Specific Management
Tailor soil preparation techniques to microclimates and field conditions, using test results and technology to match the right method with the right site.
Adapt these hacks judiciously within your operation, and you’ll enjoy the combined benefits of enhancing crop yields, soil fertility, and environmental sustainability.
Farmonaut: Precision Agriculture for Sustainable Soil Management
Incorporating advanced technology into soil prep is a game-changer for modern farming and forestry. Farmonaut presents a revolution in precision agriculture by providing:
- Satellite-based crop health monitoring: Receive real-time insights on soil moisture, plant vigor, and detect issues before they become visible—enabling timely, targeted interventions for better yields and resource use.
- AI-powered advisory: Our Jeevn AI system analyzes satellite data, soil condition, and environmental trends to offer personalized crop and soil management advice—helping you select the right soil preparation techniques under changing climates.
- Carbon footprint tracking: Monitor and mitigate the environmental impact of soil preparation with Farmonaut’s carbon tracking feature.
- Blockchain traceability: Secure your product’s journey and strengthen consumer trust with Farmonaut’s supply chain transparency tools.
- Fleet/resource management: Make efficient use of your machinery for site preparation or maintenance with streamlined fleet management solutions.
- APIs for developer integration: Incorporate robust, real-time agri data into your own systems or applications with the Farmonaut API and developer documentation.
Farmonaut empowers everyone from smallholder farmers to global agribusinesses to manage soil, crops, and resources with unprecedented accuracy, affordability, and sustainability.
Get tailored crop, plantation, and forest management advice from Farmonaut for every stage of soil and crop establishment.
Farmonaut Subscription Options
Whether you manage a small field or large-scale agricultural enterprise, Farmonaut offers scalable, flexible subscriptions for all user needs. Choose from app access, advanced real-time analytics, and developer APIs—all designed to boost your precision agriculture and sustainable soil management.
FAQ: Soil Preparation & Sustainable Farming
What is soil preparation and why is it important?
Soil preparation is a set of techniques aimed at improving soil physical, chemical, and biological properties to create an optimal seed bed, encourage root growth, and ensure better water and nutrient availability for crops and trees. Proper soil preparation boosts yields, prevents erosion, and lays the foundation for sustainable agriculture.
Which are the most sustainable soil preparation methods?
Conservation tillage (no-till, reduced tillage), cover cropping, crop rotation, and organic amendments are highly sustainable. They improve soil health and structure, protect the surface, and promote long-term fertility with minimal environmental impact.
How does cover cropping improve soil?
Cover cropping prevents erosion, adds organic matter, suppresses weeds, boosts soil biodiversity, and enhances both nutrient cycling and water retention in soil. It’s a key hack for improving overall productivity and resilience.
How can Farmonaut help with soil preparation?
Farmonaut offers satellite-based crop monitoring, AI-driven farm advisory, resource management, and real-time data on soil moisture, organic content, and field conditions. These insights help farmers choose and refine the best soil preparation practices for sustainable, high-yield outcomes.
What are the main challenges in implementing soil preparation techniques?
Transitioning from traditional methods to conservation or organic approaches may require investment in knowledge, training, and sometimes equipment. Adapting to local climate and soil conditions also plays a critical role. Technology and ongoing advisory support can help overcome these hurdles.
Does soil preparation impact water retention?
Absolutely. Proper methods (like no-till, mulching, and organic amendments) increase water retention in soil, reducing irrigation needs and withstanding drought stress.
Conclusion
Soil preparation remains the bedrock of sustainable, resilient food and forestry systems. By strategically combining techniques—such as conservation tillage, cover cropping, organic amendments, and cutting-edge monitoring tools—we can achieve improved soil fertility, robust structure, water efficiency, and enhanced crop yields with minimal environmental footprint. Modern solutions like Farmonaut make it feasible, affordable, and precise for farms and forests of any scale.
Let’s commit to smarter soil management, continuous education, and responsible stewardship—securing food security, economic success, and a thriving environment for generations.
Take the next step toward transformative, sustainable farming—explore Farmonaut, embrace the secrets of soil preparation, and watch your yields soar!
Ready to revolutionize your soil and boost your yields? Start your sustainable journey with Farmonaut today!