Agriculture Industry Solution: 10 Game-Changers for Farms
“Precision agriculture can increase crop yields by up to 20% while reducing input costs by 15%.”
Agriculture’s Transformative Shift—Why Advanced Solutions Matter
The agriculture industry is facing a transformative shift as farms and forestry operations worldwide adopt innovative solutions to tackle mounting challenges: labor shortages, climate change, and resource optimization. Precision agriculture, smart irrigation systems, AI-driven analytics, and other cutting-edge technologies are empowering us to boost crop yields, improve efficiency, and ensure sustainability for generations to come.
Having witnessed the impact of climate change and increasing resource scarcity, we understand that relying on traditional practices alone is not enough. The integration of advanced agricultural solutions is not just a trend—it’s a necessity to enhance productivity, manage variability in fields, reduce input costs, and meet growing demands for food security.
The future of farming hinges on adopting methods and systems that allow us to monitor and manage every facet of crop and livestock production with timely interventions and informed decisions. Let us delve into the 10 game-changing innovations shaping today’s agriculture landscape.
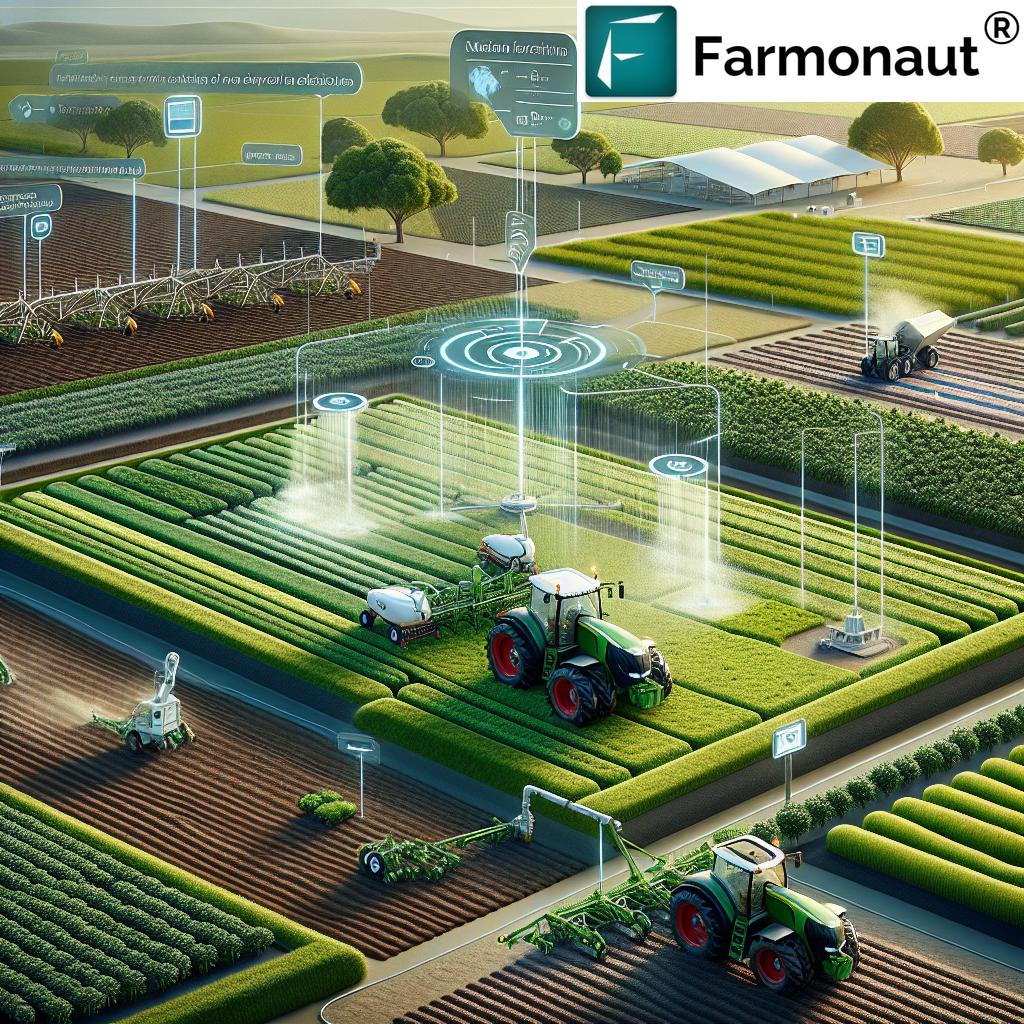
1. Precision Agriculture: Optimizing Every Inch
Focus Keyword: Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture stands at the forefront of the industry’s technological revolution. By harnessing GPS, IoT sensors, satellite imagery, and data analytics, we can manage fields by zones or even individual plants—maximizing efficiency, enhancing yields, and minimizing waste.
