Farming Process Steps: 10 Keys for High-Yield Crops
Introduction: Why Farming Process Steps Matter for High-Yield Crops
Farming is more than just planting seeds and waiting for the crops to grow. It’s a science, an art, and a complex process that involves expert management of soil, water, seeds, nutrients, and the entire farm ecosystem. Each step—from initial soil preparation to final harvesting and produce handling—significantly influences the quality, yield, sustainability, and profitability of your farm. In this hands-on, data-powered era, technologies like those provided by Farmonaut can amplify our decision-making at every stage, promoting sustainable farming and helping us thrive in competitive and changing agricultural markets.
Stepwise Comparison Table: Farming Process Steps for High-Yield Crops
| Step Number | Farming Process Step | Key Actions | Estimated Yield Improvement (%) | Brief Tips / Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Soil Preparation | Clearing debris, tilling, testing, and amending with organic matter | Up to 30% | Proper structure and fertility boost root penetration and crop health |
| 2 | Seed Selection & Sowing | Select disease-resistant seeds, optimize depth and spacing, use best method | Up to 25% | Quality seeds with ideal conditions increase success rates |
| 3 | Irrigation & Fertilization | Install drip/sprinkler systems, apply fertilizers as per soil test | 15-25% | Consistent moisture and tailored nutrients accelerate development |
| 4 | Weed & Pest Management | Routine removal, integrate biological and chemical controls judiciously | 10-20% | Prevents damage and resource competition, preserves yields |
| 5 | Crop Maintenance | Monitor growth, prune, thin and support plants as needed | 5-15% | Addresses stress/disease and enhances structure |
| 6 | Harvesting | Assess maturity, use proper methods and timing | 10-20% | Reduces waste and maximizes quality and returns |
| 7 | Post-Harvest Handling | Clean, sort, grade, and store produce effectively | 5-10% | Preserves product integrity for consumers and markets |
| 8 | Marketing & Distribution | Package, transport, and leverage diverse sales channels | 5-10% | Efficient product flow ensures higher profits |
| 9 | Soil Conservation & Sustainability | Adopt crop rotation, cover cropping, and minimum tillage | 15-25% (long-term) | Enhances soil fertility and resilience, prevents erosion |
| 10 | Record Keeping & Farm Management | Document inputs/outcomes, manage finances and innovations | 5-10% | Optimizes resources and supports continuous improvement |
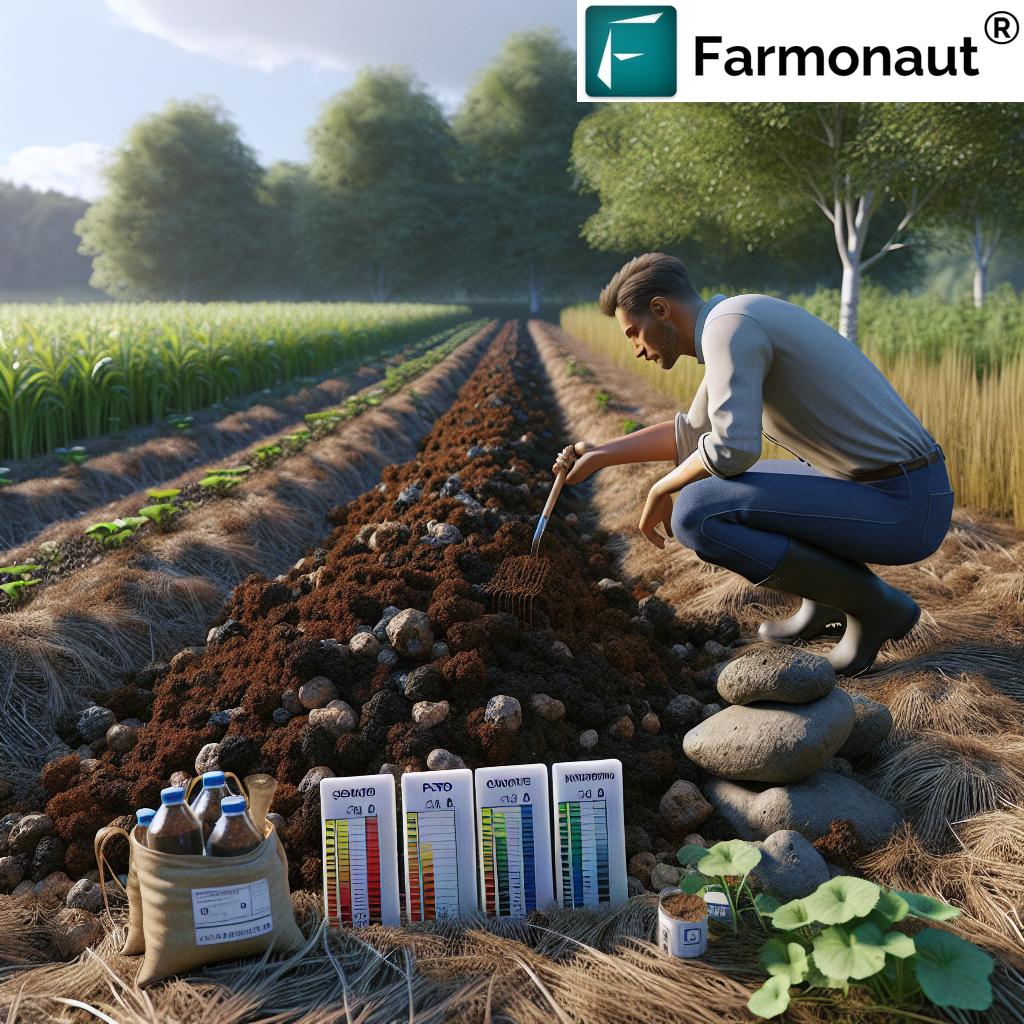
1. Soil Preparation for Farming: Building the Foundation
The first and most influential step in the farming process is soil preparation for farming. Quality soil forms the essential bedrock for healthy crops, optimal root penetration, and nutrient uptake. Let’s deconstruct this foundational process:
Key Actions in Soil Preparation:
