Technology Development in Agriculture: 7 Shocking Innovations
“Precision agriculture can increase crop yields by up to 30% using AI-driven data analysis and robotics.”
Table of Contents
- Summary: Understanding Today’s Agricultural Technology Revolution
- Precision Agriculture
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Agriculture
- Robotics and Automation: Agricultural Machines Shaping Our Fields
- Controlled-Environment Agriculture (CEA): Vertical Farming & Aeroponics
- Nanotechnology in Agriculture: Real-Time Monitoring
- Blockchain in Agriculture Supply Chain: Traceability & Trust
- Cellular Agriculture: Cultivation Beyond Soil
- Comparative Innovation Impact Table
- Emerging Trends, Future Prospects & Sustainable Methods
- How Farmonaut Empowers Precision Agriculture
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Summary: Understanding Today’s Agricultural Technology Revolution
The agricultural sector is undergoing a remarkable transformation, fueled by cutting-edge technology advancements that are redefining what’s possible on our farms. We’re witnessing a seismic shift in farming methods—from precision agriculture using satellite imagery and sensors, to the integration of AI, robotics, and blockchain into daily operations. This revolution is not just about boosting productivity; it’s about maximizing sustainability, improving resource management, and increasing the sector’s resilience to climate variability and global food demands.
As innovators and stakeholders in agriculture, it’s more vital than ever for us to understand and deploy these technologies—whether we’re farmers looking to optimize yields, agribusinesses pursuing efficiency, or policy-makers addressing sustainability challenges. Let’s explore together the seven most shocking innovations currently reshaping the future of farming.
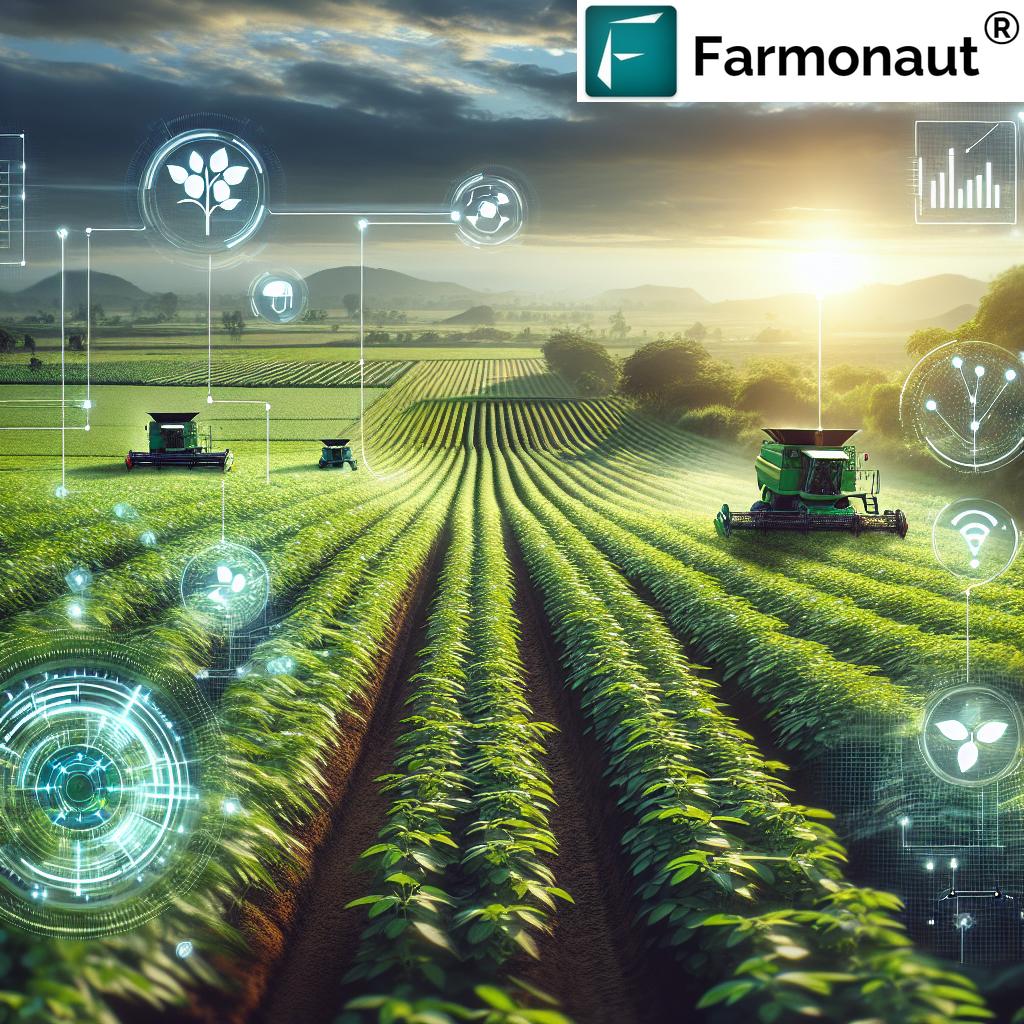
1. Precision Agriculture: Transforming Field Management
Precision agriculture represents a paradigm shift in how we approach crop production and resource management. By leveraging a suite of technologies such as GPS mapping, IoT sensors, satellite imagery, and data analytics, we now have the tools to monitor and manage field variability in real-time. This enables us to apply water, fertilizers, and pesticides precisely where and when they are needed, dramatically improving efficiency and resource use.