With real-time monitoring of soil health, moisture levels, and crop conditions, it’s possible to direct resources precisely where needed. Precision agriculture transforms our ability to apply irrigation, fertilizers, and pesticides on a site-specific basis. The immediate benefits include reduced input costs, healthier crops, and improved environmental stewardship.
- Leverages satellite data, IoT-based sensors, and advanced analytics for decision-making.
- Reduces resource wastage by applying water, nutrients, and chemicals only where— and when—they are most needed.
- Supports monitoring of variability in soil and crop health across large fields.
We’ve observed that carbon footprinting tools can further enhance this process, helping us track field-level emissions and guiding us toward more sustainable farming practices.
By embracing precision agriculture systems, farmers can realize up to 20% increase in crop yields while reducing input costs by 15%—an advancement that has already shown significant benefits in regions across the globe.
2. Autonomous Farming Equipment: The New Labor Force
Autonomous farming equipment is revolutionizing our operations in fields worldwide. With machines like self-driving tractors, drones, and robotic harvesters, we can now perform tasks—from planting to harvesting—with minimal human intervention. This addresses critical labor shortages and elevates both operational efficiency and lower long-term costs.
- Advanced autonomous tractors and robotic platforms are capable of managing fruits and vegetables, optimizing timely interventions for delicate crops.
- Drones perform rapid, data-rich surveys and even facilitate precise pest control applications on large farms.
- Responsive to weather conditions and real-time agricultural data analytics to optimize resource allocation.
We can enhance the productivity of large estates using large scale farm management platforms. These platforms enable remote oversight, fleet tracking, and integration with smart equipment for end-to-end optimization.
3. Smart Irrigation Systems: Saving Water, Boosting Yields
Smart irrigation systems use connected IoT sensors to monitor moisture, soil conditions, and weather patterns, distributing water with laser-like precision. This efficient approach is vital for improving water usage and ensuring crops receive the optimal amount of hydration.
Automated or IoT-based irrigation systems can reduce water use by up to 30% while enhancing yields and guaranteeing sustainable resource management. These systems integrate seamlessly into precision agriculture workflows.
- Monitor soil moisture and weather in real time to optimize irrigation intervals and quantities.
- Reduce water costs and improve yields by providing water only where and when needed.
- Allow for remote management and integration with agricultural data analytics.
Learn more about implementing real-time monitoring and advisory systems with Farmonaut’s platform. Our satellite-based insights help monitor field-level moisture, supporting drought resilience and efficient irrigation planning.
“Smart irrigation systems save up to 30% more water compared to traditional farming methods.”
4. Livestock Monitoring Technologies: Health and Profitability
Advanced livestock monitoring technologies contribute to improved animal health, welfare, and productivity. Through the use of wearable sensors and smart tags, we can monitor vital signs, detect early onset of diseases, and optimize feeding and breeding practices.
- Monitor location, eating, and behavior patterns of livestock 24/7, providing timely interventions when anomalies are detected.
- Reduce veterinary costs by identifying health issues before they escalate.
- Boost productivity and optimize genetic selection through data-driven management.
These solutions integrate with modern farm management systems and can be extended to large operations. In many regions, the increased monitoring capabilities are helping producers maintain profitability even in the face of climate and market uncertainty.
5. Agrivoltaics Solutions: Powering Farms with the Sun
A major breakthrough in sustainability is agrivoltaics, the co-location of solar panels and agriculture. This method allows us to produce energy and crops on the same land, increasing land use efficiency, reducing water evaporation, and even enhancing yields for certain crops.
- Solar energy can power on-farm equipment, irrigation, or processing units.
- Panels provide partial shading, reducing water loss and helping sensitive crops thrive.
