7 AgTech Solutions Revolutionizing Precision Farming
“AI-driven crop management can increase yields by up to 30% in precision farming systems.”
Introduction: AgTech and the Precision Farming Revolution
We stand at a crucial intersection in agriculture. With our global population rising and natural resources under increasing pressure, advanced agricultural technologies are no longer optional—they’re essential. Agricultural technology (AgTech) is rapidly transforming how we approach sustainable farming, increasing profitability, and improving resource efficiency in every field.
By integrating state-of-the-art technologies such as precision farming, AI-driven crop management, sensors, blockchain, and advanced fleet management tools, we usher in a new era for agricultural practices.
In this in-depth exploration of seven AgTech solutions revolutionizing precision farming, we’ll break down how diverse innovations are not only enhancing yields and efficiency but also addressing critical challenges such as resource management, pest infestations, and sustainability. Get ready to discover how our fields are transforming, right now.
1. Precision Agriculture: The Foundation of Modern AgTech
What is Precision Agriculture?
At the core of the agricultural technology revolution is precision agriculture. This data-driven crop management approach empowers farmers to monitor and manage field variability with greater accuracy than ever before. Leveraging a combination of GPS technology, sensors, data analytics, and satellite imagery, we enable optimal application of vital farm inputs.
- Variable Rate Technology (VRT): Enables us to adjust water, fertilizer, and pesticide applications based on real-time field data.
- Resource Optimization: Reduces waste and increases efficiency, leading to higher yields and reduced environmental impact.
- Satellite Imagery & NDVI: Tools like Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring give us up-to-date crop health analytics and vegetation indices to detect variability invisible to the naked eye.
With precision agriculture, we’re shifting from a uniform “one-size-fits-all” farming practice to a highly targeted approach. Imagine having the power to identify a single underperforming or pest-affected area in a vast field and immediately applying the right intervention—this is the new norm.
Precision Crop Monitoring and Data Analytics
Our ability to monitor crops through sensors, satellite imagery, and analytics is foundational.
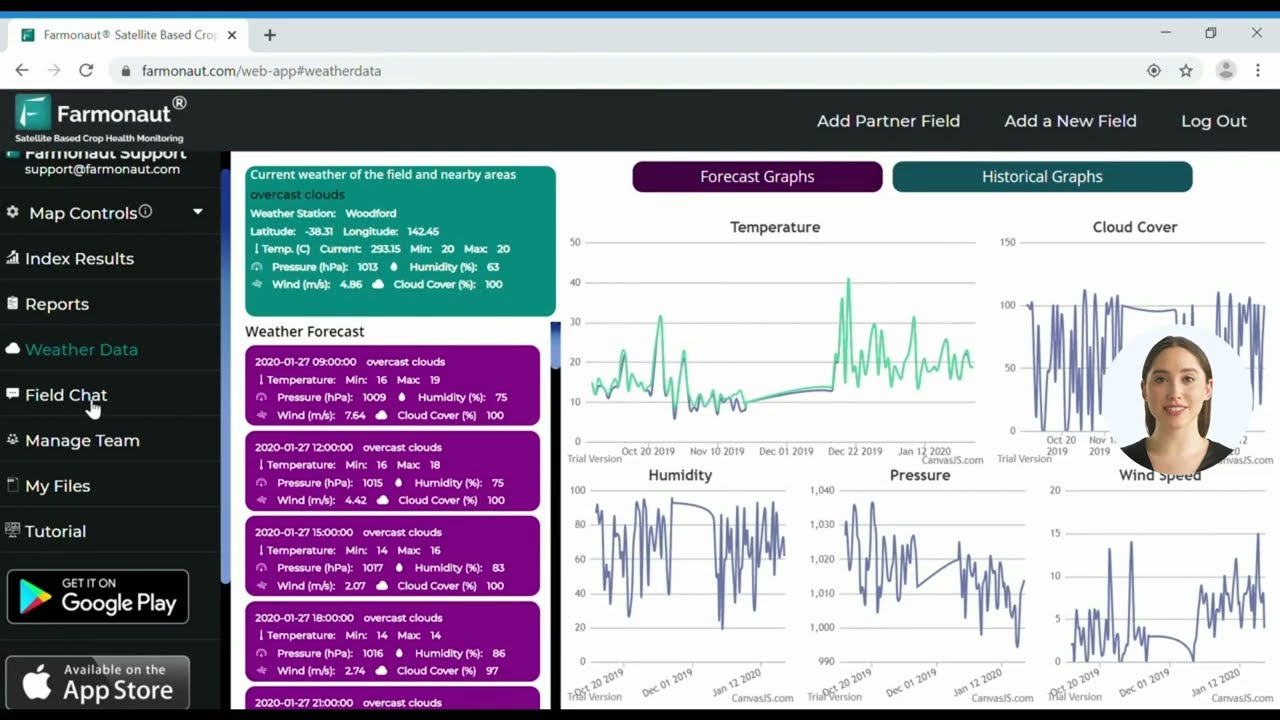
Key metrics—such as NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index), soil moisture, and temperature—must be continuously analyzed for actionable insights. With platforms like Farmonaut, precision crop monitoring is now affordable and accessible, even for smallholders.
