Wheat Risk Management: 7 Shocking Profit Strategies!
“Over 60% of wheat yield losses globally are due to unmanaged climatic risks—effective strategies can double profit margins.”
Introduction
Wheat farming is not just a pillar of global agriculture; it’s an intricate journey fraught with challenges and uncertainties. As we navigate the landscapes of wheat farming risk management, we witness how threats like climatic volatility, pest invasions, market fluctuations, and evolving regulations directly impact our yields and profitability. In today’s world—where sustainability and resilience are more critical than ever—adopting effective strategies is not a luxury but a necessity for every wheat grower.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll unravel the primary risks associated with wheat cultivation and reveal seven shocking profit strategies. We combine real-world experience with advanced tools, spotlighting the pivotal role of Farmonaut’s satellite-based farm management solutions in making cutting-edge precision agriculture accessible and affordable. Our actionable insights and data-driven approaches will empower all of us—whether smallholder or large-scale producer—to mitigate threats, enhance yields, and build a sustainable farming future.
Join us as we decode the art and science of wheat risk management, and discover how to thrive amidst the ever-shifting landscapes of modern agriculture.
Climatic Risks in Wheat Production
When it comes to wheat farming risk management, climatic factors are at the forefront. Wheat’s growth and ultimate yields are critically sensitive to the environment. Major threats such as abrupt temperature variations, prolonged drought, excessive rainfall, and harmful frost events can have devastating impact—sometimes wiping out entire harvests. For instance, unexpected drought spells can reduce germination rates and hinder seedling growth, while heavy rains may cause waterlogging, root diseases, and severe soil erosion.
Strategic Management Approaches:
- Wheat Variety Selection Strategies: It’s essential to opt for varieties with specific resistance—such as those tolerant to drought or those with a shorter maturation period—to mitigate the unpredictable effects of weather patterns.
- Soil Management Practices: Implementing proper drainage systems helps prevent waterlogging and unwelcome erosion, directly supporting root health and yield improvement.
-
Advanced Weather Forecasting Tools: By utilizing farm management solutions like Farmonaut, we can access real-time meteorological data, allowing us to anticipate adverse weather events. This empowers us to make timely decisions regarding planting and harvesting.
For developers: Integrate live weather data with your own systems using Farmonaut’s API or explore full documentation at API Developer Docs.
By weaving these strategies into our management approach, we boost resilience against climatic risks in wheat production, optimizing both yields and profitability.
Pest and Disease Risks: Managing Wheat Diseases and Pests
Pests and diseases pose one of the most persistent threats in wheat farming. Fusarium head blight, notorious for mycotoxin contamination, and aphid infestations—which worsen by spreading destructive viruses—can devastate wheat fields almost overnight. As farming becomes more intensive, so too do pest and disease challenges.
Integrated Pest Management in Wheat (IPM)
IPM is our gold standard.
- Combine Biological and Chemical Controls: We blend biological methods (like natural predators), cultural practices (such as crop rotation), physical actions (e.g., manual weed removal), and responsible chemical application to protect crops without over-reliance on pesticides.
- Resistant Varieties: Choosing wheat varieties with resistance genes against common threats is a highly effective, long-term disease management strategy.
