Active Crop Production: 7 Innovations Boosting Yield
Overview: The Power of Active Crop Production
Active crop production is at the heart of modern agriculture, serving as a critical component for feeding societies, supporting economies, and fostering global sustainability. By embracing innovative technology and integrating data-driven insights into everyday farming practices, we can dramatically enhance crop yield, quality, and the resilience of our agricultural systems.
From initial planning and soil management techniques to advanced crop monitoring technology and efficient water management in agriculture, active crop production combines both traditional knowledge and modern farming practices. In this article, we delve into every important stage, examine crucial influencing factors, reveal groundbreaking innovations—including satellite imagery, agrivoltaics, and biotechnology—and present actionable strategies for optimizing yield in today’s fast-evolving agricultural landscape.
Stages of Active Crop Production
In active crop production, every stage is a vital link in ensuring the optimal growth, yield, and sustainability of crops. Let us explore these critical stages in detail:
1. Planning and Preparation
Our journey in crop production begins with rigorous planning and careful preparation. By selecting the right crops based on climate, soil type, and local market demand, and drawing up effective planting schedules and allocation of resources, we set the foundation for a productive harvest. Modern tools help farmers with risk management strategies, including weather forecasting, soil testing, and yield planning.
2. Soil Management
Healthy soil is paramount for robust crop growth. Soil management techniques—such as soil testing, precise fertilization, and the use of organic matter—can greatly enhance fertility and structure. The practice of crop rotation and cover cropping maintains biodiversity and reduces degradation, supporting sustainable agriculture and optimal nutrient cycles.
3. Planting
Planting involves deciding on high-quality seeds, choosing the best planting depth and spacing, and ensuring suitable conditions. Modern planting machinery and scheduling apps take into account climate and weather data to optimize timing, which is crucial to avoid exposure to frost or excessive heat.
4. Crop Maintenance
Maintenance is an ongoing process, requiring regular monitoring of plant health, management of pests and diseases, and ensuring effective irrigation. The adoption of integrated pest management (IPM)—which combines biological, cultural, physical, and chemical tools—minimizes pest damage while reducing negative environmental impact.
5. Harvesting
The harvesting phase demands precise timing. Crops must be collected at their peak maturity to guarantee maximum yield, optimal quality, and high nutritional value. Post-harvest handling is equally important for maintaining crop conditions through cleaning, sorting, and storage.
6. Post-Harvest Management
After harvesting, crops enter a critical phase involving processing, packaging, and distribution. Superior post-harvest management reduces losses, prolongs shelf life, and ensures that produce meets both market and nutritional standards when it reaches consumers.
Influencing Factors in Crop Production
Active crop production is governed by a range of environmental, technological, and economic factors. Understanding and controlling these influencing factors is vital to optimizing yield, resilience, and sustainability:
- Climate and Weather: Temperature, rainfall, and sunlight directly affect plant development. The climate change impact on crops is significant—forcing us to adopt weather-smart strategies such as drought-resistant varieties and resilient planting schedules.
- Soil Health: Soil structure, organic content, and fertility influence nutrient availability and root development. Methods like carbon footprint monitoring and organic amendments bolster soil health for sustainable agriculture.
- Water Management: Efficient irrigation systems like drip irrigation are essential for ensuring plants receive the right amount of water, especially in regions facing scarcity. Advanced satellite-based resource management tools support water planning and conservation.
- Technological Advancements: Integrating advanced crop monitoring technology—from sensors and satellite imagery to smart apps—empowers us to track real-time plant health, better schedule fertilization, and improve input efficiency.
- Market Dynamics: Global demand, economic trends, and trade policies can shift prices and guide our decisions on crop selection and diversification.
- Pests and Diseases: The evolving threat of pests and plant diseases demands continuous vigilance and the integration of both modern and traditional defense strategies.
Key Farmonaut Apps and Tools
- Farmonaut Mobile & Web App – Monitor crop health, weather, and soil conditions in real time, empowering smarter decisions for every planting and harvesting phase.
- Carbon Footprinting – Track your farm’s emissions, reduce inputs, and support agri-sustainability.