- Optimized Irrigation: Modern automated irrigation systems utilize real-time sensor data to determine the exact water demands of crops. This not only supports optimal plant growth but also conserves water and reduces costs.
- Soil Health Monitoring: Sensors embedded across the field provide constant updates on soil moisture, nutrient content, and conditions, allowing us to make smarter decisions about fertilization and planting schedules.
- Yield Optimization: By minimizing input waste, precision agriculture increases overall productivity, supports sustainability, and improves the environmental impact of farming.
The impact of these smart farming solutions is undeniable—studies show that yield improvements of up to 30% are achievable. Platforms like Farmonaut make these solutions accessible to farmers globally, utilizing satellite imagery and AI to help us monitor crop health, soil moisture, and even predict pest risks.
2. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Agriculture
Artificial intelligence in agriculture and machine learning (AI & ML) are rapidly reshaping how we analyze datasets, predict crop yields, and detect diseases. Advanced AI models sift through massive amounts of data from satellite imagery, soil sensors, and weather stations to offer actionable insights at every stage of the farming cycle.
- Precision in Decision-Making: AI enables targeted fertilization and irrigation, reducing input costs and environmental impact.
- Disease and Pest Detection: Automated surveillance tools, using AI, can spot early signs of diseases or infestations—empowering us to take preventive measures swiftly.
- Predictive Analytics: Using machine learning, we can forecast planting schedules, weather disruptions, and yields with remarkable accuracy.
Solutions such as Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI Advisory System integrate satellite data and AI-driven analytics, delivering real-time, personalized advisory for every farm. The system’s capacity to continuously learn and adapt to local conditions unlocks fresh possibilities for boosting productivity and sustainability.
Explore Farmonaut’s API for real-time crop health data: https://sat.farmonaut.com/api | API Developer Docs
“Blockchain technology in agriculture can reduce food supply chain fraud by as much as 50%.”
3. Robotics and Automation: Agricultural Machines Shaping Our Fields
The emergence of robotics in farming and automation is transforming operational efficiency in agriculture. Self-driving tractors, robotic harvesters, and autonomous drones are now fundamental to large and small farms alike.
- Labor Optimization: Automated machines alleviate the burden of labor shortages while working longer hours without fatigue—reducing both labor costs and human error.
- High Precision Tasks: From planting to weeding and harvesting, robotics guarantee accurate, consistent execution, supporting yield increases and resource savings.
- Resource Management: Through GPS-guided routes and AI, tractors and harvesters ensure optimal fuel use and efficient field management.
We can even integrate data from these machines into centralized management systems for tracking resource usage, fleet maintenance, and operational efficiency.
Farmonaut provides comprehensive fleet and resource management tools to help us monitor, optimize, and secure agricultural machinery—supporting cost savings and scaling across the sector.
