Biochar Secrets: Boost Yields & Soil Fast!
What is Biochar? Uncovering an Agricultural Miracle
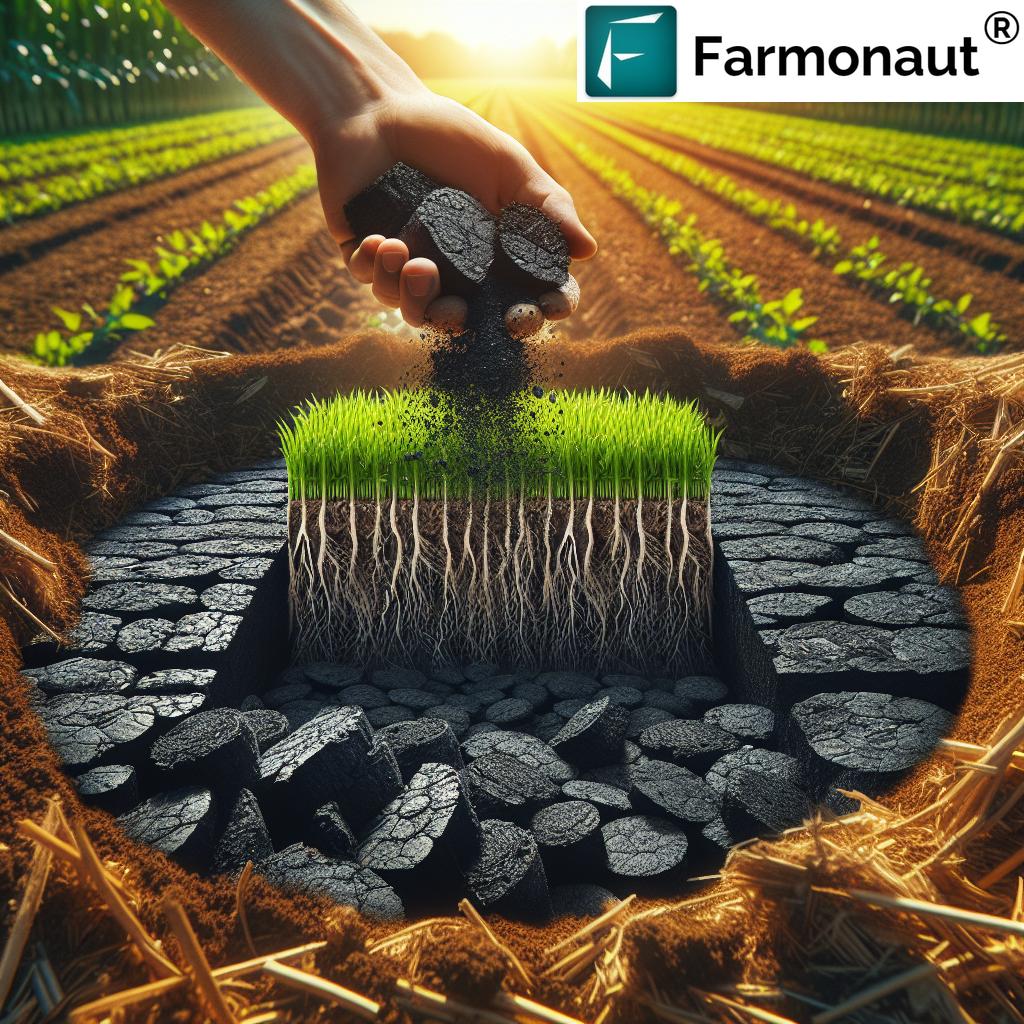
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to sustainability, innovation, and empowering farmers to achieve higher productivity using advanced science. In this context, one solution has gained global momentum—biochar. This porous, carbon-rich product forms when we heat organic biomass (such as crop wastes, forestry residues, or even some types of municipal waste) in an oxygen-limited environment. The result? An exceptional, stable material that, as countless studies confirm, improves soil health, water retention, crop yields, and fights climate change via carbon sequestration.
Curious how biochar works as a soil amendment, the secrets behind its benefits in agriculture, and how we can harness it in sustainable farming and forestry? Let’s dive into everything you need to know about biochar for soil health, increased yields, and eco-friendly growth.
