Sustainability: Climate Resilient Farming for 2025
“By 2025, climate-resilient farming could boost global food production by up to 17% despite changing weather patterns.”
Sustainability in agriculture is increasingly recognized as a cornerstone for securing food systems amid the mounting challenges posed by climate change, environmental degradation, and a rapidly increasing global population. As we advance into 2025 and beyond, there’s an urgent need for both a deeper understanding of sustainable practices and rapid action to integrate climate resilient farming into agricultural systems worldwide.
In this comprehensive guide, we explore what is sustainability in agriculture, why climate resilience is vital for our future food security, and how soil, water conservation, technology, and community-centered approaches can help us achieve a more productive, equitable, and resilient agricultural sector.
What is Sustainability in Agriculture?
When we talk about sustainability — what’s that — climate resilient agriculture comes to mind. But what is sustainability in agriculture, and how does it differ from traditional models?
- Sustainable agriculture refers to farming practices that meet current food and fiber needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet theirs.
- It integrates environmental health, economic profitability, and social equity, creating systems that are productive yet conserve natural resources.
- This means using methods that protect soil, water, and biodiversity while minimizing pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
- These holistic systems strive for a balance—feeding present populations while preserving our planet for the future.
The Concept of Climate-Resilient Agriculture (CRA)
CRA—or climate resilient agriculture—is a forward-thinking approach that focuses on adapting to and mitigating the adverse impacts of climate change. As extreme weather events—such as droughts, floods, and heatwaves—become more frequent and intense, building agricultural systems that can withstand climate shocks is essential.
- It combines traditional knowledge with innovative technologies to enhance the tolerance of both crops and livestock to climatic stresses.
- CRA is not stand-alone; it’s a vital part of sustainability and conservation efforts within agriculture.
To summarize, climate resilient farming is both about adaptation—preparing for risks and uncertainties—and mitigation—reducing negative impacts on the environment.
Intersecting Sustainability and Climate Resilience
Where sustainability and climate resilience intersect, we find climate resilient sustainable agriculture. This approach goes beyond simply enduring climate shocks; it is about reducing the ecological footprint of agriculture, enhancing productivity, and making the sector more robust against future risks.
- Practices like agroforestry, conservation tillage, crop diversification, and integrated pest management lead to better ecosystem functions and minimize vulnerability to climate risks.
- This intersection creates a sustainable, productive, and environmentally sound agricultural pathway for the years ahead—including 2025 and far beyond.
- Climate resilient sustainable agriculture ensures farms thrive while preserving soil, water, and biodiversity for generations.
Key Principles and Practices of Climate Resilient Sustainable Agriculture
- Soil Health Management: Maintaining and restoring soil organic matter, using cover cropping and organic amendments, and minimizing tillage to enhance fertility and water retention.
- Water Conservation and Management: Efficient irrigation; rainwater harvesting; watershed management to ensure sustainable use of water resources.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Encouraging crop diversification, integrated farming systems, and agroforestry for a more stable ecosystem.
- Renewable Energy: Incorporating solar-powered irrigation, biogas, and other alternatives to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
- Technology and Innovation: Using digital tools, satellite monitoring, AI-advisories, and blockchain for real-time, data-driven farming decisions.
- Social and Economic Inclusion: Empowering smallholder farmers, promoting fair trade, and building community-led resource management for equity in agriculture.
Comparative Table: Traditional vs. Climate-Resilient/Sustainable Practices
| Farming Practice | Traditional Method | Climate Resilient/Sustainable Method | Estimated Impact on Yield (%) | Estimated Water Savings (%) | Soil Health Improvement (Scale 1-5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crop Selection | Monoculture; Cash crop focus | Diversification; Stress-tolerant/indigenous varieties | +5–10% | 0–10% | 3 |
| Irrigation | Flood or furrow irrigation | Drip/sprinkler systems; Rainwater harvesting | +10% | 20–35% | 4 |
| Fertilizer Use | Heavy chemical fertilizer reliance | Organic compost; Integrated nutrient management | +3–7% | 5–15% | 5 |
| Soil Conservation | Conventional tillage | Minimum/reduced tillage; Cover cropping | +10–15% | 10–20% | 5 |
| Pest Management | Chemical pesticides | Integrated pest management; Biological controls | +2–5% | 5–10% | 4 |
“Sustainable agriculture practices can reduce water usage by 30% while maintaining soil health and ecosystem productivity.”
Farmonaut: Advancing Climate-Resilient Sustainable Agriculture with Technology
At Farmonaut, we believe that climate resilient farming and sustainability can—and must—coexist with productivity and profitability for farmers everywhere. Our solutions leverage a unique mix of satellite imagery, artificial intelligence, and blockchain to empower farmers and agribusinesses to:
- Monitor soil health, crop condition, and resource usage in real time
- Get AI-driven advisories and weather forecasts to anticipate climate risks
- Adopt carbon footprinting to quantify and reduce greenhouse gas emissions; See our Carbon Footprinting Solutions
- Ensure product traceability across the supply chain from field to fork with Blockchain Traceability Tools
- Digitally manage resources and equipment fleets for optimized operations
- Access our technology via Web, Android, and iOS Apps—see links below:
Our platform also offers robust API access for seamless integration and advanced developer documentation.