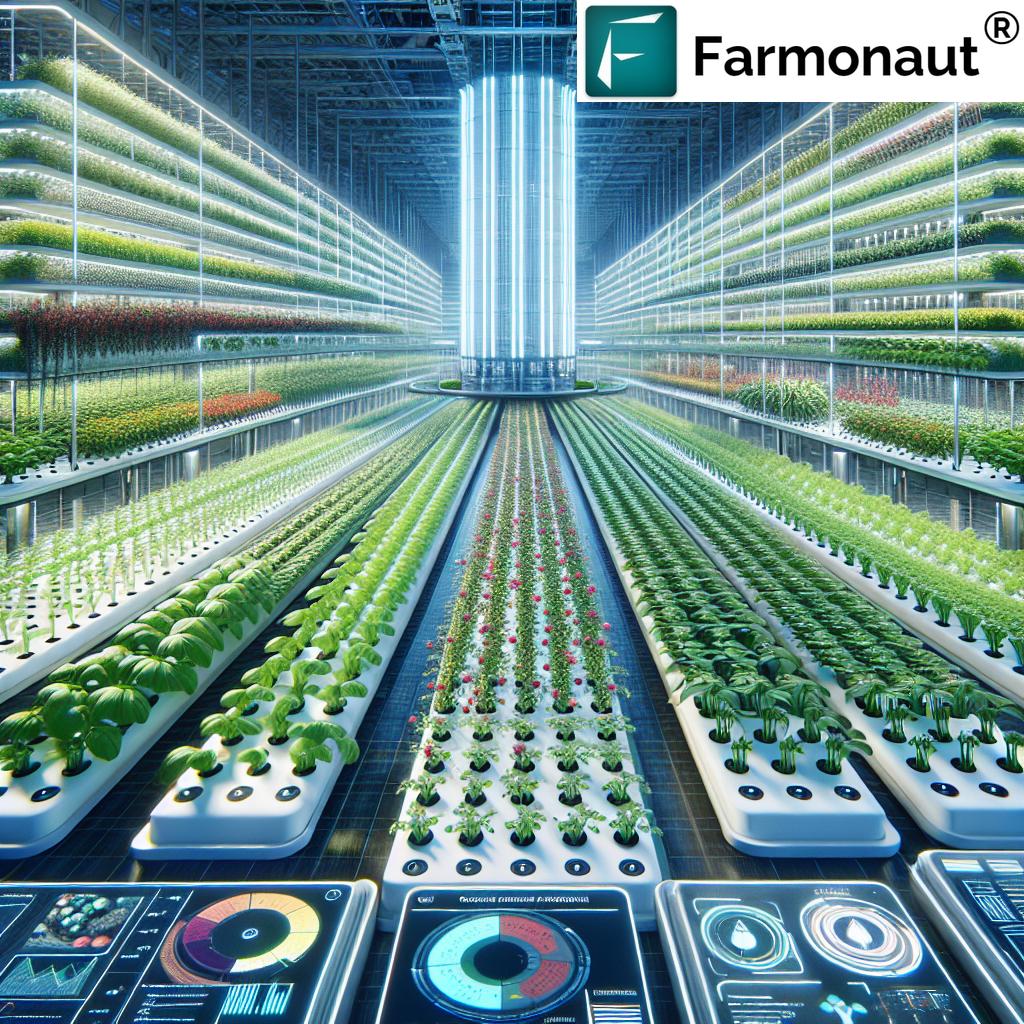
4. Controlled-Environment Agriculture (CEA): Vertical Farming & Aeroponics
The future of farming extends beyond open fields. Controlled environment agriculture (CEA) harnesses visionary methods—like vertical farming and aeroponics—to cultivate crops in optimized indoor spaces.
- Vertical Farming: By stacking crops in layers within climate-controlled facilities, we drastically reduce land requirements while enabling year-round, high-density production near urban centers.
- Aeroponics: Crops are grown with their roots suspended in air, nourished by a fine nutrient mist. This method slashes water usage (often up to 95% less than traditional agriculture) and accelerates plant growth.
- Environmental Control: By fine-tuning light, temperature, humidity, and nutrients, CEA ensures optimal planting conditions—yielding higher productivity, resource savings, and vastly reduced pesticide use.
CEA also minimizes transportation costs and spoilage, supporting fresher produce with a lower environmental impact.
For those looking to manage multiple operations, Farmonaut’s large-scale farm management application is ideal for implementing controlled-environment and smart farming methods at scale.
5. Nanotechnology in Agriculture: Real-Time Monitoring & Soil Health
Nanotechnology in agriculture has opened up revolutionary pathways for monitoring crop and soil health. Nano sensors embedded in fields detect changes at the molecular level, reporting real-time data on soil moisture, nutrients, pathogen presence, and environmental contaminants.
- Smart Sensing: Nano sensors track pH levels, pest infestations, and moisture, alerting us to subtle shifts and allowing proactive interventions.
- Efficient Resource Use: With real-time insights, we can optimize irrigation, fertilizer, and pesticide application—lowering input costs while minimizing environmental impact.