Biochar Production: Pyrolysis, Biomass, and More
To understand the benefits of biochar, let’s start with its origin. Unlike traditional charcoal, biochar is specifically produced for use as a soil amendment. We make it through pyrolysis, a controlled process of heating organic materials (or feedstock). The temperature ranges from 300°C to 700°C, always in an environment with little or no oxygen. This prevents the biomass from combusting, instead breaking down into:
- Stable carbon (biochar)—great for carbon sequestration
- Synthetic gases (syngas)
- Bio-oil
The chemical structure, stability, and effectiveness of finished biochar depend on:
- Type of feedstock: Crop residues (straw, husks, shells), forestry by-products, or certain municipal organics
- Pyrolysis conditions: Temperature, residence time, and moisture levels
As a result, not all biochars are identical. Some will offer exceptional water retention, others excel at improving nutrient retention or pH moderation. Therefore, tailoring our production and application methods to specific agro-ecological conditions is vital for maximizing the benefits.
Biochar for Soil Health: Unlocking Rich, Productive Soils
Why is biochar application in agriculture generating global excitement? It’s because biochar directly tackles many of the limitations of degraded soils and intensive farming:
- Biochar soil amendment leads to soil fertility enhancement. Its unique porous structure and high surface area help soils retain essential nutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium), which would otherwise be prone to leaching in sandy or heavily irrigated soils.
- Biochar’s stability ensures these fertility gains are long-lasting compared to most compost and chemical fertilizers that degrade rapidly.
- Greenhouse gas mitigation: Incorporating biochar means carbon is stored in a stable form rather than quickly returning to the atmosphere as CO₂ or methane through decomposition. Biochar truly is a carbon negative solution!
- Soil structure improvement: Biochar physically enhances soil aggregation, reducing compaction, improving root penetration, and supporting a thriving microbial environment.
- Erosion control: By boosting aggregation and stability, it also significantly decreases both wind and water erosion, which are major problems in arid or sloping regions.
These benefits make biochar for soil health not merely a trend, but a revolutionary advancement in sustainable land management.
Biochar for Water Retention and Drought Resilience
Did you know? “Adding biochar to soil boosts water retention by 18% and reduces fertilizer runoff by up to 50%.”
Water stress is a leading threat to global food security. One of the most critical advantages of biochar is its exceptional impact on soil water retention:
- Biochar’s high surface area and porosity allow it to retain water much better than bare soil.
- This means plants have easier access to moisture during dry periods.
- In arid and semi-arid regions (such as parts of Western Australia, sub-Saharan Africa, and India’s Deccan Plateau), biochar application can extend the time between irrigations and reduce crop losses during drought.
- Additionally, biochar application in agriculture can cut irrigation costs while supporting soil health enhancement.
In short, biochar for water retention offers both practical agronomic and environmental benefits.
Soil pH Moderation & Nutrient Availability: Biochar’s Subtle Power
Another unsung hero among biochar applications is its ability to moderate soil pH:
- Many tropical or intensively cropped soils tend toward acidity (ph below 6), which limits nutrient availability and plant uptake.
- Biochar typically raises pH, especially when produced from alkaline residues or at higher pyrolysis temperatures.
- This pH adjustment supports healthier, more productive plant growth by unlocking essential nutrients, reducing toxicity (from aluminum, manganese), and fostering beneficial soil organisms.
- In forest soils, pH moderation helps restore fertility and supports natural reforestation.
Thus, the role of biochar as a pH regulator is particularly important for regions battling acid soil degradation.
Effects of Biochar on Crop Yields and Agricultural Productivity
Perhaps the most compelling story is in the field: effects of biochar on crop yields. Numerous trials and meta-analyses confirm:
- Yield increases of 10-25% are possible, especially on nutrient-poor or degraded soils.
- Root crops, cereals, and legumes show major yield improvements under biochar soil amendment.
- Enhanced water and nutrient retention set the stage for healthier, faster, more resilient plant growth.
- Lower fertilizer run-off and reduced nutrient leaching mean more efficient fertilizer use and lower input costs overall.
For farmers, that’s more profit, less risk—and for the environment, that’s less chemical pollution and superior long-term sustainability.
Comparing Biochar, Compost, and Fertilizer: Benefits at a Glance
| Amendment Type | Soil Health Improvement (Estimated % Increase) |
Crop Yield Boost (Estimated % Increase) |
Carbon Sequestration Potential (tCO₂/ha/year) |
Impact on Soil Water Retention | Sustainability Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biochar | 15-30% | 10-25% | 2.2 – 5 | High (+15-25%) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Compost | 10-20% | 5-15% | 0.1 – 0.4 | Moderate (+8-15%) | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| Synthetic Fertilizer | Short-term Only | 10-30% | Negative | Low | ⭐ |
Data compiled from peer-reviewed studies and sustainable agriculture sources for typical application rates.