- Agrivoltaics solutions also contribute to grid resiliency and carbon footprint reduction.
Over 500 agrivoltaic sites now exist in the United States alone, with a combined capacity of 9 GW—a testament to the growing recognition of this dual-use approach.
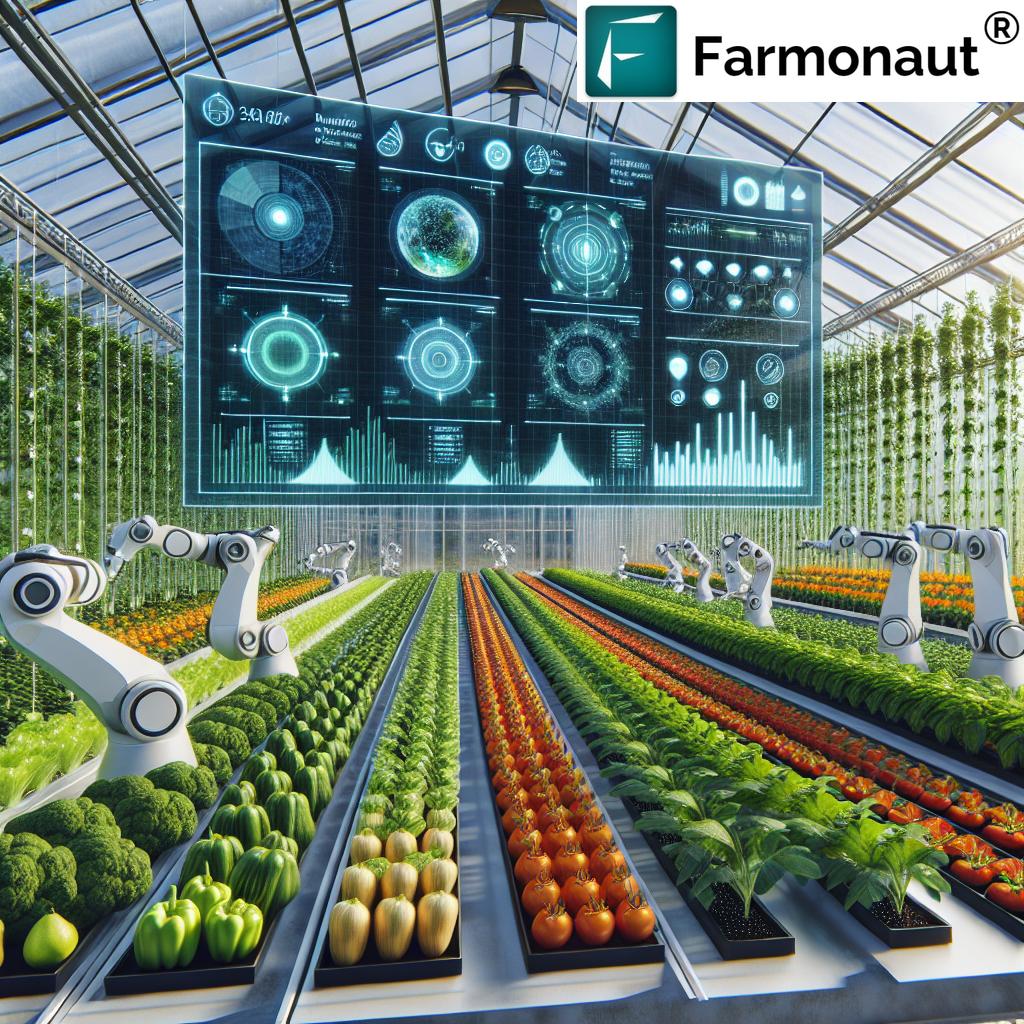
6. Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA): Year-Round Food Security
Controlled environment agriculture (CEA) encompasses vertical farming, hydroponics, and other methods of growing crops indoors or in highly managed environments. This means fresh food can be produced in urban or climate-challenged locations all year round.
- Enables year-round production regardless of outdoor weather conditions.
- Reduces water usage dramatically and limits the need for chemical pest control.
- Drives urban agriculture and lowers the carbon footprint of food supply chains.
The infusion of big data analytics and AI in CEA enables us to optimize resource use and get precise control over factors like light, humidity, and nutrients. This not only makes farming more resilient to climate change, but also increases access to fresh, nutritious crops in cities.
