Crop Yield Mapping: 7 Powerful Ways Technology Boosts Yields
“Precision agriculture can increase crop yields by up to 20% through advanced yield mapping and data-driven field management.”
Summary: Crop Yield Mapping and Technological Innovation
Crop yield mapping is a pivotal element of precision agriculture technology, allowing farmers to precisely monitor and manage spatial variability in crop production across their fields. Through the integration of advanced technologies—such as GPS, remote sensing, powerful sensors, and data analytics—farmers generate highly detailed yield maps that reveal hidden variations in soil, moisture, and grain output.
By leveraging these actionable insights, farm managers can optimize resource allocation, inform smarter decisions, and drive up productivity, while supporting sustainable agricultural practices. Advanced machine learning in crop production further amplifies the value, offering predictive power over yield outcomes.
Crop yield mapping doesn’t merely capture what exists—it empowers transformation through data-driven precision!
Understanding Crop Yield Mapping
Crop yield mapping is the process of systematically collecting and analyzing georeferenced data on crop yields and related variables (such as moisture content) during the harvesting process. The heart of yield mapping lies in its ability to reveal performance variations across specific field zones, arming farmers with knowledge to understand and manage spatial variability as never before.
The Core Process of Yield Mapping in Agriculture
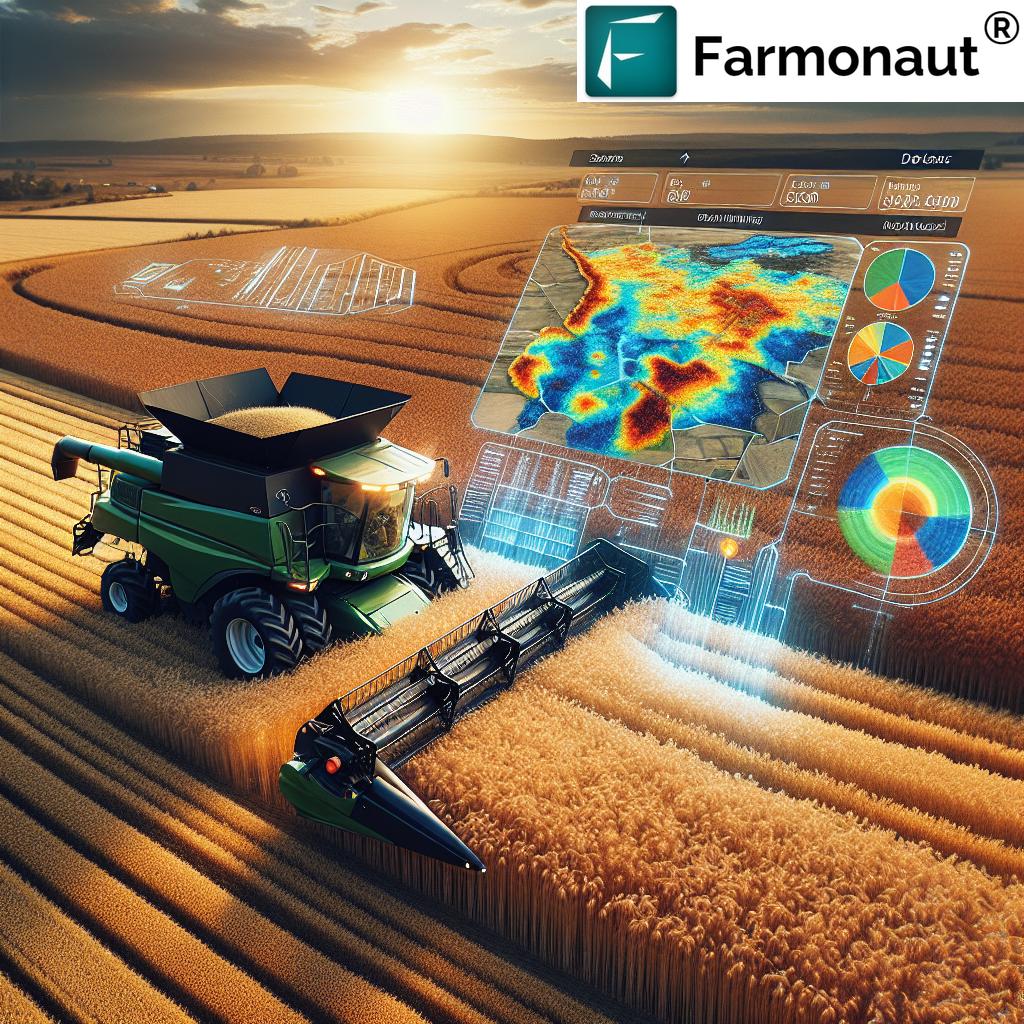
Specialized harvesting equipment—like combine harvesters—are mounted with sensors to measure the flow of grain, levels of moisture, and the volume harvested at each moment. These measurements are then linked to precise locations using a GPS receiver, enabling the creation of maps that show yield variations across the field.