Biochar Applications in Forestry & Forest Soils
Aside from croplands, forest soil improvement is a major arena for biochar. Here’s how we utilize biochar in forestry:
- Biochar amendment restores soil structure in degraded or deforested zones, stimulating faster and healthier tree growth.
- By converting logging and thinning residues (branches, small trunks) into biochar, we not only manage forest waste but return valuable carbon and nutrients to the ecosystem.
- Biochar carbon sequestration is especially powerful when biochar is incorporated in forest soils, locking carbon away on human time scales.
Forestry applications of biochar thus deliver a win-win: soil rehabilitation + climate mitigation.
Biochar and Carbon Sequestration: Climate Change Mitigation
Let’s get to the heart of the matter: How does biochar help fight climate change?
- When we make and apply biochar, we “freeze” carbon that would otherwise decompose and return to the atmosphere as CO₂ or methane.
- One ton of applied biochar can sequester an average of 2.2 tons of CO₂ equivalent. This sequestered carbon is exceptionally stable—often lasting hundreds or even thousands of years in soil!
- The impact goes further: Using biochar reduces the need for chemical fertilizers—which themselves have a heavy greenhouse gas footprint from manufacture and transport.
- Biochar and climate change mitigation thus go hand in hand, providing one of agriculture’s most accessible ways to make a real difference in carbon emissions.
Farmers, foresters, and land managers all have a stake in this game—the more biochar we use appropriately, the more robust our fight against the planetary climate crisis.
For data-driven tracking of carbon footprinting in agriculture, Farmonaut offers an advanced platform for carbon monitoring and reporting. This tool helps organizations and farmers verify their emissions reductions and move toward compliance and sustainability goals.
Challenges and Key Considerations in Biochar Application
Despite the immense benefits of biochar, scaling its use isn’t without hurdles:
- Variability: The effectiveness of biochar is tied to its origin (feedstock used) and how it’s produced (pyrolysis temperature and time). It’s critical to match the right biochar to the right soil and crop.
- Costs: Biochar production and transport can be expensive, especially for remote farms or those far from biomass sources.
- Potential contaminants: Not all biochars are equal—feedstock from treated wood, plastics, or contaminated residues may introduce harmful substances into soil. Always use certified, carefully produced biochar!
- Best practices: It’s essential to test small plots, monitor soil and crop responses, and refine application rates for your region, climate, and farming system.
Addressing these challenges will involve ongoing research, local adaptation, and support for education and guidance in biochar adoption.
Farmonaut: Powering Sustainable Agriculture & Carbon Monitoring
At Farmonaut, our mission aligns with the core principles of precision, sustainability, and data-driven decision-making. While we don’t produce biochar ourselves, our cutting-edge agricultural satellite monitoring platform enables farmers and organizations to:
- Monitor crop health in real time using satellite imagery, NDVI, and soil moisture analytics—an ideal way to assess the impact of biochar application over time.
- Use AI-based advisory systems to receive custom farm improvement recommendations, including resource management for water, soil amendments, and pest control.
- Track and reduce carbon footprints at the farm and organizational level via real-time monitoring, analytical dashboards, and emissions reporting. Explore Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting Tool →
- Ensure product traceability with blockchain-based supply chain transparency; vital for organizations looking to prove sustainable sourcing (including biochar-optimized produce).
- Streamline operations and logistics with fleet management technology, ensuring fertilizers, biochar, or other amendments are applied on-time and tracked accurately.
- Integrate Farmonaut’s rich API into your agtech stack, with full API documentation for developers and enterprises.
- Manage large estates with ease via our Large Scale Farm Management Solution that brings all your sustainability and productivity tools into one intuitive dashboard.
We empower farmers and the agriculture ecosystem with real, actionable intelligence—making biochar and other sustainable practices easier to implement, monitor, and scale.
How to Use Biochar in Farming: Practical Steps and Best Practices
Now that we understand the effects of biochar on soil health and yields, how do we maximize these benefits in the field?
- Source quality biochar: Only use certified biochar made from safe, clean biomass (avoid industrial, painted, or pressure-treated sources).
