Table of Contents
- Introduction: Sustainable Wheat Farming & Soil Health
- The 7 Shocking Soil Secrets in Sustainable Wheat Farming
- Comparative Benefits: Sustainable vs. Conventional Wheat Farming
- Farmonaut’s Role in Sustainable Wheat Farming
- Challenges and Implementation Considerations
- FAQs about Sustainable Wheat Farming
- Conclusion: Paving the Way for Sustainable Futures
“Sustainable wheat farming can reduce chemical fertilizer use by up to 50%, significantly improving long-term soil health.”
Sustainable Wheat Farming: 7 Shocking Soil Secrets!
As our global demand for wheat continues to rise, so does our responsibility to ensure its production remains environmentally sound, socially responsible, and economically viable. Sustainable wheat farming offers a transformative approach by focusing on practices that enhance soil health, conserve water, reduce chemical inputs, and promote biodiversity. By adopting this balance-centered approach, we not only safeguard our own future food security but also ensure the vitality of our farmlands for the generations to come.
The practice of sustainable wheat farming is rooted in stewardship—harmonizing cutting-edge agricultural techniques with traditional wisdom. This creates dynamic systems that do more than just maximize wheat yields; they actively improve soil structure, preserve organic matter, and minimize ecological impact. Let’s unlock the seven shocking soil secrets that underpin the future of sustainable wheat production!
The 7 Shocking Soil Secrets in Sustainable Wheat Farming
At the core of sustainable wheat farming are seven pivotal “soil secrets”—proven principles and methods that drastically enhance fertility, conserve resources, and future-proof wheat production. We explore these secrets in-depth, sharing how embracing them creates a winning strategy for our environment, economy, and society.
“Fields using sustainable practices show up to 30% higher soil biodiversity compared to conventional wheat farms.”
#1 Conservation Tillage Practices – The Foundation of Soil Stewardship
Conservation tillage stands at the heart of sustainable wheat farming, offering a complete paradigm shift from traditional intensive tilling. Where conventional tillage can cause erosion, organic matter loss, and decreased soil fertility, conservation methods such as no-till and reduced-till preserve the soil’s inherent structure.
- Zero tillage can reduce soil erosion by up to 90% and enhance water infiltration by 50%.
- Leaving crop residues on the field improves organic matter levels, feeding beneficial soil organisms and enhancing nutrient cycles.
- A stable soil structure means stronger wheat root systems, improved water retention, and greater resistance to drought.