- Pathogen Detection: Nano-based biosensors enable early detection of plant diseases, nipping outbreaks in the bud before they devastate yields.
The integration of nano tech with AI and machine learning further refines our ability to detect and adapt to field changes instantly. Data from nano networks can be aggregated via Farmonaut’s real-time monitoring platform, helping us make truly data-driven farming decisions. Learn more about Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting for sustainable practices tracking.
6. Blockchain in Agriculture Supply Chain: Traceability & Trust
Blockchain in agriculture supply chain management is a technological leap fostering trust, transparency, and food safety worldwide. By recording every transaction—from planting to shelf—on an immutable, decentralized ledger, we equip stakeholders with a secure, tamper-proof history of the food journey.
- Supply Chain Traceability: In the event of contamination, blockchain allows us to swiftly identify and remove only affected produce, minimizing recalls and risks.
- Fraud Reduction: Blockchain can slash food supply chain fraud by up to 50%, safeguarding both consumers and ethical producers.
- Consumer Confidence: With transparent proof of origin and handling, buyers gain confidence in food safety and authenticity.
We can implement blockchain technology via platforms such as Farmonaut’s blockchain-based traceability solution, ensuring transparency and compliance for end-users, retailers, and agricultural brands.
7. Cellular Agriculture: Cultivation Beyond Soil & Livestock
Cellular agriculture represents the next frontier—producing foods and fibers directly from cell cultures, without traditional farming or animal husbandry. This includes:
- Lab-Grown Meat: Cultured meat is produced from animal cells grown in nutrient-rich solutions under sterile, controlled environments—bypassing the need to rear, feed, and slaughter livestock.
- Sustainable Protein Alternatives: This innovation slashes environmental impact, reduces methane emissions, and vastly minimizes water and land use—boosting sustainability and food security.
- Enhanced Nutritional Control: Through biotechnology, cellular agriculture can tweak nutritional profiles or fortify outputs for human health benefits.
Cellular agriculture could revolutionize our approach to food security, sustainability, and ethical consumption. Our journey into these advanced cultivation methods is only beginning.
Comparative Innovation Impact Table: 7 Shocking Agricultural Technologies
| Innovation/Technology | Year Introduced | Key Application | Estimated Yield Improvement (%) | Resource Savings (%) | Sustainability Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision Agriculture | Mid-1990s | Site-specific input application, resource optimization | 10–30% | 15–40% (water, fertilizer) | Reduced waste & environmental impact |
| Artificial Intelligence (AI/ML) | 2010s | Predictive analytics, disease detection, advisory | 10–20% | 10–25% (inputs) | Improved yields, data-driven farming |
| Agricultural Robotics | 2015–Present | Automated fieldwork, labor replacement | 5–15% | 25–30% (labor, time) | Reduced labor needs, greater efficiency |
| Blockchain | 2017–Present | Supply chain traceability, fraud reduction | N/A | 30–50% (fraud, admin costs) | Secure food systems, transparency |
| Drones | 2013–Present | Aerial field monitoring, crop health analysis | 8–12% | 15–20% (field scouting time) | Efficient surveillance, less input waste |
| IoT Sensors | 2014–Present | Soil, water, microclimate monitoring | 10–18% | 18–35% (water, fertilizer) | Optimized field conditions, sustainability |
| Vertical Farming | 2010–Present | Indoor, stacked crop production | Up to 25% | 90–95% (water) | Urban food supply, fresh produce |
Emerging Trends, Future Prospects & Sustainable Farming Methods
As we look ahead, the agricultural technology advancements detailed above will continue to merge and evolve, leading to even more sophisticated, integrated, and sustainable farming systems.
- Wider AI and Robotics Automation: We anticipate further automation in complex tasks like selective harvesting and individualized plant care through machine learning and robotics.
- Enhanced Biotech: Expect crops designed for improved resilience, nutrition, and quality using gene editing and cell culture.
- Digital Farm Platforms: Platforms that aggregate satellite data, ground sensors, and AI insights will streamline resource management and risk mitigation at every scale.
- Remote Farm Management: With mobile and web-based dashboards, farmers can oversee vast operations, respond to anomalies, and optimize inputs directly from their phones.
- Regenerative and Sustainable Methods: Emphasis on carbon footprint management, closed-loop nutrient cycles, and integrated pest management to bolster sustainability and mitigate environmental impact.
Farmonaut embodies these trends by providing accessible, scalable smart farming solutions—empowering stakeholders across the agricultural sector to transition towards a more productive, resilient, and sustainable future.
