Regenerative Farming Methods: 7 Shocking Soil Secrets
“Regenerative farming can increase soil organic matter by up to 21% in just five years.”
- Introduction: Setting the Soil Stage
- Core Principles of Regenerative Farming
- Regenerative Farming Methods: 7 Shocking Soil Secrets
- Comparative Overview Table
- Benefits of Regenerative Farming
- Farmonaut: Empowering Regenerative Agriculture
- Challenges and Considerations
- FAQs: Regenerative Farming Uncovered
- Conclusion: Building a Living Legacy With Soil
Introduction: Setting the Soil Stage
Regenerative agriculture is taking root as a revolutionary approach to modern farming—one that doesn’t just sustain, but restores and rejuvenates ecosystems from the ground up. At the heart of this movement is the understanding that healthy soil is more than just a medium in which we plant crops; it’s a dynamic, living ecosystem that supports productivity, resilience, and sustainability.
Unlike conventional farming, which often relies on intensive tillage and chemical inputs that deplete soil fertility and harm beneficial organisms, regenerative farming practices focus on increasing soil organic matter, improving biodiversity, and creating sustainable farming systems. By transitioning to methods that nurture the Earth rather than exploit it, we aim to address environmental challenges such as climate change, pest outbreaks, and food security.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve deep into the powerful secrets hidden beneath our feet—exploring the seven most shocking soil revelations that regenerative farming can unleash, and showing how new technologies from companies like Farmonaut are accelerating the transition to a more eco-friendly agricultural future.
Core Principles of Regenerative Farming
The core principles of regenerative agriculture are the golden threads that weave together a new, vibrant tapestry of farming. These principles are simple but profound, and when combined, they build resilient, productive ecosystems that thrive year after year. Let’s examine these guiding lights more closely:
- Minimizing Soil Disturbance: Reducing tillage preserves soil structure, boosts water retention, and supports beneficial soil organisms essential for health and productivity.
- Maintaining Soil Cover: Keeping the soil covered with vegetation or organic materials protects against erosion, retains precious moisture, and nourishes the life within.
- Enhancing Biodiversity: Introducing a variety of plant and animal species through crop rotation, intercropping, or agroforestry supports resilience, natural pest control, and enriches nutrient cycling.
- Integrating Livestock: Managed rotational grazing strategies recycle nutrients, stimulate plant growth, and naturally control pests with livestock inclusion.
- Promoting Nutrient Cycling: Composting, responsible manure management, and cover cropping techniques return nutrients to the land, reducing dependency on synthetic fertilizers and supporting organic nutrient cycling.
When applied holistically, these principles not only improve soil health and structure but also increase farm biodiversity, minimize resource wastage, and promote sustainability and climate resilience in farm systems.
Regenerative Farming Methods: 7 Shocking Soil Secrets
Now, let’s reveal the seven transformative secrets buried beneath the surface—each a regenerative farming method proven to improve soil health, enhance fertility, and boost biodiversity in sustainable farming systems. These soil secrets are powerful tools, allowing us to build back better from the ground up.
“Fields using cover crops show a 50% boost in earthworm populations, enhancing soil fertility naturally.”
1. No-Till and Reduced Tillage: Preserving Soil Structure and Life
Excessive tillage—the mechanical breaking and overturning of soil—may suppress weeds for a season, but it comes at a high price. Tillage destroys soil structure, exposes organic matter to oxidation, and disrupts the delicate web of beneficial organisms like fungi, bacteria, and earthworms. These impacts reduce fertility and leave soil vulnerable to erosion and drought.
With no-till or reduced tillage practices, we allow the soil ecosystem to thrive. Intact soil structure preserves moisture, supports root penetration, and promotes efficient nutrient cycling. Furthermore, this approach greatly reduces erosion during heavy rains and wind events, conserving the precious topsoil we rely on for food production.
- Main benefit: Improved soil health, structure, and resilience to climate extremes.
- Best when combined with: Cover cropping techniques and residue management.