Soil Health Management: Foundation of Sustainable Farming
The condition of our soil is central to sustainability in agriculture. Without healthy soil organic matter, no farming system can be truly productive, resilient, or climate-friendly.
Why Soil Health is Critical
- Soil organic matter acts as a natural sponge, enhancing water retention—crucial during droughts and dry spells.
- Increased soil fertility leads to better crop yields and healthier plants, cutting the need for chemical inputs and reducing pollution.
- Resilient soils absorb shocks from floods and extreme weather events, a key resilience-building strategy in 2025.
Best Soil Health Practices
- Adopting conservation tillage and cover cropping
- Applying organic amendments such as manure and compost
- Crop rotation and diversification to break pest-disease cycles and enhance soil biodiversity
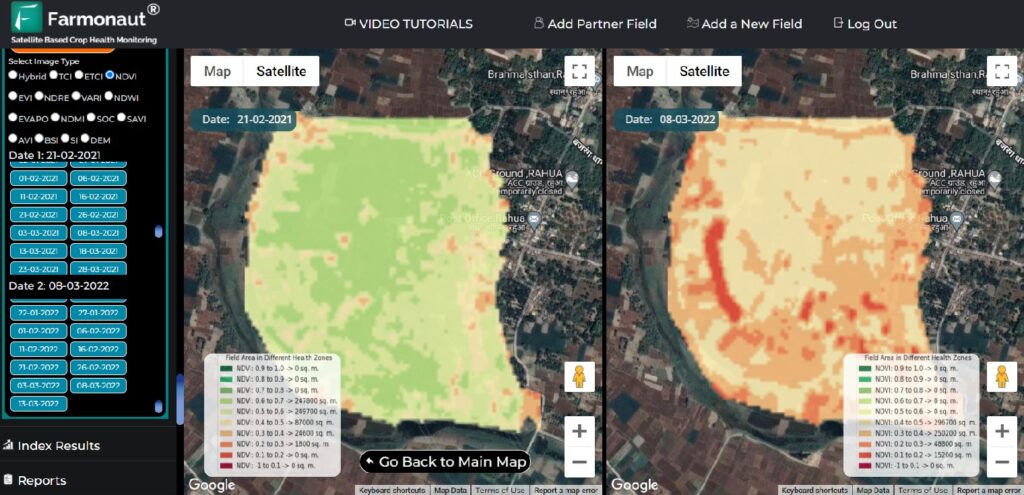
Satellite data, like ours, enables real-time monitoring of soil moisture and organic matter changes, giving farmers actionable insights for management improvements.
Water Conservation and Management Techniques
In 2025 and beyond, water conservation stands as a pillar of climate resilient sustainable agriculture. With water resources under stress from overuse and erratic rainfall, sustainable irrigation and rainwater harvesting become non-negotiable.
Key Water-Smart Practices
- Efficient irrigation systems (drip, sprinkler) deliver water directly to roots—reducing waste by up to 35%.
- Rainwater harvesting and watershed management ensure water availability during dry spells.
- Monitoring water productivity using advanced technology helps optimize use and secure future access for all.
- Farmonaut Large-Scale Farm Management tools streamline water usage across the enterprise.
The convergence of water efficiency and data-driven decisions in 2025 agriculture ensures we meet the needs of growing populations without compromising environmental integrity.
Biodiversity and Integrated Systems for Resilience
Biodiversity conservation is fundamental to sustainability in agriculture. Farms rich in plant, insect, and microbial diversity are far more resilient to climate shocks, pest outbreaks, and market volatility.
- Crop diversification and mixed livestock-crop systems minimize risk and stabilize production.
- Agroforestry—the strategic integration of trees, crops, and sometimes livestock—enhances ecosystem functions and can sequester carbon, boosting soil health and water retention.
- Integrated pest management uses natural predators, biological controls, and crop rotation to reduce reliance on external chemical inputs.
Integrated, biodiverse ecosystems SEQUESTER more carbon, support pollinators, and ensure year-round productivity—even as climate variability increases.
Renewable Energy, Emissions, and Carbon Footprinting
A vital part of climate resilient sustainable agriculture is minimizing the sector’s greenhouse gas emissions. By 2025, renewable energy and carbon footprinting become industry standards.
- Solar-powered irrigation pumps and biogas digesters replace fossil fuel-based power sources, cutting emissions & operational costs.