- Precision: Data is recorded at high frequency, providing detailed, actionable insights at sub-field resolution.
- Integration: By integrating with soil moisture sensors and other environmental inputs, a richer picture of yield determinants is formed.
The resulting yield maps allow for a visual and quantitative understanding of where crops thrive and where they underperform—fundamental for the advancement of precision agriculture technology.
Key Components of a Yield Mapping System
Building an effective yield mapping system requires careful selection and calibration of several core components. Each element plays a vital role in ensuring accuracy and meaningful analysis of crop performance data:
- Grain Flow Sensor: This sensor measures the volume of grain harvested in real time, enabling calculation of yield rates.
- Moisture Sensor: Assesses moisture content in each portion of harvested grain, providing crucial information for yield calculations and safe storage or processing.
- GPS Receiver: Georeferences every data point, linking yield measurements to specific locations (zones) within the field—a cornerstone of precision mapping.
- Data Logger & Display: Records all collected data and displays real-time yield variations to field operators during harvest.
Calibration of all hardware (especially sensors) is crucial. Inadequate calibration affects data integrity, leading to errors in resource allocation and poor management decisions.
Explore more about system calibration here.
Applications of Crop Yield Mapping in Agriculture
The applications of yield mapping in agriculture are vast, transforming both decision-making and day-to-day farm management. Yield mapping empowers farmers to:
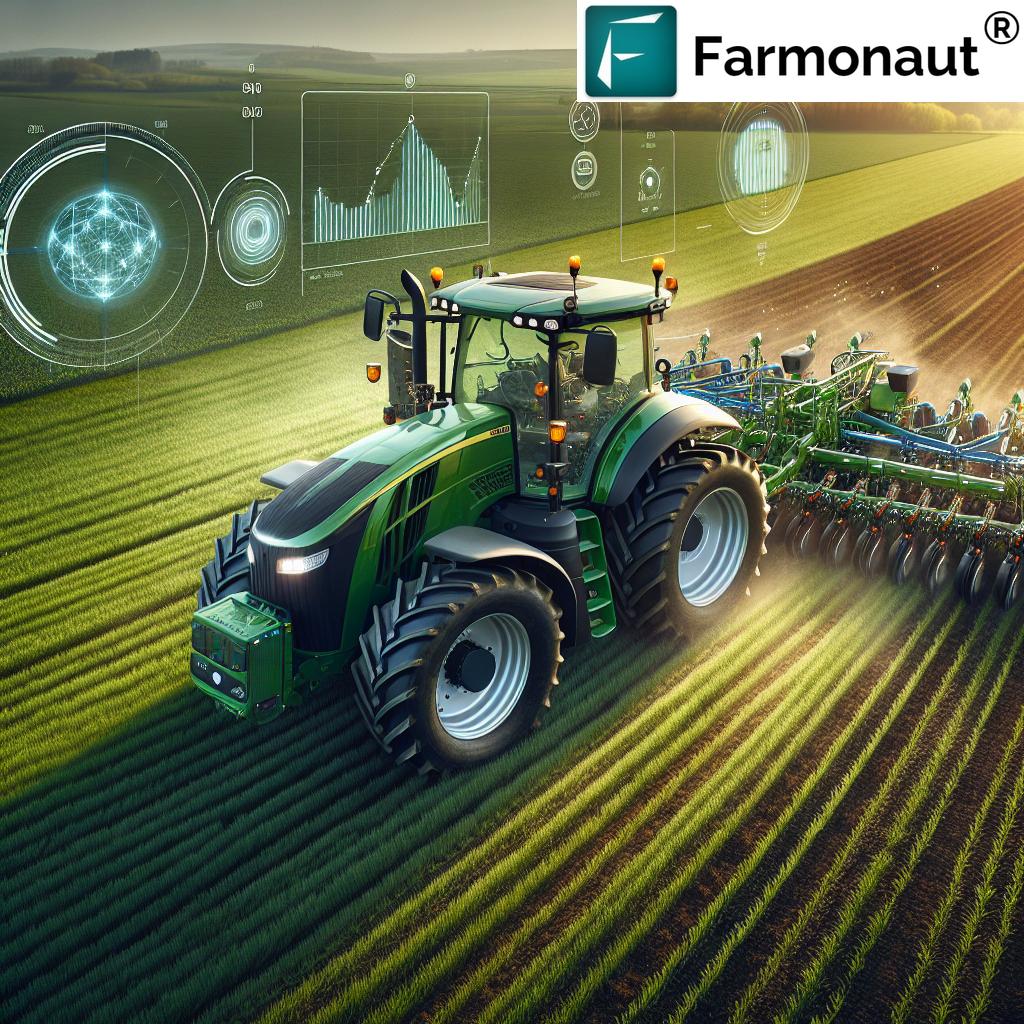
1. Enable Variable Rate Technology in Farming
Variable rate technology in farming uses yield data to pinpoint zones with differing production capacities. Inputs—like fertilizers, pesticides, or water—are then applied at rates tailored to each area’s specific needs. The result: improved resource use efficiency, higher yields, and reduced environmental impact.