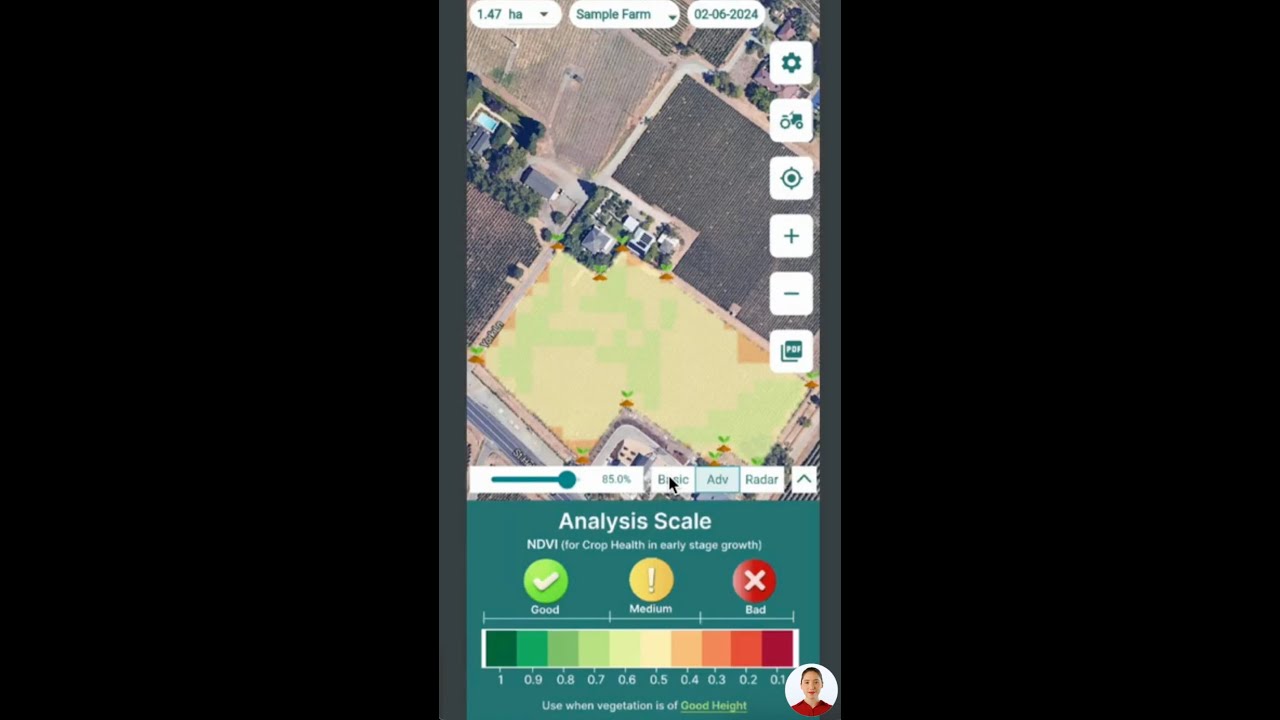
- Regular Monitoring and Rapid Response: Frequent field checks using real-time monitoring tools, like Farmonaut’s large-scale farm management platform, enable us to detect early pest or disease symptoms and respond rapidly—often saving the crop.
-
Farmonaut Crop Health Monitoring: We can visualize vegetation health and detect pest hotspots using Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop health monitoring. NDVI and soil moisture mapping help us take immediate action to limit damage and optimize inputs.
Learn more about Farmonaut’s web app for large-scale wheat farm monitoring
By implementing these approaches, we significantly reduce losses from pests and diseases—steering our wheat farming toward greater profitability and sustainability.
Price and Market Risks: Strategies for Dealing with Wheat Price Fluctuations
Market volatility and wheat price fluctuations are ongoing threats to our financial security as farmers. Changes in global trade policies, exchange rate shifts, and supply-demand imbalances can rapidly erode income, making risk management essential.
Key Market Risk Strategies:
- Forward Contracts & Agreements: By locking in future prices, we stabilize income and reduce exposure to sharp market swings.
- Futures and Options Contracts: These financial instruments allow us to hedge against unfavorable price movement, providing a formal structure for managing market uncertainty.
- Diversification: To avoid over-dependence on wheat revenue, we can cultivate additional crops or invest in value-added processing (like flour milling). This spreads risk across products and markets.
- Farmonaut’s Blockchain Traceability: Want to build premium markets or ensure transparent supply chains? Farmonaut’s blockchain-based product traceability solution enables us to demonstrate quality, origin, and compliance—often earning higher returns.
These strategies empower us to face price fluctuations head-on—making wheat farming a more stable and rewarding venture.
Operational Risks in Wheat Farming
Operational issues—like labor shortages, equipment breakdowns, and logistical failures—can halt production, delay deliveries, and increase costs, making operational risk management a priority for wheat farmers.
Solutions to Operational Challenges
- Training and Development: Investing in education for ourselves and our teams enhances adaptability and efficiency, especially when dealing with evolving technologies and complex equipment.
- Preventive Maintenance: Scheduling regular equipment maintenance reduces breakdowns during critical farming periods and maximizes machinery life.
- Supply Chain Management: Robust planning for input sourcing, harvest delivery, and market access is essential to maintain smooth operations. Farmonaut’s Fleet and Resource Management module helps us track and optimize the use and location of agricultural machinery—improving timeliness and cutting costs.
- Harvest Scheduling with Satellite Data: Advanced monitoring platforms like Farmonaut help us monitor wheat maturity and schedule harvesting for peak yield and quality.
Financial Risks: Financial Strategies for Wheat Farmers
The ever-increasing costs of seeds, fertilizer, and fuel—combined with fluctuating revenue—demands sharp financial acumen. Financing solutions and cost control are vital for wheat farm profitability.