By minimizing disturbance, we support an active soil food web—bacteria, earthworms, fungi, and other organisms work together naturally to breakdown residues, fix nutrients, and maintain long-term fertility.
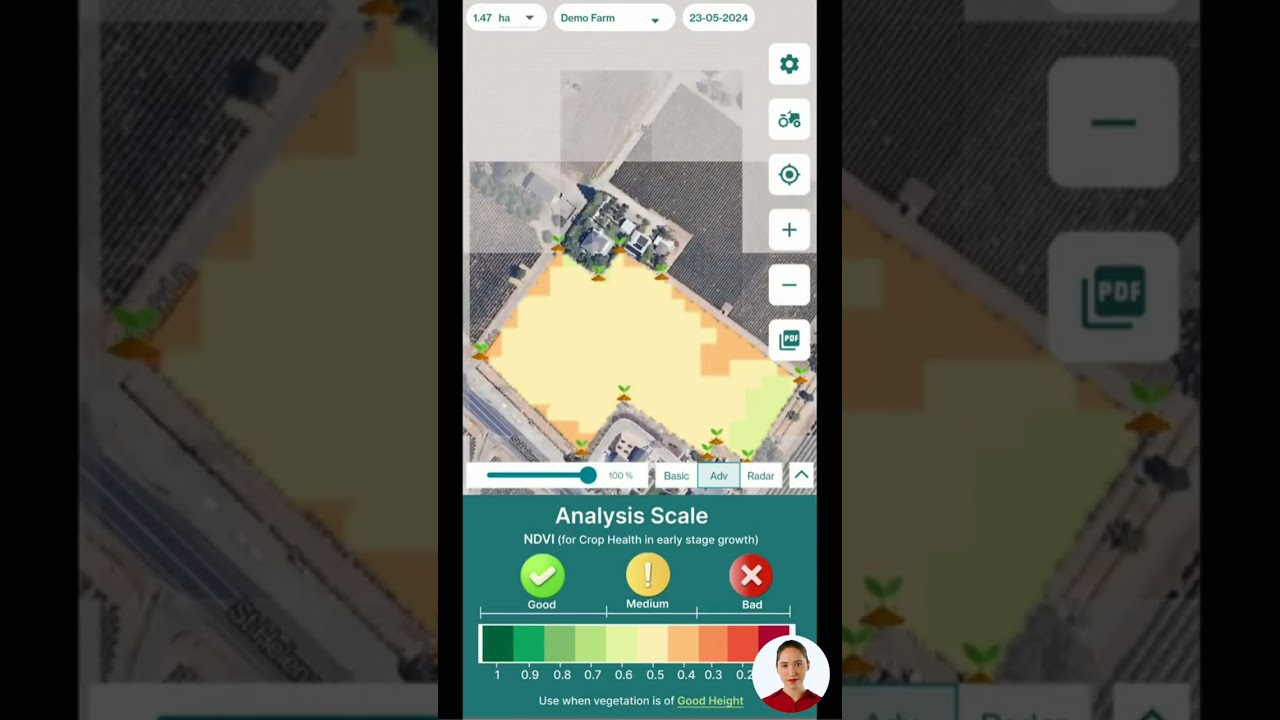
Implementing these conservation tillage practices is made easier with modern digital tools. Farmers can track their progress and monitor external changes using advanced technologies. For example, satellite apps like Farmonaut offer crucial large scale farm management analytics, supporting smart tillage choices with real-time soil health data and soil moisture indices.
#2 Crop Rotation and Diversification – Strengthening Soil’s Natural Balance
The power of crop rotation lies in its ability to break the cycles of pests and disease while naturally boosting nutrient availability. Crop rotation benefits include higher soil fertility, reduced need for synthetic fertilizers, and increased biodiversity. Here’s how:
- Growing wheat in rotation with legumes such as beans or peas encourages nitrogen fixation, enriching the soil, and cutting dependency on chemical inputs.
- Intercropping systems foster a variety of beneficial insects and microbes, making the system more resilient to environmental shocks.
- Diversity in crops not only improves soil structure but also supports pollinators and stabilizes yields across variable climate conditions.
Leveraging digital tools and advisory services allows us to design diverse crop plans and spot disease outbreaks with greater accuracy. Advanced traceability systems further guarantee that our sustainable crops can be managed, documented, and certified through blockchain-backed records.
Fact: Multi-year studies indicate that fields practicing rotation and diversification host up to 30% more soil biodiversity than monocultures—improving nutrient cycling, crop resilience, and overall soil vigor.
#3 Integrated Pest Management for Wheat – Smart, Balanced Defense
Integrated pest management (IPM) is our secret weapon for reducing chemical pesticide reliance while maintaining crop health. This ecologically sound approach combines biological, cultural, physical, and chemical tools:
- Monitoring pest populations—using data-driven scouting and sensors—helps us implement control measures only when needed, protecting beneficial insects and minimizing disruption.
- Natural control agents—such as predators, parasitoids, and microbial solutions—are prioritized over chemicals.
- Cultural methods like shifting planting dates or rotating varieties break pest and disease cycles naturally.
- Targeted pesticide use occurs only as a last resort and at reduced doses compared to conventional practices.