Learn more about the impact of precision input management
2. Tailor Soil Management and Fertilization
Yield maps reveal persistent low-yield areas that may be nutrient-deficient or suffer from poor soil health. Targeted fertilization or soil amendment strategies can be developed, often linked with soil moisture sensors, to address each zone’s unique needs—improving both efficiency and yield consistency.
Deep dive into yield mapping’s role in soil fertility management
3. Optimize Irrigation Planning
Analysing yield maps with moisture data lets farmers identify under-watered areas versus sites with sufficient water supply. This supports dynamic irrigation planning and helps conserve water by only irrigating where needed—key in sustainable agriculture.
See the benefits of matched irrigation and yield monitoring
4. Inform Crop Rotation and Planning
Using historical yield data, farmers develop intelligent crop rotation plans, adjusting future plantings and rotations to both increase overall yields and sustain soil health.
More about planning rotation with yield maps
5. Support Financial Documentation and Planning
Yield maps serve as reliable, objective records of farm performance. This verifiable documentation aids farmers and agribusinesses in securing loans, insurance, or rental contracts, demonstrating productivity to lenders and stakeholders.
Learn more on financial verification benefits
“Over 60% of large farms now use yield mapping technology to monitor field variability and optimize productivity.”
Technological Advancements in Yield Mapping
Today’s crop yield mapping is supercharged by continuous advancements in technology, making data collection, integration, and interpretation unprecedentedly precise and affordable for farmers worldwide.
-
Remote Sensing for Crop Yields: Satellite imagery (like Sentinel-2’s multispectral data) brings a bird’s-eye view, monitoring crops across vast fields and enabling analysis of crop health, yield variability, and spatial patterns.
Discover the science behind yield monitoring by satellite -
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs/Drones): Drones equipped with multispectral cameras capture ultra-high-resolution data, perfect for monitoring field micro-zones and rapidly assessing crop vigor and stress. This fast, flexible approach complements satellite data in precision agriculture technology.
Read more about UAV tech in precision farming - IoT and Smart Soil Moisture Sensors: Integration of soil, weather, and crop-based sensors brings real-time, sub-meter precision to yield mapping in agriculture. Soil moisture sensors are crucial for dynamic resource management.
-
Machine Learning in Crop Production: Data analytics platforms apply machine learning to layer yield, weather, and soil data for robust predictive modeling of future productivity and actionable insights for input strategies.
Explore academic research on ML in yield forecasting
Comparative Technology Impact Table: 7 Tech Solutions Transforming Yield Mapping
| Technology Name | Estimated Yield Improvement (%) |
Field Variability Monitoring Effectiveness |
Example Application | Potential Productivity Gain (tons/hectare/year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPS-Guided Equipment (e.g., GPS yield monitoring) |
8–12% | High | Yield mapping, auto-steered fieldwork | 0.5–0.8 |
| Satellite Imagery | 10–15% | Medium–High | Satellite imagery for crop management & health monitoring | 0.7–1.2 |
| Drones (UAVs) | 7–11% | High | Targeted field scouting, biotech applications | 0.6–1.0 |
| IoT Soil Moisture Sensors | 5–10% | High | Soil moisture mapping and irrigation control | 0.4–0.8 |
| Variable Rate Technology | 8–14% | High | Fertilizer, pesticide, irrigation optimization | 0.5–1.0 |
| Farm Management Software | 6–12% | Medium | Data recording, field history and planning | 0.5–1.0 |
| Data Analytics Platforms | 10–18% | High | Machine learning in crop production prediction | 0.9–1.5 |
Key Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of high-tech crop yield mapping and precision agriculture technology are clear, some challenges persist:
-
Data Calibration and Accuracy: Precision of measurements depends on meticulous sensor calibration and ongoing validation against ground-truth samples. If calibration lapses, data-driven decisions may become unreliable.
More on calibration for reliable mapping - Data Integration and Interpretation: Combining yield maps with soil, weather, and operational metadata demands skillful use of advanced analytics platforms—or the assistance of API-based integration of satellite and weather data.
- Investment and Accessibility: Hardware and software for yield mapping in agriculture can represent a significant up-front cost. Fortunately, with scalable, cloud-driven and subscription-based platforms now available, farmers of all sizes can increasingly benefit from precision agriculture’s promise.
Ongoing development and education in data analytics in agriculture are key to further lowering adoption barriers and improving outputs on all scales of operation.