- Clearing the Land: We begin by removing rocks, old vegetation, and all debris from the surface. This provides a clean workspace, prevents pest carryover, and ensures farm tools, plows, or tillers operate smoothly.
- Tilling: Using plows or tillers, we break up compacted soil to enhance its aeration and drainage. Proper tillage allows for better root penetration and easier sown seed germination.
- Soil Testing: We collect and analyze soil samples to measure nutrient content and pH levels. Accurate testing enables us to apply suitable amendments, maximizing future yield.
- Amending the Soil: We incorporate organic soil amendments such as compost and manure. This not only increases fertility, structure, and moisture retention, but also jumpstarts soil microbial life.
Optimized soil structure and tailored fertility guarantee strong plant establishment, early vigor, and damage resistance. Our process aligns perfectly with sustainable farming practices.
Tips & Examples:
- After removing all debris, we use deep tillage in clay soils but opt for shallow tillage where moisture needs conservation.
- Incorporating 20-30 tons of compost per hectare can significantly elevate organic matter—ideal for soil fertility improvement.
For ongoing soil analysis and moisture monitoring, Farmonaut’s satellite-based farm management platform provides real-time, field-level insights. These enable smarter irrigation and input applications, streamlining every aspect of soil preparation and farm management.
Unlock farm performance insights with the Farmonaut App and API-powered analytics (API Access).
2. Seed Selection and Sowing Methods for Productive Farms
Our choice of seeds forms the genetic base of our anticipated crop yields. The seed selection and sowing methods we employ directly impact plant health, resilience, and harvesting success rates.
Best Practices in Seed Selection & Sowing:
- Seed Selection: Choose only high-quality, clean, disease-free, and regionally adapted seeds. Hybrid and certified seeds improve germination, resist pest/disease damage, and enhance yield.
- Sowing Methods: Depending on our farm scale, we can use manual sowing (broadcasting or drilling), mechanized seed drills, or precise dibbling for larger seeds.
- Depth and Spacing: Each seed has its ideal planting depth and spacing for healthy roots and canopy development. Overcrowding leads to nutrient competition and increased pest risk.
Correct sowing practices and well-chosen seed varieties lay the basis for uniform, vigorous plant stands. This early uniformity is crucial for synchronized crop management and efficient use of water and nutrients.
Tips & Examples:
- Sow maize at 5cm depth with 25cm plant-to-plant spacing for best root penetration and yield outcomes.
- Always check local climate and rainfall patterns when choosing seed maturity length and sowing window.
Did you know? Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI advisory system analyzes satellite and climate data to empower us with the best seed selection and sowing recommendations for each field.