With real-time data from satellite and sensor platforms, we get immediate alerts about potential pest outbreaks, supporting rapid, precise responses. Platforms such as Farmonaut provide scalable:
- Real-time crop health monitoring for early pest/disease detection,
- AI-based pest management advice, and
- Custom reporting for smarter pesticide application.
By consistently integrating IPM for wheat, we significantly reduce chemical inputs in farming, protecting both the environment and our farm’s bottom line. To further digitize your IPM approach, Farmonaut’s API enables developers and businesses to implement tailored data streams into their own precision agriculture dashboards.
#4 Soil Health Management – The Key to Resilient Wheat Farming
Sustainable wheat farming’s longevity relies on ongoing, adaptive soil health management. Healthy soils act as the true foundation for resilient, high-yield systems. Essential practices include:
- Adding organic matter through compost, manure, and crop residues to boost vital carbon stocks and microbial activity.
- Using cover crops (e.g., clovers, radish) during fallow periods to prevent erosion, suppress weeds, and conserve living roots in the soil.
- Limiting soil disturbance by minimizing tillage and heavy machinery traffic.
- Testing soil regularly—using digital or lab-based diagnostics—to tailor input application precisely to what the crop and soil actually need.
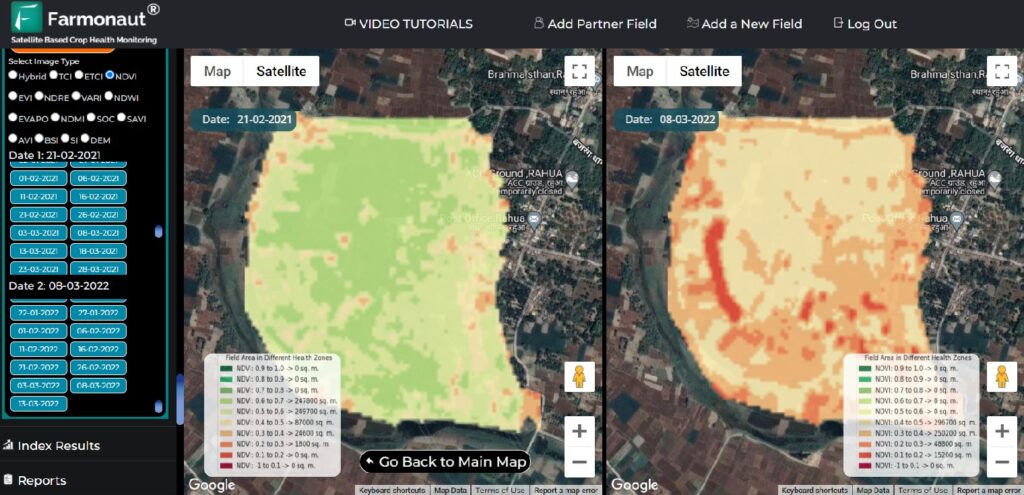
Technologies such as Farmonaut’s satellite-based soil monitoring deliver up-to-date information on parameters like NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index), soil moisture, and temperature. This enables fact-based management decisions and supports:
- Higher yields with less resource waste,
- Improved drought resilience, and
- Long-term carbon sequestration—a crucial aspect in climate-smart carbon footprinting and reporting for wheat farms.
Soil Secret Bonus: Healthy soils consistently display better infiltration, lower compaction, and greater resistance to both flood and drought stress, making them indispensable for long-term farm sustainability.
#5 Precision Agriculture Techniques – Maximizing Inputs, Minimizing Waste
The integration of precision agriculture techniques transforms wheat production by allowing us to apply water, fertilizers, and pesticides exactly where needed—no more, no less. Precision approaches utilize:
- GPS mapping, drones, and soil sensors to monitor crop variability in real-time.
- Variable rate technology (VRT) to deliver custom input applications, saving money and reducing unwanted environmental impact.
- Satellite data to optimize irrigation, sowing, and spraying—responding instantly to infield changes.