7. AI in Agriculture: Data, Analytics, Decisions
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning in agriculture marks a new era of decision-making. AI-driven analytics help us predict yields, detect crop diseases, optimize resource allocation, and aid in carbon sequestration strategies.
- Analyze large agricultural datasets for forecasting and improved management.
- Enable early disease detection and automated pest identification using satellite and drone imagery.
- Empower farmers to make data-driven decisions on input application and timing.
Farmonaut offers a Jeevn AI advisory system that delivers real-time insights, weather forecasts, and expert crop management strategies, all tailored to the unique conditions and crop types in each field.
Benefit from blockchain-based product traceability—ensuring transparency, traceability, and security from farm to consumer.
8. Nanotechnology: The Smallest Game-Changer
The application of nanotechnology in agriculture unlocks new dimensions of precision and insight. Nanosensors embedded in fields can monitor soil health, nutrient status, water content, and even detect pathogens at the molecular level, providing unmatched data granularity.
- Graphene-based nanosensors can swiftly measure nitrate and phosphate levels, enabling efficient fertilization and pest management.
- Enhance soil management and minimize chemical input by triggering precise application protocols.
- Real-time alerts and AI integration for fast, informed decisions.
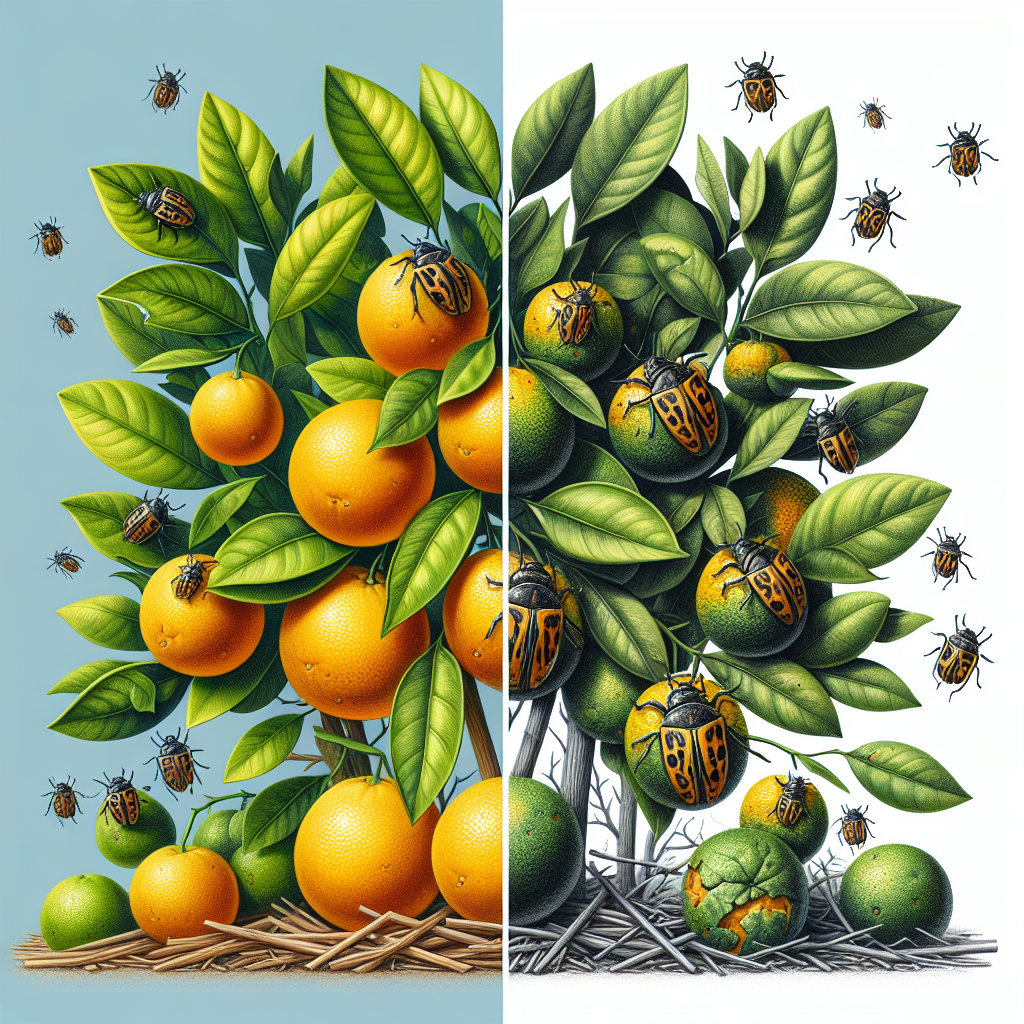
9. Biological Pest Control: Nature’s Defenders
Biological pest control reimagines crop protection by releasing beneficial insects—often via drones—to prey on harmful pests. This eco-friendly solution greatly reduces dependence on chemical pesticides, promoting environmental sustainability while maintaining crop yields.