3. Irrigation and Fertilization Strategies for Consistent Crop Growth
Proper irrigation and fertilization strategies guarantee the right balance of moisture and nutrients at all crucial crop development stages. We must tailor both water and fertilizer delivery to crop type, stage, and soil conditions, always using soil test recommendations.
Common Practices:
- Irrigation: Use efficient drip irrigation or sprinkler systems to deliver precise amounts of water, thus preventing both drought stress and waterlogging.
- Fertilization: Apply fertilizers—both organic (like compost or manure) and inorganic NPK mixes—based on soil test results. Balanced nutrition supports steady growth, flowering, and high-grain or fruit set.
- Timing: Synchronize fertilizer application with plant nutrient uptake curves, especially during vegetative and reproductive phases for optimal outcomes.
Real-time advisories for fertilizer application and irrigation scheduling are available using Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring tools. Precision insights help conserve resources and prevent leaching or runoff, thus supporting both sustainability and profitability.
Examples:
- Installing drip irrigation can reduce water usage by up to 50% compared to flood watering and increase yields.
- Use split fertilizer doses—half during sowing, half at tillering or fruit setting—to maximize nutrient efficiency and reduce wastage.
Explore Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting module for data-driven resource management and improved environmental sustainability in your farm’s irrigation and fertilization system.
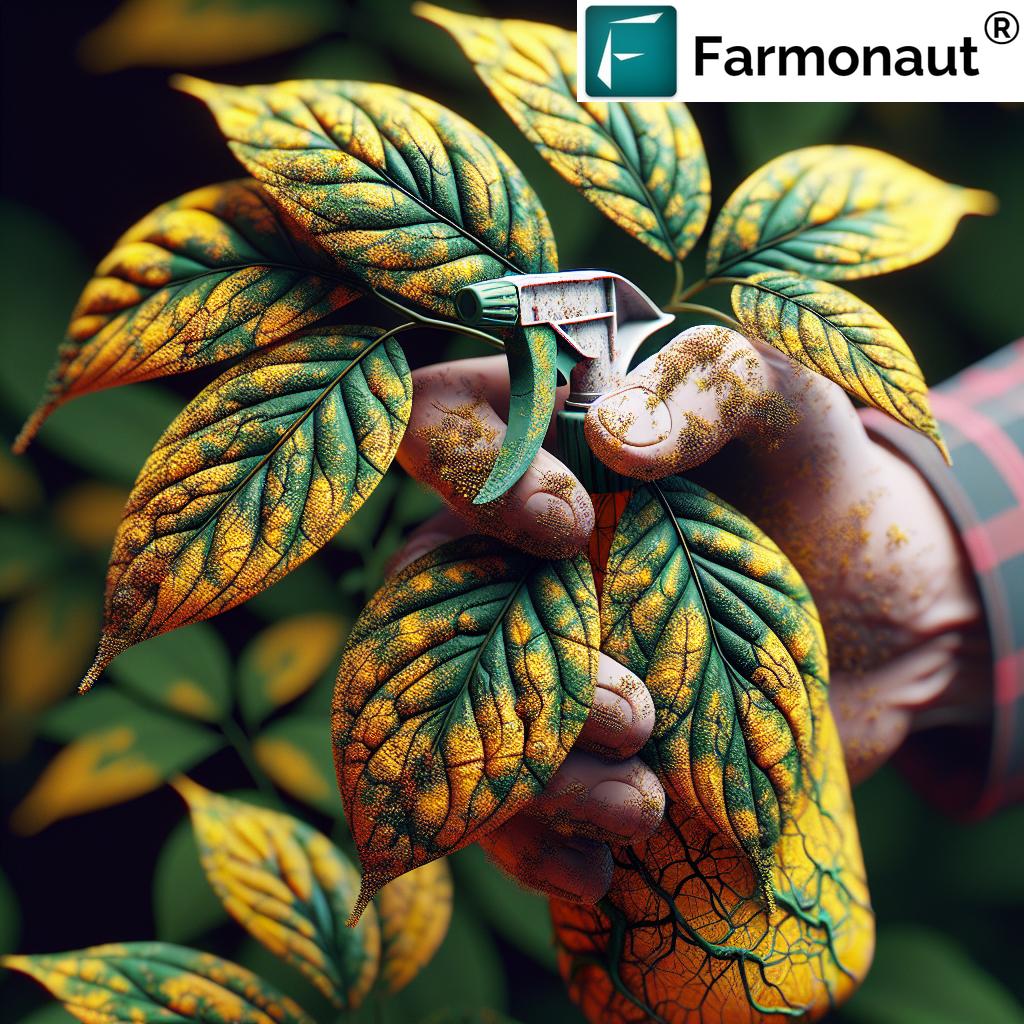
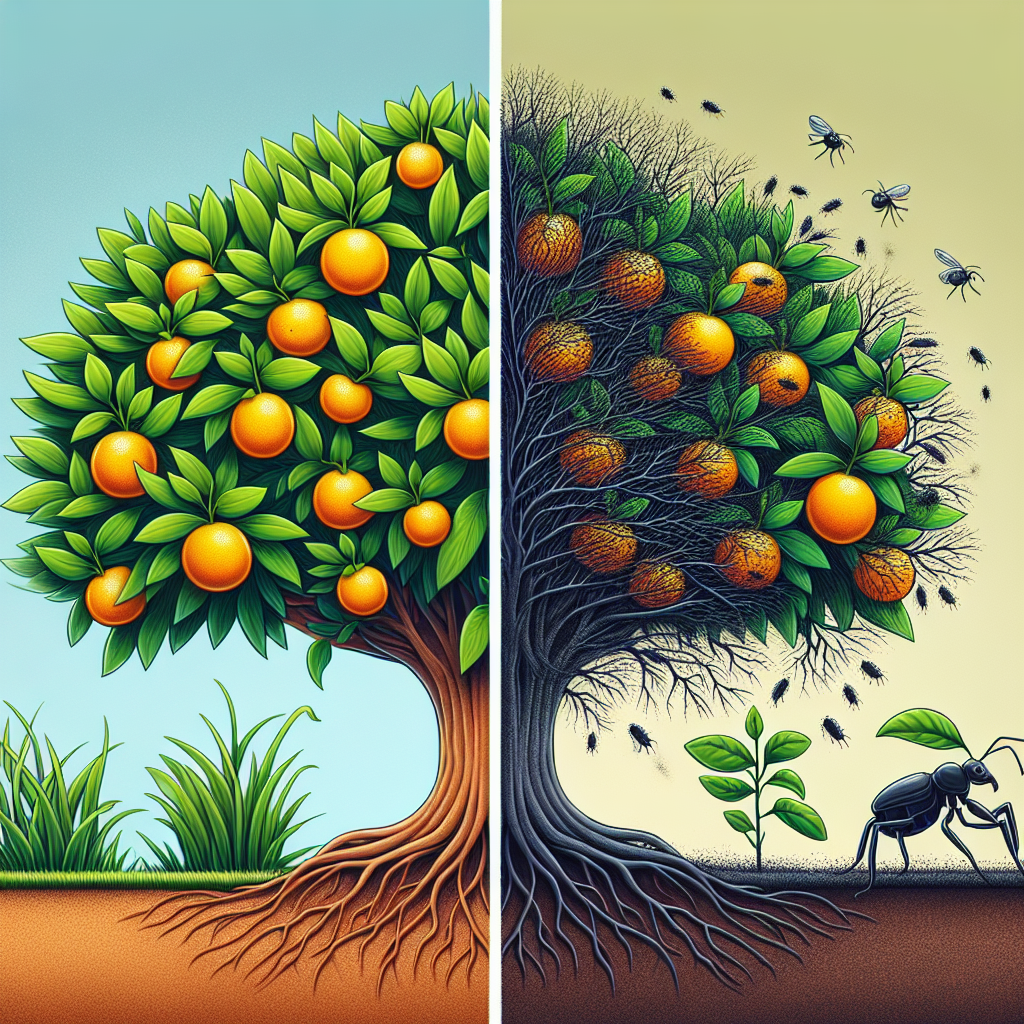
4. Weed Control in Agriculture & Crop Pest Management
Strong weed control in agriculture and proactive crop pest management are vital for attaining top yield and preserving crop quality. Weeds and pests compete with plants for water, sunlight, and nutrients or directly cause damage via feeding, disease transmission, or contamination.
Strategies for Managing Weeds and Pests:
- Weeding: Perform timely mechanical or manual removal, especially in early crop stages when competition is most damaging.