2. Cover Cropping: Nature’s Blanket for Fertility and Biodiversity
Bare soil is a recipe for disaster—leaving it exposed triggers erosion, dries out the land, and robs it of its organic matter. Cover cropping techniques involve planting a variety of non-harvested crops (such as legumes, grasses, and brassicas) during fallow periods or after the main crop is removed. These living roots continue to feed soil organisms year-round.
A healthy cover prevents erosion, maintains soil structure, and retains moisture. Even more remarkably, carefully chosen covers (like clover or vetch) fix atmospheric nitrogen into the soil and help break pest and disease cycles. Over time, cover cropping significantly increases soil carbon, boosts microbial diversity, and supports the ecosystem as a whole.
- Main benefit: Enhanced nutrient cycling and dramatic increases in organic matter.
- Key support for: Reducing dependency on synthetic fertilizers and improving crop rotation benefits.
3. Crop Rotation and Diversification: Breaking the Pest and Disease Cycle
Growing the same crop in the same field year after year invites soil exhaustion and attracts a host of pests and diseases specific to that crop. Crop rotation—alternating between different plant species with varying nutrient needs and rooting depths—breaks these cycles and restores balance.
Rotation benefits go beyond mere pest control: alternating crops (grains, legumes, oilseeds, and cover crops) enhances biodiversity, improves fertility, and strengthens resilience to climate shocks. As an added bonus, rotational diversity feeds a wider range of beneficial organisms, increasing the ecosystem’s productivity and ability to recover from stress.
- Main benefit: Healthier, more fertile soils and increased yields over time.
- Pairs well with: Cover cropping and reduced tillage for holistic regeneration.
4. Agroforestry: Trees and Shrubs as Soil Saviors
Integrating trees and shrubs into agricultural fields transforms traditional plots into diversified, multistory agroforestry systems. These woody perennials serve as windbreaks, shade providers, and homes for wildlife—significantly increasing biodiversity and stabilizing microclimates.
[Trees help protect against erosion](https://betterground.org/on-your-land/farms-and-rural-living/regenerative-agriculture/?utm_source=openai), keep soil moist and cool, and drop organic matter through leaf litter. This new structure supports life above and below ground, and the diverse products (fruit, nuts, timber, honey, forage) offer new revenue streams.
- Main benefit: Diversified production, enhanced soil health, and greater ecosystem resilience.
- Best adopted alongside: Managed grazing and permanent ground cover for maximum benefit.
5. Managed Grazing: Livestock as Partners in Regeneration
Traditional, continuous grazing often depletes pastures and compacts soil, but managed rotational grazing transforms livestock into allies for soil regeneration. By moving animals frequently among subdivided paddocks, we mimic natural herd movements. This prevents overgrazing, allows vegetation to recover, and distributes manure evenly, enhancing soil fertility and structure.
The inclusion of livestock in regenerative systems also helps recycle nutrients and control weed pressure naturally, reducing the need for chemical inputs. When well-executed, such grazing methods increase carbon sequestration, promote organic nutrient cycling, and support greater biodiversity, laying the groundwork for long-term sustainability.
- Main benefit: Improved soil structure, fertility, and a richer web of soil organisms.
- Boosted by: Integrating with diverse cropping and agroforestry systems.
6. Composting and Manure Management: Recycling Nature’s Nutrients
Waste from plants and animals is not a problem in regenerative systems—it’s an opportunity! Composting converts organic residues into nutrient-rich amendments, while responsible manure management ensures that nutrients return to the soil efficiently and safely.
By utilizing compost, we stimulate beneficial microbial activity, accelerate the breakdown of residues, and avoid the pollution often associated with synthetic fertilizer runoff. Manure, when applied correctly, builds soil carbon and fosters biological activity, closing the loop between plants, livestock, and people in sustainable agriculture.
- Main benefit: High-quality organic matter for soil, further reducing reliance on external chemical fertility inputs.
- Critical for: Balanced nutrient cycling across diversified farm systems.
7. Fostering Beneficial Soil Organisms: The Invisible Engine of Productivity
Regenerative agriculture wouldn’t be possible without the often-unseen army beneath our boots. Bacteria, fungi, earthworms, and a host of micro- and macro-organisms transform dead plant matter into life-supporting nutrients and help stabilize soil structure. Their activities support pest control, disease suppression, and nutrient uptake.