Farmonaut’s platform delivers actionable insights—from precise soil moisture alerts to pest pressure warnings—empowering even small farms to leap into the era of data-driven sustainable wheat farming. For business users and developers, full documentation and integration options are available via Farmonaut’s API Developer Docs.
Fact: Precision agriculture can reduce input costs by up to 35%, supporting the economic viability of sustainable agriculture while protecting freshwater supplies and minimizing emissions.
#6 Water Conservation in Agriculture – Protecting Every Precious Drop
Water conservation in wheat farming is more crucial than ever, as climate change and overuse threaten availability. Key techniques include:
- Implementing drip and sprinkler irrigation systems which deliver water directly to plant roots.
- Harvesting rainwater and storing it for off-season or critical growth stages.
- Selecting drought-resistant wheat varieties and employing zero tillage to reduce surface evaporation losses.
- Mulching and cover-cropping for improved moisture retention.
With near-real-time notifications of soil moisture depletion and emerging drought risks, farmers can take fast action—protecting yields while minimizing over-irrigation and runoff. All these data-backed decisions are readily accessible through the Farmonaut platform, available on web and mobile.
Result: Farms adopting water conservation in agriculture report 20-40% better soil moisture retention, reduced energy costs, and improved wheat resilience throughout the season.
#7 Biodiversity in Wheat Farming – Nature’s Shield for Wheat Fields
A thriving diversity of plants, insects, microbes, and animals is the secret ingredient to robust and resilient wheat fields. Biodiversity in wheat farming not only protects against pest and disease outbreaks but also enhances pollination and soil health.
- Planting hedgerows, flower strips, and mixed cropping areas creates vital habitats for pollinators and pest predators.
- Diverse rotations nurture a richer soil biota, driving nutrient cycling and plant health.
- Soil biodiversity, measured in number of distinct species/ha, increases carbon sequestration potential and enhances system resilience to extreme events.
Recent studies have established that sustainable practice fields support up to 30% more species than their conventional counterparts, making our farming systems both highly productive and more resilient in a changing world.
Ready to improve your field’s biodiversity and ecological balance? Learn more about crop plantation and forest advisory solutions for in-depth guidance on integrating natural areas seamlessly into wheat production fields.
Comparative Benefits: Sustainable vs. Conventional Wheat Farming
| Soil Health Factor | Conventional Farming (Estimated Values) | Sustainable Farming (Estimated Values) | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Organic Matter (%) | 1.2% | 2.5% | Conventional: Poor soil stability; Sustainable: Enhanced nutrient cycling |
| Water Retention Capacity (ml/cm³) | 0.6 ml/cm³ | 1.1 ml/cm³ | Conventional: More runoff; Sustainable: Improved drought resistance |
| Chemical Fertilizer Used (kg/ha) | 180 kg/ha | 90 kg/ha | Conventional: Leaching, pollution; Sustainable: Reduced input costs, lower impact |
| Biodiversity Index (species/ha) | 12 | 18 | Conventional: Increased pest/disease risk; Sustainable: Stronger ecological balance |
| Carbon Footprint (kg CO₂e/ha) | 3700 kg | 2300 kg | Conventional: Higher emissions; Sustainable: Supports climate goals |
Farmonaut’s Role in Sustainable Wheat Farming
Transitioning from traditional methods to sustainable wheat farming can be daunting for many. Farmonaut, a leader in agricultural technology, provides accessible and affordable solutions that empower farmers of all scales to adopt these principles:
- Satellite-Based Monitoring: Real-time NDVI and soil moisture analytics help identify where and when to apply conservation tillage, irrigation, and precision agriculture techniques.
- AI-driven Jeevn Advisory: Personalized farm insights, weather forecasts, and crop management advice help reduce input waste and maximize productivity.
- Blockchain Traceability: Every wheat harvest is recorded for transparency—vital for exporting to markets that require proof of sustainable production.
- Discover the benefits of secure food supply chains with Farmonaut Traceability.