- Fleet Management – Organize and monitor all agricultural machinery for greater efficiency across productive seasons.
- Blockchain-Based Traceability Solutions – Ensure transparency and trust in the journey of food from farm to market.
- Crop Loan & Insurance Verification – Satellite-based verification for fast and reliable agriculture loan/insurance processes.
Developers, access Farmonaut’s powerful satellite & weather data via our API (API Docs).
7 Technological Innovations Boosting Crop Yield Optimization
Harnessing technology, we have made crop production smarter, more efficient, and significantly more sustainable. Let’s explore the seven core innovations reshaping modern agricultural systems and helping us overcome today’s challenges in yield optimization:
1. Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring and Management
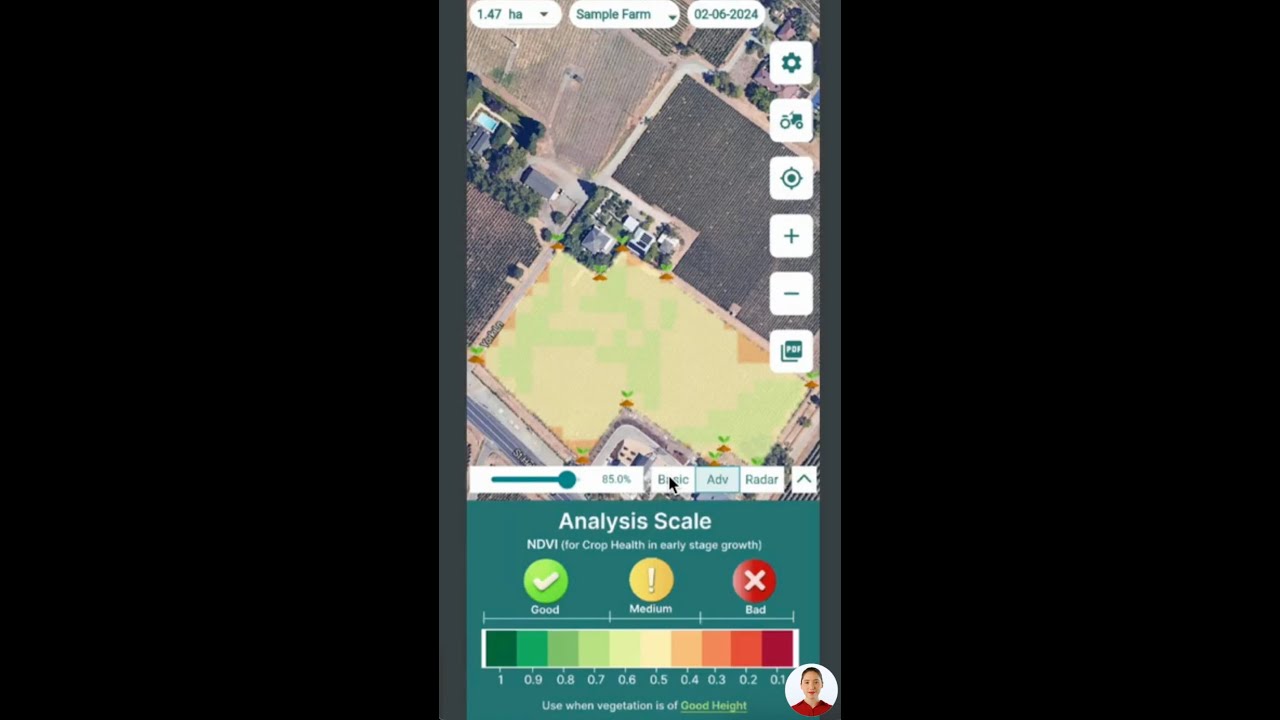
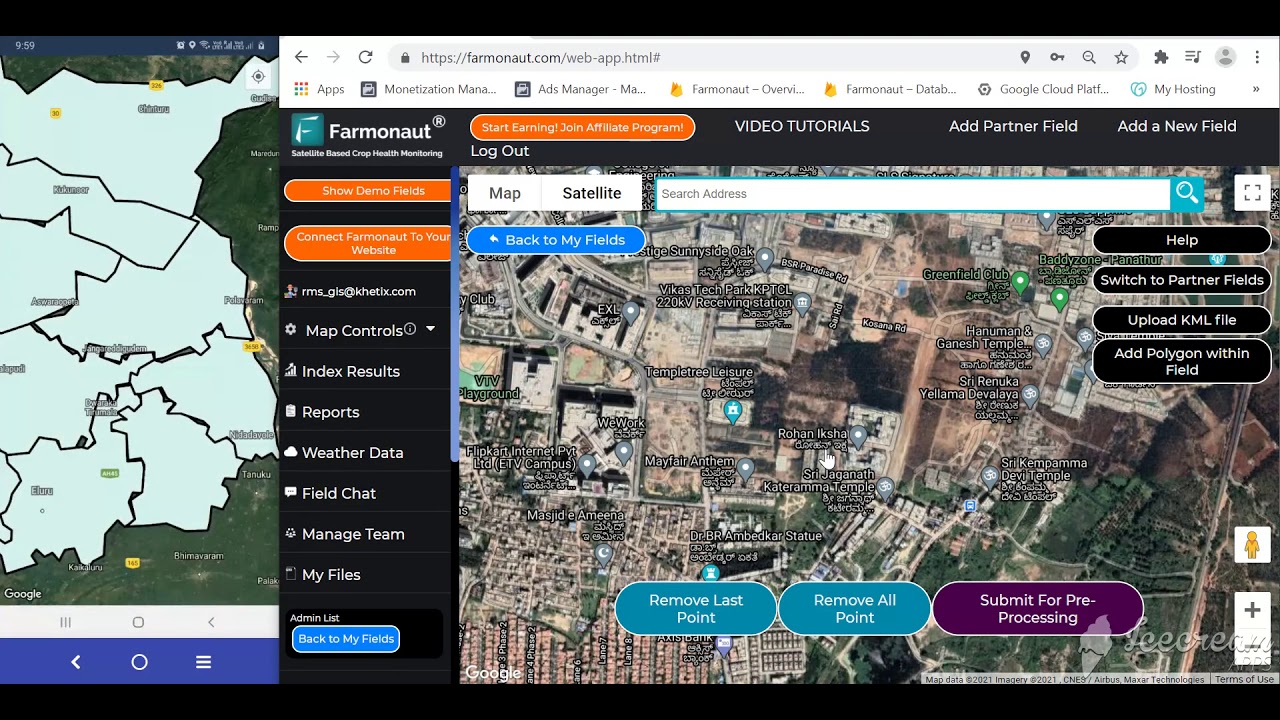
Satellite imagery and remote sensing have revolutionized how we approach field-level monitoring and management. By capturing multispectral data across the visible and infrared spectrums, platforms like Farmonaut deliver continuous updates on vegetation health (e.g., NDVI), soil moisture, and crop stress. These insights power smarter irrigation, fertilization, and pest detection, minimizing resource waste while optimizing yield.
Farmonaut’s Android, iOS, and Web platforms empower farmers of all sizes with real-time data, making precision agriculture accessible and affordable globally. This innovation is central to modern soil management techniques and crop yield optimization.
2. Advanced AI-Driven Farm Advisory Systems
Artificial intelligence (AI) now plays an increasingly decisive role in planting schedules, pest and disease prediction, and dynamic resource allocation. AI systems analyze large datasets—including weather, soil, and crop health data—and offer customized strategies for every stage.
Farmonaut’s AI-powered Jeevn Advisory System delivers practical, farm-specific guidance for soil testing, watering schedules, and integrated pest management—empowering proactive decision-making and mitigating risks in real time.
3. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) with Remote Sensing
IPM now benefits from the power of advanced monitoring—identifying pest infestations or diseases early using satellite data and sensors. Rather than blanket chemical application, farmers apply precise, targeted interventions, combining biological, cultural, and chemical methods. This both reduces chemical inputs and minimizes environmental impact—leading to more sustainable agriculture and healthier crops.
4. Water Management in Agriculture: Automated Irrigation Systems
Modern water management in agriculture is defined by smart irrigation controllers, moisture sensors, and remote scheduling. Automated systems like drip irrigation deliver exactly what each plant requires, conserving water and reducing disease pressure linked to overwatering.