Regenerative farming focuses on minimizing chemical disturbance, maintaining organic residues, keeping living roots year-round, and avoiding compaction—all to foster this underground diversity. Healthy populations of beneficial soil organisms not only drive ecosystem services but act as an insurance policy for future climate variability.
- Main benefit: Enhanced resilience, improved yields, and natural pest and disease suppression.
- Amplified by: All previous regenerative methods working in concert.
Comparative Overview Table: 7 Regenerative Methods and Their Impacts
| Method | Description | Estimated Impact on Soil Organic Matter (%) | Estimated Increase in Biodiversity (%) | Environmental Benefit Highlight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No/Reduced Tillage | Minimizes soil disturbance to preserve structure and microbial life. | +15–21% | +10–13% | Prevents erosion and water loss, stabilizes soil surface. |
| Cover Cropping | Uses non-cash crops to shield, feed, and enrich soil between main crops. | +18–20% | +30–33% | Reduces erosion, enhances fertility, supports earthworm populations. |
| Crop Rotation | Alters crop species and families across seasons for natural pest and disease break. | +12–15% | +24–26% | Improves nutrient cycling, reduces input needs, balances food webs. |
| Agroforestry | Integrates trees/shrubs into crop/livestock systems for diversified ecosystems. | +19–21% | +35–40% | Stabilizes microclimates, increases carbon sequestration, boosts resilience. |
| Managed Grazing | Rotates livestock for nutrient cycling and prevents overgrazing. | +15–18% | +20–23% | Enhances fertility, control weeds, strengthens belowground diversity. |
| Composting & Manure Management | Turns organic waste into fertility gold; reduces synthetic fertilizer reliance. | +12–16% | +9–11% | Enriches soil, avoids pollution, supports beneficial microorganisms. |
| Fostering Beneficial Soil Organisms | Protects the underground food web through organic practices and residue cover. | +21% | +50% | Powers natural nutrient cycling and soil self-repair mechanisms. |
Benefits of Regenerative Farming: Why Go Regenerative?
Adopting regenerative farming practices isn’t just good for the environment—it’s an effective, proven path to sustainable prosperity for farmers, their communities, and the planet.
Let’s break down the multifaceted benefits of regenerative farming:
-
Improved Soil Health and Water Retention:
Enriched organic matter and diverse microbial communities enhance soil’s ability to absorb and retain water. This means resilient crops in times of drought and less soil runoff during storms. -
Increase Farm Biodiversity and Crop Resilience:
Biodiverse ecosystems built through crop rotation, cover cropping, and agroforestry systems encourage natural balance, break pest/disease cycles, and support pollinators and wildlife. -
Climate Change Mitigation:
By restoring organic carbon to the soil, regenerative methods naturally sequester atmospheric CO2, helping to combat climate change while improving yields. -
Economic Resilience & New Market Opportunities:
Diverse, regenerative farms are less reliant on expensive external inputs, produce multiple value-added products, and open doors to premium markets (e.g., certified organic and eco-branded goods). -
Reduced Erosion and Depletion:
Intact soil structure and year-round cover prevent erosion, slow depleting processes, and build the foundation for future generations. -
Enhanced Nutrient Cycling and Fertility:
Active management of compost, cover crops, and rotations reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers, closes nutrient loops, and keeps resources on the farm.
Regenerative agriculture’s climate benefits are amplified by modern monitoring:
Discover Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting tool. This enables farms to track, verify, and optimize their carbon sequestration, proving sustainability to partners and consumers—and meeting new environmental standards with real-time data.