How Farmonaut Makes Advanced Crop Yield Mapping Accessible
As a leading agricultural technology company, Farmonaut is transforming how farmers and agribusinesses approach yield mapping in agriculture. We deliver a suite of accessible, subscription-based solutions built for precision and affordability spanning web, iOS, and Android platforms:
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: We harness multispectral satellite imagery (including NDVI and soil moisture data) to provide real-time crop health monitoring. This enables better irrigation planning, targeted fertilization, and dynamic response to emerging field issues.
- AI-Driven Advisory (Jeevn AI): Our platform provides actionable, expert-backed advice using AI and machine learning—integrating massive yield datasets, weather trends, and satellite observations to guide in-season decisions.
- Blockchain-Based Traceability: Major agribusinesses and food companies use our blockchain-enabled traceability solutions for transparent product tracking from field to consumer—improving trust and integrity within supply chains.
- Resource and Fleet Management: Our fleet management tools help organizations optimize machinery usage and route planning, lowering operational costs while increasing overall productivity.
- Environmental & Financial Solutions: Reduce your environmental impact with real-time carbon footprint tracking, or secure lending and insurance through satellite-backed verification for crop loans and insurance.
- Large Scale & Plantation Management: Manage multiple operations/satellite-monitored farms at scale with large scale farm management solutions.
Farmonaut’s mission is to democratize access to precision agriculture. By leveraging satellite data and AI insights, we empower farmers and professionals to optimize yields, reduce costs, and foster sustainable agricultural practices—without the prohibitive costs of traditional hardware-heavy precision platforms.
Try the Farmonaut API | Developer Docs
7 Powerful Ways Technology Boosts Crop Yields
Harnessing breakthrough technology in crop yield mapping empowers farmers to dramatically improve productivity and sustainability. Here are the seven top ways these technologies—used individually or in synergy—deliver impact:
- Precision Input Application: Deploying variable rate technology in farming based on accurate yield maps ensures optimal use of fertilizers, pesticides, and water. Precision reduces waste, saves costs, and directly boosts yields.
- Real-Time Crop Health Monitoring: Using remote sensing for crop yields (via satellites or drones), farmers detect variations in plant health early, intervening proactively before small issues reduce yields.
- Efficient Water Management: Integration of soil moisture sensors into dynamic irrigation planning helps conserve water and direct resources to zones that need it most.
- Targeted Soil and Nutrient Management: Through stackable analytics (combining soil, moisture, and historical yield data), farmers focus on areas and zones with persistent underperformance for tailored improvement.
- Yield Prediction Using Machine Learning: Machine learning in crop production leverages rich datasets for seasonal yield forecasting, better risk assessment, and smarter business decisions.
- Sustainable Farm Management: By employing carbon footprinting tools and analytics, farmers and managers can monitor environmental impacts while optimizing output.
- Comprehensive Record-Keeping and Compliance: Digital farm management software automates collection, analysis, and documentation of yield data—supporting compliance, traceability, and access to financial services.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Crop Yield Mapping & Technology
What is crop yield mapping and why is it important?
Crop yield mapping is the spatial collection and analysis of georeferenced yield data across a field. It’s crucial because it enables farmers to measure yield variability, understand influencing factors, and implement tailored management for increased performance and profitability.
How does remote sensing or satellite imagery contribute to yield mapping?
Remote sensing provides multispectral satellite data that helps track crop health, vigor, and canopy development across entire fields. When combined with ground yield data, it refines yield predictions and supports real-time decision-making in crop management.
Can small farms benefit from yield mapping in agriculture?
Yes. With cloud-based solutions, affordable mobile apps, and API-integrated platforms, farms of all sizes can access yield mapping insights—improving their resource allocation, sustaining yields, and ensuring better returns.
What role does machine learning play in crop yield mapping?
Machine learning is used to develop predictive models by analyzing patterns in historical yield, weather, and soil data. This helps farmers anticipate future yields and make proactive, informed decisions for their operations.
How do I get started with accessible yield mapping technology?
Start by using a platform such as Farmonaut’s web or mobile apps, which offer satellite-based yield maps, crop health reports, and resource management tools. Sign up for a subscription that fits your acreage and data refresh requirements, and leverage built-in analytics for actionable insights.
Future Outlook: Precision Agriculture and Sustainable Productivity
The future of crop yield mapping is bright. Advancements in sensor technology, machine learning, and data connectivity will make high-resolution, field-level monitoring affordable to all. Farmers everywhere will have the ability to optimize resource allocation, reduce waste, and increase yields while complying with the demands of sustainable agriculture.
As influential technologies continue to become more accessible, platforms like Farmonaut stand ready to empower users to thrive in an increasingly data-driven, efficient, and sustainable agricultural ecosystem. The results aren’t just better yields; they are smarter management, stronger businesses, and a healthier planet for all.