- Particle size matters: Finer biochar (<5mm) has increased surface area and is easier for soil and plant roots to interact with.
- Pre-charge biochar: Uncharged biochar, when added to soil, can initially absorb nutrients, temporarily reducing plant-available nutrients. Pre-charge by mixing with compost, manure, or a diluted fertilizer before application.
- Application rate: Start with 5–10 tons per hectare and monitor results. Some soils do best with less, some may benefit from more.
- Uniform incorporation: Mix biochar into the root zone (top 10–20 cm), ideally just before planting, or together with other soil amendments.
- Combine with organic matter: Best results are seen when biochar is used alongside compost, natural manure, or cover crops.
- Monitor and record: Use satellite or ground-based monitoring (such as provided by Farmonaut) to track changes in soil condition, moisture, and crop performance season-to-season.
With these steps, farmers in diverse regions—from Australian drylands to Indian subtropics to European organic holdings—are already seeing biochar’s difference in agronomic and economic outcomes.
To support all these practices, Farmonaut offers integrated field and environmental monitoring—making the transition to biochar-powered agriculture smarter and more trackable than ever before.
Expert Forest, Plantation, and Crop Advisory Tools
Embracing biochar for soil, crop, or forest improvement? Our advisory services deliver actionable, satellite-powered and AI-based insights for smarter planting, monitoring, and sustainable resource management.
Precision Crop Monitoring for Sustainable Loans and Insurance
Applying biochar is an investment in long-term farm health—our Crop Loan & Insurance Verification platform leverages satellite data to streamline approvals and foster access to green finance.
Frequently Asked Questions: Biochar in Agriculture
What exactly is biochar and how is it different from charcoal?
Biochar is a stable, carbon-rich material produced by heating biomass (plant residues, forestry waste, or clean organic matter) in very limited oxygen (pyrolysis). While both biochar and traditional charcoal are formed by similar processes, biochar is intentionally made for soil improvement—whereas regular charcoal is typically used as fuel. Biochar also undergoes stricter control for contaminants and particle size.
What are the top benefits of biochar for soil health?
Biochar improves soil structure, boosts fertility and nutrient retention, increases water retention, provides long-lasting carbon sequestration, moderates soil pH, enhances microbial activity, and reduces soil erosion.
How does biochar help address climate change?
By stabilizing carbon in soil (instead of it returning as greenhouse gases), biochar carbon sequestration locks away CO₂ for centuries. This reduces net emissions and helps agriculture shift from being a carbon source to a carbon sink.
How much biochar should I apply?
Application rates depend on soil type, crop system, and biochar quality—but a common starting range is 5–10 tons per hectare (0.5–1 kg per square meter). More is not always better; field trials and local advice are recommended.
Can I use any biomass to make biochar?
Not all biomass is suitable. Use clean, untreated organic materials (crop waste, wood chips, husks). Avoid painted, treated, or contaminated materials, as they can introduce harmful contaminants into your soil.
Is biochar safe and sustainable for all types of soils and climates?
Biochar is generally safe and sustainable, but it works best when matched to local soils, climates, and crops. In very alkaline soils, caution is advised. Always ensure you’re using certified, high-quality biochar appropriate for your farm or region.
How can I track the effects of biochar on my farm?
Use satellite-based crop monitoring tools, such as those offered by Farmonaut, for real-time NDVI, soil moisture, and yield tracking. This makes assessing the impact of biochar application transparent and data-driven.
Farmonaut Subscriptions: Affordable Precision Agriculture for All
Ready to unlock smarter, greener farming solutions? Explore our flexible, subscription-based services:
Conclusion: Biochar, Farmonaut & the Future of Sustainable Agriculture
Biochar stands at the intersection of ancient wisdom and cutting-edge sustainability science. By using it as a soil amendment, we unlock dramatic improvements in soil health, crop productivity, water retention, and long-term carbon sequestration. The result: higher yields, greater resilience, and a positive climate impact for generations.
At Farmonaut, we are proud to support farmers and land managers worldwide with real-time, satellite-enabled, and AI-powered tools—making sustainable transitions like biochar adoption measurable, accessible, and effective. Our affordable platform, data intelligence, and transparent reporting ensure everyone—smallholders, agribusinesses, and policymakers—can thrive on smarter, greener agriculture.
The secret’s out—biochar is transforming agriculture and the environment. Let’s harness this power, together!