Effective Financial Risk Management Approaches:
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Diligent record-keeping and forecasting help us anticipate cash flow gaps, plan investments, and set realistic revenue targets.
- Resource Efficiency: Leveraging satellite data from Farmonaut, we track soil moisture and crop health to reduce wasteful input use. This directly cuts operating costs and improves yields.
- Access to Credit: Establishing relationships with lenders or using Farmonaut’s crop loan and insurance verification services makes it easier to secure loans or insurance, often with better terms thanks to transparent farm data.
- Farmonaut Carbon Footprinting: Monitoring and minimizing emissions through Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting service can help us comply with regulations, qualify for sustainability programs, and—for climate-conscious buyers—command premium prices.
By implementing these financial strategies, we boost both our economic security and environmental responsibility.
Regulatory & Policy Risks in Wheat Cultivation
Continual shifts in agricultural policies, environmental laws, and trade agreements can upend our best-laid farm plans. Whether it’s limits on agrochemicals, changing subsidies, or new export tariffs, policy dynamics require us to be vigilant and adaptive.
Navigating Regulatory and Policy Risks:
- Policy Monitoring: Stay regularly informed about pending laws affecting farming, so we can make timely shifts in crop choice, input use, or compliance protocols.
- Compliance Programs: Build robust systems to ensure environmental and safety standards are always met—this can mean the difference between maintaining market access or losing it due to infractions.
- Stakeholder Engagement: By being active in industry associations or agri-networks, we help influence policy in ways favorable to sustainable and profitable wheat cultivation.
-
Farmonaut’s Blockchain Traceability Tools: Our transparent and tamperproof records of input use and production practices—enabled by Farmonaut—make compliance and auditing much simpler, offering a competitive advantage in increasingly regulated markets.
Explore Blockchain Traceability in Agriculture
Technological Risks in Wheat Farming
While adopting new technological solutions (like sensors and farm management platforms) brings benefits, it also presents certain risks: high upfront costs, potential obsolescence, and the learning curve associated with unfamiliar tools.
Key Strategies for Technological Risk Management
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Assess each new tool’s ROI. Affordable, scalable solutions—like Farmonaut’s satellite-based platform—often provide outsized value, especially compared to capital-intensive ground systems.
- Training Programs: Continuous education is vital. Staying up to date with best practices and platform features ensures full return on investment.
- Scalability: Prioritize technologies that can grow with us. Farmonaut allows us to start with a single field and expand, so our technological upgrades always match farm size and budget.
- API Integration: Tech-savvy farmers and agribusinesses can connect Farmonaut’s data feeds to existing apps using its comprehensive API—futureproofing our data infrastructure.
Thoughtful evaluation, staff training, and adaptable solutions are the keys to leveraging technology without exposing ourselves to unnecessary risk.
Environmental Risks & Sustainable Wheat Farming Practices
The future of wheat depends on how well we manage environmental risks: soil degradation, water scarcity, and the accelerating impacts of climate change. Our response must be both immediate and far-sighted.
Strategies for Sustainability and Environmental Risk Reduction:
- Adopt Sustainable Practices: Conservation tillage, rotation with legumes, and organic amendments restore soil health and organic matter—reducing erosion and boosting yields over time.
- Efficient Water Management: Techniques like targeted irrigation, soil moisture monitoring (with Farmonaut’s satellite analytics), and rainwater harvesting help us make every drop count.
- Climate Adaptation: Integrate wheat yield improvement techniques proven in local conditions, such as earlier planting or new cultivars, to buffer against shifting weather trends.
- Track & Reduce Farm Emissions: Monitor your carbon footprint and meet regulatory demands—or just improve sustainability branding—using Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting service.
Embedding sustainable wheat farming practices into our operations isn’t just good for the planet—it also supports long-term profitability and regulatory compliance.
“Sustainable wheat farming practices can reduce input costs by up to 30%, significantly improving long-term financial resilience.”