How Farmonaut Empowers Precision Agriculture & Smart Farming
As a pioneering agricultural technology company, Farmonaut democratizes precision agriculture by making advanced, satellite-based monitoring and AI-driven advisory affordable and accessible to all. Our mission: bring transformational technology to every corner of the farming world—across individual farms, agribusinesses, NGOs, government agencies, and financial institutions.
Key Technologies
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Using multispectral satellite images, we monitor crop health, optimize fertilizer and irrigation, and ensure timely interventions.
- Jeevn AI Advisory: Our AI-driven platform combines real-time data, weather forecasts, and best-practice recommendations to deliver actionable insights for every stage of plant growth.
- Blockchain-Based Traceability: Seamlessly record every step of the supply chain for transparency and trust—see our product traceability solution for more details.
- Fleet and Resource Management: Manage your tractors, vehicles, and input logistics efficiently with our dedicated tools—explore fleet management.
- Carbon Footprint Monitoring: Quantify and reduce your environmental impact, visualizing emissions in real-time across operations—check out our full carbon footprinting platform.
Broad Audience and Scalable Access
- Individual Farmers: Affordable, easy-to-use crop health, soil moisture, and weather analytics to optimize yields and reduce input waste.
- Agribusinesses: Plantation management, logistics optimization, and full-fleet monitoring across thousands of hectares, boosting efficiency and resource management.
- Government & NGOs: Centralized dashboards for area estimation, yield mapping, subsidy management, and climate-resilient farm initiatives.
- Financial Institutions: Satellite-based verification for risk-free crop loans and insurance, accelerating approvals, and minimizing fraud.
- Corporates & Brands: Blockchain-backed traceability for secure and transparent food or textile supply chains.
Ready to transform your operations?
Start with our Web, Android, or iOS apps—see links above. For developer integration, check our open API and detailed developer docs.
Farmonaut Subscription Options
Unlock scalable access to all our features with flexible subscription packages designed for every type of user, from individual farmers to enterprise agribusinesses. Choose a plan that fits your farm size, data update needs, and budget.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is precision agriculture and how does it benefit farmers?
Precision agriculture utilizes technologies like GPS, sensors, and satellite imagery to monitor fields and apply resources (water, fertilizer, pesticides) only where needed. This reduces waste, saves money, increases yields, and minimizes the environmental impact of farming.
How is artificial intelligence transforming agriculture?
AI in agriculture analyzes vast datasets to predict crop yields, detect diseases early, optimize planting schedules, and recommend tailored interventions. This enables more precise and data-driven farm management, improving productivity and sustainability.
What are the benefits of robotics and automation in the agricultural sector?
Robotics reduce labor dependency, improve consistency, and optimize field operations like planting, weeding, and harvesting. This reduces costs, alleviates manual labor challenges, and helps ensure timely cultivation even during labor shortages.
What is controlled-environment agriculture (CEA)?
CEA refers to advanced cultivation methods such as vertical farming and aeroponics. It provides tightly optimized conditions for plant growth indoors, reducing land use, conserving water, and enabling year-round production.
How does blockchain promote transparency in agriculture?
Blockchain technology records each transaction in the agricultural supply chain, ensuring data cannot be tampered with. This enables full traceability, reduces fraud, and helps quickly identify issues like contamination, improving food safety and consumer trust.
What are nano sensors and how do they improve crop health?
Nano sensors are microscopic devices that monitor soil health, moisture, and disease threats in real time. They provide granular data that allows precise input application, improving crop vitality and reducing environmental damage.
How is Farmonaut different from other agricultural technology providers?
Farmonaut offers affordable, satellite-based precision agriculture, AI-driven advisory, blockchain-backed traceability, and comprehensive management tools. Our easy accessibility via web and mobile apps, scalable plans, and developer API integration empower a broad spectrum of users, from smallholder farmers to governments and corporates.
Conclusion: Embracing the Agricultural Technology Revolution
The evolution of technology in agriculture is not just an impressive trend but a necessity for the future. By adopting smart farming solutions—from precision agriculture and AI to blockchain and advanced robotics—our sector can achieve higher productivity, sustainability, and operational resilience.
At Farmonaut, our goal remains clear: to enable everyone in farming to access and benefit from these life-changing technologies—improving yields, reducing costs, and safeguarding the environment for the generations to come.
Join us in shaping a more sustainable, efficient, and secure future for global agriculture.