- Pest Control: Use Integrated Pest Management (IPM), which combines resistant varieties, crop rotation, biological controls, and judicious chemical pesticide use.
- Monitoring: Early detection with field scouting and satellite-based health monitoring (like Farmonaut offers) can guide targeted pest interventions and protect beneficial insects.
Consistent weed and pest suppression minimizes input wastage, increases usable produce, and upholds sustainable farming practices.
Examples:
- Rotating legumes with cereals breaks pest cycles and naturally suppresses weed populations.
- Using neem-based organic insecticides protects crops while preserving pollinator health.
With Farmonaut’s AI-based crop advisory, you receive real-time alerts and pest/disease risk maps for targeted, eco-friendly action.
5. Crop Maintenance for Optimal Yield and Health
Routine crop maintenance bridges the gap between planting and harvest, ensuring plants remain healthy, productive, and resilient. Proactive management here often distinguishes average fields from exceptional ones.
Essential Crop Maintenance Activities:
- Monitoring Growth: Visual inspection and satellite crop health monitoring spot stress, disease, or nutrient deficiencies early.
- Pruning and Thinning: Remove diseased shoots/branches to enhance air, reduce pest risk, and permit optimal light penetration and development.
- Supporting Plants: Use stakes, trellises, or nets to prevent lodging and maximize fruit or grain set, particularly in vine, fruit, and tall cereal crops.
Farmonaut’s farm management solution offers continuous plant growth progressions using satellite imagery. Satellite-powered monitoring sharply reduces labor costs and ensures nothing escapes our attention—even on the largest farms!
Tips:
- Thin dense seedling patches in pulses/vegetables to maintain ideal stand density for airflow and higher yield.
- Prune tomato and grapevines to boost sunlight access and fruiting success.
Enhanced field-level monitoring with Farmonaut’s Large Scale Farm Management Tools helps us scale crop maintenance best practices for every hectare we oversee.
6. Harvesting and Post-Harvest Handling for Premium Quality Produce
The harvesting and post-harvest handling phase determines actual realized yields and final produce quality. Precision in timing, methods, and handling prevents avoidable damage and value loss.
Key Stages:
- Maturity Assessment: Use visual cues, moisture meters, and test threshing/picking to pinpoint optimal maturity for each crop.
- Harvesting Methods: Employ hand tools for sensitive produce (fruits, vegetables) and machinery for grains. Minimize delays to limit pest or weather harm.
- Post-Harvest Handling: Quickly clean, sort, and grade produce. Discard anything with visible disease or pest damage. Store in temperature or humidity-controlled environments as needed to maintain shelf life.
Farmonaut’s blockchain-based traceability tools ensure that from farm to consumer, each stage of produce movement remains transparent and accountable.
Examples:
- For rice and wheat, harvest at 20–22% grain moisture for maximum yield and milling quality.
- Handle perishable vegetables with padded carts to avoid bruising and microbial contamination.
Track and secure your post-harvest chain with Farmonaut’s Product Traceability for complete supply chain confidence.
7. Marketing and Distribution of Farm Produce
Reaching consumers efficiently is essential for maximizing profit and minimizing waste. Modern marketing and distribution strategies link farmers directly to lucrative markets while protecting produce integrity.
Important Steps:
- Packaging: Choose formats that prevent bruising, extend shelf life, and visually appeal to buyers.
- Transportation: Deploy fast, well-planned logistics from field to market, using a combination of family labor, rented vehicles, or—on large farms—fleet management systems.
- Sales Strategies: Engage in direct sales, contract farming, or farmer co-ops to command better prices and secure stable demand streams.
Farmonaut provides digital resource and route planning (Fleet Management Tools) for logistical precision, lower costs, and better market access.
Tips:
- Use stackable crates for tomatoes, cucumbers, and fruits to reduce transport damage.
- Implement scheduled harvest and delivery runs to meet regional market peak demand windows.
8. Soil Conservation and Sustainable Farming Practices
Championing sustainable farming practices and soil conservation isn’t just an ethical move—it’s a smart productivity investment. Healthy soils support higher long-term crop yield and resilience to erratic weather.
Core Sustainability Strategies:
- Conservation Tillage / No-Till Farming: Limit soil disturbance to retain organic matter and moisture, as outlined in no-till farming best practices.
- Cover Cropping: Plant cover crops like clover or vetch in off-seasons to shield soil from erosion, suppress weeds, and enhance soil fertility.