- Drones can rapidly distribute natural enemies such as parasitoids and predatory beetles across fields.
- Proven to reduce chemical usage and pest-induced crop losses.
- Supports regenerative agriculture and drives biodiversity enhancements.
10. Big Data Analytics: Predict, Plan, Prosper
Today’s agriculture industry is fundamentally data-driven. By aggregating weather data, soil conditions, market trends, and IoT device streams, big data analytics enable us to make precise, impactful decisions.
- Supports accurate forecasting of crop yields, input requirements, and potential pest outbreaks.
- Enhances resource optimization—ensuring water, fertilizer, and labor are allocated where they will have the most impact.
- Empowers financial planning and risk mitigation through historical and real-time data fusion.
Farmers and agribusinesses can access big data platforms through Farmonaut’s ecosystem—combining satellite imagery, AI, and management tools in a unified, cross-device solution for field management.
Sustainable and Regenerative Farming Practices
No set of innovative technologies is complete without sustainable farming practices at its core. Regenerative agriculture—incorporating crop rotation, agroforestry, and bio-based fertilizers—restores soil health, enhances biodiversity, and reduces chemical reliance.
- Restores soil carbon and organic matter, reversing erosion and decline in soil fertility.
- Accelerates environmental sustainability and improves ecosystem resilience.
- Supports food security and empowers rural communities by reducing dependency on expensive inputs.
By integrating these practices with data-rich platforms like Farmonaut, we are able to merge the best of tradition and innovation—ensuring a resilient, abundant future for our farms and forestry operations.
Comparative Feature-Benefit Table: The 10 Game-Changers
| Technology/Innovation | Key Feature | Estimated Yield Improvement (%) | Estimated Cost Savings (%) | Sustainability Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision Agriculture | Data-driven crop & soil management with IoT, GPS, AI | 15–20 | 10–15 | High (Reduces input, increases efficiency) |
| Autonomous Farming Equipment | Robotic machinery for planting, monitoring, and harvesting | 10–15 | 10–20 | Medium (Addresses labor, reduces fuel use) |
| Smart Irrigation Systems | Sensors-based water delivery matching crop needs | 10–12 | 15–20 | Very High (Reduces water usage dramatically) |
| Livestock Monitoring Technologies | Wearables & sensors for animal welfare & productivity | 5–10 | 8–12 | Medium (Improves animal health, lowers waste) |
| Agrivoltaics Solutions | Dual land use with solar panels & crop cultivation | Up to 10 | 5–12 | High (Energy generation, limits evaporation) |
| Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) | Indoor, vertical farming with year-round yield | Up to 30 | Up to 25 | Very High (Reduces water use, chemicals) |
| AI & Machine Learning | Predictive analytics & automated decision making | 5–12 | 10–15 | High (Enhances resource optimization) |
| Nanotechnology | Nanosensors for soil, water, and pathogen detection | 5–10 | 8–12 | Medium (Reduces chemical use, informs management) |
| Biological Pest Control | Drones deploy beneficial insects as natural pest control | Up to 10 | 7–14 | Very High (Eco-friendly, promotes biodiversity) |
| Big Data Analytics | Aggregate field, market, and weather data for decisions | 5–15 | 10–17 | High (Optimizes all resource usage) |
Farmonaut: Leaders in Satellite-Driven Agriculture Solutions
At the heart of these industry-transforming technologies is: Farmonaut. Our global mission is to democratize access to precision agriculture, putting actionable, cloud-connected data into the hands of farmers, agribusinesses, and institutions worldwide.