If you manage large-scale plantations or agribusinesses, check out Farmonaut’s Large Scale Farm Management Solution—tailored specifically for comprehensive, multi-field resource optimization.
2. Automation and Robotics: Transforming Farm Operations
Automation in Agriculture: Efficiency Redefined
Automated systems—like autonomous tractors, robotic harvesters, and self-driving drones—are rapidly overhauling traditional farming tasks. Where labor shortages and high operational costs once imposed barriers, automation in agriculture now gives us powerful tools for planting, harvesting, spraying, and field monitoring.
- Autonomous Tractors: Operate with precision, using AI-guided GPS to plant seeds and spray fertilizers/pesticides with minimal human intervention.
- Robotic Harvesters: Machine learning-driven robots identify ripe crops, reducing time and minimizing waste and crop damage.
- Weeding Robots: Precisely target pests and weeds, limiting herbicide use and environmental exposure.
By minimizing human error and reducing labor dependency, robotic automation not only curtails costs but also allows us to scale operations efficiently.
Efficient automation is further enhanced by integrated systems management. For logistics, Farmonaut provides Fleet Management Tools for vehicle tracking, optimal deployment, and cost savings.
Automation and Precision Crop Application
- Highly automated VRT-capable devices apply fertilizers and pesticides only where necessary, reducing input waste.
- Resource savings can reach up to 25% in critical inputs with accurate automation in agriculture.
3. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Crop Management
AI in Crop Management: The Next Leap
We’re now leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to analyze vast datasets—from weather patterns to soil nutrient profiles—and generate actionable recommendations for farmers. AI-powered solutions like Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI Advisory System instantly process satellite and weather data to provide tailored crop management advice.
- Predict Yields: Machine learning algorithms predict expected yields months in advance, allowing optimal market planning.
- Detect Diseases and Pest Infestations: Deep learning models can identify early-stage crop diseases or pest outbreaks for timely interventions.
- Optimal Decisions: By combining field-level data, we receive data-driven guidance for irrigation, fertilization, and harvesting schedules.
The real value of AI in crop management lies in its ability to adapt to individual fields and even microzones within a farm, facilitating targeted solutions rather than generic ones.
Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI Advisory System is a powerful example of how AI is democratizing access to advanced advice for every farmer. These systems are revolutionizing how decisions are made in agriculture.
Unlock the benefits of AI-driven advisories and real-time crop monitoring via Farmonaut’s app and web platform—Get Started today!
4. IoT Sensors for Farming: Real-Time Data for Smarter Decisions
Enabling Data-Driven Agriculture: The Internet of Things
IoT sensors for farming orchestrate a network of interconnected devices (sensors and smart meters) across the farm landscape. This network constantly monitors key parameters such as soil moisture, soil nutrients, field temperature, crop health, and humidity.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Continuous live streams of data help us detect issues—from dry or nutrient-deficient areas to waterlogged soil.
- Precision Interventions: These insights enable targeted irrigation, pesticide application, and fertilization, improving crop health and efficiency.
- Irrigation Management: Smart irrigation systems automate water delivery based on real field requirements, saving significant resources.
Systems like Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring platform expand the capabilities of IoT, providing remote sensing data that covers field-wide variability at scale.
For developers and agribusinesses needing direct sensor and weather data, Farmonaut API access and Developer Documentation provide seamless integration with third-party platforms, unlocking new analytical possibilities.
IoT-powered systems are now indispensable for achieving sustainable, efficient agriculture. By enabling continuous monitoring and tailored interventions, they ensure that every drop of water and bit of nutrient is put to the best use.
5. Drones in Agriculture and Aerial Imaging
Drones: The Eyes in the Sky
Drones in agriculture have given us unprecedented aerial views and real-time insights over our fields. Equipped with multispectral cameras, these flying sentinels rapidly capture high-resolution images, revealing hidden crop health and soil patterns for informed decision making.
- Precision Crop Monitoring: Identify pest infestations, nutrient deficiencies, irrigation problems, and damaged areas within days, not weeks.