- Resource Management: Track your entire operation (people, vehicles, machinery) for better economic efficiency. Explore fleet management solutions to reduce costs and optimize on-farm logistics.
- Carbon Footprinting Tools: Quantify GHG emissions in real-time, supporting regenerative soil and climate stewardship aligned with international sustainability standards. Learn more about carbon footprinting services.
Whether you manage a large wheat operation, a community cooperative, or a single field, Farmonaut’s platform is scalable, mobile-accessible, and subscription-based for complete flexibility. For research institutes, agri-corporations, and government projects, our large-scale farm management tools help oversee sustainability across wide geographies with ease.
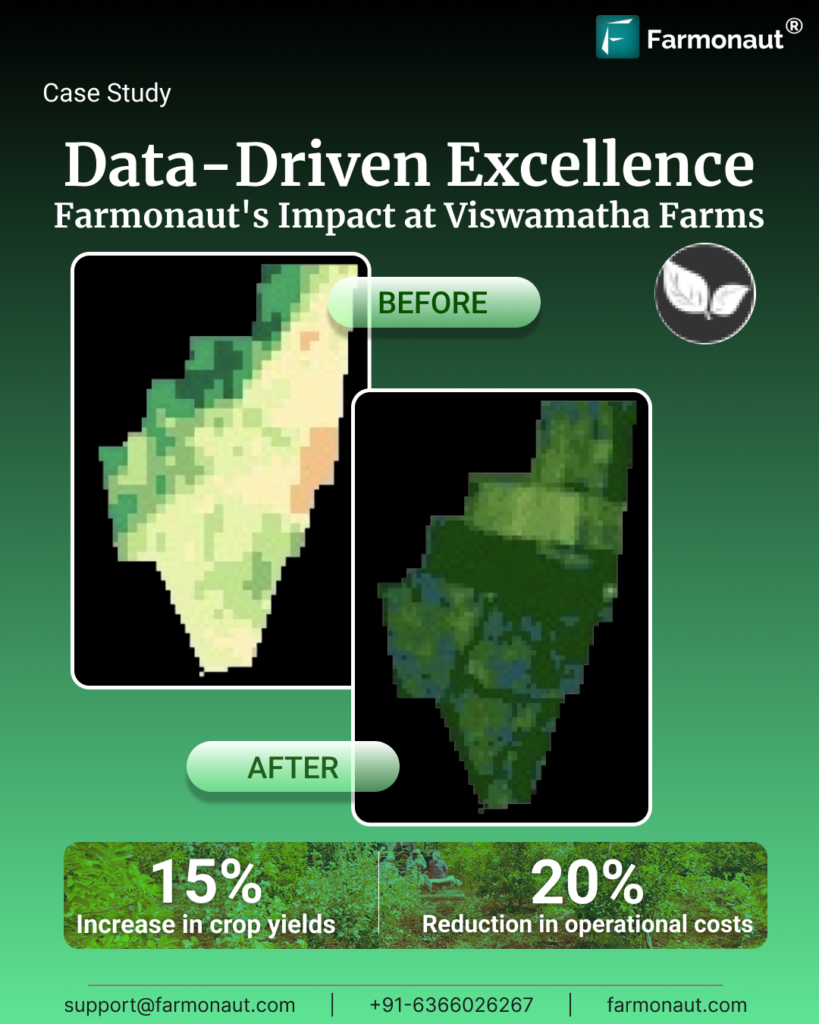
The adoption of advanced, data-driven platforms ensures better decision-making, stronger economic returns, and the safeguarding of vital natural resources.
Farmonaut Subscriptions – Flexible, Scalable Solutions for Every Farmer
Challenges and Considerations for Sustainable Wheat Farming Implementation
While the advantages of sustainable wheat farming are undeniable, real-world implementation does present challenges. It’s crucial we address these head-on and identify strategies to overcome them:
- Education & Training: Transitioning from traditional to sustainable methods requires knowledge and practical skill-building.