Data-driven irrigation planning, as enabled by platforms like Farmonaut, converts traditional water usage into a highly efficient process—helping address regional water scarcity and reduce environmental impact.
5. Agrivoltaics: Solar Energy Meets Sustainable Agriculture
Agrivoltaics refers to the simultaneous use of land for both solar energy production and agriculture. Modern studies, including those from Iowa State University, highlight how shade from solar panels can support certain vegetables and heat-sensitive crops—sometimes delivering better yields than crops grown in full sunlight. In arid or drought-prone regions, agrivoltaics can lower field temperatures, reduce water evaporation, and promote resilient agriculture systems. (Source: Axios)
6. Vertical Farming Methods and Indoor Agriculture
Vertical farming methods are transforming urban and land-limited environments. By stacking crops in vertically inclined surfaces or controlled indoor environments, we maximize space, minimize waste, and achieve faster, year-round production cycles. Vertical farms use hydroponics or aeroponics, precise nutrient dosing, and controlled lighting to ensure optimal plant growth. This method reduces transportation costs and opens new possibilities for local food production in densely populated regions.
7. Biotechnology and Improved Crop Varieties
Modern biotechnology enables the creation of resistant, high-yield, and nutrient-enriched crop varieties. Genetic advancements target both abiotic stresses (drought, salinity) and biotic threats (pests and diseases). This means we can cultivate more resilient crops—responding to the climate change impact on crops and growing demand for sustainable nutrition in our societies.
Comparative Technology Impact Table: The 7 Key Innovations
Below, we compare the leading innovations in active crop production based on technology type, function, impact, and applicability—supporting your decision-making for more productive and eco-friendly agriculture.
| Innovation Name | Technology Type | Main Function | Estimated Yield Increase (%) | Estimated Cost Reduction (%) | Environmental Impact | Scalability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring | Satellite Imagery, Data Analytics | Real-time field health, resource optimization | 10–20% | 10–25% | Reduced chemical inputs, less resource wastage | All scales |
| AI-Driven Advisory Systems | Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning | Custom strategies, weather/pest prediction | 10–15% | 5–20% | Efficient planning, sustainability | All scales |
| Integrated Pest Management (Remote Sensing) | Monitoring Systems, Sensors | Early pest/disease intervention | 6–18% | 10–30% | Minimized pesticide use | All scales |
| Automated Irrigation Systems | IoT Sensors, Automation | Efficient water management | 5–22% | 10–30% | Reduced water usage, less runoff | All scales |
| Agrivoltaics | Solar Panels, Environmental Sensors | Dual use: crop + solar power | Varies (0–10%) | Up to 20% | Lower field temps, reduced evaporation | Land-limited, large scale |
| Vertical Farming | Controlled Environment, Hydroponics/Aeroponics | Maximize space, urban agriculture | 20–30% | 10–35% | Reduced land/water usage | Urban/vertical, small–medium scale |
| Biotechnology / Improved Varieties | Genetic Engineering, CRISPR | Drought/pest resistance, improved nutrition | 15–40% | Varies | Lower chemical input, higher resilience | All scales |
How Farmonaut Empowers Modern Crop Production
Farmonaut stands at the forefront of agricultural technology, providing farmers, agribusinesses, and governments with the data and tools required to maximize productivity and sustainability across all stages of crop production. Here’s how our integrated approach supports every phase, every crop, and every climate:
Satellite-Based Field Monitoring
- Vegetation Indices (NDVI): Easily detect areas of poor health or stress so you can intervene early—improving outcome and reducing losses.
- Soil Moisture & Fertility: Satellite data combined with on-ground testing enables targeted fertilization and irrigation schedules for optimal plant growth.
To learn how you can benefit, check our large scale farm management solutions.
AI-Driven Decision Support & Farm Advisory
- Jeevn AI: Our proprietary system synthesizes crop, soil, and weather data to deliver personalized advice—enhancing yield and lowering risks at each turn.
- Automated Alerts: Receive actionable updates on weeds, pests, disease outbreaks, and water stress as soon as they arise.