- Timely Interventions: Access to 2D/3D field maps and time-lapsed visuals enables swift intervention, reducing crop loss risk.
- Optimizing Input Applications: Drones facilitate variable rate spraying—reducing chemical use and boosting effectiveness.
Aerial imaging from drones integrates seamlessly with platforms like Farmonaut, making it easy to overlay multiple data sources (satellite, drone, on-ground sensors) for a complete precision agriculture solution.
We recommend that forward-thinking farms utilize a hybrid of drone-based and satellite-based monitoring systems to maximize field coverage and decision accuracy.
“Over 60% of precision agriculture solutions now use satellite imagery for real-time field monitoring.”
6. Blockchain in Agriculture Supply Chain and Traceability
Why Blockchain?
Blockchain is best known for powering cryptocurrencies, but its impact on traceability and security in agriculture is even more profound. Blockchain in agriculture supply chain ensures an immutable, transparent record of every step—from farm to table.
- Transparency: Blockchain ledgers document every transaction (from harvest, storage, transport, to retail).
- Authenticity and Trust: Each data point is unchangeable, building consumer confidence in organic, fair trade, or region-specific products.
- Efficient Supply Chains: Blockchain-driven documentation streamlines compliance and reduces fraud risk.
Major food and textile companies are already leveraging blockchain-based traceability. Farmonaut’s traceability solution (visit Product Traceability) is helping industries add transparency—vital for premium certifications and market access.
Blockchain is expected to underpin the future of secure, ethical, and profitable agriculture supply chains.
7. Gene Editing and Advanced Breeding Techniques
Unlocking Crop Resilience and Quality
Gene editing technologies such as CRISPR are rapidly evolving how we breed crops for higher yields, climate resilience, and pest resistance. Advanced breeding techniques allow us to introduce or enhance traits with precision.
- Pest and Disease Resistance: Creating crop varieties that withstand attacks with minimal pesticide use.
- Drought and Flood Tolerance: Improving survivability under variable climatic conditions.
- Higher Nutritional Value: Specifically editing genes for enhanced protein or micronutrient content in staple crops.
These technologies support global food security by producing hardier, more nutrient-rich crops for a growing planet. Gene-editing is set to be one of the most significant advancements in agriculture in the 21st century.
Comparative Features Table: 7 AgTech Solutions Revolutionizing Precision Farming
| AgTech Solution | Technology Used | Primary Function | Yield Improvement (%) | Sustainability Impact | Adoption Rate | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision Agriculture | GPS, Satellite Imaging, Data Analytics | Targeted resource & crop input management | +15–25% | Reduces fertilizer/pesticide usage by up to 25% | 40–50% | Field-level NDVI mapping for input optimization |
| Automation & Robotics | Autonomous Vehicles, Robotics, Sensors | Automated planting, harvesting, spraying | +10–20% | Minimizes labor & input waste; lowers carbon footprint | 15–20% | Autonomous tractor for precision planting |
| AI & Machine Learning | Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Satellites | Predictive crop analytics, disease/pest detection | +20–30% | Prevents loss, optimizes decisions, reduces chemical input | 20–30% | AI forecast for pest outbreaks & resource needs |
| IoT Sensors | IoT Devices, Sensors, Wireless Networks | Real-time soil, climate, crop condition monitoring | +10–15% | 30%+ water savings via precision irrigation | 25–35% | Smart irrigation on moisture sensor data |
| Drones & Aerial Imaging | Drones, Multispectral Cameras, AI Algorithms | Aerial crop inspection & input targeting | +12–20% | Reduces chemical drift/environmental exposure | 10–15% | Drone-based disease mapping & spot spraying |
| Blockchain Traceability | Blockchain, Data Ledgers, Mobile Apps | Product traceability, supply chain validation | Indirect; higher market value/less loss | Prevents fraud, enhances food security & safety | 8–12% | Transparent cotton traceability solution |
| Gene Editing/Breeding | CRISPR, Biotech, Genomic Data | Develop climate-resilient, high-yielding crops | +30–50% | Enables pesticide reduction/food security | 5–10% | Drought tolerant wheat via gene editing |
AgTech, Sustainability, and Resource Management
The future of agriculture is unthinkable without a firm commitment to sustainable farming practices. AgTech solutions play a pivotal role here by:
- Enabling precision irrigation and nutrient application to conserve water and prevent runoff.
- Using AI and IoT-driven automation to reduce pesticide use and preserve ecological balance.
- Deploying blockchain traceability for ethical, sustainable supply chain management.
- Employing gene editing to develop climate-resilient crops for a changing environment.
Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting tool helps large agribusinesses and organizations monitor their environmental footprint in real time. This supports both compliance and tangible progress toward sustainability goals.
When we adopt these technologies at scale, the cumulative impact on our soil, water, climate, and global food security is transformational.
Farmonaut: Affordable Precision Agriculture for the World
Making the promise of advanced farming technologies affordable and accessible is at the core of Farmonaut’s mission. By relying on satellite data instead of expensive on-field hardware, Farmonaut’s platform ensures even small and medium-sized farmers can experience the benefits of precision agriculture.
- Crop Loan and Insurance Services – Satellite-based verification for streamlined farm loans and crop insurance, reducing fraud and improving access to credit.
- Blockchain Product Traceability – For food and textile companies seeking secure, trusted supply chains.
- Carbon Footprinting – Real-time monitoring and management of agricultural emissions for sustainability compliance.
- Large Scale Farm Management – Satellite and AI-powered tools for plantation managers and agribusiness heads.
Explore everything through Farmonaut’s Android, iOS, or web platforms for field-to-satellite precision monitoring.
AgTech Adoption Challenges and Barriers
Despite the compelling benefits, there are real-world challenges in the adoption of agricultural technology solutions:
- High Initial Investment: Many farmers struggle to finance new hardware/software systems, despite long-term savings.
- Technical Know-how: The complexity of advanced technologies can be daunting for those unfamiliar with digital tools.
- Connectivity Barriers: Limited or unreliable internet in rural areas hampers live data streaming and app usage.
- Cultural Resistance: A reluctance to change traditional practices may slow adoption.
- Data Security and Privacy: Concerns regarding the use and sharing of field data must be addressed.
To accelerate the broader adoption of AgTech, stakeholders must advocate for affordable pricing, supportive policies, targeted training and infrastructure improvements at local, regional, and global scales.
The Future of AgTech: What’s on the Horizon?
Looking ahead, the pace of innovation in agriculture shows no sign of slowing. As quantum computing, advanced AI, multispectral satellite fleets, and next-generation sensors mature, the scope for precision farming will expand dramatically.
- Increasing affordability and accessibility will bring precision technology within the reach of even the smallest farms.
- Sustainable practices will become the norm, driven by regulation and consumer demand for transparency and environmental care.
- The integration of real-time data with AI-powered advisories (like the Jeevn AI system) will further optimize every decision—from the soil up.
We believe the next decade will see collaborative, technology-driven communities of farmers building more productive, sustainable, and resilient food systems across every continent.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is precision agriculture and why is it important?
Precision agriculture is a data-driven approach to farm management that enables farmers to optimize resource application (water, fertilizers, pesticides) based on real-time field variability. It improves yields, efficiency, sustainability, and reduces input waste.
How do AI and machine learning enhance crop management?
AI in crop management analyzes diverse field datasets (weather, soil, satellite imagery) to predict diseases, detect pests, optimize inputs, and recommend tailored interventions, leading to improved productivity and reduced losses.
What role do drones play in agriculture?
Drones in agriculture provide aerial imaging to monitor crop health, identify problem spots, and assist in targeted spraying and data gathering—greatly improving the speed and effectiveness of interventions.
How does blockchain create transparency in agriculture?
Blockchain in agriculture supply chain records every transaction in an immutable ledger, ensuring authenticity and transparency for end-users while preventing fraud and enabling efficient market access.
How can smallholder farmers access precision agriculture?
Affordable, satellite-based tools like Farmonaut’s app and web platform provide real-time, actionable insights for smaller farms, eliminating the need for expensive hardware.
What is Farmonaut’s unique value proposition?
Farmonaut delivers real-time crop health monitoring, AI-based advisory, blockchain traceability, efficient farm management, carbon footprint tracking, and financing solutions—making advanced AgTech accessible worldwide.
Where can developers access satellite and weather datasets for agriculture?
Farmonaut’s API and developer docs provide direct, affordable access to satellite imagery and crop weather data.
What are key barriers to AgTech adoption?
Major barriers include high costs, technical literacy demands, poor rural internet, cultural resistance, and data security concerns.
Conclusion: A New Era for Agriculture
This is a watershed moment for agriculture. AgTech solutions—ranging from precision farming and automation to AI, IoT sensors, drones, blockchain, and gene editing—are fundamentally transforming how we approach the stewardship and productivity of our land. For farmers, agribusinesses, and policymakers, the adoption of advanced agricultural technologies is key to unlocking higher profitability, sustainability, and food security.
At Farmonaut, our mission is to make precision agriculture universal—affordable, accessible, and data-driven for every farmer on the planet.