- Crop Rotation Techniques: Alternate crop species over seasons to diversify nutrient use, break pest cycles, and naturally regenerate soil.
With satellite soil monitoring and carbon tracking, Farmonaut supports farm-wide adoption of sustainable agricultural methods and long-term productivity metrics.
Examples:
- Rotate cereals with legumes to naturally fix nitrogen and improve soil structure in the next cycle.
- Grow cover crops during monsoons or winters to protect bare soil and enhance moisture retention.
9. Record Keeping and Farm Management: Driving Continuous Improvement
“What gets measured, gets managed.” Record keeping and farm management are indispensable for sustained farm profitability and innovation.
Good Practices:
- Documentation: Keep detailed records of sowing dates, irrigation events, fertilizer and pesticide applications, and harvest yields.
- Financial Management: Track input costs and output sales—not just to monitor profits, but also to inform future investments and risk management.
- Continuous Learning: Stay updated via field results, extension bulletins, and modern agritech tools like Farmonaut AI advisories.
Digital records help scale up, comply with food safety requirements, and secure crop loans or insurance. For easier farm management, access crop loan & insurance eligibility verification modules on the Farmonaut platform.
10. Farmonaut: Technology Support for Each Farming Process Step
Agricultural technology is our greatest ally for implementing every step of high-yield farming effectively, affordably, and at scale. Farmonaut’s precision agriculture platform makes it possible for us to:
- Remotely monitor soil moisture and crop health in real time for thousands of fields, guiding exact irrigation and fertigation events.
- Utilize the Jeevn AI advisory system for climate-smart recommendations—from best sowing dates to disease and pest preventive actions.
- Track all stages of produce journey using secure blockchain traceability, enabling credible farm-to-consumer confidence.
- Save time and cut losses with fleet and logistics optimization, streamlined via mobile and web apps accessible from anywhere.
- Choose from flexible, scalable subscription packages based on farm size and operational needs.
The Farmonaut platform is available on Web, Android, iOS, and can even be integrated into existing apps or business systems through Farmonaut API.
We farm smarter, easier, and more sustainably with Farmonaut—empowering our pursuit of quality, traceability, and sustainability at every step.
Farmonaut Subscription Plans
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the first crucial step in the farming process for high yield?
The foundation of any successful crop is meticulous soil preparation, which includes clearing, tilling, soil testing, and adding organic amendments like compost or manure. These steps help boost soil fertility, structure, and long-term yield potential.
How important is seed selection and what are the best sowing methods?
Selecting high-quality, climate-suited seeds is critical to maximizing harvest success. Use sowing methods like precise drilling, proper depth, and optimal spacing for uniform emergence and growth. This prevents nutrient competition and reduces loss.
How does Farmonaut help in pest management and resource optimization?
Farmonaut provides AI-powered advisories and satellite-based crop monitoring for early detection of pest risks, soil deficiencies, and weed outbreaks. This enables timely and targeted intervention, conserving resources and boosting yields.
What role does sustainable farming play in the crop production process?
Sustainable farming practices like minimal tillage, crop rotation, and cover cropping protect long-term soil health and fertility while reducing input needs and environmental impacts. These practices are central to enduring farm productivity.
Can I integrate Farmonaut with my existing farm management system?
Yes! Farmonaut offers a robust API for data integration. Developers can reference full documentation at API Developer Docs.
How can Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting tool help my farm?
Farmonaut’s carbon footprint tracking gives real-time emission data, helping you cut inputs, qualify for sustainability certification, and reduce your environmental impact. Learn more at Farmonaut Carbon Footprinting.
How do I start using Farmonaut resources?
Download the Farmonaut app on Google Play or App Store, access the web platform, or use the API for scalable satellite-powered farm management.
Conclusion: Achieve High-Yield Crops with Stepwise Process and Smart Tools
The journey from seed to harvest is intricate—each farming process step intricately linked with the next, determining final yield and farm sustainability. By focusing on quality soil preparation, diligent seed selection and sowing, targeted irrigation and fertilization, robust crop protection, and post-harvest handling, we can unlock far higher outputs and profits. Embracing digital platforms like Farmonaut supercharges every step, making precision agriculture a reality—whether you manage a single plot or thousands of hectares.
Let’s build a future where our crops are healthier, the environment is cared for, and sustainability is at the core of every harvest.