-
Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Multispectral satellite imagery constantly monitors every hectare for NDVI (health), soil moisture, and anomalies—helping farmers decide the best timing for irrigation, fertilization, and defensive pest control.
Affordable, accessible—no need for expensive hardware. - Jeevn AI Advisory System: Delivers real-time, AI-based crop management advice—from weather to disease forecasting—increasing efficiency for individual farmers and corporate clients alike.
-
Blockchain-Based Product Traceability: Use the traceability module to digitize your produce’s journey, ensuring security, transparency, and premium value in connected supply chains.
Verifiable origin data for textiles, food, and export crops. - Fleet and Resource Management: Total oversight of tractors and vehicles with fleet management tools—reducing operational costs and enhancing field safety.
-
Carbon Footprinting: Accurately measure on-farm emissions and monitor sustainability compliance with the carbon management dashboard.
Perfect for food brands & agribusinesses looking to lead in climate-smart practices. -
API Access: For researchers, developers, and institutions, API and documentation enable custom product integrations and back-end analytics.
Explore Farmonaut API - Crop Loan & Insurance: Secure satellite-based verification for lending and insurance with digital crop monitoring and claims validation.
Our subscription-based plans serve everyone from smallholder farmers needing affordable crop monitoring to large-scale agribusinesses seeking comprehensive field management.
Industry-Wide Challenges & Key Considerations
While these game-changing innovations hold immense promise, we must address several considerations to ensure equitable adoption and lasting impact.
- Initial Costs: Advanced technologies require upfront investment, which might deter resource-limited farmers. Solutions like Farmonaut’s subscription model seek to close this gap affordably.
- Technical Expertise: Integrating AI, IoT, and data analytics into daily farming practices demands an increased comfort with digital tools; ongoing training and support are essential.
- Data Privacy: With increasing monitoring and blockchain traceability comes the need for robust data privacy, ethical use, and transparency throughout the industry.
- Labor Impacts: Automation and autonomous farming equipment may affect employment patterns. Focusing on upskilling and transitioning roles is key for rural resilience.
- Equity & Accessibility: Ensuring that smallholder and marginalized farmers can access these solutions prevents further inequality within the agriculture industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is precision agriculture and why is it a game-changer?
Precision agriculture leverages technologies like sensors, GPS, satellite imagery, and data-driven analytics to manage farm resources on a site-specific basis. This approach maximizes yield, minimizes input costs, and increases sustainability by delivering precisely what each crop or soil section needs.
How do smart irrigation systems save water?
Smart irrigation systems use IoT sensors to monitor soil moisture, local weather, and crop conditions. They automate and adjust water application, ensuring crops get optimal hydration with minimal waste, typically reducing water use by up to 30% compared to traditional irrigation.
What role does AI play in modern agriculture?
AI in agriculture provides predictive analytics for yield, pest, and disease risk. It powers real-time advisory systems, automates field operations, and analyzes big data from multiple sources, allowing for more informed, timely farming decisions and resource allocation.
Can smallholder farmers access these technologies?
Yes. Platforms like Farmonaut are specifically designed to be accessible and affordable for individual and smallholder farmers, using satellite-based monitoring services that don’t require expensive on-field equipment. Subscription models lower the entry barrier for advanced agriculture management.
How does biological pest control compare to chemical methods?
Biological pest control uses natural predators to manage crop pests rather than relying on synthetic chemicals. This method is more environmentally friendly, reduces chemical residue in food and soil, and supports regenerative farming practices—though, in some cases, a hybrid approach is most effective.
Conclusion: The Road Ahead for Agriculture Industry Solutions
As we embrace the fusion of technology, data, and sustainable practices, the future of the agriculture industry looks brighter than ever. Adopting these 10 game-changing solutions will not only elevate yields and efficiencies on our farms but also build a resilient, sustainable system ready to feed the world.
With tools like satellite-based monitoring, real-time AI advisory, seamless resource management, and robust traceability, companies like Farmonaut empower every stakeholder in the food chain—from small-scale farmers to large enterprises and government bodies.
Together, we can champion an agriculture industry solution that is scalable, inclusive, and future-proof—supporting our collective mission toward increased productivity, environmental care, and long-term security in feeding the planet.