- Farmonaut Carbon Footprinting gives agribusinesses real-time insights to monitor, report, and reduce emissions, ensuring compliance with environmental standards and responding to consumer demand for greener food.
- Carbon sequestration methods including cover cropping, perennial planting, and soil regenerative techniques.
The resulting footprint reduction is crucial for farm viability—and for our planet’s health.
Technology and Innovation for Climate Resilient Farming in 2025
The future of farming is digital, interconnected, and data-driven. Technology is pivotal to climate resilient sustainable agriculture, offering tools for proactive risk management, real-time monitoring, and knowledge-sharing.
- Satellite-based crop and soil health monitoring—such as the Farmonaut platform—delivers live updates on NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index), water stress zones, and pest hotspots.
- AI-powered advisory services generate weather alerts, customized crop/livestock management plans, and pest/disease predictions.
- Transparent blockchain-based traceability ensures authenticity and trust across the agri-food value chain. Learn more about Farmonaut Traceability Solutions.
- Resource and fleet management tools reduce wasted inputs, improve safety/logistics, and optimize energy usage.
In 2025, these technological breakthroughs are fundamental, not optional, for climate resilient farming.
Social and Economic Dimensions: Empowering Farmers & Communities
Lastly, truly sustainable agriculture addresses not only the environment, but the social and economic wellbeing of those who produce our food.
- Smallholder farmers need better access to credit, insurance, and digital education/training. Affordable solutions such as Crop Loan and Insurance make this possible.
- Community engagement and embracing local/traditional knowledge create more resilient farming systems, ensuring practices are both relevant and practical.
- Economic incentives—like carbon credits, sustainable certification, and better market access—reward farmers adopting climate-smart practices.
- Gender equity, fair labor, and social inclusion are non-negotiable for ethical and effective sustainability.
Future Outlook: Securing Food, Ecosystems, and Water
By 2025, the intersection of sustainability and climate resilient farming will define competitive, productive, and equitable agricultural sectors globally. As models predict more erratic weather, shrinking resources, and increasing pressure to feed the world, urgent action across all fronts—policy, private innovation, education, and on-ground change—is critical.
- Farmers and agribusinesses must be empowered with knowledge, finance, and digital tools.
- Policy frameworks should incentivize sustainable land use, diversification, water stewardship, and emissions reduction.
- Consumers should support brands and supply chains that prove transparency and ecological integrity.
- Innovative technologies (like those of Farmonaut) will underpin global progress towards sustainability and resilience.
Farmonaut Subscription and App Access
Ready to monitor, manage, and scale your climate-resilient farm operations in 2025? Farmonaut provides affordable, pay-as-you-grow subscriptions for everyone—from smallholders to governments to food brands.
FAQ: Sustainability & Climate-Resilient Agriculture
What is sustainability in agriculture?
Sustainability in agriculture refers to farming practices that fulfill current food and fiber needs without compromising the resources and environment needed by future generations. It means maintaining soil, water, and biodiversity health while achieving economic efficiency and social equity.
What are climate-resilient agriculture practices?
Climate-resilient agriculture includes practices like crop diversification, conservation tillage, integrated pest management, efficient irrigation, rainwater harvesting, agroforestry, and the adoption of renewable energy. These help farms adapt to and mitigate adverse impacts of climate change.
How does soil health management build resilience?
Healthy soil with abundant organic matter retains water better, supports stable crop yields, and resists droughts, floods, and other climate extremes. Managing soil health is foundational to all sustainable farming efforts.
Why is water conservation essential for sustainable farming in 2025?
Water resources are under increasing pressure from population growth and climate change. Conservation efforts—like efficient irrigation and rainwater harvesting—ensure enough water for food production without degrading environments or future supplies.
How does Farmonaut help in sustainable agriculture?
We provide advanced, satellite-based monitoring, real-time AI advisories, resource management, and blockchain-based traceability. Our tools help farmers and agribusinesses make data-driven decisions, reduce waste, increase yields, and lower emissions for a more sustainable and resilient agricultural future.
Can sustainable agriculture really boost yields?
Yes. By improving soil, water, and pest management, sustainable agriculture can maintain or even boost yields, often with lower input costs and increased resilience to climate shocks, according to global research and projections for 2025.
What is the role of technology in climate resilient sustainable agriculture?
Technology is crucial: satellites, AI, and big data enable precise monitoring, forecasting, and advisory, allowing decision-making to be responsive and effective, thus maximizing resilience while minimizing environmental footprints.
Sustainability in agriculture means building systems that produce food efficiently—now and in the future—while protecting soil, water, and biodiversity. Integrating climate resilient farming ensures our farms, communities, and ecosystems flourish amid climatic uncertainty. As we move further into 2025, climate resilient sustainable agriculture is not simply a recommendation; it is a necessity for a food-secure and environmentally sound planet.
Take your first step towards a climate-resilient, data-driven future with Farmonaut today!