Resource and Fleet Optimization
-
Fleet Management: Track machinery, monitor utilization rates, and optimize movements—minimizing downtime and maximizing economic return.
Explore: Farmonaut Fleet Management
Supply Chain Transparency & Traceability
-
Blockchain Integration: Record every step of the journey—from planting and harvesting to storage and delivery. This bolsters trust and ensures compliance in high-value or regulatory markets.
Discover: Product Traceability at Farmonaut
Carbon Footprinting and Sustainability Tracking
-
Environmental Impact Monitoring: Use our platform to quantify emissions, resource use, and sustainability metrics aligned to the latest regulations and industry initiatives.
Start here: Carbon Footprinting by Farmonaut
Developers and agribusinesses: Integrate Farmonaut via API. API Docs are here.
Farmonaut Subscription Offers:
Challenges and Future Outlook for Sustainable Agriculture
While the technologies and methods above provide unprecedented opportunities, we cannot ignore the persistent and new challenges that jeopardize food security, farmer livelihoods, and ecosystem health:
- Climate Change: Erratic weather (droughts, floods, heatwaves) continues to threaten crop stability and yield. Our strategies must include resilient crop selection, insurance schemes, and advanced climate monitoring tools.
- Pest and Disease Evolution: Resistance to available chemical, biological, and management solutions requires us to continually update our integrated pest management strategies and invest in R&D.
- Labor Shortages: Mechanization, precision apps, and fleet/resource management tools are valuable in alleviating this issue—but initial investment may be high for smallholder farmers.
- Market Price Volatility: Fluctuating prices for inputs and produce risk disrupting economic sustainability. Diversification, traceability, and satellite-based loan/insurance verification can support more stable returns.
- Resource Constraints: Land, water, and energy shortages, particularly in vulnerable regions, require us to double down on efficiency, conservation, and adaptation.
The future of crop production lies in the seamless integration of traditional knowledge with precision technology—balancing productivity, ecological preservation, and economic resilience for farmers and the societies they support.
Platforms like Farmonaut are making this transition accessible, scalable, and practical for farms large and small by lowering cost barriers and delivering actionable insights when and where they’re most needed.
FAQ on Active Crop Production & Innovations
A: The stages include planning and preparation, soil management, planting, crop maintenance, harvesting, and post-harvest management.
Q2: How does technology improve soil management techniques?
A: Technology enables precise soil testing, optimal fertilization planning, and tracking of soil health via satellite monitoring, leading to enhanced fertility and reduced degradation.
Q3: Can satellite imagery really help smallholder farmers?
A: Absolutely! Solutions like Farmonaut democratize advanced crop production monitoring via cost-effective satellite-based insights—helping farmers of all scales monitor crop health, manage risks, and get tailored advisory support.
Q4: What is integrated pest management, and why is it important?
A: Integrated pest management combines multiple strategies (biological, cultural, physical, and chemical) with real-time monitoring to suppress pests in a sustainable, environmentally friendly manner. It reduces reliance on chemicals and prevents pest resistance.
Q5: How do vertical farming methods impact sustainability?
A: Vertical farming saves land, water, and nutrients while enabling controlled, indoors crop production year-round. This reduces transportation costs and supports resilient food supply chains in urban areas.
Q6: Why is blockchain important in agriculture?
A: Blockchain-based traceability offers transparent, tamper-proof records for every stage from planting to harvest and sale—improving food safety, quality assurance, and market trust, especially in high-value supply chains.
Q7: How can I start with Farmonaut services?
A: Get started by downloading the Farmonaut App (Android/iOS/Web), or learn about subscriptions above. Developers and enterprises can access our API here.
Conclusion
Active crop production is more than just growing crops—it is a dynamic, data-driven, and strategic endeavour requiring constant adaptation, innovation, and attention to sustainability. By leveraging modern technologies such as satellite-based monitoring, AI-driven advisory, and integrated resource management, we safeguard not just yield, but also quality, resilience, and the long-term viability of agriculture.
Farmonaut is committed to making these innovations accessible worldwide, supporting the present and future of crop production for farmers, communities, and the environment alike.