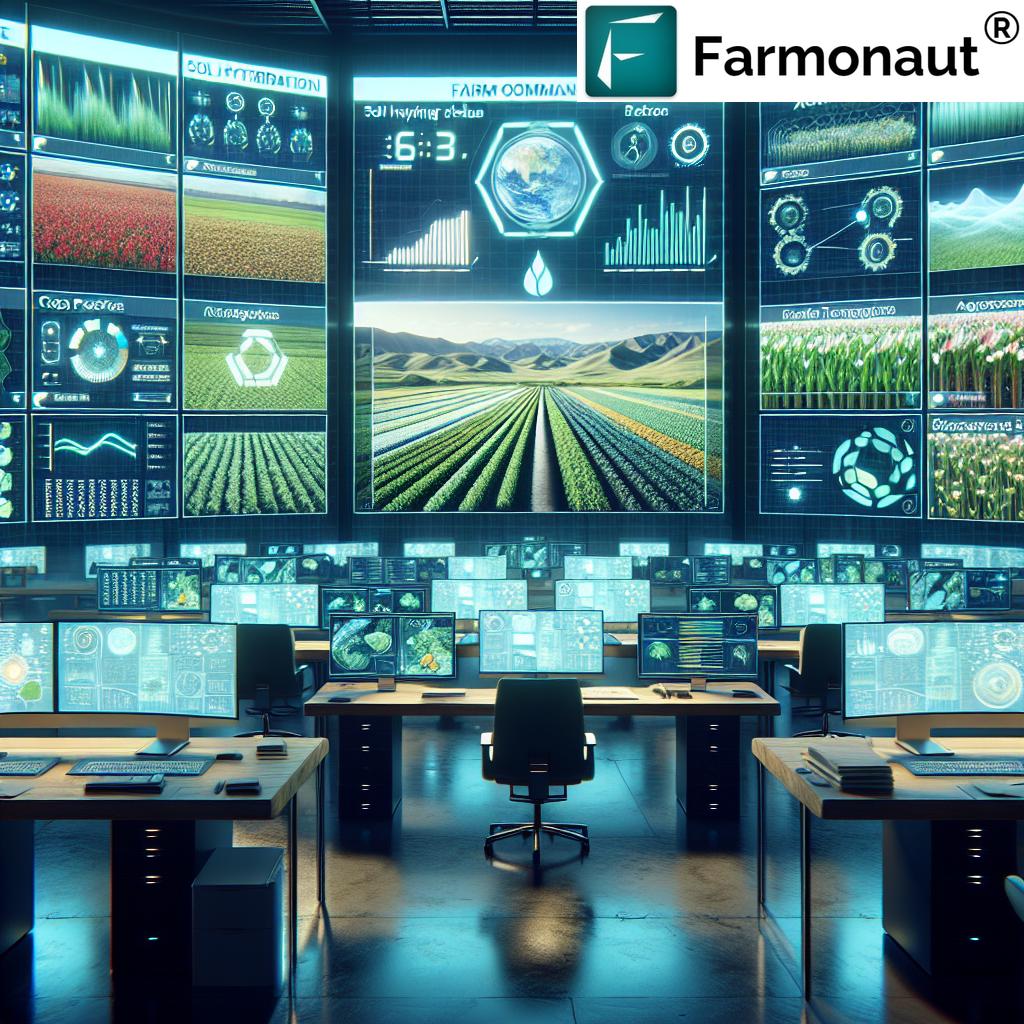
Farmonaut: Empowering Regenerative Agriculture With High-Tech Insights
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to making regenerative farming accessible, affordable, and evidence-based. Our mission aligns perfectly with the soil-first spirit of the regenerative movement, and our suite of digital solutions helps farmers monitor, analyze, and improve soil health, crop performance, and resource use.
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: We utilize advanced satellite imagery to assess crop health (NDVI), soil moisture, and real-time field conditions, enabling optimized irrigation, fertilization, and pest management for all types of regenerative fields.
- AI-Driven Farm Advisory (Jeevn AI): Our Jeevn AI system delivers hyper-local, personalized insights and weather forecasts to guide every farming decision transparently and efficiently. This service is especially useful for regenerative practices, as it provides actionable advice for cover cropping, tillage, and nutrient cycling.
-
Blockchain Traceability: With our blockchain platform, you can offer buyers and consumers full traceability and trust in your eco-friendly, regenerative produce. This feature is also essential for export compliance and access to organic and green markets.
Learn more:
Farmonaut Traceability Solutions -
Resource, Fleet & Large-Scale Farm Management:
We streamline everything from field and fleet logistics to crop production records, helping large and small farms stay efficient, compliant, and eco-conscious.