- Initial Investment: Conservation tools, monitoring sensors, and precision equipment do require up-front resources, but often pay for themselves in reduced input and increased yields over time.
- Learning Curve: Farmers face a period of adjustment as they adopt integrated pest management, customize rotations, or leverage digital insights for decision-making.
- Access to Finance: Farmers seeking to make the leap need credit and insurance tailored for sustainable investments. Satellite-based farm verification, as offered by platforms like Farmonaut’s crop loan and insurance solutions, streamlines the process and reduces fraud risk.
- Climatic & Regional Variation: Techniques may need to be tailored per region. Farmonaut’s mobile and web tools provide hyper-local, field-specific recommendations anywhere in the world.
Support, community collaboration, and continuous updates on best practices are essential to keep pace with evolving environmental challenges. Fortunately, digital monitoring and advisory platforms make these transitions smoother, reducing the barriers to adoption for all growers.
FAQs about Sustainable Wheat Farming
-
What is sustainable wheat farming?
Sustainable wheat farming is an agricultural approach designed to balance high wheat productivity with environmental stewardship, economic viability, and social responsibility. It uses methods such as conservation tillage, crop rotation, integrated pest management, and precision agriculture to reduce inputs, conserve resources, and preserve soil health for the future.
-
How does conservation tillage benefit soil health?
Conservation tillage minimizes soil disturbance, preserves soil structure, and increases organic matter, which leads to less erosion, better water retention, and improved microbial biodiversity. This results in healthier, more resilient wheat crops.
-
What is integrated pest management for wheat?
Integrated pest management (IPM) for wheat combines biological, cultural, physical, and chemical tools in a balanced, data-driven way. It focuses on monitoring the field and applying targeted controls only when necessary, minimizing pesticide use and supporting beneficial insects and ecological balance.
-
Why are precision agriculture techniques important?
Precision agriculture allows for the precise application of irrigation, fertilizer, and pesticides, reducing waste and environmental impact. By tailoring inputs to actual crop needs using data and technology, farmers can increase efficiency, lower costs, and improve wheat yields sustainably.
-
How does sustainable wheat farming enhance biodiversity?
Practices such as crop rotation, intercropping, cover cropping, and reducing chemical use increase soil biological activity and support a wider variety of plant and insect species. This biodiversity creates a stronger, more resilient farming ecosystem.
-
How can technology like Farmonaut support sustainable wheat farmers?
Farmonaut provides advanced satellite-based monitoring, personalized AI advisory, blockchain traceability, and resource management—all accessible on web and mobile. These technologies help farmers track and optimize soil health, water use, pest control, and supply chain transparency, making adoption of sustainable practices easier and more effective.
-
Where can I access Farmonaut tools?
You can access Farmonaut through its web and mobile apps, including Android and iOS applications. APIs and developer resources are available for customized business solutions.
Conclusion: Paving the Way for Sustainable Futures
By unveiling the seven shocking soil secrets of sustainable wheat farming, we place ourselves at the forefront of responsible, profitable, and resilient agriculture. These secrets—conservation tillage, crop rotation, integrated pest management, soil health management, precision agriculture techniques, water conservation in agriculture, and enhanced biodiversity—form a blueprint not just for today’s success but for a thriving, sustainable future.
The journey is ongoing: as techniques evolve and data becomes ever more accessible, it’s up to all of us—farmers, agribusinesses, scientists, and consumers—to champion soil stewardship, promote biodiversity, conserve resources, and reduce chemical inputs in farming. With support from powerful platforms like Farmonaut, the tools for success are better—and more achievable—than ever.
Our collective efforts in preserving and enhancing soil health today will secure the promise of abundant, nutritious wheat harvests for future generations, protect our planet, and honor our shared social and economic responsibilities.
Start optimizing your wheat farming journey today with the latest data-driven insights and tools.