Wheat Risk Management Strategies Comparison Table
To help us compare risk management approaches at a glance, we present this comprehensive table. It highlights specific wheat cultivation challenges, effective management strategies, estimated quantitative benefits, and their sustainability impacts.
| Risk Factor | Management Strategy | Estimated Yield Improvement (%) | Sustainability Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drought | Drought-tolerant wheat variety selection, moisture-efficient irrigation, real-time weather forecasting | 12–25% | High |
| Excessive Rainfall & Waterlogging | Improved drainage, raised bed planting, advanced soil monitoring | 8–15% | Medium |
| Pest & Disease | Integrated Pest Management (IPM), resistant cultivars, biological controls, remote crop health monitoring | 10–22% | High |
| Price Fluctuation | Forward contracts, diversification, futures/options trading | 5–18% (income stability) | Medium |
| Operational Disruption | Training, preventive equipment maintenance, digital fleet/resource management | 7–14% | Medium |
| Financial Constraints | Accurate budgeting, input efficiency via precision tools, access to satellite-based loan verification | 9–20% | High |
| Regulatory Change | Policy monitoring, compliance systems, blockchain traceability solutions | 3–8% (risk avoidance) | High |
| Soil Degradation | Conservation tillage, organic amendments, crop rotation | 10–16% | High |
| Technological Risk | Incremental tech adoption, ongoing training, modular/scalable platforms | 6–12% | Medium |
Harnessing Precision Tools: Farmonaut’s Role in Wheat Farming Risk Management
As the pressures of wheat cultivation challenges increase, modern technology becomes not just helpful—but essential. Farmonaut’s platform stands out by providing cost-effective, advanced solutions tailored to each risk on our list:
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: With NDVI and soil moisture metrics, we can track wheat health from emergence to harvest, spot stress early, and optimize inputs.
- Weather and Advisory Integration: Farmonaut’s AI-driven Jeevn Advisory provides ultra-local weather forecasts and farm-specific alerts, guiding crucial decisions on planting, irrigation, and pesticide application.
-
Blockchain Traceability: Secure, transparent records of crop origin, input use, and handling—ideal for meeting high-value buyer and export requirements.
Learn how traceability builds trust in agri-supply chains - Resource, Fleet, and Emissions Management: From fleet management to carbon footprinting, Farmonaut equips us to operate more efficiently—and more sustainably—than ever before.
- Scalability and Accessibility: Whether our farm is 1 hectare or 10,000 hectares, Farmonaut’s web, Android, iOS, and API solutions scale to our needs—and our budget.
Farmonaut Subscription Options
Ready to access precision-driven wheat risk management tools? Farmonaut’s flexible subscription plans put advanced satellite and AI technology in your hands—affordably and efficiently. Suitable for individuals, agribusinesses, cooperatives, and government institutions.
FAQ: Wheat Risk Management
What is wheat farming risk management?
Wheat farming risk management refers to the systematic identification, assessment, and mitigation of risks in wheat cultivation—including climatic, pest & disease, market, financial, and operational challenges. Effective management ensures stable yields and profitability, even in volatile environments.
How do sustainable wheat farming practices impact profitability?
Adopting sustainable practices—like conservation tillage, soil health monitoring, and efficient water use—reduces input costs, increases yields, and minimizes risk from environmental changes. In the long run, these measures significantly boost financial resilience and resource sustainability.
Which tools are most effective for managing wheat diseases and pests?
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategies—supported by digital crop health monitoring, resistant varieties, and regular field surveys—reduce pesticide dependency and curb losses from pests and diseases. Digital solutions like Farmonaut offer real-time monitoring and early warning capabilities.
Can technology help with wheat price fluctuations?
While technology can’t control global market prices, it enables precise yield forecasting, blockchain traceability for premium market access, and efficient resource use for maximum profitability despite market volatility.
What are the top three strategies to improve wheat yields?
- Variety Selection: Choose high-yielding, disease- and climate-resilient wheat varieties.
- Timely, Data-Driven Decisions: Use real-time weather and crop health data for planting and management.
- Sustainable Soil & Water Practices: Conserve and restore soil organic matter and maintain optimal moisture throughout the growing season.
Conclusion
Wheat farming, at its core, is the art of navigating risk—a dynamic balancing act between nature, markets, regulation, and technology. As we’ve explored throughout this guide, the spectrum of wheat cultivation challenges can be approached methodically: from smart wheat variety selection and integrated pest management in wheat to robust financial strategies and enduring sustainable wheat farming practices.
By embracing precision agriculture tools like those offered by Farmonaut—anchored in satellite monitoring, AI-driven insight, blockchain traceability, and scalable resource management—we are better equipped to optimize yield, secure long-term profitability, and champion the stewardship of our soils and environment.
The path of modern wheat farmers is challenging but also full of possibility. Through ongoing education, informed risk management, and continuous innovation, we can transform potential pitfalls into powerful opportunities for growth, resilience, and sustainability.
Let’s cultivate a profitable, resilient, and sustainable future—together.