Explore Farmonaut for Large Scale Farm Management -
Access and Integration: All our services are available via Android & iOS apps, web platforms, and API endpoints—making scalable, data-driven regenerative farming a reality for everyone.
– API Access: Farmonaut Satellite & Weather API
– Developer Docs: API Developer Documentation
Ready to see regenerative farming in action? Download Farmonaut’s free apps:
Challenges and Considerations in Regenerative Transition
While regenerative farming offers a world of benefits, the road to transformation can involve a few bumps. Here are the major challenges—and our recommendations:
-
Transition and Learning Curve:
Moving away from conventional practices may result in temporary yield reductions or the need for initial investment in training and equipment. However, these are often short-lived and outweighed by long-term gains in soil health and profitability. -
Economic Barriers:
The cost of implements for reduced tillage, cover cropping seed, fencing for managed grazing, or compost facilities can be substantial. Farmonaut’s satellite and digital tools help reduce guesswork and maximize every rupee invested. -
Knowledge and Community Support:
Success in regenerative transition depends on ongoing support, access to data, training, and farmer-to-farmer knowledge exchange. -
Measuring Benefits and Compliance:
Documenting and verifying the environmental and productivity gains from regenerative transitions can be challenging. With Farmonaut’s real-time monitoring and blockchain-based validation, farmers can confidently demonstrate their sustainable practices to stakeholders and regulators alike.
To address these hurdles, we recommend using advanced farm management and satellite monitoring solutions, like those from Farmonaut, alongside joining local regenerative agriculture communities and taking advantage of available training resources.
Financing your regenerative transition? Explore how Farmonaut’s Crop Loan & Insurance Verification makes it easier to secure funding, using satellite-backed transparency for fast, fair, and fraud-free loan and insurance approvals.
FAQs: Regenerative Farming Uncovered
What is regenerative farming and how does it differ from organic or conventional farming?
Regenerative farming is an approach to agriculture focused on restoring and enhancing the health of soil and farm ecosystems. Unlike organic farming (which primarily avoids synthetic chemicals) or conventional farming (which often entails intensive tillage and chemical inputs), regenerative practices actively improve soil, enhance biodiversity, and increase ecosystem resilience.
How can regenerative farming improve soil health?
By minimizing soil disturbance, keeping it covered, rotating crops, and incorporating organic materials, regenerative agriculture encourages the buildup of organic matter and the proliferation of beneficial soil organisms. This leads to better fertility, structure, and water retention over time.
Are cover crops and crop rotations necessary for small farms?
Absolutely. Cover cropping and crop rotation are scalable practices suitable for farms of all sizes. Even small plots see large gains in fertility, biodiversity, and pest control when these methods are used.
What support or technology is available for monitoring progress?
Tools like Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop health monitoring and carbon footprinting solutions allow all farmers to precisely track field conditions, soil health, and sustainability gains—enabling data-driven decisions and verifiable reporting.
Can regenerative farming practices increase my farm’s resilience to climate change?
Yes! Methods like reduced tillage, cover cropping, agroforestry, and managed grazing all contribute to improved water management, enhanced soil structure, and carbon sequestration, making your farm more adaptable to shifting weather patterns.
Where can I access resources and connect with regenerative farming experts?
Farmonaut’s digital platforms offer real-time data, AI-based advisory, and practical support for farmers at every step of the regenerative journey, whatever your crop or farming system.
Conclusion: Building a Living Legacy With Soil
Regenerative agriculture isn’t a fad—it’s a proven blueprint for transforming our relationship with the land and building lasting ecological, economic, and social abundance. By embracing the seven shocking soil secrets revealed here, we nurture not just crops, but communities, water cycles, and entire ecosystems.
With advanced monitoring and analysis tools from platforms like Farmonaut, every farmer has the power to transition to a new era of sustainable productivity and environmental stewardship. It’s time for us all to help restore, regenerate, and thrive—with healthy soil as our foundation.
Unlock the full potential of your soil and join the regenerative revolution today, powered by technology and guided by nature.
Looking for custom advice for plantation crops or agroforestry models?
Visit Farmonaut’s Forest & Plantation Crop Advisory for AI-powered insights tailored to growing trees, shrubs, and perennial systems successfully.